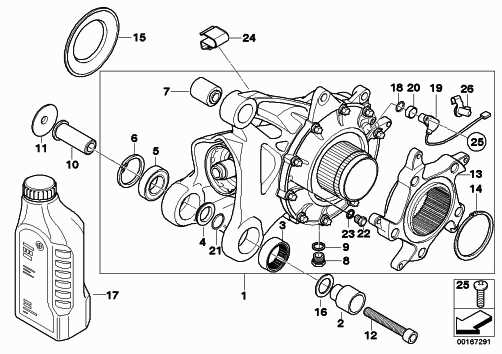
The inner workings of modern two-wheeled vehicles involve a wide array of components, each contributing to the overall performance and functionality. Understanding how these elements fit together can be crucial for maintenance, repairs, or even upgrades. This section delves into the intricate details of their construction, offering a closer look at essential features.
Every individual element within the design plays a pivotal role. Whether it’s the system ensuring smooth motion or the elements responsible for stability, each piece is interconnected. Learning how these systems collaborate can provide a deeper appreciation for the machine’s engineering marvels.
By examining various sections and their relationships, enthusiasts and technicians alike can gain valuable insight. This knowledge empowers owners to make informed decisions about upkeep and modifications.
Motorbike Component Layout Overview
The layout of two-wheeled vehicle systems involves a well-organized arrangement of critical elements, each serving a unique function. Understanding how these elements are positioned in relation to one another is essential for both maintenance and enhancements. This overview will provide insight into the structural setup, highlighting the key areas where specific elements interact and function together seamlessly.
Main Structural Elements
- Frame: Acts as the foundation, holding all other systems in place.
- Powertrain: Central unit responsible for propulsion, ensuring energy is converted into motion.
- Suspension System: Ensures stability and comfort by absorbing shocks from the road.
Supportive Components
- Braking Mechanism: Provides control and stopping power, crucial for safety.
- Electrical Wiring: Connects various sensors and devices, enabling functionality such as lighting and ignition.
- Control Levers: Allow the rider to interact with the vehicle’s systems, managing speed, direction, and more.
Frame Structure and Design Features
The framework of any two-wheeled vehicle serves as the essential foundation, providing both strength and stability. Its construction is carefully engineered to ensure durability, weight distribution, and balance. This section will explore the general structure and the design elements that contribute to a vehicle’s overall performance.
Core Elements of the Framework
The structure is typically made from high-strength materials to support the various mechanical and functional components. These materials are chosen for their lightweight properties, allowing for enhanced maneuverability without compromising stability.
Design Features
The overall design incorporates various geometric shapes and reinforcement points. These features are strategically implemented to optimize aerodynamics, reduce vibrations, and ensure that the frame can withstand different types of terrain and stress.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Reinforced Joints | Improved strength at stress points |
| Lightweight Material | Better handling and speed |
| Optimized Geometry | Enhanced stability and control |
Engine Placement and Key Elements
The arrangement of the power unit and its core components plays a crucial role in the overall performance and stability of any two-wheeled vehicle. Proper alignment ensures not only balance but also contributes to optimal energy distribution. Understanding the key features of the engine’s positioning helps in maintaining efficiency and enhancing the ride experience.
Optimal Balance
Placing the engine in a central location is essential for achieving balance. This ensures that the vehicle remains stable during acceleration, braking, and turning. The exact position varies, but the goal is always to distribute the weight evenly between the front and rear sections.
Core Functional Elements
The engine’s key components, including the cylinders, pistons, and exhaust system, are interconnected to ensure smooth operation. Each element is strategically positioned to enhance cooling, performance, and durability, all while maintaining accessibility for maintenance and adjustments.
Suspension System Breakdown
The suspension setup is essential for maintaining stability and comfort while traveling over uneven surfaces. It plays a significant role in ensuring smooth handling and absorbing shocks, contributing to overall ride quality. A well-functioning system helps balance the vehicle during cornering and impacts, making it an indispensable feature for any road-going machine.
Main Components
The suspension mechanism consists of several key elements, including springs and shock absorbers, which work together to manage the vertical movement of the vehicle. Springs help to absorb initial impacts, while shock absorbers control the rebound, ensuring the ride remains smooth and stable.
Adjustability and Performance
Many modern systems offer adjustable settings, allowing for a personalized experience depending on road conditions. This adjustability can enhance performance by fine-tuning the balance between comfort and handling, making it suitable for different terrains and speeds.
Exhaust System Configuration
The exhaust setup plays a crucial role in managing the outflow of gases from the engine. A well-designed layout enhances performance, ensuring optimal flow and reducing backpressure. It also influences noise levels and emissions, making it an essential aspect of overall design efficiency.
Key Components of the Setup
The main components include pipes, mufflers, and catalytic converters. These elements work together to channel the gases safely while minimizing environmental impact. Each component must be carefully selected and arranged for optimal performance and durability.
Impact on Performance
A properly tuned configuration can significantly improve engine response and power output. The system’s design directly affects how efficiently gases exit, which in turn influences both acceleration and fuel economy. Tailoring the arrangement to specific needs can result in smoother operation and enhanced longevity.
Braking Mechanism Components
The braking system is a critical aspect of any two-wheeled vehicle, ensuring safety and control during operation. Understanding the elements that contribute to its function is essential for maintenance and performance optimization.
- Brake Pads: These components create friction against the rotor, enabling effective deceleration.
- Brake Discs: Rotating elements that work with the pads to slow down the wheels.
- Calipers: Mechanisms that house the brake pads and apply pressure to them against the discs.
- Brake Lines: Hoses that transmit hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers.
- Master Cylinder: The control unit that generates hydraulic pressure to activate the brakes.
Each of these elements plays a vital role in the overall performance of the stopping system, contributing to both efficiency and reliability. Regular inspection and timely replacement of worn components are essential for optimal operation.
Transmission System Parts and Function

The transmission system plays a crucial role in the performance of a two-wheeled vehicle. It is responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring that the rider can control speed and acceleration effectively. Understanding the various components of this system helps in appreciating how they contribute to the overall functionality of the machine.
Key Components of the Transmission
- Clutch: Engages and disengages the engine’s power from the drivetrain, allowing for smooth gear shifts.
- Gearbox: Houses a set of gears that modify the engine’s output to match the desired speed and torque.
- Sprockets: Work in conjunction with the chain or belt to transmit power to the wheels.
- Chain or Belt: Transfers power from the gearbox to the rear wheel, playing a vital role in motion.
Functions of the Transmission System
- Power Transfer: Ensures that the engine’s power is effectively directed to the wheels.
- Speed Regulation: Allows the rider to adjust the speed by changing gears according to the riding conditions.
- Torque Management: Provides the necessary torque for acceleration and hill climbing.
Fuel Tank and Related Components
The fuel storage system is a vital element in ensuring optimal performance and efficiency of the vehicle. This section explores the structure and associated components that work in harmony to deliver fuel effectively to the engine. Understanding these components aids in maintenance and troubleshooting.
The primary function of the fuel reservoir is to hold the necessary fuel supply while maintaining a secure environment to prevent leaks and contamination. Various additional components play crucial roles in regulating fuel flow and ensuring proper delivery.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Fuel Pump | Transports fuel from the tank to the engine. |
| Fuel Gauge | Indicates the level of fuel within the tank. |
| Fuel Filter | Removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine. |
| Fuel Lines | Conduits that carry fuel between the tank and engine. |
| Cap | Seals the tank to prevent evaporation and contamination. |
Electrical System Layout
The layout of the electrical components is crucial for the overall functionality and efficiency of the vehicle’s operations. This arrangement ensures that power is distributed appropriately, allowing various systems to work seamlessly together. Understanding this structure helps in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Battery | Stores electrical energy for starting and powering systems. |
| Generator | Produces electrical power to recharge the battery and operate electrical devices. |
| Starter Motor | Engages the engine to initiate the combustion process. |
| Ignition Coil | Transforms low battery voltage into high voltage to ignite the fuel-air mixture. |
| Wiring Harness | Connects various electrical components, facilitating communication and power distribution. |
| Fuses | Protects electrical circuits from overloads by breaking the circuit if the current exceeds safe levels. |
| Switches | Controls the operation of electrical systems, allowing for user interaction. |
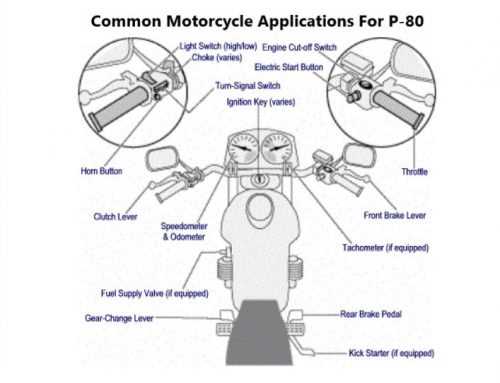
Handlebar Assembly and Controls
The handlebar assembly plays a crucial role in the overall functionality and maneuverability of a two-wheeled vehicle. This section explores the various components and controls integrated into the handlebar system, which facilitate the rider’s interaction with the machine. Understanding this assembly is essential for both maintenance and enhancing riding experience.
- Handlebar Structure: The main framework that supports the rider’s grip and control.
- Control Levers: Components for operating brakes and clutch, allowing for seamless manipulation.
- Switch Assemblies: Electrical switches for lights, horn, and other features, ensuring easy access during rides.
- Throttle Grip: A crucial element that controls the engine’s power delivery based on rider input.
- Handlebar Mounts: Fixtures that secure the assembly to the frame, providing stability and safety.
Proper maintenance and adjustment of the handlebar assembly are vital for optimal performance. Regular inspections can prevent issues and ensure that the controls function smoothly, contributing to a safer riding experience.
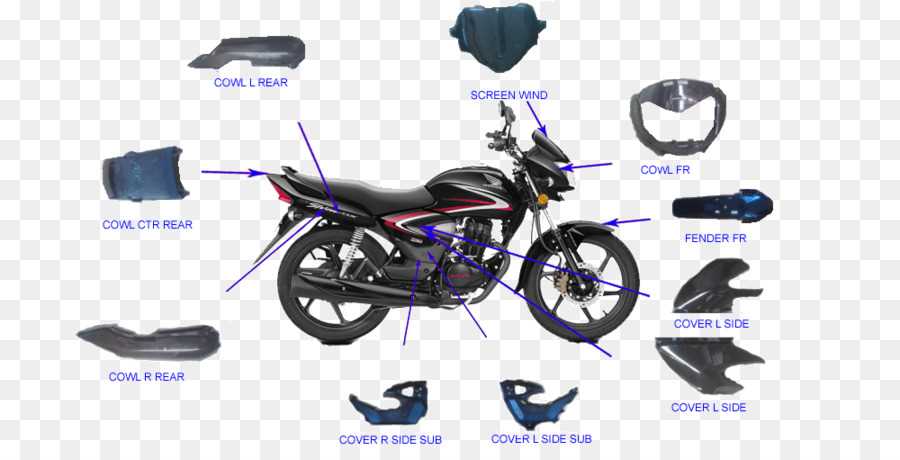
Wheels and Tire Components
The wheels and tire assembly play a crucial role in the overall performance and safety of two-wheeled vehicles. Understanding these elements is essential for ensuring a smooth ride and effective handling. This section explores the various components involved, highlighting their functions and significance.
Key Components of Wheels
- Rims: The outer circular part that holds the tire in place, providing structural support.
- Spokes: The rods connecting the rim to the hub, providing strength and stability while reducing weight.
- Hub: The central part of the wheel, which houses the axle and allows for rotation.
Tire Features

- Tread: The patterned surface that makes contact with the ground, influencing grip and handling.
- Sidewall: The rubber portion that connects the tread to the rim, protecting the inner structure.
- Inner Tube: The inflatable component that holds air, providing cushioning and support to the tire.
Lighting and Indicator Setup
This section provides an overview of the essential components involved in the illumination and signaling systems of two-wheeled vehicles. Proper arrangement and functionality of these elements are vital for safe navigation and communication with other road users.
Key Components
Effective signaling relies on several key components, including headlights, taillights, turn indicators, and reflectors. Each of these elements serves a unique purpose, contributing to visibility and safety on the road.
| Component | Function | Placement |
|---|---|---|
| Headlight | Illuminates the road ahead | Front of the vehicle |
| Taillight | Indicates presence to vehicles behind | Rear of the vehicle |
| Turn Indicator | Signals intended direction | Front and rear, on both sides |
| Reflector | Enhances visibility in low light | Strategically placed on the body |
Installation Considerations
When setting up these lighting components, ensure that each unit is securely mounted and connected to the electrical system. Proper alignment and angle are crucial for optimal performance, preventing glare and ensuring clear visibility for all road users.