In modern farming, reliable machinery is essential for efficient operations. To ensure long-term performance, it’s important to have a clear understanding of how different pieces come together and how to identify key components. This can help in maintaining, repairing, or replacing individual elements when needed.
Each machine consists of numerous elements working in harmony to achieve optimal functionality. Recognizing the placement and purpose of these elements can save time during maintenance and improve overall productivity. It’s not just about understanding the external appearance but also having knowledge of the internal structure and connections.
By having a detailed overview of the machinery’s composition, farmers and technicians can more easily diagnose issues and take the necessary steps to keep equipment running smoothly. With this information, proactive maintenance becomes a key factor in prolonging the life of agricultural machinery.
John Deere 4110 Parts Overview
The equipment discussed in this section consists of various key components that contribute to its efficient performance. Understanding the structure and individual units of the machinery is crucial for maintenance, repairs, and upgrades. Each element plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth operation of the machine, whether for agricultural or other practical purposes.
Essential Mechanical Components

Key mechanical sections, including the drivetrain, engine, and hydraulics, form the core of the system’s functionality. These mechanisms are designed to work in harmony, delivering power, maneuverability, and durability in various conditions. Regular inspection and proper upkeep of these sections ensure long-term reliability.
Additional Functional Elements
Engine Components Breakdown

The engine is a complex system composed of various interconnected elements, each playing a crucial role in ensuring its optimal operation. Understanding the arrangement and function of these components is essential for maintaining performance and longevity.
Pistons move within the cylinders, converting energy from combustion into mechanical movement. Their precise fit and operation are critical for smooth performance.
Cylinders house the pistons and are integral to the combustion process. Proper maintenance of these parts ensures efficient energy transfer.
Crankshaft translates the linear motion of the pistons into rotational energy, driving the vehicle’s movement. A balanced crankshaft is vital for reducing vibration and improving overall efficiency.
Valves control the flow of fuel and air into the engine and allow exhaust gases to
Transmission System Elements
The transmission system is a critical part of any machinery, ensuring that power from the engine is transferred efficiently to the wheels or other moving parts. Its components work together to manage speed, torque, and overall performance. In this section, we will explore the primary elements involved in the transmission system, highlighting their roles and functions.
Main Components


- Gearbox: The central unit that alters the torque and speed depending on the gear selected. It enables smooth operation by balancing power distribution.
- Clutch: This element is responsible for engaging and disengaging the power transmission from the engine to the gearbox. It allows for a seamless shift in power without stalling the engine.
- Drive Shaft: A shaft that transmits mechanical power from the gearbox to the differential or wheels, ensuring that rotational power is transferred smoothly.
Auxiliary Components

- Differential: This part distributes torque between the wheels, allowing them to rotate at different speeds, especially during turns.
- Hydraulic Systems: These systems assist in controlling various aspects of the transmission, improving the efficiency and precision of the overall system.
- Filters and Fluids: Transmission systems require proper lubrication and filtration to maintain optimal performance and prevent wear.
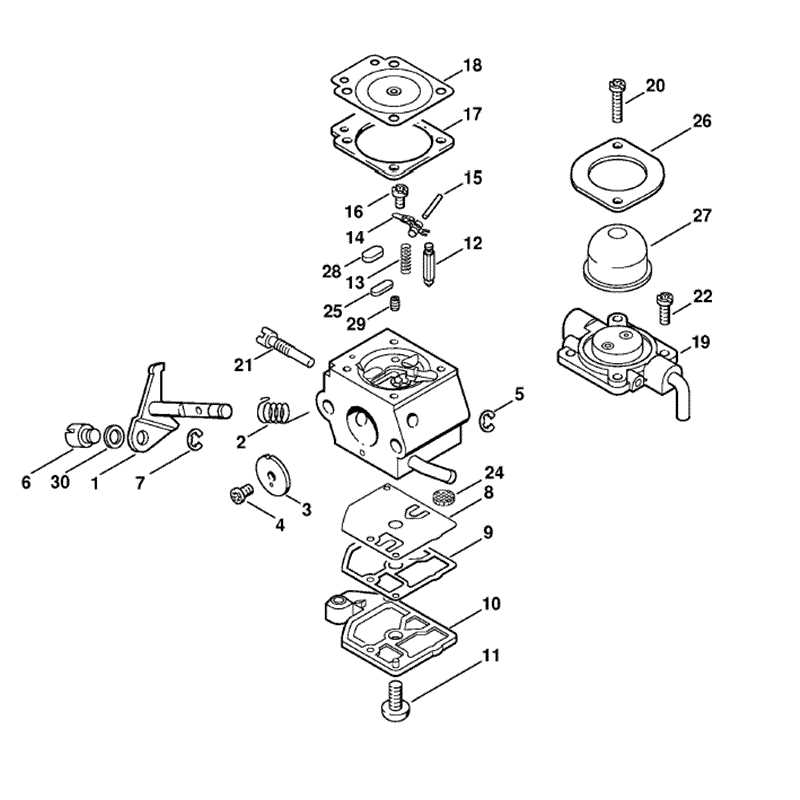
Hydraulic Mechanism Structure
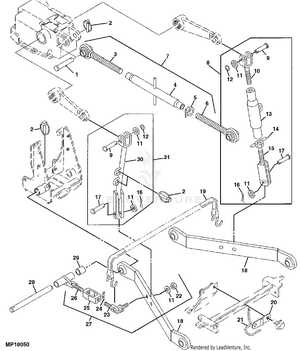
The hydraulic system is a key component of many mechanical vehicles and machines, providing essential power and motion control. Its role revolves around transferring fluid energy into mechanical energy to operate various moving parts efficiently. Understanding the structure of this mechanism is crucial for ensuring smooth operations and timely maintenance.
Main Components
The system typically consists of a pump, valves, actuators, and reservoirs. The pump initiates fluid movement, while the valves control its flow, directing pressure to the appropriate locations. Actuators, such as cylinders and motors, convert the hydraulic energy into mechanical motion, completing the cycle. The reservoir stores the hydraulic fluid, ensuring the system functions smoothly.
Flow Control and Maintenance
Proper flow regulation is vital to avoid system overloading or failure. Regular inspection of the components, checking for leaks, wear, and fluid quality, helps maintain efficiency. Adopting preventive maintenance strategies prolongs the system’s life and reduces the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
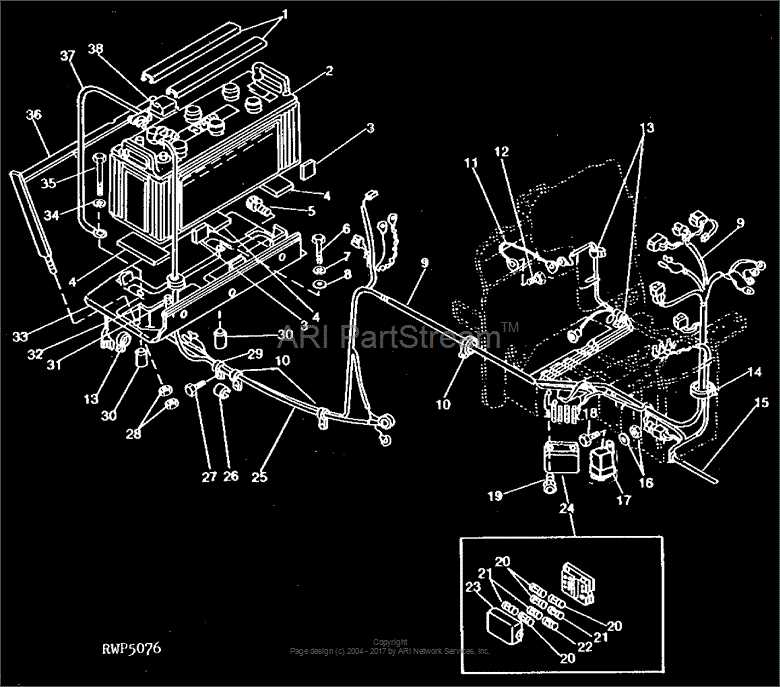
Electrical System Key Parts
The electrical system in machinery is a crucial component responsible for powering various essential functions. Without proper organization and understanding of the system’s elements, managing electrical issues or replacements becomes challenging. This section outlines the most vital elements that ensure efficient electrical performance.
Primary Components
- Battery: The heart of the system, providing the necessary power to start and run the engine, while also supplying energy to other electrical units.
- Alternator: Keeps the battery charged while the machine operates, ensuring that all electronic components continue to function properly.
- Starter Motor: A key device that engages the engine when turning the key, converting electrical energy into mechanical force to
Steering and Suspension Components

The steering and suspension system plays a crucial role in ensuring the stability and maneuverability of machinery. This system is designed to provide a smooth ride while effectively managing the vehicle’s handling and control. Proper functioning of these components is essential for maintaining optimal performance and safety in various operational conditions.
Key Steering Elements
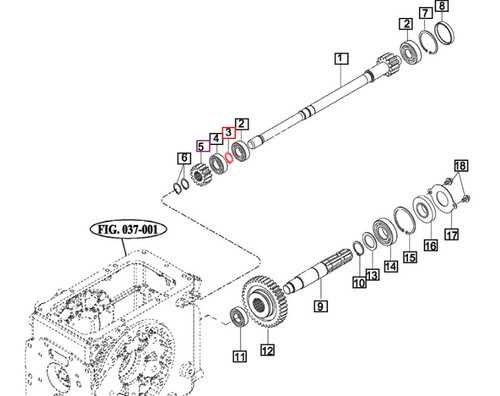
The steering mechanism includes various elements that work together to enable precise navigation. Key components such as the steering wheel, gearbox, and linkages ensure accurate direction changes. Regular maintenance and inspections of these parts are vital to prevent wear and enhance responsiveness.
Suspension Features
The suspension system is responsible for absorbing shocks and maintaining contact with the ground. Components like springs, shock absorbers, and control arms are critical in this process. Ensuring these elements are in good condition contributes to a stable and comfortable ride, minimizing the impact of rough terrain.
Brake System Parts and Function

The braking mechanism in machinery plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and control during operation. It consists of several components that work together to slow down or stop movement effectively. Understanding these elements and their specific functions is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components of the Braking Mechanism
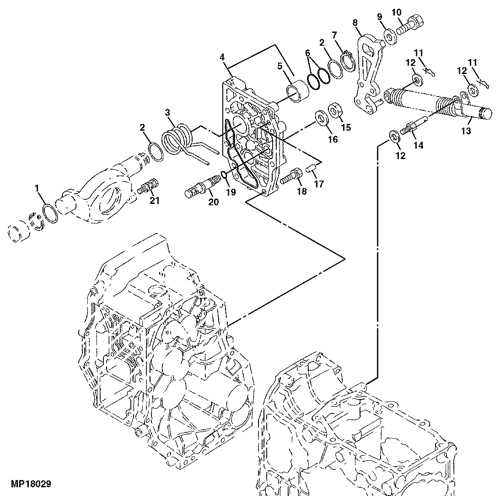
The primary components of the braking system include the brake pedal, master cylinder, brake lines, and brake calipers. The brake pedal initiates the braking process, allowing the operator to apply pressure. This pressure is transmitted to the master cylinder, which converts it into hydraulic force. The hydraulic fluid travels through the brake lines to the brake calipers, where the actual braking action occurs.
Functionality of Each Element
The brake pedal serves as the interface for the operator, while the master cylinder ensures that the hydraulic pressure is maintained throughout the system. The brake lines are designed to withstand high pressure and ensure fluid reaches the calipers efficiently. Finally, the brake calipers clamp onto the brake discs, providing the necessary friction to slow down or stop the machinery. Each component must function correctly for the entire system to operate safely and effectively.
Front Axle Assembly

The front axle assembly plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of agricultural machinery. This component is designed to provide stability and support, ensuring smooth operation and maneuverability. Understanding the structure and components of the front axle can enhance maintenance practices and improve the longevity of the equipment.
Key Components
The front axle assembly consists of several essential parts that work together to deliver optimal performance:
- Axle Housing
- Wheel Hubs
- Spindles
- Control Arms
- Steering Linkage
- Bearings
- Knuckles
Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance of the front axle assembly is vital for ensuring the efficiency and safety of the machinery. Here are some best practices:
- Regularly inspect for wear and damage.
- Lubricate moving parts as per the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Check for loose bolts and connections.
- Ensure proper alignment to prevent uneven wear.
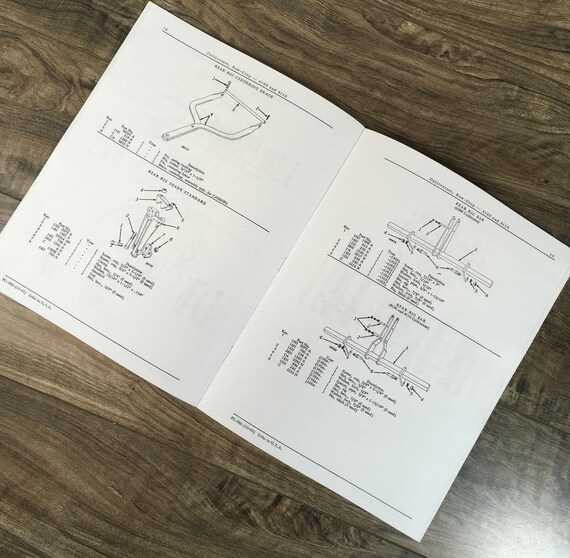
Rear Axle Diagram
The rear axle assembly is a crucial component in various vehicles, playing a significant role in providing stability and support. This section outlines the essential features and elements of this assembly, highlighting its function and importance within the overall structure.
Typically, the rear axle consists of several key parts that work together to ensure proper operation:
- Axle Housing: The main body that encases the axle and provides structural integrity.
- Differential: A mechanism that allows for the difference in wheel speeds during turns, improving maneuverability.
- Bearings: Components that support the rotating axle and reduce friction.
- Axle Shafts: Rods that transfer power from the differential to the wheels.
- Brake Components: Parts that facilitate effective stopping and control of the vehicle.
Understanding the layout and function of these components can assist in maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring longevity and optimal performance of the vehicle.
Cooling System Components
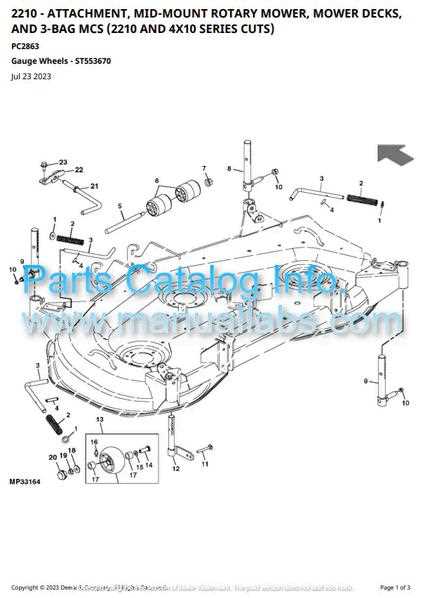
The cooling mechanism in machinery plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures and preventing overheating. This section delves into the essential elements of the cooling system, highlighting their functions and significance in ensuring efficient performance.
Key Elements of the Cooling System

- Radiator: Responsible for dissipating heat from the coolant, enabling the engine to maintain a stable temperature.
- Water Pump: Circulates the coolant throughout the system, ensuring even distribution and effective cooling.
- Thermostat: Regulates the coolant flow based on temperature, allowing the engine to warm up quickly and operate efficiently.
- Coolant Hoses: Transport coolant between various components, maintaining fluid circulation and heat exchange.
- Cooling Fan: Aids in air circulation around the radiator, enhancing heat dissipation when the vehicle is stationary or operating at low speeds.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Routine checks and maintenance of the cooling system are vital to ensure the longevity and efficiency of the machinery. Components should be inspected for leaks, wear, and blockages. Keeping the coolant at the appropriate level and quality also plays a significant role in optimal performance.
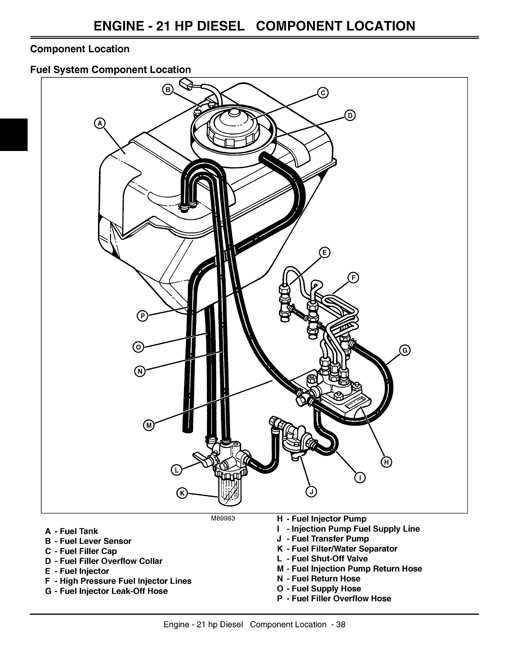
Fuel System Elements
The fuel system plays a crucial role in the efficient operation of any machinery, ensuring that the engine receives the appropriate amount of fuel for optimal performance. Understanding the components involved in this system is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting. This section outlines the primary elements that make up the fuel delivery mechanism.
- Fuel Tank: This component stores the fuel before it is delivered to the engine.
- Fuel Pump: Responsible for transferring fuel from the tank to the engine, ensuring a consistent flow under pressure.
- Fuel Filter: This part removes impurities and contaminants from the fuel, protecting the engine and other components.
- Fuel Injectors: These precision devices atomize fuel, allowing it to mix with air for efficient combustion.
- Fuel Lines: These conduits transport fuel between the tank, pump, filter, and injectors.
- Return Line: This line channels excess fuel back to the tank, maintaining proper pressure within the system.
Each element of the fuel system works in harmony to ensure that the engine operates smoothly and efficiently. Regular maintenance and inspection of these components can prevent costly breakdowns and enhance the overall performance of the equipment.
Cabin and Control Parts Layout
This section provides an overview of the arrangement of components within the operator’s compartment and control mechanisms of the equipment. A well-organized layout ensures that the operator has easy access to essential functions, enhancing the overall usability and efficiency of the machine. Understanding the positioning of these elements can greatly assist in maintenance and troubleshooting tasks.
Operator Compartment Configuration
The operator compartment is designed for comfort and accessibility. Key elements, such as the seating area, control levers, and dashboard, are strategically placed to optimize functionality. An ergonomic setup allows the user to operate the machinery with minimal effort while ensuring safety. Each control is intuitively positioned, enabling quick adjustments as needed during operation.
Control Mechanism Arrangement
The arrangement of control mechanisms plays a crucial role in the overall performance of the equipment. Various switches, levers, and buttons are positioned for ease of use. These controls typically include steering, throttle, and braking systems, all designed to be within reach. Proper layout not only enhances the operator’s experience but also contributes to effective and safe handling of the machine.