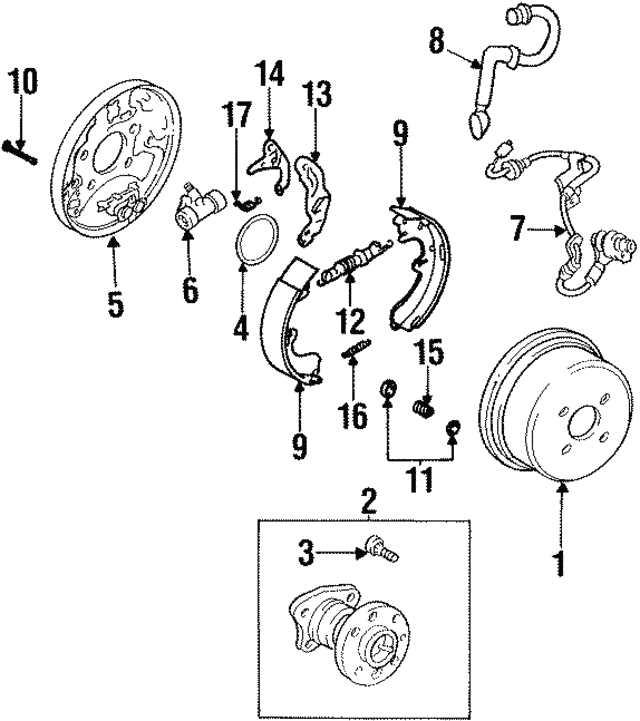
The efficiency and safety of any vehicle largely depend on its stopping system. This crucial assembly consists of various elements that work harmoniously to ensure effective deceleration. A comprehensive exploration of these components can provide valuable insights into their function and maintenance.
In this section, we will delve into the intricate arrangement of these essential units. Each component plays a significant role in enhancing the overall performance, contributing to both reliability and responsiveness during operation. A clear understanding of these parts is vital for any automotive enthusiast or technician.
By examining the layout and interaction of these mechanisms, one can appreciate the engineering prowess involved. This knowledge not only aids in troubleshooting and repair but also fosters a deeper respect for the complexities of vehicle safety systems. Join us as we uncover the details that make up this indispensable assembly.
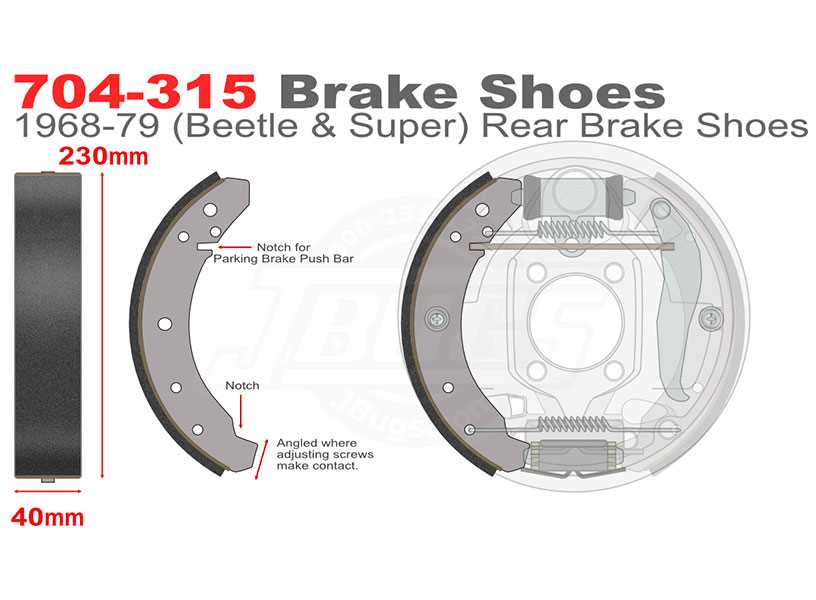
Understanding Brake Shoe Components
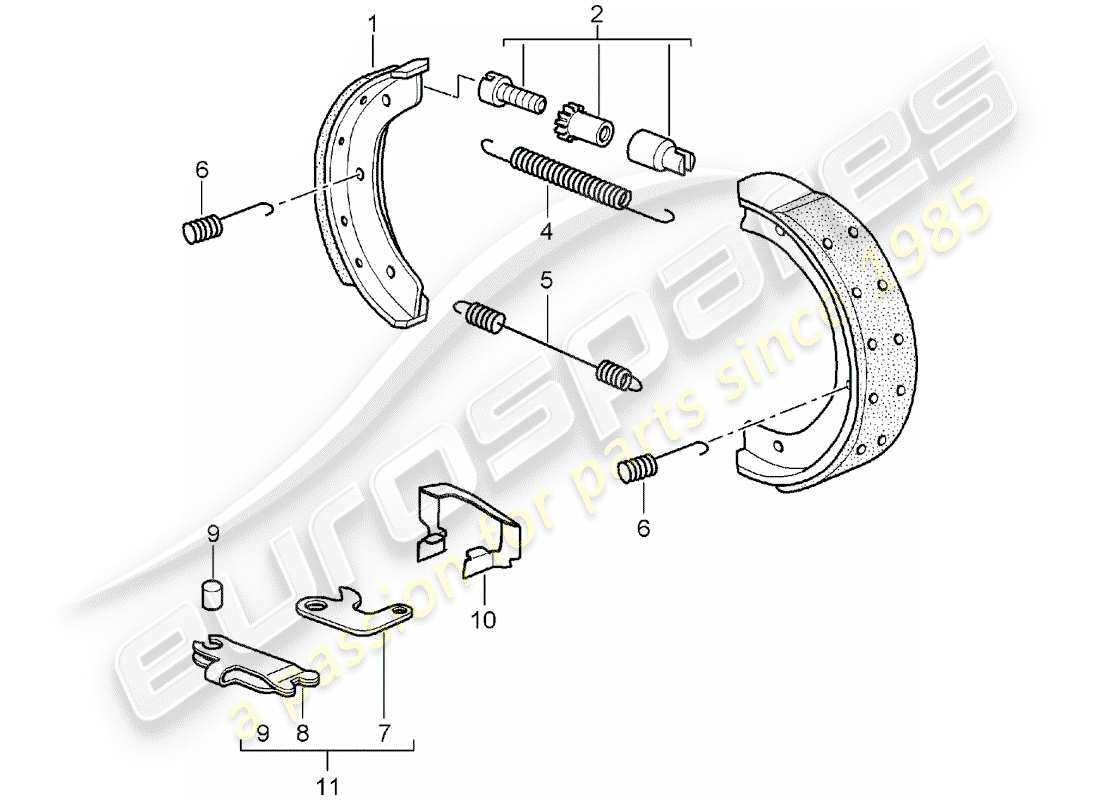
In the realm of vehicle maintenance and functionality, the assembly responsible for creating friction against the rotating drum is essential. Each element within this assembly plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance, safety, and longevity of the entire braking system. A thorough comprehension of these components allows for more effective upkeep and potential enhancements.
Key Elements of the Assembly
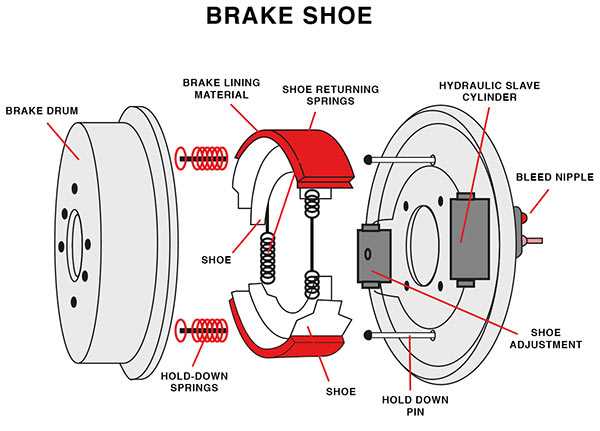
This collection consists of various integral components, each contributing to the overall efficacy. Understanding their roles helps in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance efficiently.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Friction Material | Generates the necessary friction against the drum to slow down or stop the vehicle. |
| Backing Plate | Provides structural support for the friction material and attaches to the vehicle’s framework. |
| Spring Mechanism | Ensures that the assembly returns to its original position after engagement, promoting longevity. |
| Adjuster | Maintains the proper distance between the friction material and the drum, ensuring effective contact. |
Importance of Regular Inspection
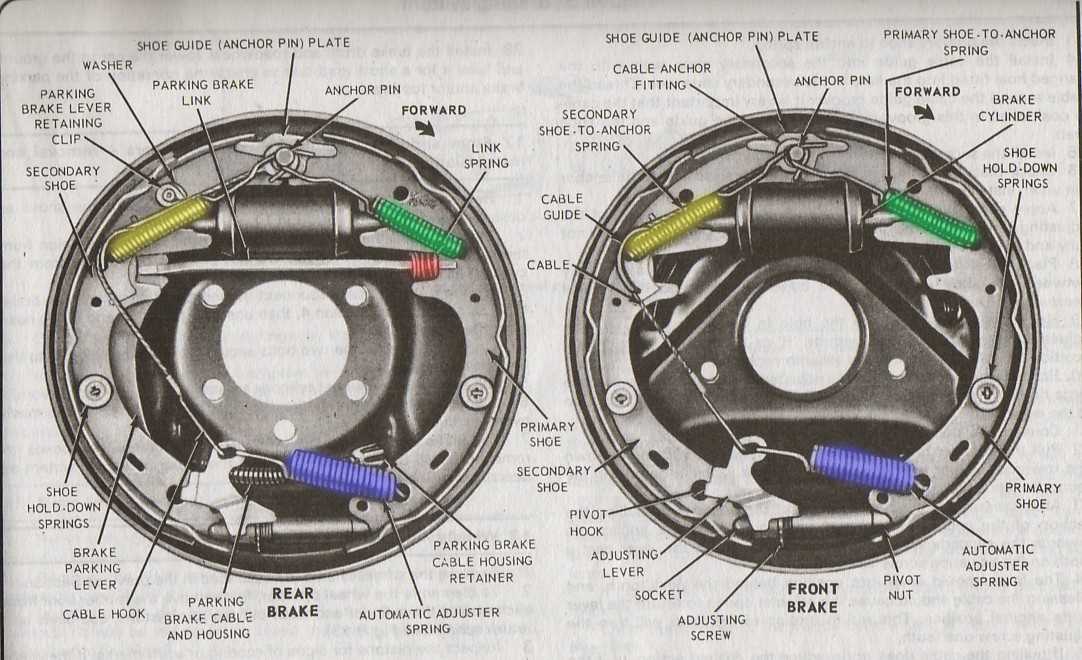
Frequent evaluation of these components is vital for maintaining vehicle safety and performance. Understanding their functions helps identify wear and tear early, preventing potential failures and enhancing driving experience.
Importance of Brake Shoes in Vehicles
The components responsible for slowing down and stopping vehicles play a crucial role in ensuring safety and control while driving. Their effectiveness directly impacts the overall performance and reliability of the braking system. Understanding their significance can help in maintaining vehicle safety and prolonging the lifespan of these vital elements.
Key Functions
- Enhancement of Stopping Power: These elements generate friction, allowing for effective deceleration.
- Heat Dissipation: They help manage heat buildup, which can lead to system failure if not properly regulated.
- Control and Stability: Proper functionality ensures that vehicles respond predictably under various driving conditions.
Maintenance and Replacement
Regular inspection and timely replacement are essential to maintaining the performance of these components. Neglecting this can result in:
- Decreased Safety: Worn elements can lead to longer stopping distances.
- Increased Repair Costs: Failing to address issues early can cause damage to other parts of the braking system.
- Driver Confidence: Well-maintained components instill a sense of security while driving.
In summary, the significance of these essential elements cannot be overstated. They are fundamental to the safe operation of vehicles, underscoring the importance of regular maintenance and timely replacement.
Key Parts of Brake Shoe Assembly
This section explores the essential components that comprise the assembly used for slowing or stopping vehicles. Understanding these elements is crucial for both maintenance and performance enhancement.
Backing Plate: The foundational component that supports other elements, providing stability and structure during operation.
Friction Material: This is the substance that generates the necessary grip against the drum, converting kinetic energy into heat and slowing the vehicle.
Spring System: A series of coils that ensure the assembly returns to its original position after engagement, crucial for effective operation.
Adjustment Mechanism: This component allows for fine-tuning of the engagement distance, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Retaining Clips: These small yet vital elements secure the various parts together, preventing any misalignment or dislocation during use.
How Brake Shoes Function in Braking
This section explores the fundamental mechanics behind a crucial component that facilitates vehicle deceleration. Understanding the interactions involved reveals how energy is transformed into friction, ultimately halting motion.
Mechanics of Friction
The system operates by pressing specialized materials against a rotating surface, creating resistance. This resistance is vital, as it converts kinetic energy into thermal energy, effectively slowing down the vehicle. The materials used are designed to withstand high temperatures while providing optimal grip.
Importance of Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of this essential mechanism are key to ensuring reliable performance. Wear and tear can diminish effectiveness, leading to compromised safety. Proper upkeep not only enhances longevity but also guarantees that the vehicle operates at its best, delivering the ultimate driving experience.
Common Materials Used in Brake Shoes
In the realm of vehicle safety, the selection of appropriate substances for friction components is crucial. Various materials are utilized to ensure optimal performance, durability, and efficiency in stopping mechanisms. Understanding these options can enhance both maintenance and functionality.
Ferrous Metals are frequently employed due to their strength and resistance to wear. They offer reliable performance under extreme conditions, making them a favored choice for many manufacturers.
Non-Ferrous Metals, such as aluminum and copper, provide lightweight alternatives that help reduce overall vehicle weight, thereby improving fuel efficiency without compromising stopping power.
Organic Compounds, including rubber and composite materials, are often chosen for their ability to minimize noise and vibration. These substances can also be engineered for a variety of driving conditions.
Semi-Metallic Options blend metal fibers with organic materials, striking a balance between durability and performance. This combination is popular for its versatility in different environments.
Ceramic Materials have gained popularity for their excellent heat dissipation properties and lower dust production, contributing to cleaner operation and extended lifespan.
Ultimately, the choice of materials is essential for achieving the desired balance of safety, performance, and longevity in vehicle stopping systems.
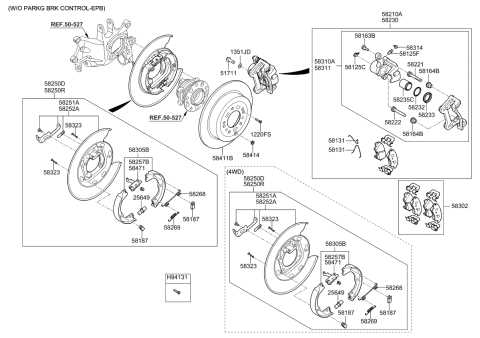
Visual Representation of Brake Shoes
This section explores the graphical depiction of essential components within a stopping mechanism, providing clarity on their structure and functionality. Understanding these elements is crucial for grasping their role in ensuring safety and efficiency in vehicle operation.
Key Elements to Observe
- Friction Material
- Support Frame
- Adjuster Mechanism
- Spring System
Importance of Visualization
A visual reference enhances comprehension, allowing individuals to:
- Identify individual components.
- Understand their interrelations.
- Grasp the overall function within the assembly.
Differences Between Drum and Disc Brakes
Understanding the distinctions between various stopping mechanisms is essential for grasping their applications and performance. Each system employs unique components and principles, affecting how vehicles respond to deceleration and handle diverse driving conditions.
Design and Structure: The fundamental configuration of these two systems varies significantly. The first type typically consists of a cylindrical housing that encases the friction material, while the latter features a flat rotor that is directly exposed. This structural difference influences heat dissipation and overall effectiveness.
Performance: When it comes to responsiveness, the second type generally offers superior performance, especially under high-stress conditions. This is largely due to better ventilation, which helps prevent overheating. Conversely, the first type may excel in low-speed scenarios, providing adequate stopping power for everyday use.
Maintenance: Maintenance requirements also differ markedly. The second type usually demands more frequent inspections and replacements of the friction components due to their exposure to environmental factors. In contrast, the first type may require less attention but can be prone to wear and tear if not properly maintained.
Cost: Finally, the initial investment and long-term costs associated with these systems can vary. The second type often involves higher upfront costs due to advanced technology and materials, while the first type might be more economical in the short term but could incur additional expenses over time due to maintenance needs.
Maintenance Tips for Brake Shoes
Proper care and regular inspection of your vehicle’s stopping components are essential for ensuring safety and performance. By adhering to a few simple guidelines, you can prolong the life of these critical elements and enhance overall driving experience.
- Regular Inspections: Schedule routine checks to identify wear and tear early. Look for signs of damage or excessive wear.
- Keep Clean: Ensure that the surrounding area is free from debris, dust, and contaminants that could affect performance.
- Monitor Performance: Pay attention to any unusual noises or vibrations when stopping, as these may indicate issues that need addressing.
Additionally, consider these practices to maintain optimal functionality:
- Ensure Proper Alignment: Misalignment can lead to uneven wear and reduce effectiveness.
- Check Fluid Levels: Regularly inspect hydraulic fluids and replace them as needed to ensure smooth operation.
- Replace Worn Components: Don’t wait until performance is compromised. Replace any worn parts promptly to maintain safety.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your vehicle’s stopping components remain in excellent condition, contributing to safer and more reliable driving.
Signs of Worn Brake Shoes
Understanding the indicators of deterioration in your vehicle’s stopping mechanisms is crucial for safety. Neglecting these signs can lead to decreased performance and potential hazards on the road.
Visual Indicators
One of the most noticeable signs is the presence of unusual wear on the friction material. If you observe significant thinning or irregular surfaces, it may be time for a replacement. Additionally, look for any cracks or chips that compromise functionality.
Performance Changes
Changes in stopping distance or unusual noises during operation are strong indicators of wear. If you hear grinding or squealing sounds, it suggests that components are no longer functioning optimally. Prompt attention to these symptoms can prevent further damage and ensure safety.
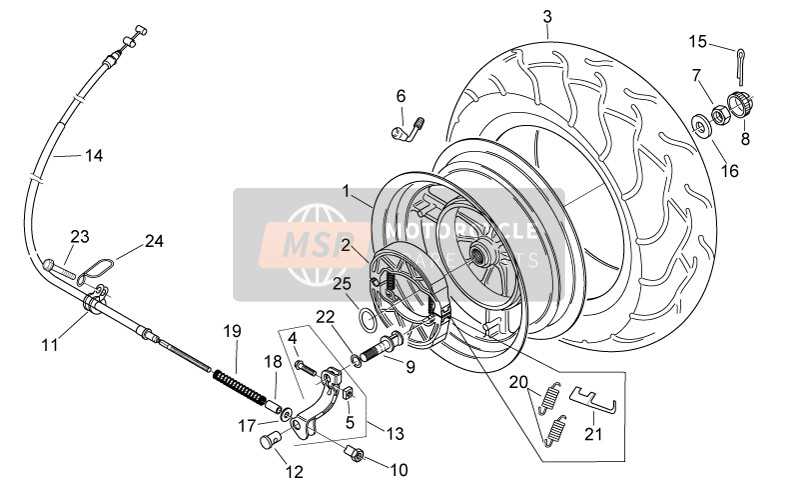
Installation Process of Brake Shoes
Proper installation of these essential components is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety. This section outlines the steps involved in the procedure, highlighting key considerations for a successful setup.
Preparation Steps
- Gather necessary tools and materials.
- Ensure the vehicle is securely lifted and supported.
- Remove the wheel to access the assembly.
Installation Procedure
- Remove old components with caution.
- Clean the assembly area thoroughly.
- Position the new components, ensuring correct alignment.
- Secure all fasteners and check for tightness.
- Reassemble the wheel and lower the vehicle.
Tools Required for Brake Shoe Replacement
Replacing essential components in your vehicle’s stopping mechanism requires a specific set of instruments to ensure a safe and effective process. Having the right tools at hand not only facilitates the task but also enhances the overall quality of the work performed.
Essential Tools:
First, you’ll need a wrench set to loosen and tighten various fasteners. A screwdriver will help with removing covers and securing components. A jack and jack stands are crucial for lifting the vehicle safely. Additionally, a brake cleaner will assist in maintaining cleanliness during the replacement process.
Optional Tools:
Consider having a torque wrench to ensure that all connections are tightened to manufacturer specifications. A pneumatic impact wrench can speed up the removal and installation of nuts and bolts, making the task more efficient.
Equipping yourself with these tools will ultimately streamline your replacement process and enhance the safety of your vehicle.
Safety Considerations When Changing Shoes
When undertaking the replacement of critical vehicle components, prioritizing safety is essential. Proper precautions can prevent accidents and ensure a smooth operation post-replacement. Understanding the risks and implementing safety measures will help maintain both personal well-being and vehicle performance.
Preparation and Equipment
Before beginning the process, gather all necessary tools and protective gear. Ensure your workspace is clean and well-lit to avoid any mishaps. Using the correct equipment reduces the risk of injury and enhances efficiency.
Proper Techniques
Always follow manufacturer guidelines when executing the task. Engaging in proper lifting techniques and securing components adequately minimizes the potential for failure. Neglecting these practices can lead to serious injuries or operational issues.
Future Innovations in Brake Technology
The evolution of stopping mechanisms is poised for remarkable advancements, driven by the need for enhanced safety and efficiency. Emerging technologies are set to revolutionize how vehicles decelerate, promising smoother interactions between components and the environment.
One of the most promising developments involves the integration of smart systems that utilize real-time data to optimize performance. By analyzing factors such as speed, weather conditions, and wear levels, these systems can adjust force application dynamically, ensuring optimal stopping power when needed most.
Additionally, advancements in materials science are paving the way for lighter, more durable components that reduce wear and enhance longevity. Innovations like carbon composites and advanced ceramics are being explored to offer better heat dissipation and resistance to fading.
Furthermore, regenerative technologies are gaining traction, allowing energy typically lost during deceleration to be recaptured and reused. This not only improves efficiency but also supports the shift towards more sustainable transportation solutions.
As these innovations continue to unfold, the ultimate goal remains clear: to create a safer, more responsive experience for all road users, enhancing overall vehicular performance and reliability.