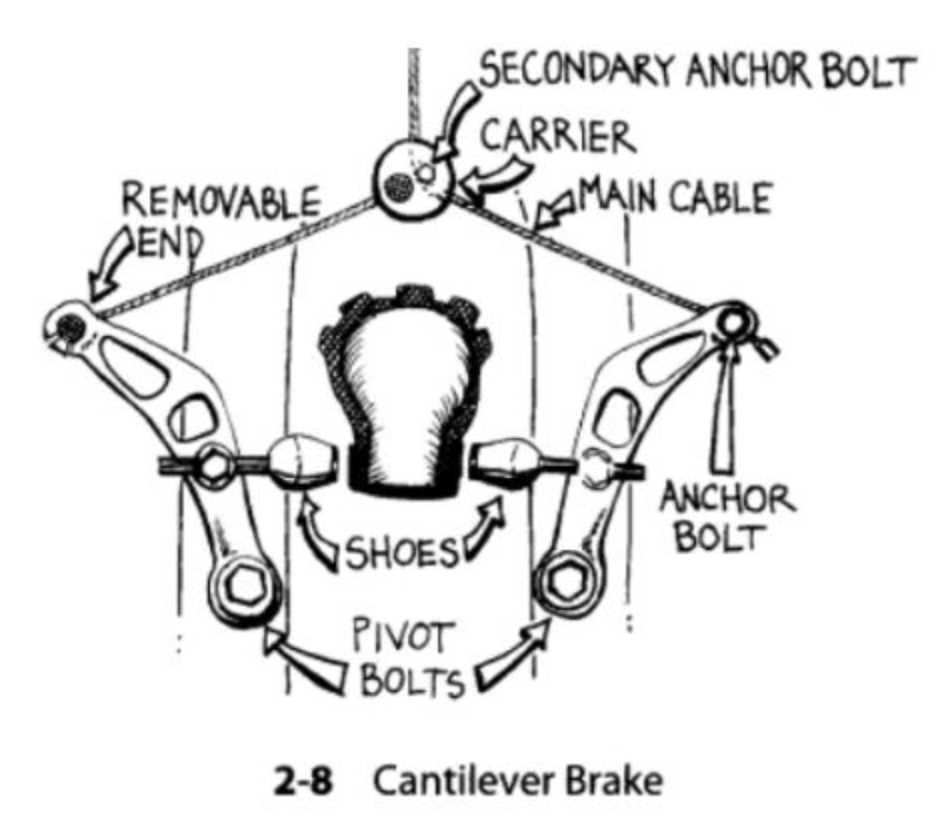
In the world of cycling, the ability to halt smoothly and efficiently is crucial for safety and performance. This section delves into the intricate elements that contribute to this vital function, offering a comprehensive look at their design and operation. Each component plays a significant role in ensuring that riders can navigate various terrains with confidence.
Visualizing the mechanics behind these stopping systems can enhance one’s understanding of how they work together. By examining the arrangement and interaction of these crucial elements, enthusiasts can appreciate the engineering that supports a seamless riding experience. The interdependence of these components highlights the importance of maintenance and awareness for all who embark on two-wheeled journeys.
In this exploration, we will break down the various sections of the stopping mechanism, focusing on their specific functionalities and how they contribute to overall performance. Whether you are a seasoned cyclist or a newcomer, grasping the details of these essential elements will empower you to make informed decisions regarding upkeep and enhancements.
Understanding Bike Brake Systems
A well-functioning stopping mechanism is crucial for any cycling enthusiast, ensuring safety and control during rides. This section delves into the essential components and functioning of these systems, providing insights into their operation and maintenance.
Various types of stopping mechanisms exist, each with distinct features and applications:
- Rim Mechanism: Utilizes pads that press against the wheel’s rim to create friction.
- Disc Mechanism: Engages pads against a disc mounted on the wheel hub, offering consistent performance.
- Drum Mechanism: Encloses components within a drum, providing protection and durability.
Understanding how these systems work is vital for effective upkeep:
- Friction: The primary force that brings the cycle to a halt, generated by the interaction between surfaces.
- Adjustment: Regular tuning is necessary to maintain optimal performance and responsiveness.
- Wear and Tear: Components naturally degrade over time, requiring timely replacement to ensure reliability.
By grasping these fundamental concepts, cyclists can enhance their experience and ensure safety on every journey.
Types of Bicycle Brakes Explained
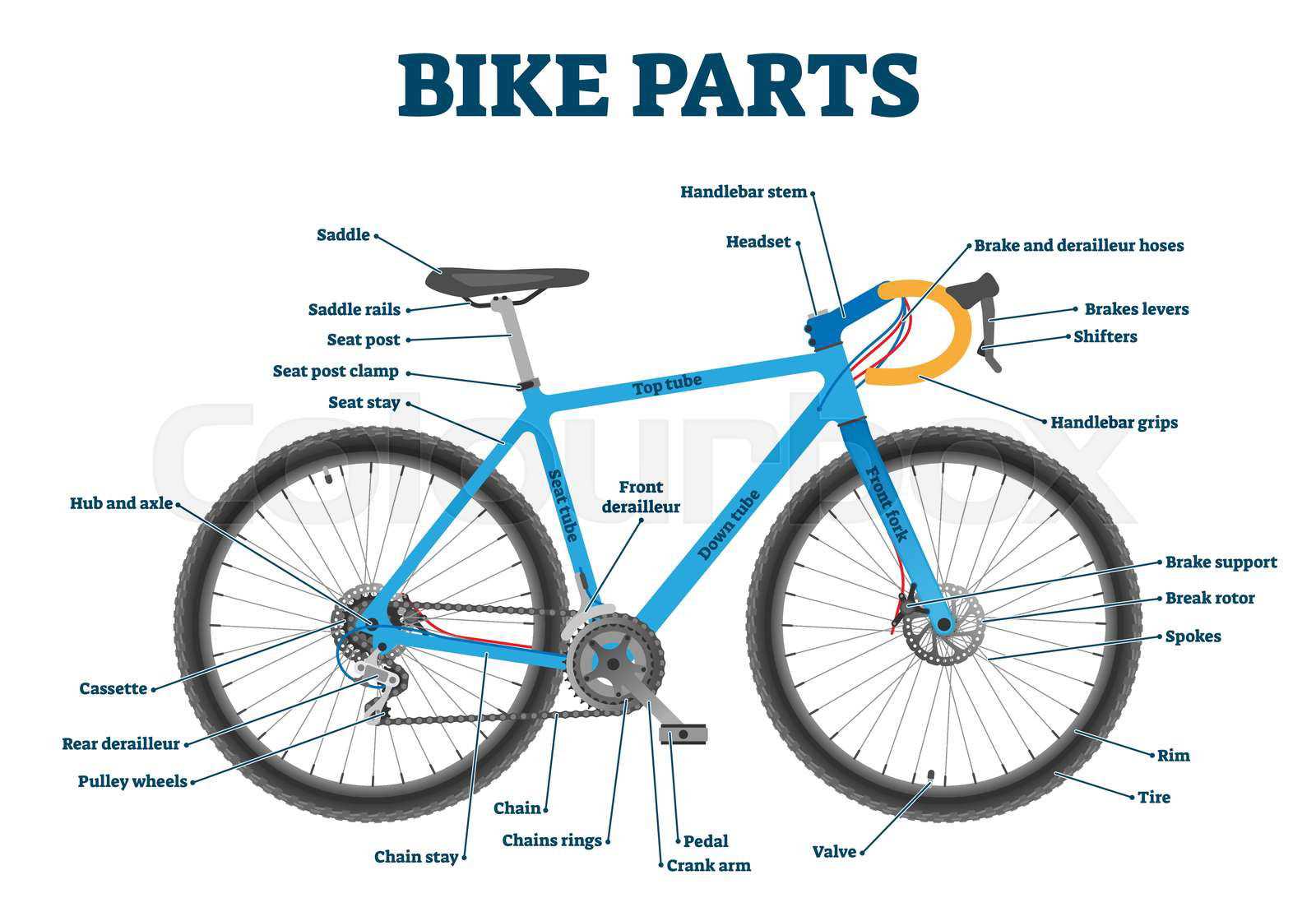
Understanding the various mechanisms that slow down or stop a two-wheeled vehicle is essential for both safety and performance. Each system has its own unique characteristics, catering to different riding styles and conditions. By exploring these mechanisms, cyclists can make informed choices that enhance their riding experience.
Rim systems utilize friction against the wheel’s outer surface to create stopping power. These are often lighter and simpler to maintain, making them popular among casual riders. In contrast, disc systems offer superior performance in varied weather conditions, providing consistent force regardless of external factors.
Drum mechanisms, typically enclosed, are less affected by dirt and moisture, making them reliable for commuting. Lastly, coaster systems engage through pedal action, making them user-friendly for beginners. Each type presents distinct advantages, allowing cyclists to tailor their experience based on personal preferences and riding demands.
Key Components of Brake Assemblies
The effectiveness of a stopping system relies heavily on its essential elements. Understanding these fundamental components is crucial for maintenance and performance enhancement. Each element plays a unique role in ensuring the system operates smoothly and efficiently, contributing to overall safety and functionality.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Lever | Acts as the control interface for engaging the stopping mechanism. |
| Cable | Transmits force from the lever to the stopping mechanism, allowing for responsive action. |
| Caliper | Houses the stopping elements and exerts pressure against the rotating surface. |
| Pads | Friction elements that create the necessary resistance against the wheel’s motion. |
| Rotors | Discs that rotate with the wheel, providing a surface for the pads to engage. |
| Mounting Hardware | Includes bolts and brackets that secure the components in place for stability and safety. |
How Brake Levers Function
The mechanism that initiates a stopping action is vital for control and safety during movement. It operates through a simple yet effective system that translates hand pressure into significant force, allowing for smooth deceleration.
When engaged, the lever pivots around a fixed point, creating a mechanical advantage that amplifies the force applied by the user. This action is transmitted through cables or hydraulic fluid, leading to the activation of stopping components.
This design ensures that minimal effort results in maximum stopping power, highlighting the importance of precision engineering in maintaining safety and responsiveness. Understanding this function is crucial for optimizing performance and enhancing overall experience.
The Role of Brake Cables
In any cycling system, the components that facilitate control and safety are crucial for a smooth experience. Among these elements, the cables serve as vital links, transmitting force from the controls to the mechanisms that engage the stopping action. Their reliability directly influences performance and responsiveness.
Cables function by transferring tension when the rider applies pressure to the handle. This action initiates a sequence that ultimately brings the wheels to a halt. The effectiveness of this system depends on several factors, including cable condition, installation, and adjustment.
Additionally, cables must withstand various environmental challenges, such as moisture and dirt, which can compromise their integrity. Regular maintenance and timely replacement are essential to ensure optimal functionality, contributing to overall safety and confidence while riding.
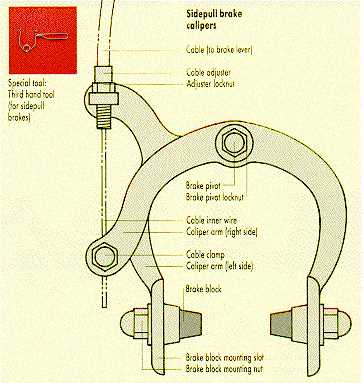
Understanding Brake Calipers
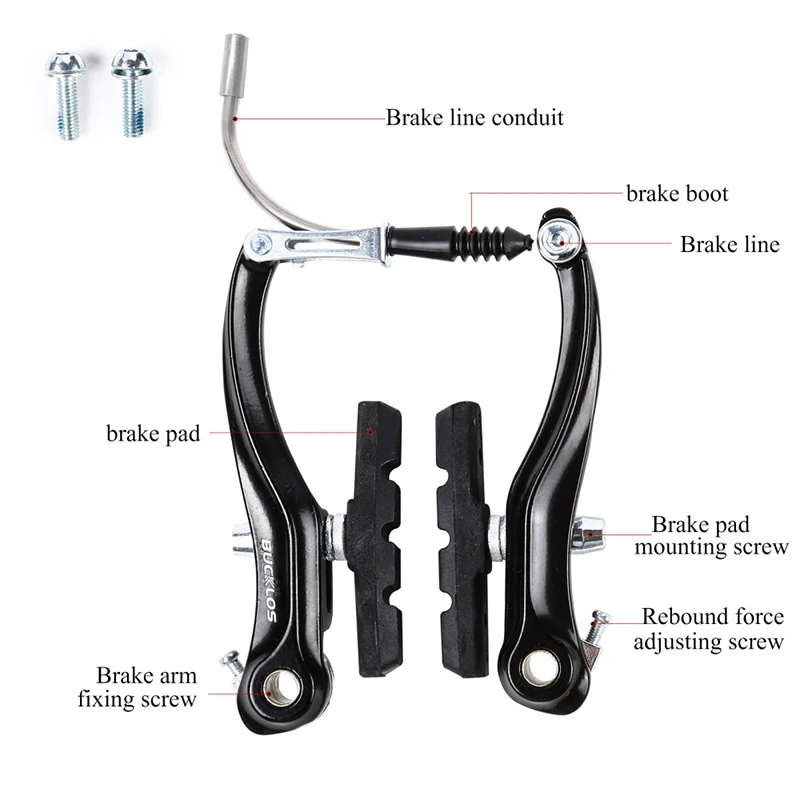

In the realm of cycling, components responsible for deceleration play a crucial role in safety and performance. Among these elements, one particularly stands out due to its intricate design and functionality. This section explores the essentials of this vital mechanism, shedding light on its operation and importance in ensuring a smooth riding experience.
Functionality and Design
The primary function of this mechanism is to apply force to the wheel’s rim or rotor, enabling effective stopping power. Typically, it consists of two main elements: the housing and the pistons. The pistons expand when activated, pressing against the friction material to create the necessary resistance. Understanding this interaction helps cyclists appreciate the engineering behind their equipment.
Maintenance and Care
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Riders should periodically inspect for wear, clean components, and replace any degraded materials. Proper care not only enhances safety but also contributes to a more enjoyable cycling experience.
Disc vs. Rim Brake Differences
This section explores the key distinctions between two popular stopping mechanisms commonly found in cycling. Understanding these variations can enhance your decision-making when choosing equipment suited to your riding style and conditions.
Performance and Conditions
- Disc systems typically offer superior stopping power in wet or muddy environments.
- Rim systems may perform adequately in dry conditions but can struggle when faced with moisture.
- Heat dissipation is generally better in disc setups, preventing fade during prolonged use.
Maintenance and Cost

- Disc mechanisms often require more frequent maintenance due to complex components.
- Rim systems are usually simpler and can be less expensive to replace.
- Long-term, the durability of disc options may offset initial costs.
Maintaining Brake Pads Effectively
Proper upkeep of stopping components is essential for ensuring safety and optimal performance. Regular attention not only prolongs their lifespan but also enhances overall functionality. Here are key practices to consider for effective maintenance.
Routine Inspections
- Check for wear and tear regularly.
- Look for cracks or uneven surfaces.
- Assess the alignment and positioning.
Cleaning Techniques
- Use a soft cloth to wipe down surfaces.
- Remove debris or contaminants with appropriate solutions.
- Ensure everything is dry before reassembly.
By following these guidelines, you can significantly improve the durability and effectiveness of your stopping mechanisms.
Common Brake Parts Wear and Tear
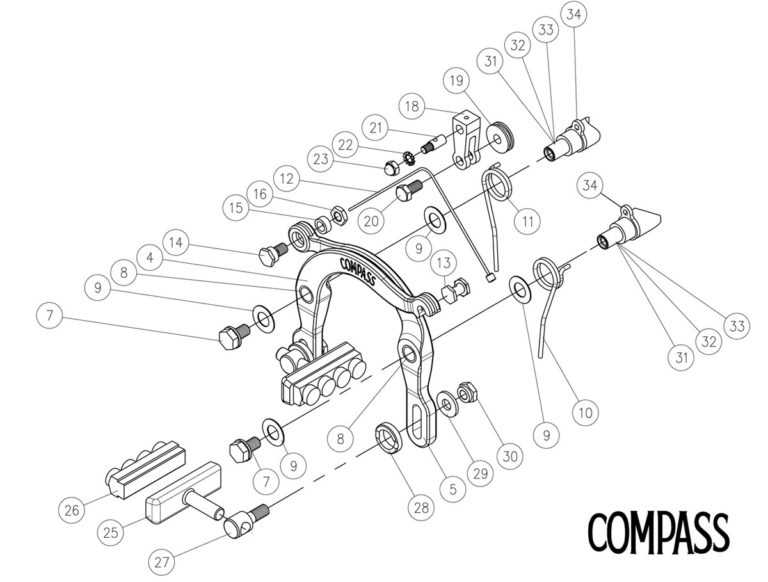
Understanding the typical degradation of essential components is crucial for optimal performance and safety. Over time, various elements experience fatigue due to regular usage, leading to diminished efficiency and potential failures. Recognizing these signs early can prevent serious issues and ensure smooth operation.
Key Components and Their Lifespan
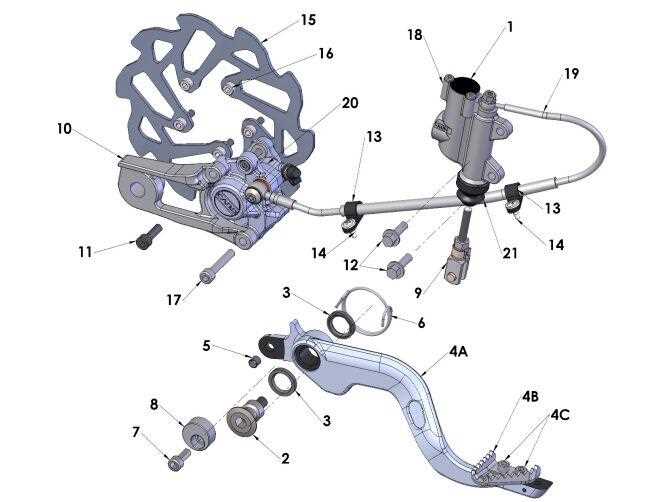
Different components exhibit unique wear patterns based on their materials and functions. Regular inspections can help identify problems before they escalate.
| Component | Common Issues | Expected Lifespan |
|---|---|---|
| Pads | Fading, uneven wear | 1,500 – 3,000 miles |
| Cables | Fraying, stiffness | 3 – 5 years |
| Calipers | Leaking, corrosion | 5 – 10 years |
Signs of Deterioration
Be attentive to unusual sounds, vibrations, or changes in responsiveness. These indicators often signal that components need immediate attention to maintain ultimate safety and functionality.
Visualizing Brake System Diagrams
Understanding the intricate workings of a stopping mechanism is essential for both enthusiasts and professionals. Clear illustrations serve as powerful tools for grasping how each component interacts, ensuring effective maintenance and troubleshooting. By representing these systems visually, one can easily identify the functionality and arrangement of various elements, leading to enhanced comprehension and improved performance.
The Importance of Clarity
Clarity in representation aids in the identification of potential issues and facilitates informed decisions during repairs. Detailed visuals enable users to explore the relationships between different sections, providing a comprehensive view of the overall setup. This fosters a deeper understanding of how each individual element contributes to the system’s efficiency.
Exploring Advanced Designs
Diving into complex layouts reveals the innovation behind modern stopping systems. By examining various configurations and enhancements, one can appreciate the evolution of design and technology. Such exploration not only highlights advancements but also encourages a proactive approach to maintenance and improvement.
Adjusting Brake Tension Properly
Ensuring optimal responsiveness is crucial for a smooth ride. Correct tension can significantly enhance performance and safety. This section outlines essential steps to achieve the right adjustment for your system.
- Begin by examining the current setup for any signs of wear or misalignment.
- Identify the adjustment mechanism, which may vary based on the design.
- Loosen the locking nut to allow for tension modification.
- Turn the adjustment screw or dial to increase or decrease tension as needed.
- Retighten the locking nut securely to maintain the new settings.
Regular checks and adjustments can lead to enhanced handling and responsiveness, ensuring an ultimate riding experience.
Upgrading Your Brake Components
Enhancing your stopping system is essential for improving performance and safety. Upgrading components can lead to a more responsive and reliable experience, allowing for greater control and confidence during rides. Whether you’re seeking better modulation or increased durability, investing in higher-quality elements can make a significant difference.
Consider the following factors when exploring enhancements: material quality, weight reduction, and compatibility with existing systems. Choosing advanced materials can result in improved heat dissipation and reduced wear, while lighter components can enhance overall handling. Additionally, ensuring compatibility will guarantee a seamless integration into your setup.
Upgrading is not only about performance; it can also bring aesthetic appeal. Many high-end components come in various finishes and colors, allowing you to personalize your ride. Ultimately, the right upgrades will elevate your experience, providing both functionality and style.
Safety Tips for Bike Braking
Ensuring a secure stopping experience is essential for every cyclist. Proper techniques and awareness can significantly enhance safety while navigating various terrains.
- Always maintain a safe distance from other riders and obstacles.
- Regularly check and maintain your stopping mechanisms for optimal performance.
- Use both stopping systems simultaneously for maximum effectiveness.
- Practice emergency stops in a safe environment to build confidence.
- Adjust your speed according to weather conditions and terrain type.
Being aware of surroundings and practicing these strategies can lead to a safer and more enjoyable journey.