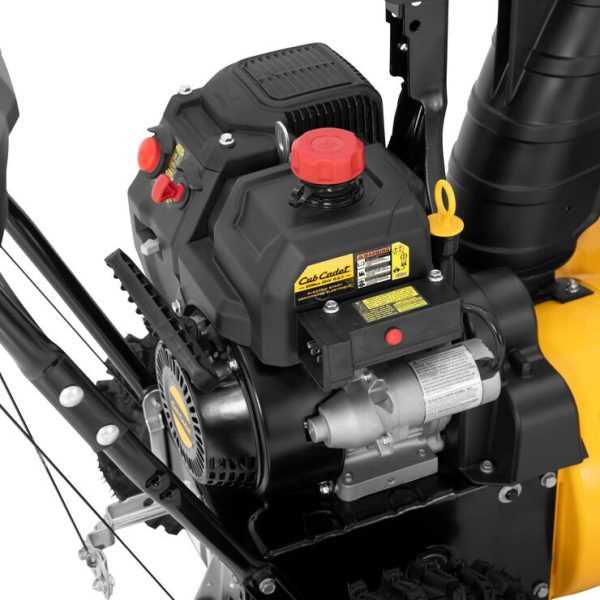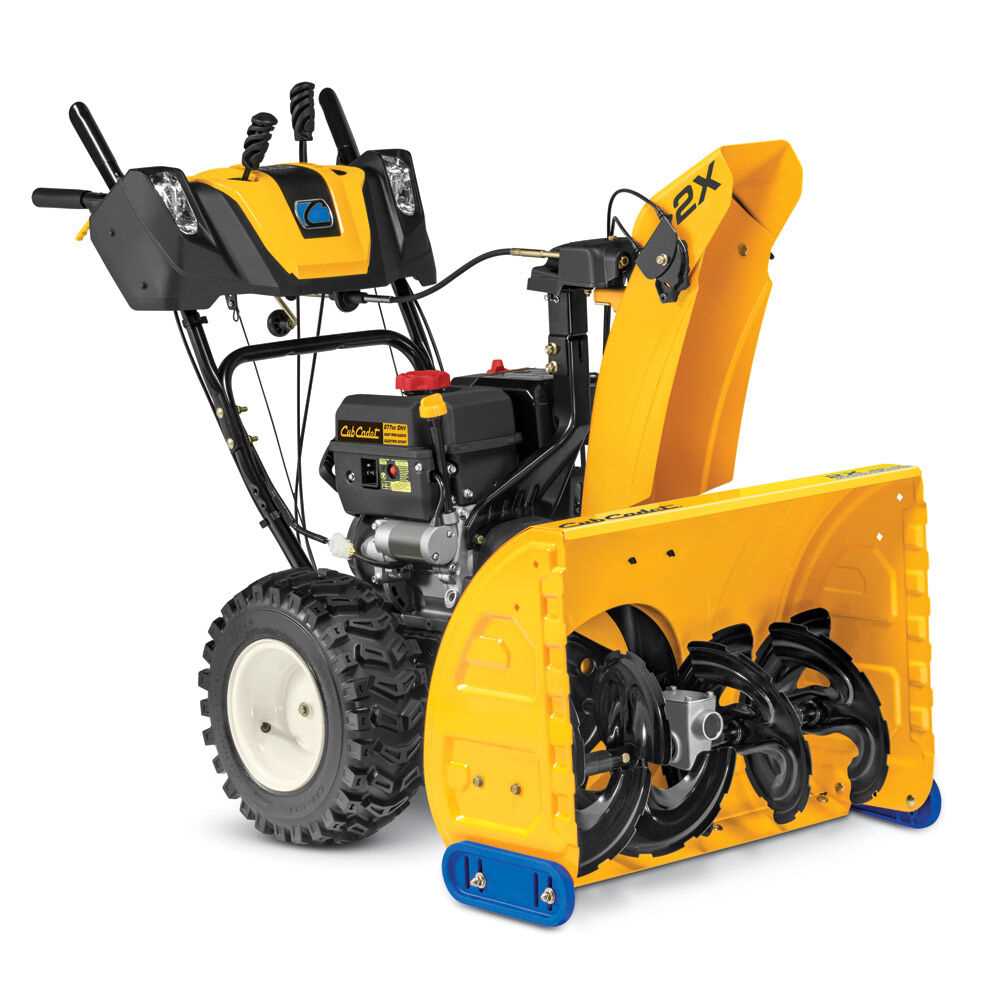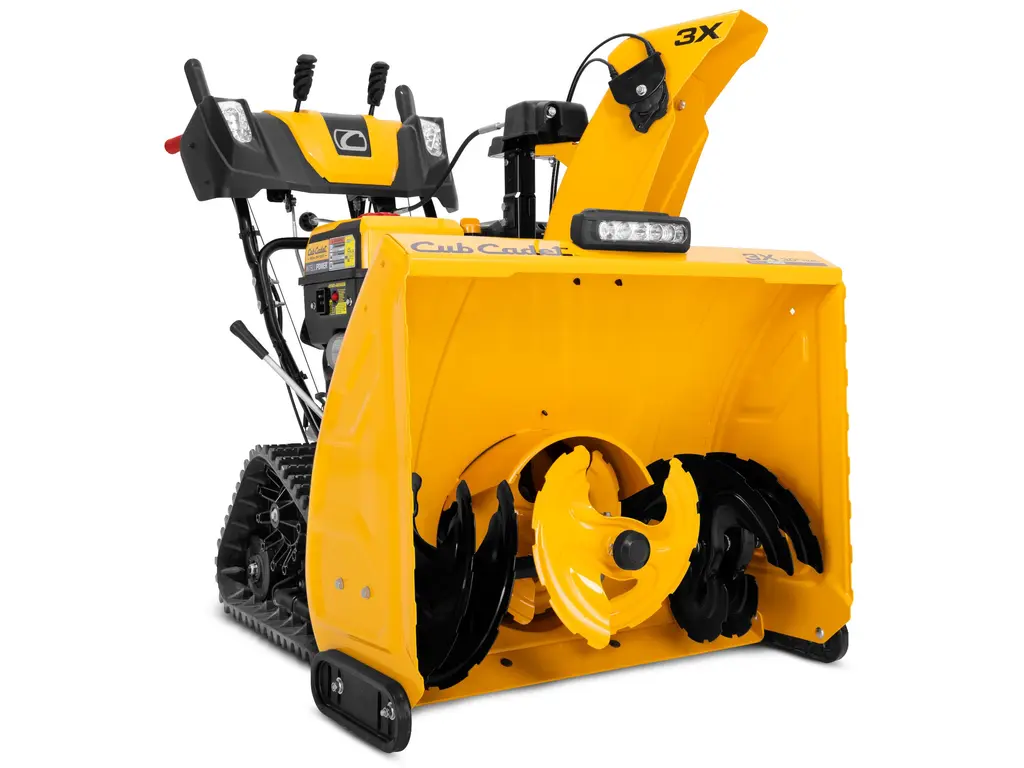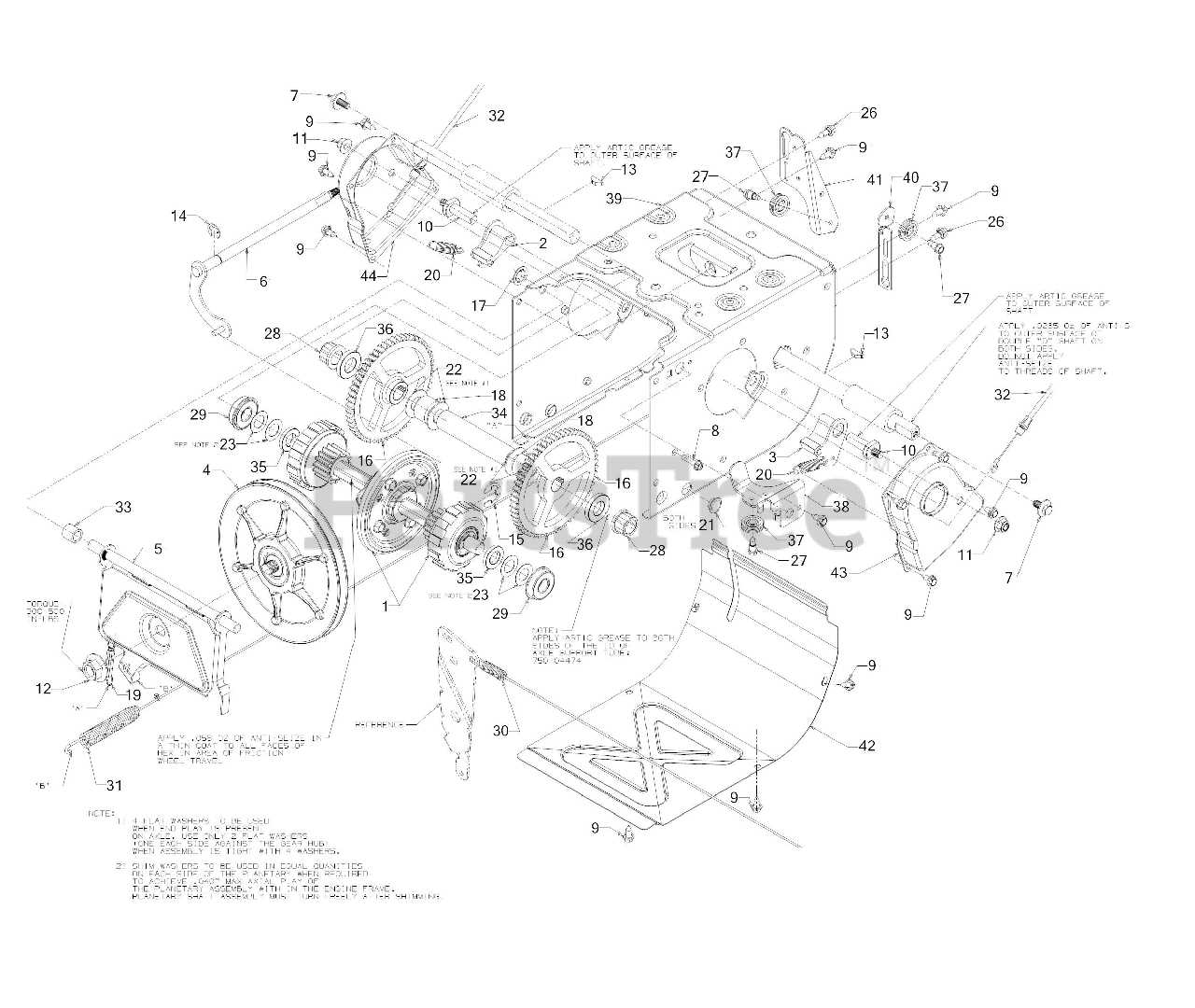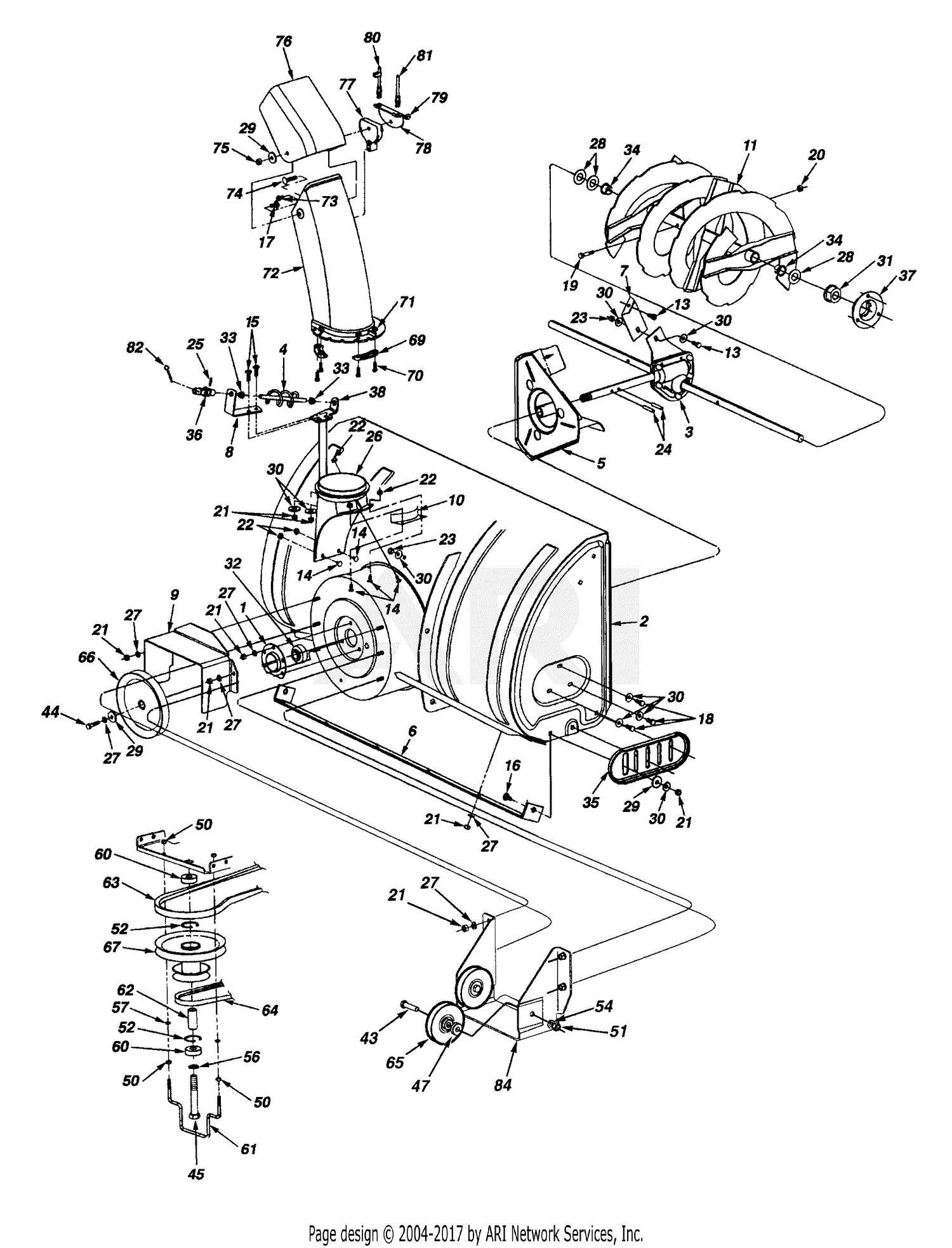
When it comes to maintaining reliable equipment during the colder months, ensuring that every element is functioning correctly becomes essential. Regular upkeep and attention to individual mechanisms contribute to the longevity and efficiency of your machine, making challenging tasks more manageable.
In this guide, we will delve into the intricacies of key elements that work together to deliver consistent results. From the core driving system to smaller components that influence operation, understanding how these elements interact is crucial for optimal performance.
Whether you’re looking to enhance functionality or troubleshoot potential issues, having a clear understanding of how each piece contributes to the overall process can make a significant difference. This breakdown will provide you with the insights needed to keep your machine running smoothly.
Understanding Cub Cadet 2X Components
The mechanics of dual-stage clearing machines involve multiple key elements working together to ensure efficient operation. Each part of the system plays a role in moving material, controlling direction, and maintaining stability, all of which contribute to its performance in difficult conditions. A proper understanding of these elements allows for better maintenance and troubleshooting.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Auger | Responsible for gathering material and directing it towards the impeller. |
| Impeller | Pushes the collected material through the chute for expulsion. |
| Drive System | Enables controlled movement and speed adjustments during operation. |
| Chute | Directs the output material in the desired direction. |
Key Features of Snow Blower Assembly
The construction of a high-performance clearing machine involves several essential elements that work together to deliver efficient operation. Understanding these components ensures better functionality and easy maintenance, especially during winter months. This section outlines the main features, emphasizing the structural and operational parts critical to the unit’s effectiveness.
Essential Mechanical Components
The primary components include the engine, which powers the system, the auger responsible for gathering debris, and the chute that directs it away. These parts must be robust to endure harsh conditions and provide continuous operation without frequent repairs.
Assembly Overview
| Component | Function | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engine | Supplies power for the entire system. | |||||||||||||
| Component | Function | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engine |
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Gears | Transmit power and alter speed |
| Shafts | Support rotating elements and transfer torque |
| Bearings | Reduce friction and support rotating shafts |
| Belt/Pulley System | Transfer rotational energy between components |
| Chains | Provide a robust connection for power transmission |
Guide to Impeller and Housing Design
The efficiency of a snow-clearing machine greatly depends on the design of its components. Two critical elements in this system are the rotating fan and the surrounding casing. Understanding their structure and functionality can enhance performance and durability. A well-designed setup ensures optimal snow displacement and minimizes strain on the engine.
Functionality of the Rotating Fan
The rotating fan serves as the primary mechanism for moving snow through the system. Its blades are engineered to generate a powerful airflow, propelling snow away from the machine. The angle and shape of these blades influence how effectively the snow is captured and expelled. Proper maintenance of this component is essential for consistent performance and longevity.
Significance of the Surrounding Casing
The surrounding casing plays a vital role in directing the airflow generated by the rotating fan. Its design should allow for smooth transitions of snow while preventing blockages. The material used for the casing also affects the overall weight and resilience of the machine. Regular inspection and care of the casing are crucial to ensure uninterrupted operation and to extend the lifespan of the equipment.
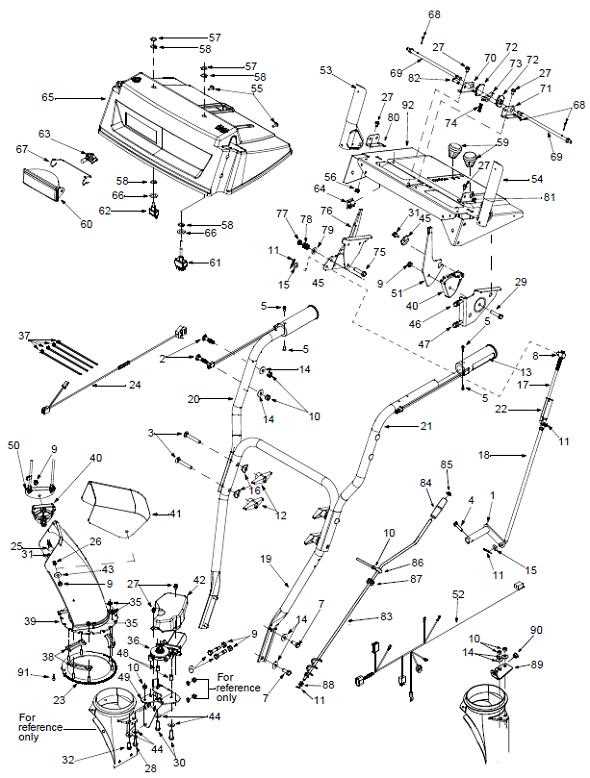
Handle and Control Setup Analysis
This section delves into the configuration and functionality of the operating components that facilitate user interaction with the equipment. Proper adjustment and understanding of these elements are crucial for achieving optimal performance and efficiency during operation.
Effective handling mechanisms enhance maneuverability and control, allowing users to navigate various terrains with ease. Here are key aspects to consider:
- Control Lever Arrangement: Proper positioning and accessibility are vital for user comfort and responsiveness.
- Handle Height Adjustment: Ensuring the handle is set to an appropriate height minimizes fatigue and enhances control.
- Grip Design: Ergonomically designed grips improve handling and prevent slippage during use.
Additionally, regular inspection and maintenance of these components are essential for ensuring reliable operation. Addressing any wear or malfunction promptly can prevent operational difficulties and enhance overall effectiveness.
Chute and Deflector System Explained
The mechanism responsible for directing and controlling the flow of discharged material plays a crucial role in the efficiency of any outdoor equipment designed for winter conditions. Understanding how this system operates helps users achieve optimal performance during usage, ensuring that snow and ice are effectively managed during removal tasks.
This assembly typically consists of two main components: the chute and the deflector. The chute is designed to guide the expelled material away from the machine, while the deflector allows for fine-tuning of the discharge angle. Users can adjust these elements to target specific areas, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the equipment. Proper maintenance of these components ensures smooth operation and longevity, making it essential for operators to familiarize themselves with their functionality.
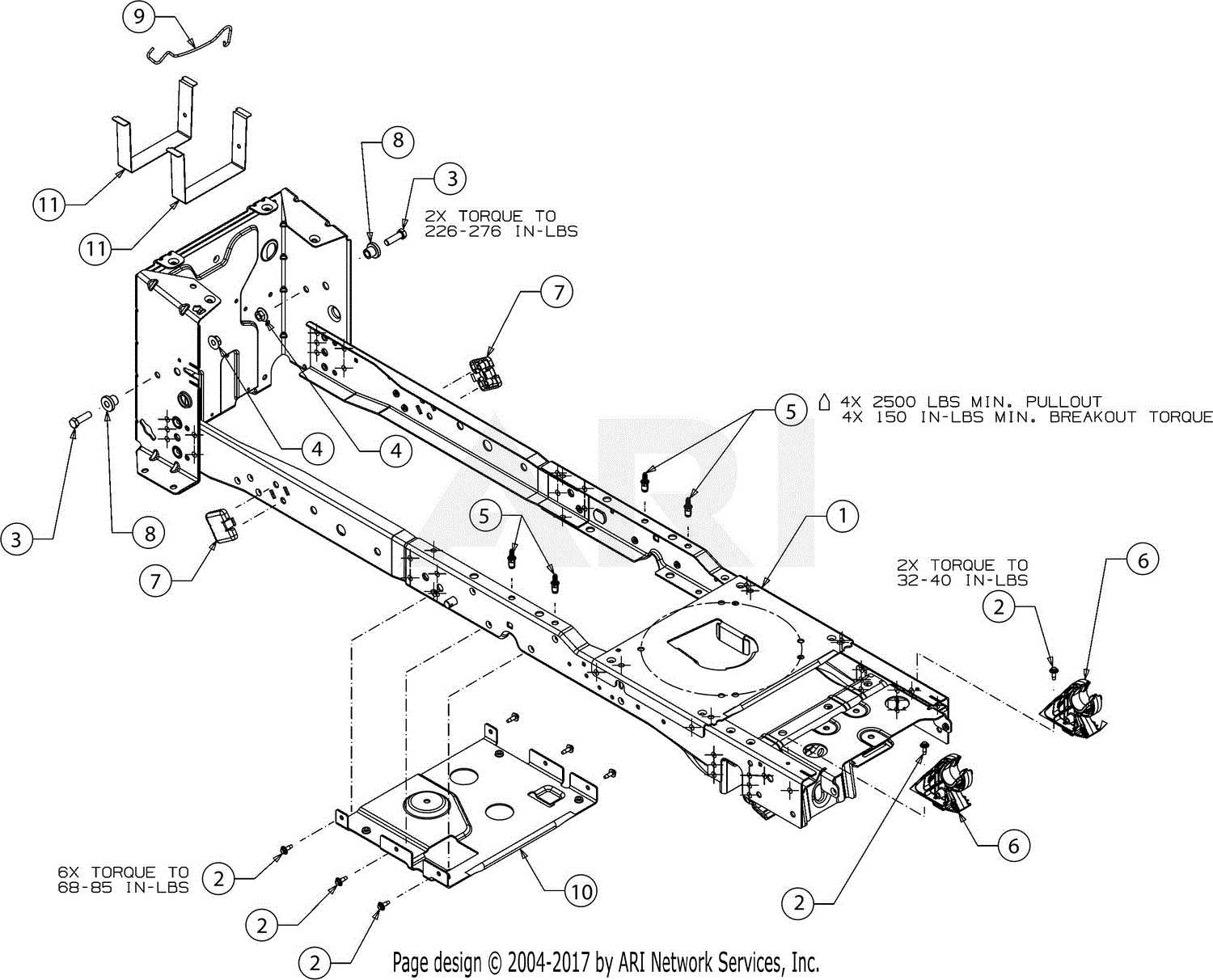
Wheel and Track Support Structures
The design and configuration of the support mechanisms for wheels and tracks play a crucial role in enhancing the overall functionality of outdoor equipment. These structures ensure stability, facilitate movement, and provide necessary balance during operation, making them integral components for effective performance in various terrains.
Importance of Robust Support Mechanisms
Strong support frameworks are essential for maintaining the integrity of the machinery, especially when navigating uneven surfaces. They help distribute weight evenly, preventing undue stress on individual components. Additionally, these structures can absorb shocks and vibrations, thereby increasing durability and extending the lifespan of the equipment.
Components of Support Structures

The support assemblies typically consist of brackets, mounts, and linkages, which work together to secure wheels and tracks in place. Brackets provide the necessary anchoring points, while mounts facilitate smooth attachment and detachment. The design of these components often incorporates materials that enhance resistance to wear and tear, ensuring reliable performance even under harsh conditions.
Understanding Belt and Pulley Systems
Belt and pulley configurations play a crucial role in transferring motion and power between components in various machines. This system is designed to efficiently transmit energy from one part to another, ensuring smooth operation and optimal performance.
In these configurations, belts are typically made of flexible materials, enabling them to stretch and flex as needed. Pulleys, on the other hand, are circular components that guide and support the belts. Together, they form an essential mechanism that enhances the functionality of many mechanical devices.
Components of Belt and Pulley Systems

- Belt: The flexible medium that transmits power.
- Pulley: The wheel that changes the direction of the belt.
- Tensioner: A device that maintains proper tension on the belt.
- Drive pulley: The pulley connected to the power source.
- Driven pulley: The pulley that receives power from the drive pulley.
Common Types of Belts
- V-belts: Commonly used in many applications due to their efficient grip.
- Flat belts: Often found in older machinery for basic power transmission.
- Timing belts: Designed for synchronous motion, ensuring precise timing between parts.
- Round belts: Flexible and used in light-duty applications.
Understanding the dynamics of these systems is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting. Proper alignment, tension, and condition of the belts and pulleys can significantly impact the overall efficiency and lifespan of the machinery.