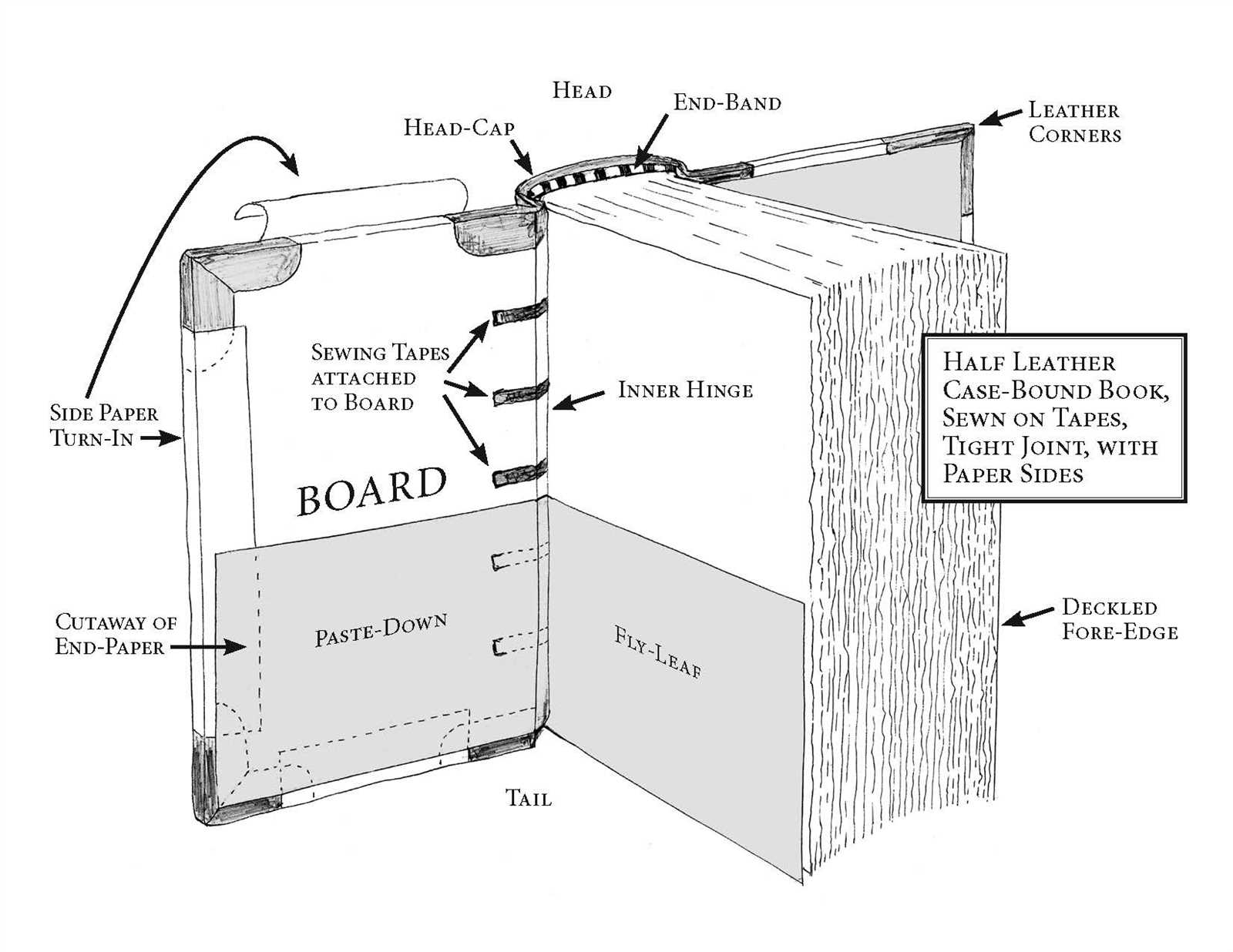
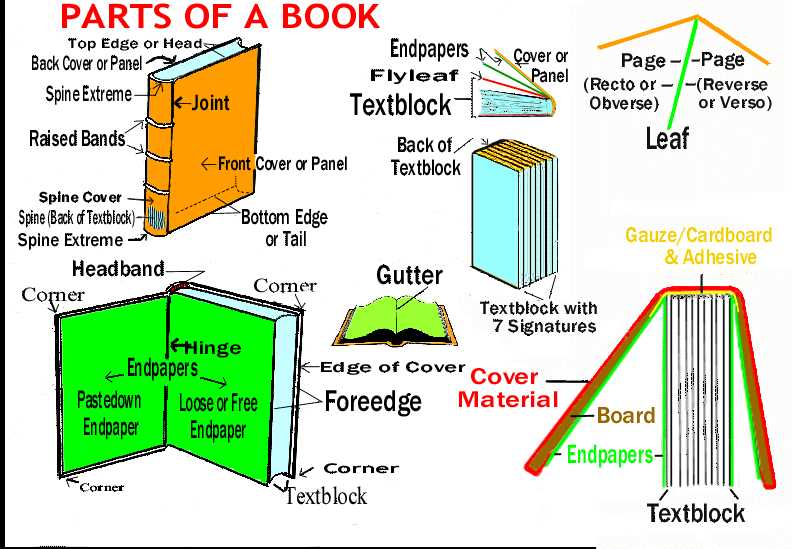
Every piece of written work consists of various elements that contribute to its overall structure and flow. By examining these essential features, readers can gain a deeper appreciation of how narratives are crafted and how information is conveyed. This exploration sheds light on the intricate design behind literary creations.
Analyzing these crucial elements reveals their significance in guiding the reader’s journey. From introductory remarks to concluding thoughts, each section plays a pivotal role in shaping the reader’s experience. Diving into these features allows for a greater understanding of both style and substance.
Ultimately, recognizing how these components interact enhances the reading process, making it more engaging and insightful. Whether it’s fiction or non-fiction, every literary work invites readers to delve into its construction, fostering a richer connection with the text.
Understanding the Structure of Books
The architecture of written works is a fascinating interplay of various components that contribute to the overall experience of the reader. Each element plays a crucial role in guiding the audience through the narrative or information presented. Recognizing how these segments function together can enhance one’s appreciation and comprehension of the material.
Key Components of a Book
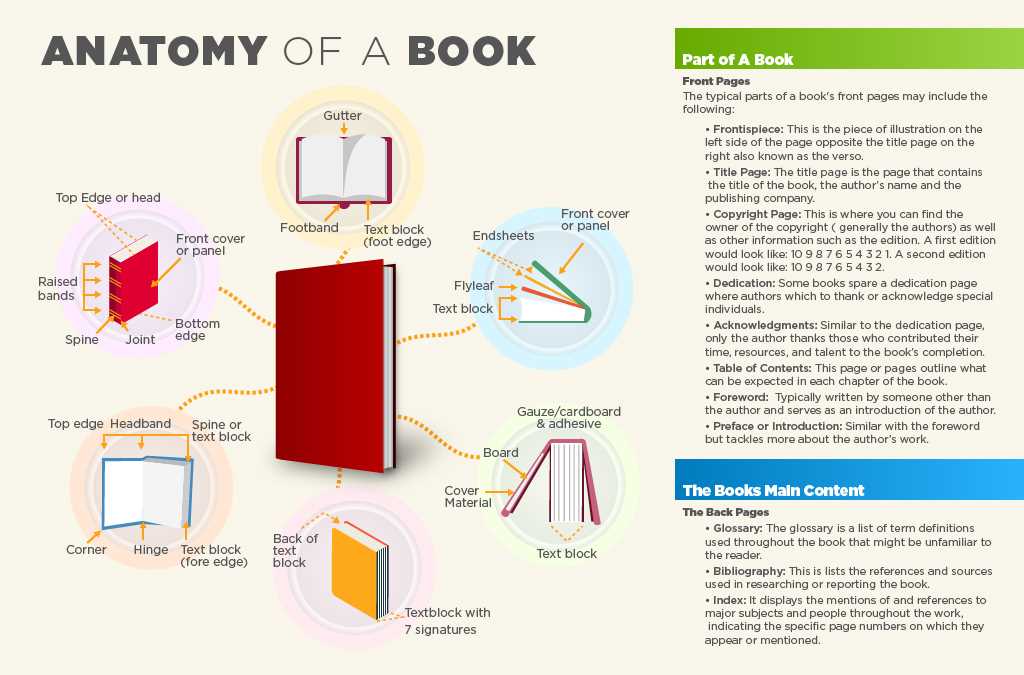
Understanding the essential elements of a literary work is crucial for grasping its structure and function. Each segment plays a significant role in enhancing the reader’s experience and conveying the author’s message effectively.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Cover | The outer layer that protects the content and provides visual appeal. |
| Title Page | Displays the name of the work, author, and publisher, setting the stage for what follows. |
| Table of Contents | A roadmap that outlines the chapters or sections, facilitating navigation. |
| Chapters | The main divisions that organize the narrative or subject matter into manageable parts. |
| Appendix | Supplementary material that adds depth and context to the primary content. |
Importance of Book Layout
The arrangement and design of printed materials significantly influence how readers engage with the content. A well-structured format enhances comprehension, guides the reader’s journey, and creates a more enjoyable experience. Effective layout not only showcases the narrative but also ensures that information is accessible and appealing.
Enhancing Readability
Proper organization of text and visuals plays a crucial role in readability. Elements that contribute to this include:
- Font choice and size
- Line spacing and margins
- Chapter divisions and headings
These aspects help to reduce eye strain and facilitate smoother navigation through the content, allowing readers to immerse themselves fully in the material.
Creating Visual Appeal
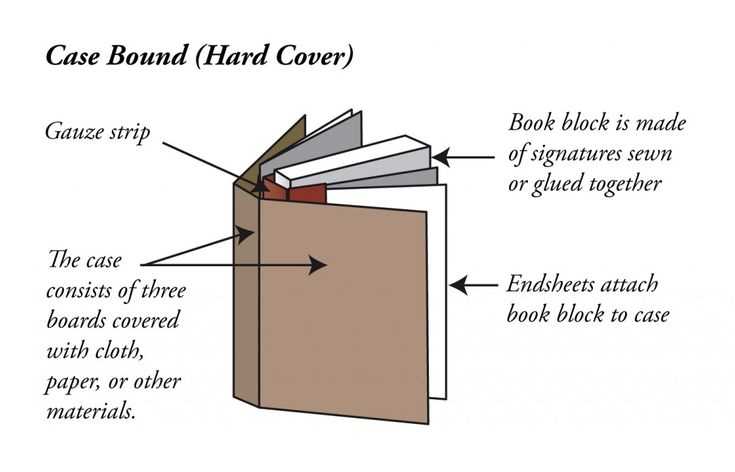
Aesthetic elements significantly impact a reader’s initial impression. Consider the following factors:
- Use of imagery and illustrations
- Color schemes and design consistency
- Overall flow and harmony of the layout
When visually appealing, a publication can attract and retain the attention of its audience, encouraging them to explore further and engage with the themes presented.
Types of Book Covers Explained
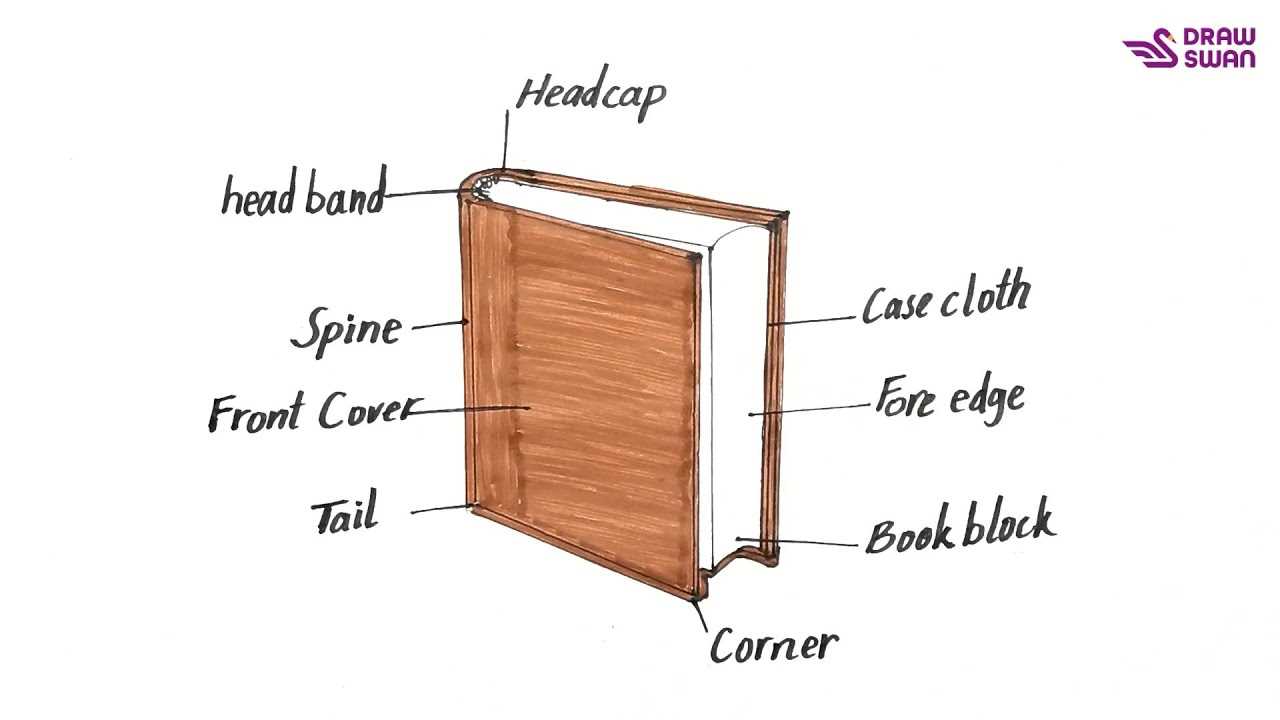
Exploring the various forms of exterior designs for literature reveals how aesthetics and functionality converge. Each style serves not only to protect the content but also to attract readers and convey the essence of the narrative within.
Common Types

- Hardcover: Durable and often more expensive, these covers feature a rigid outer layer.
- Paperback: Lightweight and flexible, they are popular for their affordability and portability.
- Dust Jacket: An additional layer for hardcovers, usually adorned with artwork and details about the work.
- Graphic Novel Covers: Often colorful and illustrative, designed to reflect the genre’s vibrant storytelling.
Specialized Variants
- Leather-bound: These luxurious editions are made from high-quality leather, appealing to collectors.
- Slipcase: A protective box that holds one or more volumes, enhancing their display and preservation.
- Illustrated Covers: Featuring artwork that provides a visual summary of the story, captivating potential readers.
Exploring Table of Contents
The layout of a publication is a crucial aspect that guides readers through its structure. A well-crafted outline serves as a roadmap, enabling individuals to navigate various sections with ease. This organization not only enhances readability but also enriches the overall experience of engaging with the material.
Importance of Structure
An effective framework ensures that information is presented logically, allowing readers to find relevant topics quickly. It highlights the relationship between different segments, making it easier to understand the flow of ideas. A thoughtfully arranged index can significantly impact the comprehension and retention of content.
Elements of an Outline
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Chapters | Main divisions that cover significant themes or topics. |
| Subsections | Smaller units within chapters that delve into specific details. |
| Page Numbers | Indications of where each section begins, facilitating quick reference. |
| Appendices | Additional material that provides supplementary information. |
Role of Chapter Titles
Chapter titles serve as vital signposts within a narrative, guiding readers through the unfolding journey. They encapsulate the essence of each section, providing insight into the forthcoming content while piquing interest.
Functionality is key; these headings not only help in organizing the material but also enhance navigation. A well-crafted title can evoke curiosity, setting the stage for what lies ahead and encouraging deeper engagement with the text.
Symbolism often plays a significant role, with titles reflecting themes or emotional undertones that resonate throughout the narrative. This connection between title and content fosters a cohesive reading experience, allowing the audience to immerse themselves fully in the story.
Significance of Forewords and Prefaces
The introductory segments of a literary work play a vital role in setting the tone and context for what follows. They serve not only as a gateway for readers but also as a means for authors to convey essential background information and insights that enrich the reading experience.
Establishing Context
One of the primary functions of these introductory sections is to provide context. They often include:
- Historical background of the subject matter
- Author’s motivations and intentions
- Insights into the research or creative process
This context helps readers understand the significance of the content and encourages deeper engagement with the material.
Connecting with Readers
These segments also serve as a bridge between the author and the audience. They can:
- Offer personal anecdotes that resonate with readers
- Pose questions that invite reflection and critical thinking
- Set expectations regarding the style and structure of the work
By establishing this connection, authors can foster a sense of intimacy and investment in the narrative that follows.
Understanding Page Numbers and Indexes

Page numbering and indexing are essential components that enhance navigation and comprehension within textual works. They serve as vital tools that help readers locate specific content quickly and efficiently, streamlining the reading experience.
Importance of Page Numbers
Page numbers provide a structured framework that allows readers to:
- Track their progress through the content.
- Reference specific sections or topics accurately.
- Easily cite information in academic or professional contexts.
Role of Indexes
Indexes act as comprehensive guides, offering a systematic way to find information by:
- Listing key terms and topics alphabetically.
- Indicating page numbers where each topic can be found.
- Enhancing the overall accessibility of the material.
Analyzing Illustrations and Images
Visual elements within written works serve as crucial tools for enhancing understanding and engagement. They provide additional context and can evoke emotions that text alone may struggle to convey. A deeper exploration of these graphics can reveal layers of meaning and intention that enrich the overall narrative.
Importance of Visuals

- Enhance comprehension of complex ideas
- Break the monotony of text
- Engage readers on an emotional level
Techniques for Analysis
- Examine the choice of colors and their emotional impact.
- Consider the composition and its relationship to the text.
- Explore symbols and their potential meanings.
- Assess the role of images in conveying messages.
Footnotes and Endnotes: What They Are
Footnotes and endnotes serve as vital tools in academic writing, providing additional context, clarification, or references for readers. These elements enhance the understanding of the main text without interrupting the flow of the narrative. They allow authors to delve deeper into specific points, offering insights and sourcing that might be too lengthy to include in the primary discussion.
Understanding Their Function
Both footnotes and endnotes play similar roles but differ in their placement within the text. Footnotes appear at the bottom of the page where the reference is made, while endnotes are compiled at the end of a chapter or the entire work. This distinction allows readers to choose their preferred method of accessing supplementary information.
Comparison of Footnotes and Endnotes
| Feature | Footnotes | Endnotes |
|---|---|---|
| Placement | At the bottom of the page | At the end of a chapter or document |
| Accessibility | Immediate reference | Requires scrolling to the end |
| Usage Context | Common in texts requiring quick clarification | Ideal for extensive explanations |
| Reader Preference | Preferred for concise notes | Preferred for less cluttered pages |
Ultimately, the choice between using footnotes or endnotes depends on the author’s intent and the preferences of the target audience. Each serves its purpose, contributing to a richer reading experience by allowing exploration beyond the immediate text.
Evaluating the Back Matter in Books
The concluding sections of a publication often provide crucial insights and resources that enhance the reader’s understanding and experience. Assessing these elements can reveal their significance and utility in the broader context of the narrative or content.
Key components to consider include:
- Appendices: Additional material that supports the main text.
- Glossaries: Definitions of terms that may be unfamiliar to the audience.
- Bibliographies: Lists of sources that offer further reading and validation.
- Indexes: Alphabetical listings that facilitate navigation through topics.
When evaluating these sections, consider the following criteria:
- Relevance: Do the materials directly support the main themes?
- Clarity: Are the explanations and definitions easy to understand?
- Comprehensiveness: Do the resources cover the necessary breadth of topics?
- Accessibility: Is the information presented in a user-friendly manner?
Ultimately, a thorough examination of these concluding elements can enhance the overall value of a publication, guiding readers toward deeper comprehension and engagement.