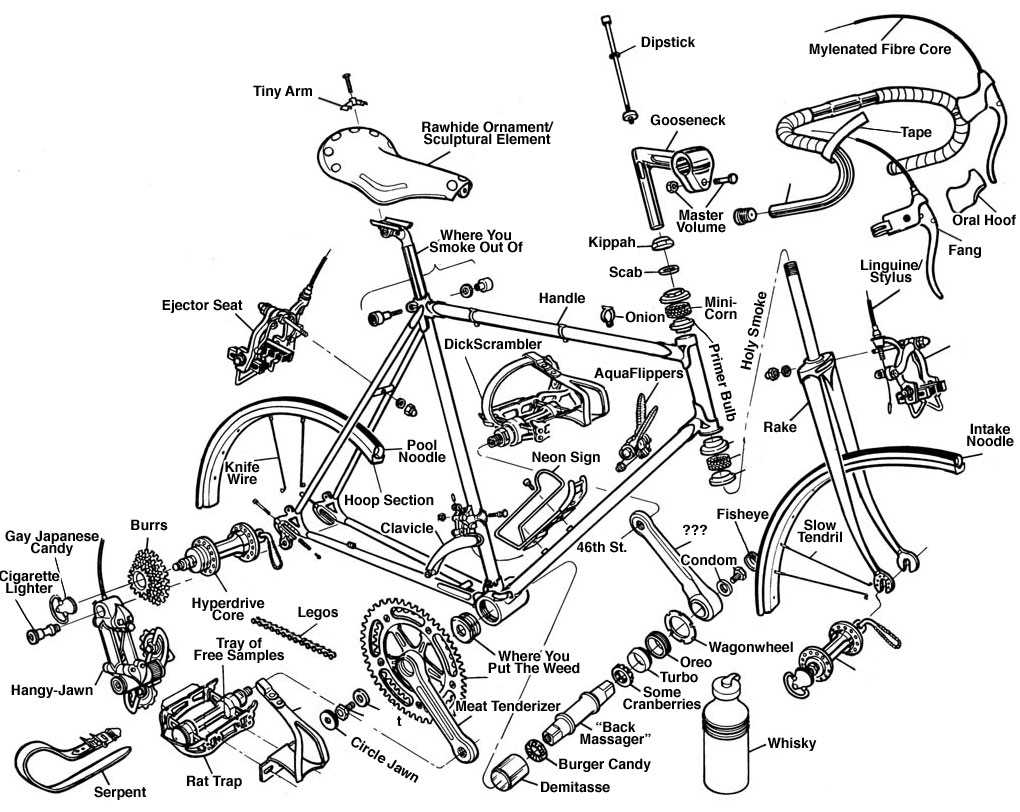
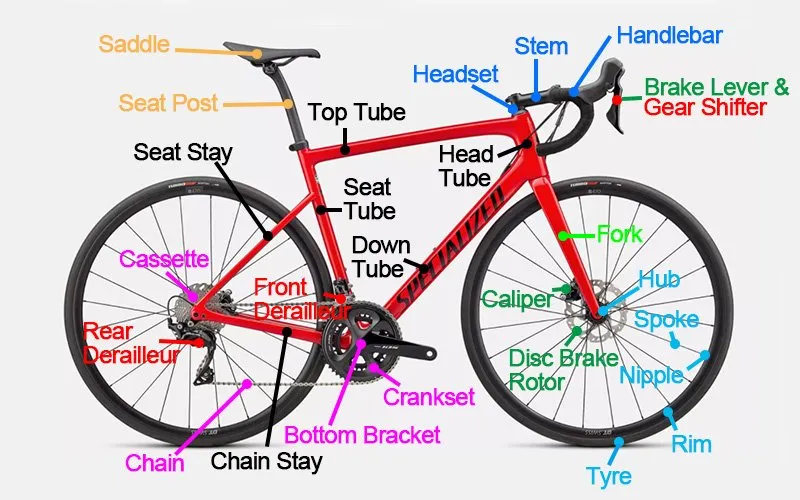
When it comes to freestyle riding, having a clear understanding of each element that makes up the vehicle is crucial for both performance and maintenance. Whether you are looking to improve your skills or simply ensure that your two-wheeler is in top condition, knowing how all the pieces work together is key to mastering the art of the ride.
The structure of this unique type of two-wheeler consists of various interconnected elements, each playing a specific role in ensuring smooth operation. From the framework that provides stability to the mechanisms that control speed and movement, every detail contributes to the overall experience of riding. Recognizing these elements can help you make informed decisions when upgrading or maintaining your setup.
In the following sections, we will explore the essential elements of this freestyle vehicle, explaining their function and importance. This guide aims to give you a deeper understanding of how each component interacts, enhancing both your knowledge and your riding experience.
BMX Components Overview
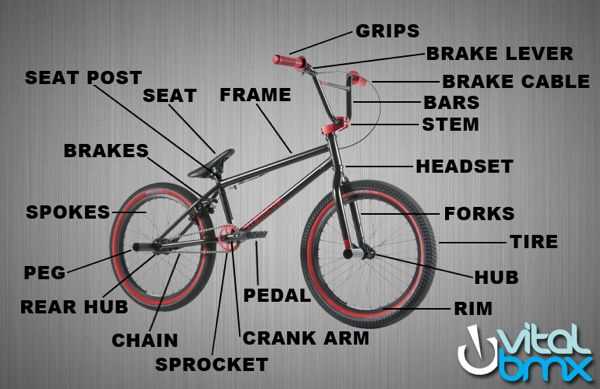
Understanding the structure of a performance two-wheeler is essential for enthusiasts and riders alike. Each element of the setup is designed for optimal performance and durability, ensuring smooth maneuverability and control during various tricks and stunts. Below is a breakdown of the key elements contributing to this high-performance machine.
Core Elements
- Frame: The foundation, providing strength and balance. Usually crafted from lightweight, durable materials for enhanced agility.
- Wheels: Designed for stability and grip, these often feature thicker treads for better traction on different surfaces.
- Handlebars: Shaped for easy control, allowing precise movement and stunts.
- Seat: Typically compact, providing comfort while maintaining the rider’s ability to move freely during tricks.
Additional Components

- Brakes: Essential for controlling speed, offering quick and reliable stopping power.
- Pedals: Durable and lightweight, designed to provide a secure foothold during rapid movement.
- Crankset: Transfers the rider’s energy into motion, key for acceleration and maintaining speed.
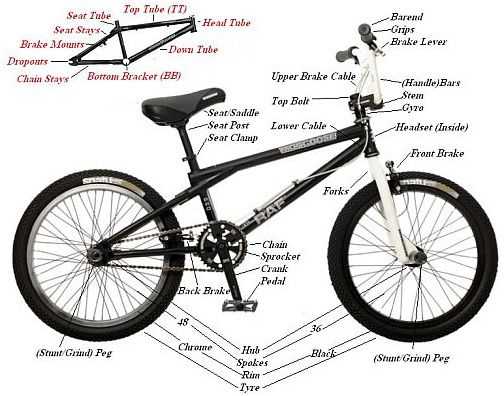
Frame Structure and Design
The frame serves as the core foundation, offering support and balance for various components. Its design significantly impacts overall performance, from handling and maneuverability to durability. By understanding the architecture and material choices, you can appreciate how the structure influences agility and resilience in different terrains.
The table below outlines key aspects of frame construction:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Material | Commonly used materials include steel, aluminum, and carbon fiber, each offering distinct advantages in strength, weight, and flexibility. |
| Geometry | The angles and dimensions of the frame dictate the rider’s posture, enhancing control and stability during movement. |
| Welds and Joints | Reinforced welds and precise joint connections ensure structural integrity and longevity, even under stress. |
Wheels and Tire Specifications
The structure and composition of wheels play a crucial role in maintaining control, stability, and performance. Understanding the specifications of the rims and tires helps in optimizing the ride for various terrains and conditions, ensuring both safety and durability.
Wheel Composition
The wheels consist of several essential components, each contributing to their strength and function. The choice of materials and design impacts the overall durability and responsiveness.
- Rim material: Alloy or steel are the most common materials, chosen for their lightweight and durability.
- Spoke count: Higher spoke counts provide better strength and stability, especially during intense riding conditions.
- Hub type: The hub design affects the wheel’s ability to spin smoothly and transfer power efficiently.
Tire Characteristics
The tires are equally important in defining traction and speed. The size, tread pattern, and pressure are all key factors in how they interact with different surfaces.
- Tread pattern: Aggressive treads are suitable for rough terrains, while smoother patterns are ideal
Handlebars and Steering Mechanism
The handlebars and steering mechanism play a crucial role in providing control and stability during rides. They are designed to offer comfort, responsiveness, and precision, allowing the rider to easily maneuver in different environments. Understanding their structure and function is essential for maintaining a smooth and controlled riding experience.
Below is an overview of the key components of the steering system:
Component Description Handlebars The horizontal bar that the rider grips, designed to offer balance and control. Stem Connects the handlebars to the front fork, ensuring a stable connection for steering. Headset Houses the bearings that allow smooth rotation of the front assembly, providing effortless steering. Fork The component that holds the front wheel, ensuring the rider can steer Braking System Components

The braking system is essential for ensuring control and safety during rides. It consists of various elements that work together to regulate speed and bring the rider to a stop when needed. Understanding these components is crucial for maintaining efficiency and enhancing overall performance.
Brake Levers serve as the primary control mechanism, allowing the rider to apply pressure and engage the brakes. They are mounted on the handlebars and connected to the rest of the system through cables or hoses.
Cables or hoses transmit the force from the levers to the braking mechanism itself. These are vital for seamless operation, requiring regular maintenance to avoid wear and tear.
The calipers or brake arms play a key role by squeezing the wheel’s rim or rotor, generating the friction necessary to slow down or stop. Different designs and materials affect their efficiency and response time.
Pads are the contact points that directly engage with the rim or rotor, creating the friction needed to halt motion. These wear out over time and must be replaced periodically to ensu
Pedals and Crankset Anatomy
The relationship between pedals and cranksets is crucial for the overall functionality and performance of any cycling apparatus. Understanding their components and how they work together enhances efficiency and control during rides. This section delves into the intricate design and mechanics of these elements.
Key components of pedals and cranksets include:
- Pedals: These are the platforms where the rider applies force to propel the vehicle forward. They come in various styles to suit different riding preferences.
- Crank Arms: These connect the pedals to the main structure, converting the linear motion of the pedals into rotational force.
- Bottom Bracket: This houses the spindle, allowing the crankset to rotate smoothly while being securely attached to the frame.
- Spindle: The rod that connects the crank arms, providing the central point around which they rotate.
- Chainring: Attached to the crankset, it engages with the chain, enabling power transfer to the rear wheel.
Each component plays a vital role in achieving optimal performance and comfort. Riders often customize their setup based on personal preferences, riding style, and terrain.
For effective maintenance, it is essential to regularly check the integrity and functionality of these components, ensuring a smooth and safe riding experience.
Seat and Seatpost Features

The seat and seatpost play a crucial role in providing comfort and stability during rides. These components are designed to enhance the overall riding experience by ensuring proper posture and support. Various features contribute to their functionality and adaptability for different riding styles.
Key attributes of the seat include:
- Padding: The thickness and material of the cushioning affect comfort levels, especially during prolonged use.
- Shape: The contour of the seat influences rider positioning and can vary between narrow and wide designs.
- Material: Seats can be made from various materials, including synthetic leather and plastic, which impact durability and weight.
As for the seatpost, it offers important functionalities such as:
- Height Adjustment: Many seatposts allow for easy height modifications, enabling riders to find their ideal position.
- Material Composition: Common materials include aluminum and carbon fiber, each providing different weight and strength characteristics.
- Design: Options like integrated suspension or fixed posts can cater to specific riding preferences and styles.
Understanding these features can help riders make informed decisions when selecting components that best suit their needs.
Chain and Drivetrain Assembly
The drivetrain assembly is a crucial component of any cycling setup, facilitating the transfer of power from the rider to the wheels. This system consists of various elements that work together to ensure smooth and efficient motion. Understanding its components and their functions is essential for optimizing performance and maintenance.
Components Overview

At the heart of the drivetrain are the chain, sprockets, and crankset. The chain plays a pivotal role, linking the crankset to the rear sprocket and enabling propulsion. The sprockets, or gears, come in different sizes to provide varying resistance levels, allowing the rider to adapt to different terrains. The crankset serves as the interface for the rider’s pedaling, converting their energy into rotational movement.
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance of the drivetrain assembly is vital for longevity and optimal performance. Keeping the chain clean and well-lubricated prevents wear and tear, while checking the tension ensures efficient power transfer. Inspecting the sprockets for signs of damage or wear can help avoid potential issues during rides.
Fork Functionality and Setup
The front component of a cycling apparatus plays a crucial role in steering and overall control. Its design significantly influences the rider’s experience, impacting factors such as stability, responsiveness, and maneuverability. Understanding the mechanics and proper adjustment of this component is essential for achieving optimal performance and comfort during rides.
Understanding Fork Mechanics
The primary purpose of the front element is to connect the front wheel to the frame, allowing for smooth navigation over various terrains. Its construction typically includes materials that provide both strength and lightweight properties. Various geometrical configurations affect how the rider interacts with the ground and handles different obstacles.
Setup Considerations

Proper installation and adjustment of the front component are vital for safety and performance. Factors such as height, angle, and stiffness must be carefully calibrated to match the rider’s preferences and riding style. A well-set front element can enhance responsiveness while providing a stable ride.
Adjustment Parameter Description Impact on Performance Height Determines the distance from the frame to the wheel. Affects overall handling and comfort. Angle Influences the steering response. Changes the agility and stability of the ride. Stiffness Refers to how rigid the element feels during use. Impacts shock absorption and control during landings. Headset and Stem Integration
The connection between the upper assembly and the handlebars plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal control and stability. This integration affects not only the performance but also the overall feel of the ride. A well-designed system contributes significantly to the rider’s experience, influencing handling and maneuverability.
The upper assembly serves as a housing for the bearings that facilitate smooth rotation of the handlebars. It connects seamlessly with the stem, which acts as the intermediary between the handlebars and the frame. Together, they ensure that the force applied by the rider translates effectively into directional control.
Choosing the right combination of these components is essential for achieving desired geometry and responsiveness. Compatibility between the upper assembly and stem is vital, as variations in size and shape can lead to performance issues. Proper installation and alignment are equally important, as they ensure longevity and reliability.
Maintenance of this integration should not be overlooked. Regular checks for wear and tear, along with lubrication of moving parts, can enhance performance and extend the lifespan of the assembly. A well-maintained system not only ensures safety but also provides a more enjoyable riding experience.
Rim and Spoke Arrangement

The configuration of the circular component and its radial supports plays a crucial role in the overall performance and stability of a two-wheeled vehicle. This arrangement not only influences the weight distribution but also impacts the strength and responsiveness of the assembly during various maneuvers. Understanding the intricacies of this setup can significantly enhance the rider’s experience, providing better control and durability.
Typically, the circular element is designed to hold the tire securely, while the radial supports connect it to the central hub. These supports are strategically placed to ensure even tension across the surface, which helps maintain structural integrity. A well-executed arrangement can lead to improved handling, reduced risk of failure, and enhanced efficiency during movement.
Different configurations exist, with variations in the number and placement of the supports, each offering distinct advantages. For instance, a higher count of supports can distribute loads more evenly, resulting in a more robust assembly. Conversely, fewer supports may reduce weight but could compromise stability under extreme conditions. Evaluating the optimal configuration depends on the intended use and riding style.
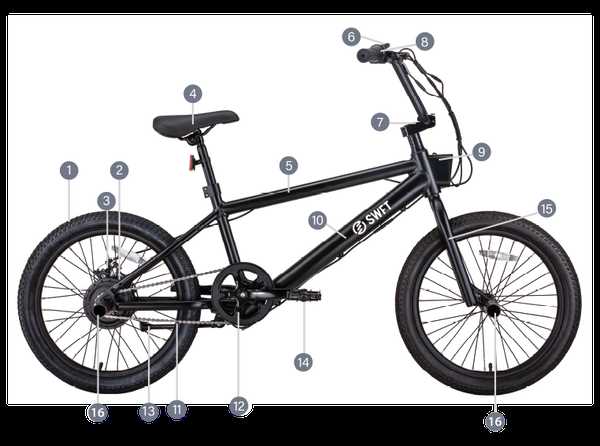
Hub and Axle Configuration
The arrangement of the central mechanism and its supporting rod is crucial for the overall performance of wheeled vehicles. This system plays a vital role in ensuring smooth rotation, stability, and strength during various maneuvers.
Components of the Hub and Axle System
The main elements of this configuration include:
- Hub: This is the core unit that houses the axle and connects to the wheel. It facilitates rotation while maintaining structural integrity.
- Axle: A sturdy rod that connects the two wheels, allowing them to spin simultaneously. It also bears the weight of the rider and the vehicle.
- Bearings: Located within the hub, these components reduce friction between the rotating hub and stationary axle, enhancing efficiency.
Types of Configurations
There are several configurations that can be observed:
- Rear Hub: Typically wider and often features a freewheel mechanism, allowing for coasting without pedaling.
- Front Hub: Usually simpler, designed for direct attachment to the fork and facilitating steering.
- Axle Types: Options include solid axles for durability or hollow axles to reduce weight.
Understanding these components and their configurations can significantly enhance performance, allowing for better control and maneuverability.