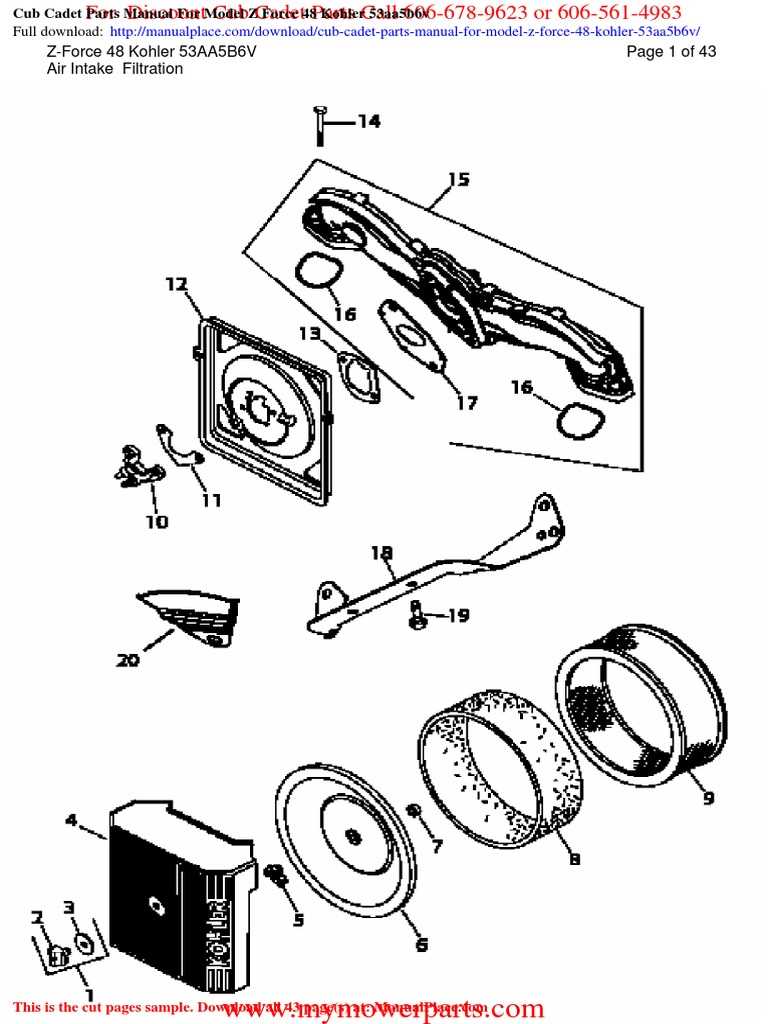
When working with complex machinery, having a clear understanding of how various elements are arranged can significantly ease maintenance and repair tasks. A detailed overview of the individual mechanisms and their connections can help ensure that everything functions as intended, offering both safety and efficiency.
Exploring the structure of these systems provides insights into how different mechanical units work together. Whether you are addressing routine upkeep or specific malfunctions, familiarizing yourself with the organization of essential mechanisms is crucial to optimizing performance.
By gaining a deeper knowledge of the internal components and their respective locations, anyone can improve their ability to troubleshoot, repair, and maintain various devices more effectively.
Essential Components of the Cub Cadet 1811
The machinery in question includes several vital elements that ensure its smooth performance and longevity. Each component plays a crucial role in keeping the equipment functional and efficient. Understanding these key elements will help in maintaining the device and addressing any potential issues that may arise during operation.
Among the critical aspects to consider are the power unit, responsible for driving the entire mechanism, and the system that manages fuel distribution. Additionally, the framework and operational controls are essential for the operator’s comfort and control, while the wheels and motion systems provide mobility and stability. These core parts are interdependent, working together to create a robust and reliable machine.
Engine Assembly Overview
The engine is a critical component in any machine, providing the necessary power for various operations. Understanding the structure and function of the engine assembly helps in maintaining and ensuring smooth performance. This section will provide an overview of the main elements that make up the engine, along with their roles in the overall mechanism.
At the heart of the engine, key components work together to convert fuel into motion. These include the combustion chamber, pistons, crankshaft, and other essential elements that coordinate to drive the mechanical processes. Each part is designed to perform specific tasks, ensuring efficient power generation.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components can significantly extend the lifespan of the engine, ensuring reliable operation. Being familiar with how the assembly functions can help in identifying potential issues early, allowing for timely repairs and adjustments.
Steering System Parts Breakdown
The steering mechanism is a critical component that ensures smooth control and maneuverability. This system involves various interconnected elements working together to provide precise direction and stability. Below is a breakdown of the essential components that contribute to the overall functionality of the steering system.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Steering Wheel | The primary interface that allows the operator to control the direction of the vehicle. |
| Steering Column | Connects the steering wheel to the steering mechanism, transmitting input from the operator. |
| Steering Gearbox | Converts the rotational movement of the steering wheel into linear motion to turn the wheels. |
| Steering Linkages | These rods and joints transfer motion from the gearbox to the wheels, ensuring coordinated turning. |
| Tie Rods | Connect the steering linkages to the wheels, providing final movement adjustments. |
| Ball Joints | Allow smooth movement between the steering linkages and other components while maintaining flexibility. |
Detailed View of the Transmission
The transmission system plays a crucial role in transferring power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring smooth and efficient operation. Understanding its layout and components is essential for maintaining optimal performance and resolving any potential issues.
Core Components
Within the transmission, several key elements work together to regulate speed and torque. Gears, shafts, and clutches interact to adjust the output, allowing the machine to function in different conditions. Each component must be inspected regularly to avoid wear and tear.
Maintenance Tips
Routine checks and lubrication of the transmission parts can significantly extend its lifespan. Ensuring proper alignment and addressing any minor faults promptly can prevent larger issues from developing. Always consult the service manual for specific recommendations on upkeep.
Front Axle and Wheel Diagram
The structure of the front axle and wheels plays a crucial role in ensuring stability and smooth operation. Understanding the components involved and their assembly is important for maintaining optimal performance. This section will provide a breakdown of the key elements that connect the steering and support mechanisms.
- Axle Beam: The main horizontal component that supports the wheels and connects them to the steering system.
- Wheel Hub: The central part where the wheel attaches, allowing rotation around the axle.
- Steering Knuckle: A pivotal part that connects the axle to the wheels, enabling directional movement.
- Bearing Assembly: Helps the wheels rotate smoothly while reducing friction and wear.
- Spindle: A rotating shaft that holds the wheel hub and allows the wheel to turn.
Each of these components must work together seamlessly to provide proper steering and weight distribution during movement.
Electrical Wiring Components
Understanding the various elements involved in electrical wiring is crucial for ensuring the proper functioning of machinery. Each component plays a vital role in establishing connections, delivering power, and enabling control mechanisms. This section delves into the essential wiring components that contribute to the overall electrical system.
Key Components
- Wires: Conductors that facilitate the flow of electricity.
- Connectors: Elements used to join two or more wires securely.
- Relays: Electromechanical switches that control larger currents with a smaller signal.
- Switches: Devices that open or close electrical circuits.
- Fuses: Safety devices that protect circuits from overload by breaking the connection when current exceeds a certain level.
Wiring Techniques
- Ensure proper gauge wire is used for the intended load.
- Employ color-coding for easy identification of different circuits.
- Utilize secure connections to prevent accidental disconnections.
- Regularly inspect wiring for signs of wear or damage.
Hydraulic System Structure
The hydraulic system is a crucial component that enables efficient power transmission in machinery. It operates by using pressurized fluid to perform various functions, such as lifting, steering, and controlling attachments. Understanding its design and function is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
This system typically consists of several key elements, including a pump, cylinders, hoses, and valves. The pump generates pressure by moving fluid from the reservoir to the cylinders, where it is utilized to create mechanical movement. Hoses connect these components, allowing fluid to flow seamlessly, while valves regulate the flow and direction of the hydraulic fluid, ensuring optimal performance.
Regular inspection of the hydraulic system components is vital to prevent leaks and ensure smooth operation. Proper maintenance practices, such as checking fluid levels and inspecting hoses for wear, can significantly enhance the lifespan and efficiency of the system.
Exhaust System Configuration
The exhaust system plays a vital role in managing engine emissions and enhancing overall performance. Proper configuration ensures efficient gas flow and minimizes back pressure, leading to improved efficiency and longevity of the engine. Understanding the components and their arrangement is crucial for maintenance and upgrades.
Typically, the configuration includes elements such as the manifold, muffler, and various connectors. Each component is designed to work together seamlessly, directing exhaust gases away from the engine and reducing noise levels. Regular inspection of the system is essential to identify potential leaks or blockages that could hinder performance.
When considering modifications or repairs, it’s important to choose compatible components that align with the original design to maintain optimal functionality. Proper installation practices will further enhance the reliability of the exhaust system, contributing to a smoother operational experience.
Fuel System Parts Identification
The fuel system is crucial for the efficient operation of any engine, ensuring that the right amount of fuel reaches the combustion chamber. Understanding the components involved in this system is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance. This section will provide an overview of the main elements related to fuel delivery, helping you identify and understand their functions within the assembly.
Key Components of the Fuel System
Each part of the fuel delivery system plays a significant role in maintaining optimal performance. Below are some of the primary components you’ll encounter:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | Holds the fuel supply for the engine. |
| Fuel Pump | Moves fuel from the tank to the engine. |
| Fuel Filter | Removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine. |
| Carburetor | Mixes air and fuel in the correct ratio for combustion. |
| Fuel Lines | Transport fuel between the tank, pump, and engine components. |
Identifying Issues in the Fuel System

Regular inspection of the fuel components can help prevent performance issues. Look for signs such as leaks, blockages, or deterioration, as these can indicate that specific elements require maintenance or replacement. Understanding each part’s role is essential for effective troubleshooting and ensuring the engine runs smoothly.
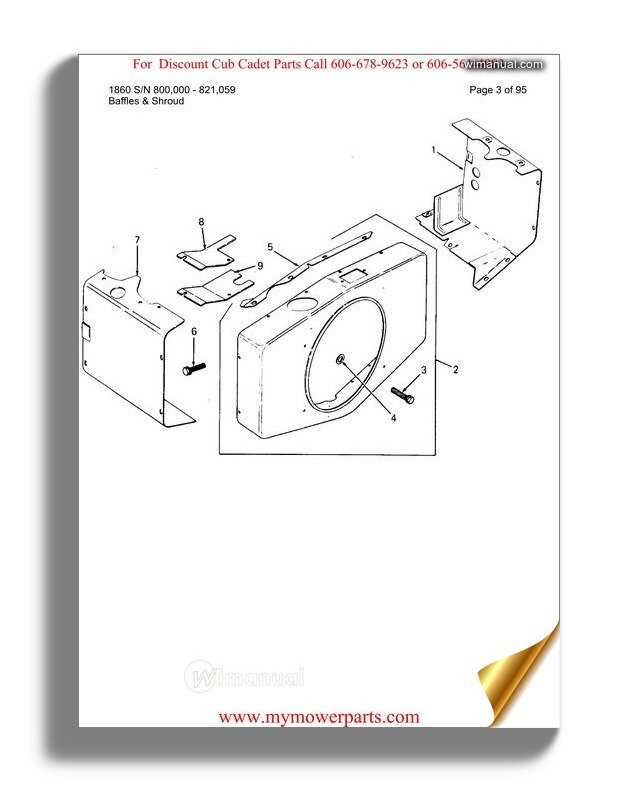
Chassis and Frame Diagram
The structure and base components of any machinery play a crucial role in its overall performance and stability. Understanding the layout of these elements is essential for maintenance and repair, ensuring that the equipment operates efficiently and safely. This section focuses on the arrangement of the foundational parts that support the machine, providing insight into their configuration and interconnections.
Key Elements: The main support structure is typically designed to withstand various stresses while providing a stable platform for other components. The configuration often includes vital attachments for essential systems and features, facilitating smooth operation and maintenance. An overview of these components allows users to grasp the assembly and troubleshoot potential issues effectively.
Maintenance Tips: Regular inspection of the frame and support systems can prevent significant mechanical failures. Look for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment, and address these promptly to extend the lifespan of the equipment. Understanding the structure will aid in identifying problem areas quickly, enhancing overall efficiency.
Brake System Components
The brake system is crucial for ensuring safety and control in machinery. It consists of various elements that work together to effectively slow down or stop the vehicle when necessary. Understanding the components involved can help in maintenance and troubleshooting efforts.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Brake Pedal | The part that the operator presses to engage the braking mechanism. |
| Brake Cylinder | A hydraulic component that converts the force from the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure. |
| Brake Lines | Hoses that carry hydraulic fluid from the brake cylinder to the brake assembly. |
| Brake Shoes | Friction components that press against the brake drum to create stopping power. |
| Brake Drum | A cylindrical part that rotates with the wheel and provides a surface for the brake shoes to press against. |
| Adjusting Mechanism | A system that ensures the brake shoes are positioned correctly for optimal performance. |
Seat and Operator Controls Layout
The arrangement of seating and control mechanisms plays a crucial role in ensuring comfort and functionality for the user. A well-designed layout facilitates ease of operation and enhances overall efficiency during use. This section outlines the key components found in this essential area.
- Operator Seat: Provides a stable and comfortable position for the user, often featuring adjustable settings to accommodate different preferences.
- Control Panel: Centralized area where the primary controls are located, including:
- Throttle lever
- Ignition switch
- Headlight controls
- Foot Pedals: Located for easy access, allowing for intuitive operation of:
- Acceleration
- Brake functions
- Steering Wheel: Designed for optimal grip and maneuverability, essential for navigating various terrains.
- Safety Features: Includes mechanisms such as seat belts and emergency shut-off switches to ensure user safety during operation.
Overall, the thoughtful arrangement of these elements contributes significantly to a user-friendly experience, making it easier to perform tasks efficiently and safely.
Safety Features and Shields
Ensuring user protection is a crucial aspect of any machinery design. Various safety elements are integrated into equipment to prevent accidents and promote secure operation. Shields and guards play a significant role in safeguarding operators from moving parts and potential hazards.
These protective components are designed to minimize the risk of injury while enhancing the overall safety of the machine. Regular inspection and maintenance of these features are essential to ensure they function effectively and provide the necessary protection.
| Safety Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Shielding Covers | Protects operators from rotating components and debris. |
| Emergency Stops | Allows immediate shutdown of the equipment in case of an emergency. |
| Operator Guards | Prevents accidental contact with moving parts. |
| Safety Interlocks | Ensures the equipment cannot operate when certain conditions are not met. |