To achieve precise and efficient cutting, a specialized tool relies on multiple interconnected elements. Each section of the tool plays a vital role in ensuring smooth operation and optimal performance. Understanding the specific functions and design of these components helps in proper maintenance and troubleshooting, ultimately extending the lifespan of the equipment.
The intricate assembly of these elements works in harmony to facilitate cutting tasks, whether in professional forestry work or home use. By examining the individual features and their arrangement, users can gain insight into how each piece contributes to the overall effectiveness of the tool.
Familiarizing oneself with the layout and functionality of these key components is essential for anyone looking to improve their skills and efficiency in handling cutting devices. From the guiding elements to the sharp blades, each part must be in top condition to deliver optimal results.
Understanding Chainsaw Chain Components

To fully grasp how a cutting tool operates, it is essential to recognize the individual elements that contribute to its overall performance. Each segment plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth and efficient cutting, with specific functions that work in harmony. Knowing the details of these components allows for better maintenance, troubleshooting, and optimization of the tool’s efficiency.
The essential elements that make up this cutting mechanism can be categorized into several key sections. Each section has a distinct job that enhances the effectiveness of the entire setup. To better understand how these components function together, here are the main elements to focus on:
- Teeth: These are the parts responsible for penetrating the material, typically made from durable, sharpened steel.
- Drive links: These components connect the entire structure and transmit power from the motor to the cutting teeth, enabling movement.
- Depth gauges: Positioned near the cutting teeth, these elements control the depth of each cut, ensuring consistency and precision.
- Rivets: Small, cylindrical pieces that hold the structure together, providing stability and flexibility to the whole assembly.
- Spikes: Help maintain stability during the cutting process, anchoring the tool firmly against the surface being cut.
Each of these components plays an indispensable role, and the interaction between them dictates the cutting efficiency and overall safety. Proper care and regular inspection are critical to keeping the mechanism in top working condition and extending its operational life.
Key Parts of a Chainsaw Chain Explained
Understanding the essential components of a cutting mechanism is crucial for proper maintenance and effective use. Each element contributes to the overall performance, from ensuring sharpness to maintaining smooth motion. Familiarity with these components allows for better care and prolonged durability.
Teeth and Cutting Links
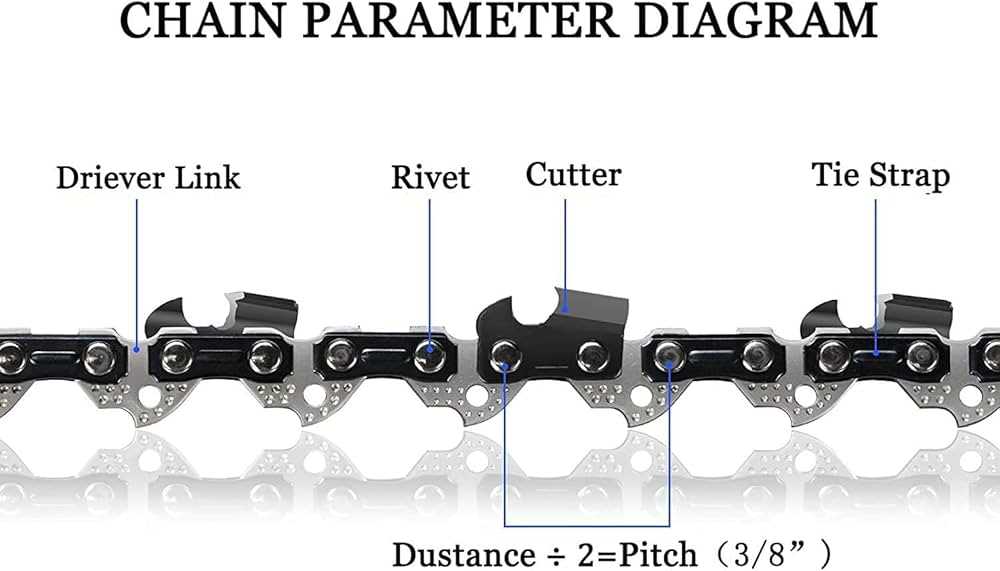
The sharp blades on the links are the primary elements responsible for slicing through wood. They are designed to cut in both directions, delivering efficient power and speed. The angle and sharpness of these cutting edges play a significant role in the ease and effectiveness of the job. Regular sharpening and maintenance are necessary to keep them at peak performance.
Drive Links and Groove
Drive links play an important role in the mechanism, engaging with the sprocket to transfer power from the motor to the cutting elements. The groove within the drive link ensures the guide bar remains in place, maintaining smooth movement. Keeping this area clear of debris is essential for maintaining operational efficiency.
The Role of the Drive Links
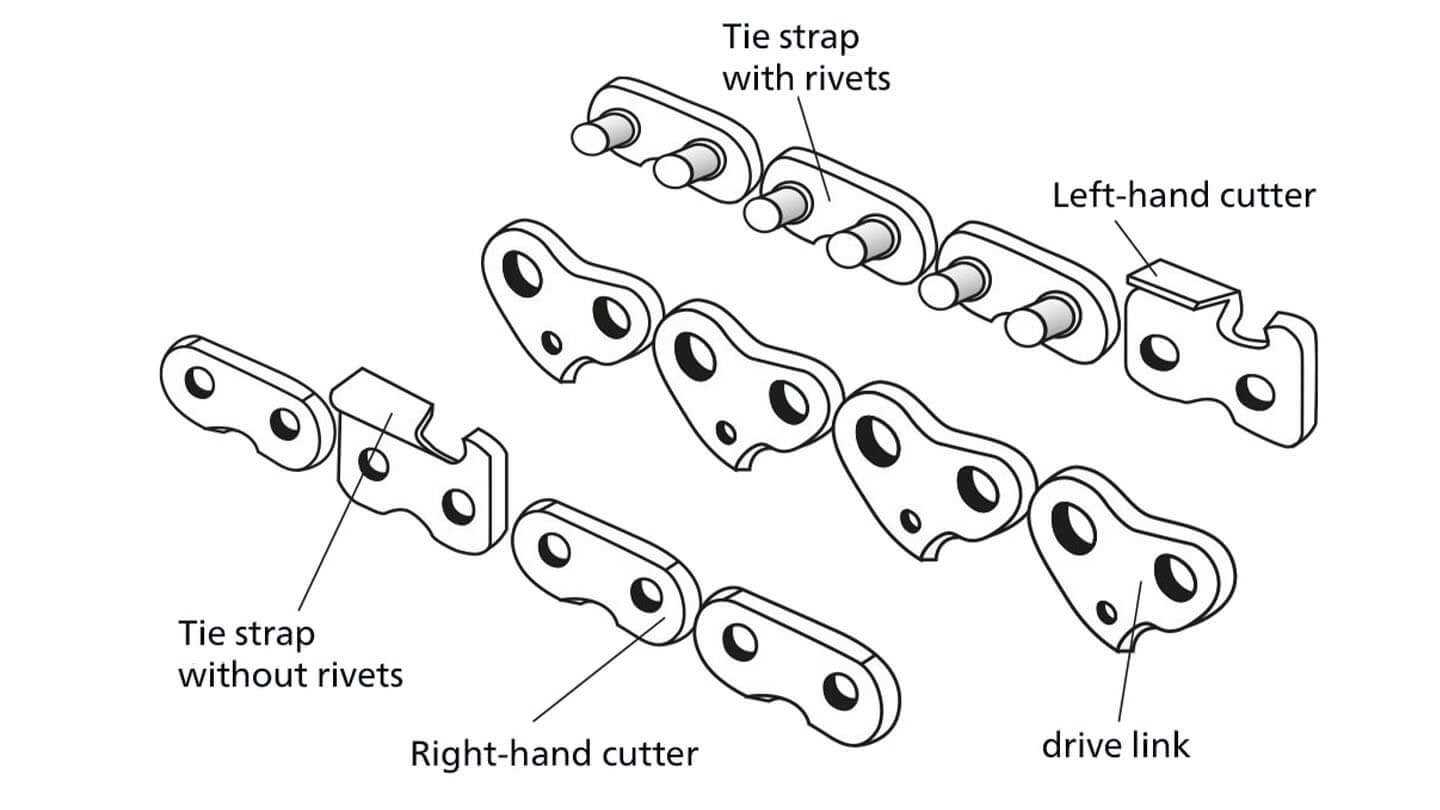
Drive links play a crucial role in the overall functioning of a cutting mechanism. They are essential for transmitting power from the engine to the moving cutting elements, ensuring smooth and efficient operation. Without these components, the energy generated by the motor would not be properly transferred, resulting in poor performance.
These specialized links have several key functions:
- Power Transmission: They act as the direct link between the motor and the moving cutting segments, ensuring that the necessary force is applied to the teeth for effective cutting.
- Guiding Mechanism: Drive links also help guide the moving sections, allowing them to maintain proper alignment during operation. This prevents misalignment and ensures the cutting edges stay on course.
- Durability: Made from high-strength materials, these links are designed to withstand continuous stress and friction, ensuring a long lifespan even under heavy usage.
- Safety: They help maintain a stable and secure connection between moving parts, reducing the risk of malfunction and accidents during operation.
In summary, drive links are indispensable for the efficient transfer of energy and stability of the cutting process, making them fundamental to the overall performance and safety of the tool.
What Are Cutter Links?
Cutter links play a crucial role in the cutting performance of any cutting device. They are the components responsible for slicing through the material being worked on. These links are designed with sharp edges and a specific geometry to ensure efficient and effective cutting. Their design allows them to maintain their sharpness and withstand the forces encountered during operation.
The cutter links are typically found at regular intervals along the cutting mechanism. They work in coordination with other elements, contributing to the smooth and precise action needed for tasks such as trimming, pruning, or more intensive cutting jobs. The durability and sharpness of these links are vital to the overall functionality and longevity of the tool.
How the Depth Gauge Impacts Cutting
The depth gauge is a crucial element in the cutting process, playing a vital role in how effectively the tool slices through wood or other materials. It controls the depth of each individual tooth’s engagement with the surface, determining how much material is removed during each pass. This small but significant component can influence both the efficiency and quality of the cut, as well as the overall performance of the equipment.
The depth gauge directly affects cutting in the following ways:
- Cutting Speed: A properly adjusted depth gauge allows the teeth to make optimal contact with the material, resulting in faster and more efficient cuts.
- Cutting Quality: If the gauge is too high, the teeth may not penetrate deeply enough, leading to uneven or rough cuts. Conversely, if it is too low, the teeth could dig in too aggressively, causing a rough and potentially dangerous operation.
- Tool Wear: Correct depth gauge settings reduce excessive strain on the cutting teeth and the rest of the equipment, helping to maintain sharpness and reduce wear over time.
- Safety: Proper depth adjustment ensures that the cutting action remains stable, minimizing the risk of kickback or other operational hazards.
In summary, the depth gauge plays an essential role in optimizing both the speed and precision of the cutting process, and its adjustment is key to ensuring consistent, safe, and high-quality results.
Importance of the Tie Straps
The tie straps are essential components that play a crucial role in maintaining the functionality and safety of the cutting mechanism. They connect various elements together, ensuring that all parts remain properly aligned and operate efficiently. Without these connectors, the system would be prone to misalignment, reducing its effectiveness and increasing wear and tear.
Maintaining Alignment
One of the primary functions of the tie straps is to keep the teeth and other moving sections in a straight and precise arrangement. This ensures smooth operation and reduces the chances of the system binding or snagging during use. Proper alignment is vital for achieving optimal cutting performance and preventing unnecessary damage to the equipment.
Durability and Safety
Durable tie straps also contribute to the overall longevity of the cutting mechanism. They withstand the forces of operation and help prevent premature wear. Furthermore, they play a key role in safety, as misaligned or loose sections can lead to dangerous situations. Strong and secure connectors ensure that all parts remain in place, minimizing the risk of accidents.
How the Chain Links Function Together
Each link in the cutting system works in harmony with the others to ensure efficient movement and effective cutting action. The smooth interaction between individual components is crucial for optimal performance and safety during operation.
The links are designed to work as a cohesive unit, each performing specific tasks in the sequence of cutting. When the engine power is transmitted, the movement travels along the connected links, with each one pushing and pulling the others in a synchronized manner. This coordination allows the cutting teeth to engage the material and remove wood efficiently.
- Drive links: These are responsible for transferring the rotational energy from the motor to the teeth, propelling the system forward.
- Cutting teeth: Positioned strategically along the system, these specialized parts make precise incisions in the material, ensuring clean and accurate cuts.
- Rivets: These fasteners connect the links together, allowing them to pivot smoothly while maintaining structural integrity.
- Spacers: Spacers are crucial in maintaining proper distance between the links, ensuring the correct positioning and preventing friction that could lead to wear and tear.
By working together in such an organized manner, the individual links create a seamless flow of motion, allowing the device to cut through wood with minimal effort and maximum efficiency. Proper maintenance and alignment of these components are essential for prolonging their lifespan and ensuring consistent performance.
Why the Chain’s Rivets Matter
Rivets play a crucial role in ensuring the proper function and durability of cutting tools. These small but significant components serve as the connection points that hold individual segments together, allowing the entire system to operate smoothly and with precision. Without proper rivet alignment and integrity, the entire mechanism could suffer from decreased efficiency and increased wear over time.
Functionality and Performance
The rivets are responsible for maintaining the alignment of the links, which directly impacts the cutting efficiency. When these connections are strong and secure, each link moves freely, reducing friction and improving the overall cutting performance. Weak or damaged rivets can cause misalignment, leading to uneven cuts, increased resistance, and unnecessary strain on the tool.
Durability and Maintenance
Rivets are also key to the longevity of the tool. Properly manufactured and maintained rivets ensure that the segments do not shift or degrade prematurely. Regular inspection and occasional tightening of the rivets can prevent long-term damage and extend the operational life of the entire system.
| Issue | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Loose Rivets | Increased friction, uneven cutting, potential damage | Tightening or replacing worn rivets |
| Corroded Rivets | Weakened structural integrity, rust buildup | Regular cleaning and use of protective oils |
| Misaligned Rivets | Decreased cutting efficiency, excess wear | Alignment checks and replacement of damaged links |
Identifying the Chain’s Shank and Heel

Understanding the key components that contribute to the cutting performance of your tool is essential for proper maintenance and effective use. Among these, certain sections play a crucial role in ensuring optimal precision and efficiency. Recognizing the shank and heel can help in identifying how the cutting elements engage with the material and how they wear over time. These sections are vital to the overall operation, providing balance and strength to the tool as it moves through the wood.
The Shank
The shank refers to the portion of the cutting link that extends back toward the center of the working element. This part is responsible for connecting the cutting link to the rest of the assembly, ensuring stability as the tool is used. It also plays a role in the durability of the tool by absorbing some of the pressure exerted during operation. The shank should be checked regularly for signs of wear or damage, as it directly affects the performance and safety of the tool.
The Heel

The heel is the rear part of the cutting element that follows the shank. It provides the necessary leverage to maintain consistent cutting depth while minimizing friction against the material. The heel’s design influences the cutting angle, which is crucial for making smooth, precise cuts. Regular inspection of the heel ensures that it remains sharp and free from dullness or deformation, which could compromise the efficiency of the tool.
Both the shank and heel contribute significantly to the overall functionality. Knowing how to identify these features can enhance your understanding of how the tool works and how to maintain it for long-term use.
Function of the Chain’s Cutting Teeth
The cutting teeth of a saw’s moving segment play a crucial role in the process of slicing through wood and other materials. These sharp, specialized components are designed to make clean, efficient cuts by penetrating and removing material with each pass. Their primary function is to provide the necessary force and precision for smooth and effective cutting, ensuring that the tool works quickly and with minimal effort from the user.
The cutting edges are shaped to engage with the material, creating a continuous feed of wood chips that helps clear the path of the blade. The geometry of these teeth is essential for maintaining consistent performance and reducing wear and tear on both the tool and the operator. By distributing the pressure evenly, they prevent the tool from becoming stuck or bogged down, allowing for faster and more accurate cuts.
Additionally, the sharpness of the cutting teeth plays a key role in determining the overall efficiency of the tool. Dull teeth can cause the machine to work harder, leading to increased fatigue and a slower cutting process. Regular maintenance and sharpening of these components are necessary to keep the performance optimal and ensure the best results when working with various materials.
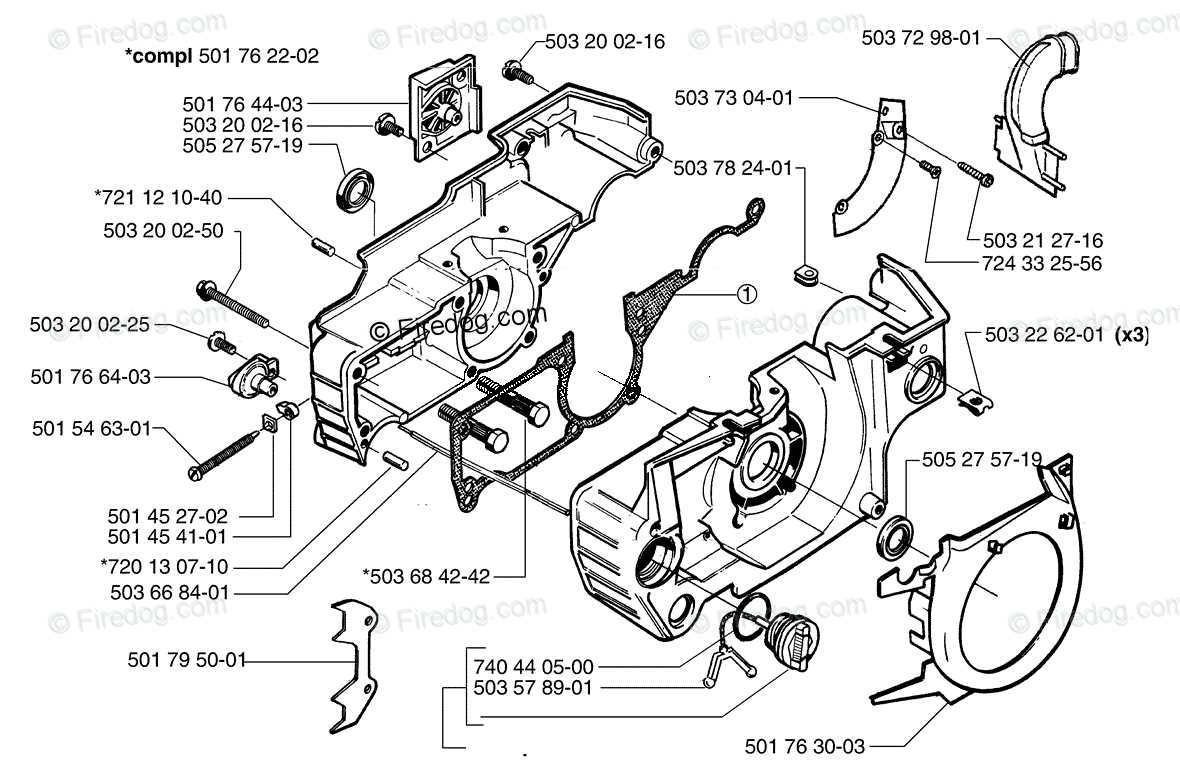
How to Maintain Chainsaw Chain Tension
Proper tensioning of the cutting loop is crucial for efficient and safe operation of your tool. If the loop is too loose or too tight, it can lead to reduced performance, increased wear, and even safety hazards. Regularly checking and adjusting the tension helps ensure smooth cutting, less strain on the motor, and a longer lifespan for your equipment.
To maintain optimal tension, follow these steps:
- Turn off the machine and disconnect the power source. Always ensure the tool is powered off before making adjustments to avoid accidents.
- Inspect the current tension. With the tool off, lift the loop slightly away from the guide bar at the midpoint. There should be minimal slack. If the loop droops or is difficult to move by hand, adjustment is necessary.
- Loosen the guide bar bolts. This allows you to adjust the tensioning mechanism without causing damage to the machine.
- Adjust the tensioning screw. Turn the screw clockwise to tighten and counterclockwise to loosen. Tighten until the loop sits snugly against the guide bar, but still allows you to pull it slightly by hand.
- Tighten the guide bar bolts back. Once the desired tension is reached, secure the bolts to lock the adjustment in place.
- Check the tension again. After tightening, manually move the loop to ensure it remains properly tensioned and is neither too tight nor too loose.
Remember to regularly check the tension during use, especially if the tool is being subjected to heavy workloads. Proper care will extend the life of your equipment and provide safer, more efficient performance.
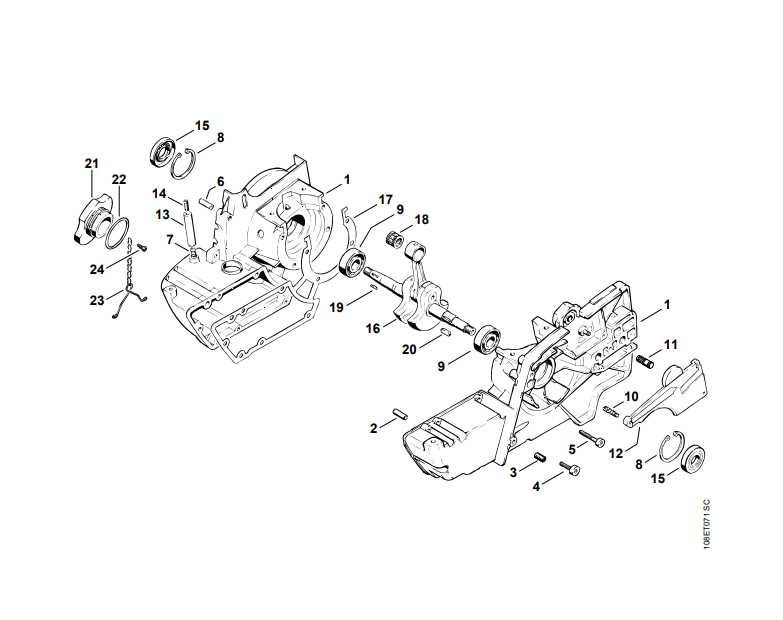
Visual Guide to Chainsaw Chain Diagrams
Understanding the different elements of a cutting mechanism is essential for both professionals and hobbyists. Knowing how each component interacts ensures better performance, safety, and longevity. This guide will break down the key features of the system, providing a clear visual representation of each element’s function and position. Familiarity with these components helps in selecting the right tools and maintenance strategies.
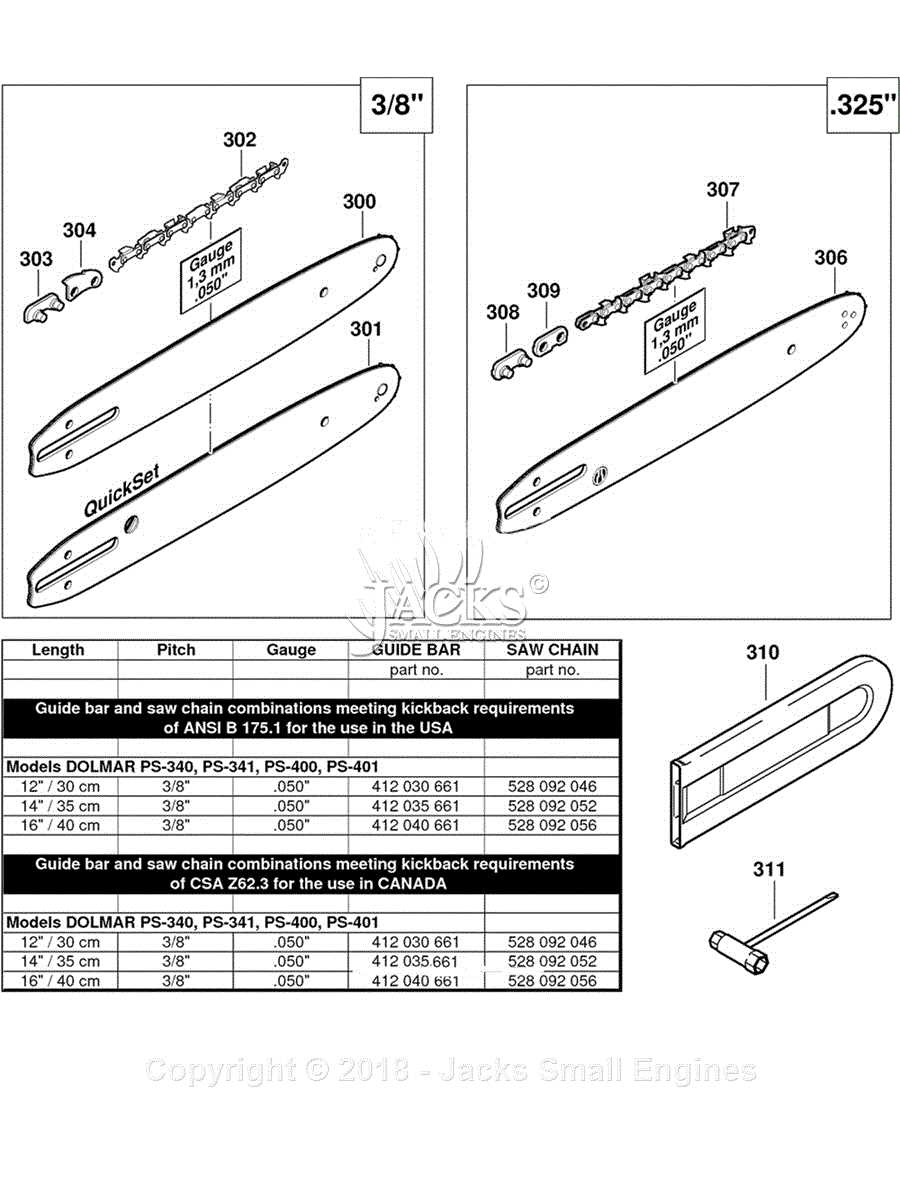
Key Components of the Cutting System
- Teeth: These are the primary elements responsible for slicing through wood, designed with specific angles for optimal efficiency.
- Drive links: These elements connect to the machine, transferring the power needed for the teeth to operate.
- Depth gauges: Positioned in front of the teeth, they control the depth of each cut, ensuring smooth operation without excessive strain on the mechanism.
- Rivets: These fasten the different sections of the tool together, allowing movement and flexibility while maintaining stability.
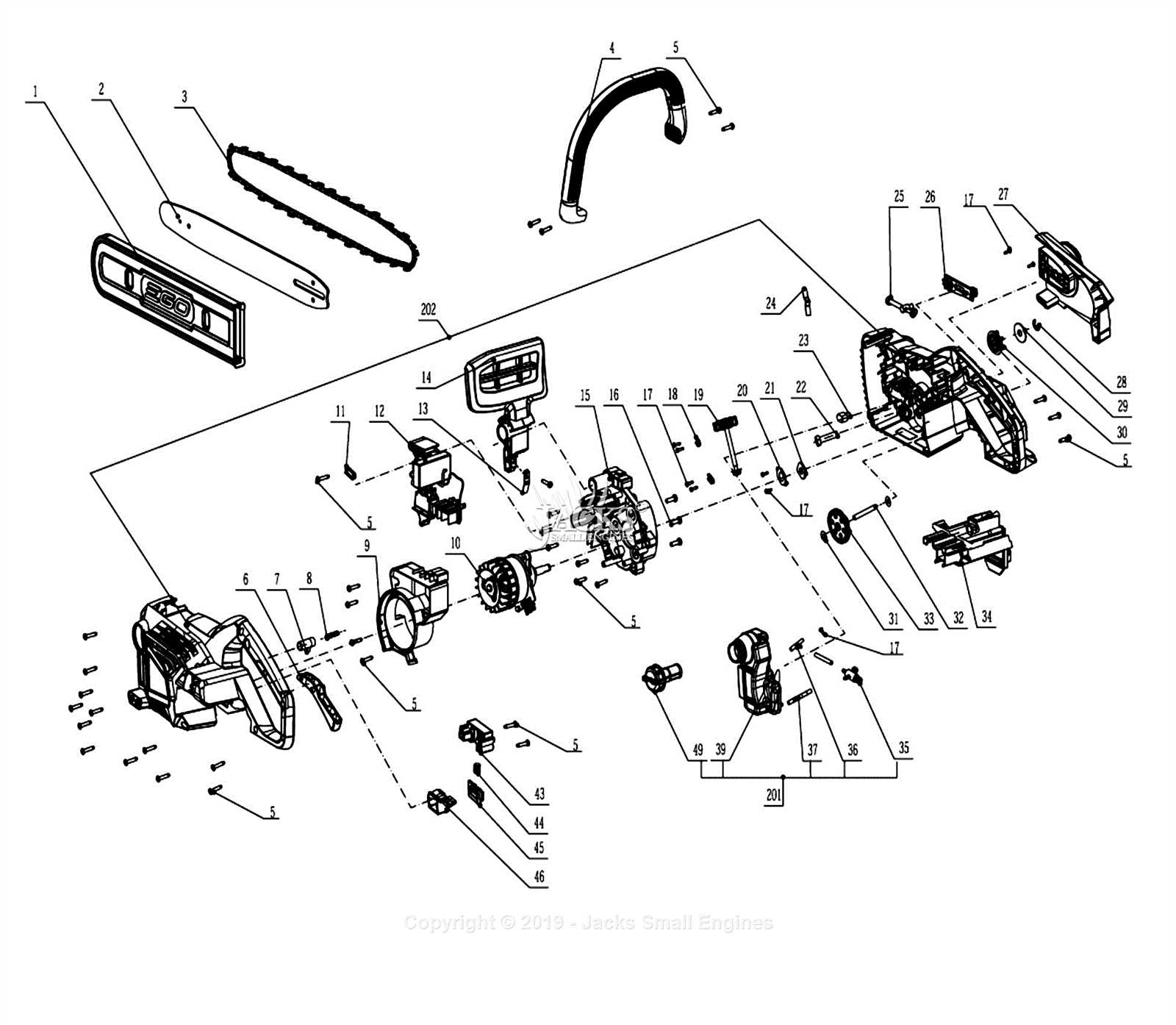
Understanding the Configuration
- Front teeth: Positioned at the leading edge, these parts begin the cutting action, taking the initial load.
- Middle section: This part supports the cutting process and maintains balance, enabling a steady flow of power.
- Rear teeth: The final elements help smooth the cut and remove debris efficiently.
- Drive links placement: These provide essential traction, guiding the entire mechanism through the material with precision.