
The functionality of a vehicle’s deceleration mechanism is crucial for safety and performance. Various elements work together to ensure effective and reliable operation, providing confidence during travel. A comprehensive exploration of these components reveals their importance in the overall mechanism of a vehicle.
Each segment of the deceleration assembly plays a vital role in the system’s efficiency. From the initiating mechanism to the friction materials, every aspect contributes to the overall effectiveness. Understanding how these elements interact can assist in identifying issues and ensuring proper maintenance for optimal functionality.
In this section, we will delve into the intricate arrangement of the components involved in the deceleration process. By breaking down the structure and examining individual elements, we aim to provide clarity on how these crucial parts function together to enhance the vehicle’s performance.
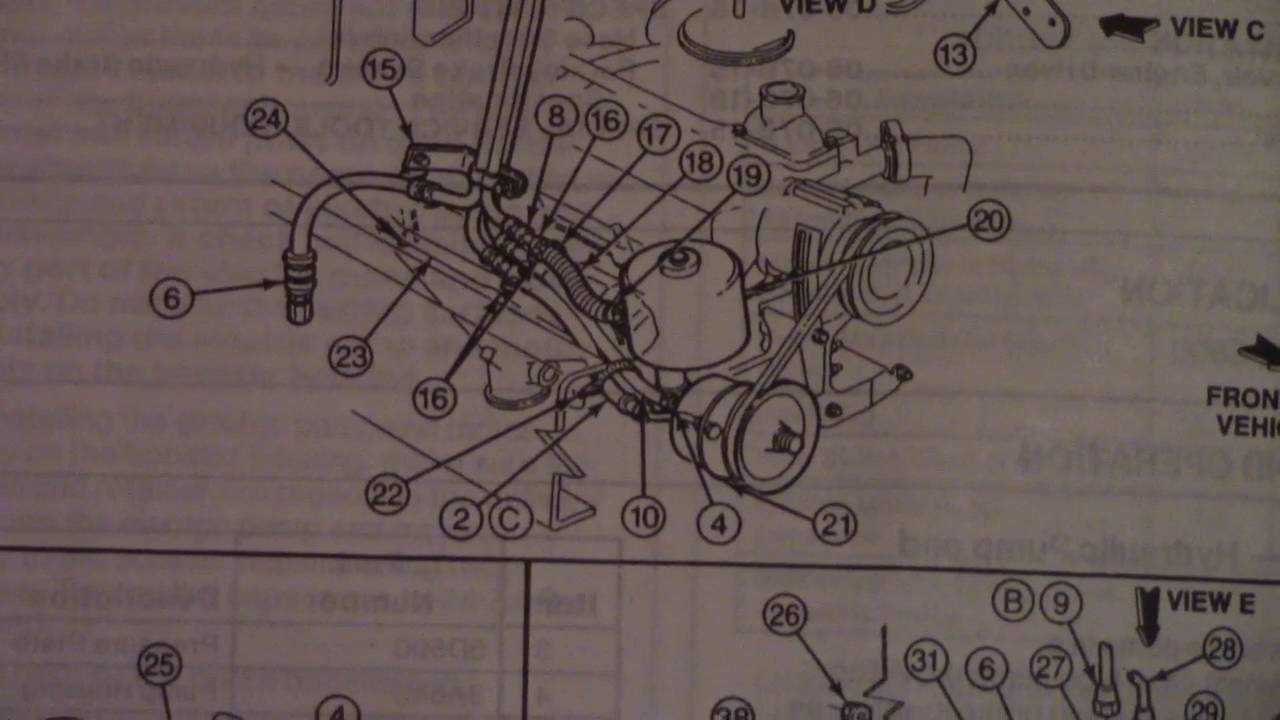
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the essential elements involved in the stopping mechanism of large vehicles. Understanding these components is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
-
Master Cylinder
The heart of the hydraulic system, responsible for generating pressure when the operator engages the stopping mechanism.
-
Calipers
These components house the friction material and play a key role in clamping down on the rotating disc to bring the vehicle to a halt.
-
Friction Material
Commonly referred to as pads or shoes, this material is essential for converting kinetic energy into heat energy through friction.
-
Brake Lines
These conduits transport hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers, ensuring the system functions efficiently.
-
Rotors
Attached to the wheel hub, these components serve as the surface against which the calipers press the friction material.
-
Drums
In certain configurations, these components replace rotors and house the friction material on the inside, creating the necessary stopping force.
By understanding these critical components, one can ensure optimal performance and longevity of the vehicle’s stopping system.
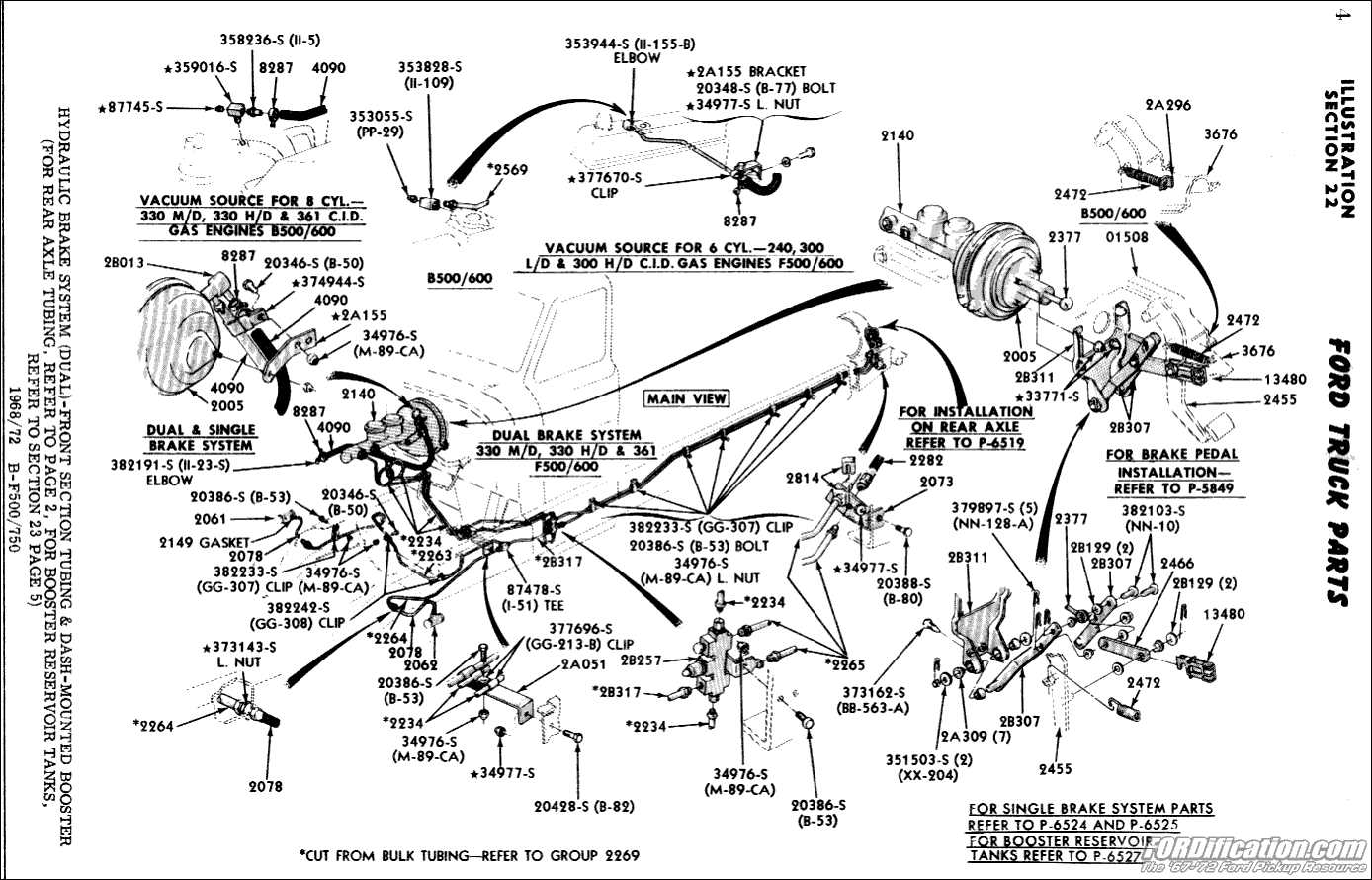
Overview of Ford F800 Braking System
The stopping mechanism in heavy-duty vehicles is crucial for ensuring safety and control during operation. Understanding the various components and their functions can aid in maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring optimal performance in demanding conditions. This section provides insights into the essential elements of this system, highlighting the importance of each component in the overall functionality.
At the core of the stopping system are several key components that work together to deliver effective deceleration and control. Each element plays a vital role, from the engagement mechanism to the pressure modulation systems, all contributing to the vehicle’s ability to halt efficiently.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Master Cylinder | Generates hydraulic pressure to activate the stopping mechanisms. |
| Calipers | Holds and squeezes the friction material against the rotating elements to slow down the vehicle. |
| Friction Material | Provides the necessary friction to convert kinetic energy into thermal energy. |
| Brake Lines | Transmits hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the engagement mechanisms. |
| Proportioning Valve | Regulates fluid pressure to the engagement mechanisms based on load and braking conditions. |
Understanding these components and their interactions is essential for maintaining the reliability and efficiency of the stopping mechanism in heavy-duty vehicles. Regular inspections and timely replacements can prevent failures, ensuring safety and performance on the road.
Common Brake Issues in F800

Vehicles often encounter various challenges related to their stopping systems, which can significantly impact safety and performance. Recognizing these issues early can help maintain optimal functionality and prevent further complications.
Worn Components: Over time, the elements responsible for deceleration can wear down due to constant friction. This degradation can lead to reduced effectiveness and a longer stopping distance, making it crucial to inspect these components regularly.
Fluid Leaks: The hydraulic system relies on fluid to operate effectively. Any leaks can result in diminished pressure, leading to a spongy pedal feel or complete failure to engage the stopping mechanism. Regular checks can help identify and address such leaks promptly.
Noise During Operation: Unusual sounds when applying the stopping mechanism may indicate problems such as misalignment or the presence of debris. These noises should not be ignored, as they can signify underlying issues that require immediate attention.
Vibration: If the vehicle experiences vibrations while coming to a halt, it could point to issues with the rotors or drums. Warped surfaces can cause uneven contact, leading to an uncomfortable driving experience and potential safety hazards.
Warning Lights: Modern vehicles often come equipped with warning indicators that alert drivers to potential issues within the stopping system. If these lights illuminate, it is essential to seek professional assistance to diagnose and rectify the problem.
Importance of Regular Maintenance

Routine upkeep is essential for ensuring the longevity and functionality of any vehicle. By adhering to a consistent maintenance schedule, owners can prevent unexpected failures, enhance performance, and promote safety. This proactive approach not only saves money in the long run but also contributes to a more reliable driving experience.
Regular checks and servicing of essential systems help in identifying potential issues before they escalate. Neglecting these responsibilities can lead to significant problems that may compromise the vehicle’s efficiency and safety. Below is a table highlighting key benefits of maintaining your vehicle:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Safety | Routine inspections help ensure all components are functioning correctly, reducing the risk of accidents. |
| Improved Performance | Regular maintenance keeps the vehicle operating at its best, ensuring optimal performance on the road. |
| Cost Savings | Identifying issues early can prevent costly repairs and prolong the life of the vehicle. |
| Higher Resale Value | A well-maintained vehicle typically has a better resale value, making it a smart investment. |
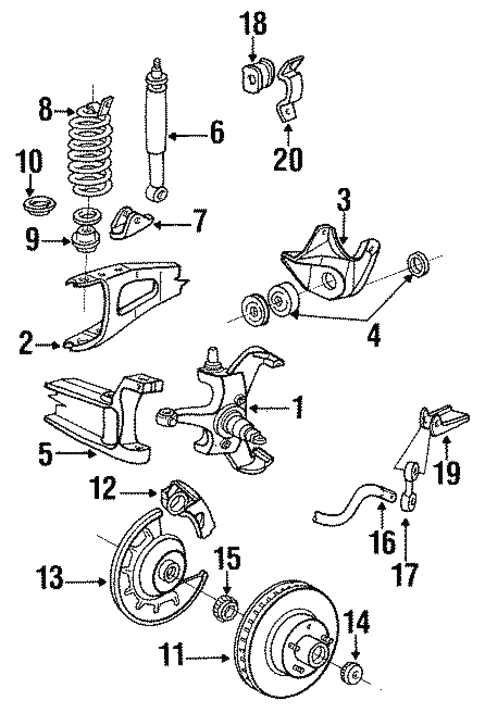
Parts Identification and Functionality
This section focuses on the essential components that play a vital role in the stopping mechanism of heavy-duty vehicles. Understanding these elements is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring optimal performance and safety. Each component has a specific function, contributing to the overall efficiency of the system.
Key Components Overview
Among the primary elements are the friction materials that create the necessary grip for effective deceleration. Additionally, the hydraulic system facilitates the transfer of force from the pedal to the stopping mechanism. Other significant components include the calipers, which house the friction materials, and the rotor, which the vehicle’s wheels are mounted on.
Functionality Insights
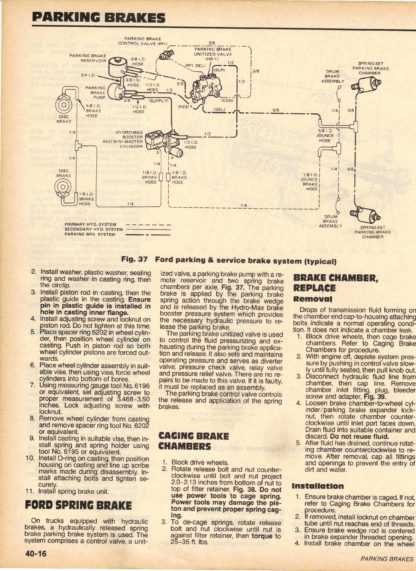
Each component’s design and interaction with others determine the effectiveness of the system. The friction materials are essential for generating the necessary stopping force, while the hydraulic system ensures that this force is distributed evenly. The calipers must apply adequate pressure to the friction materials against the rotor to achieve reliable deceleration, thereby ensuring the vehicle can stop safely in various conditions.
Tools Required for Brake Repair

Performing maintenance on a vehicle’s stopping system requires specific tools to ensure safety and efficiency. Having the right equipment on hand can simplify the repair process and contribute to a successful outcome. This section outlines essential tools needed for effective service.
Essential Equipment
Before beginning any work, it is crucial to gather all necessary implements. This preparation helps prevent delays and ensures a smooth workflow. The following table lists commonly used tools in the repair process:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Socket Set | For loosening and tightening fasteners. |
| Torque Wrench | To apply the correct amount of force to bolts. |
| Brake Cleaner | To remove dirt and debris from components. |
| Pliers | For gripping and manipulating parts. |
| Jack and Stands | To lift the vehicle securely for access. |
| Rubber Mallet | To gently tap components without damage. |
Additional Considerations
In addition to the primary tools, various other items may be beneficial depending on the specific task at hand. Keeping a well-stocked toolbox can enhance efficiency and ensure readiness for unexpected challenges during the repair process.
Brake Pad Replacement Process
Replacing the friction components of your vehicle’s stopping system is essential for maintaining optimal performance and safety. This procedure not only enhances stopping power but also prolongs the life of associated mechanisms. Proper knowledge and tools are crucial for effectively executing this task.
Before starting the replacement, ensure you have all necessary tools and materials ready. Here’s a step-by-step guide to assist you:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Lift the vehicle using a jack and secure it on jack stands. |
| 2 | Remove the wheel to access the stopping system. |
| 3 | Disconnect the caliper by removing the retaining bolts. |
| 4 | Carefully slide the caliper off the rotor. |
| 5 | Remove the old friction components from the caliper bracket. |
| 6 | Clean the caliper and bracket surfaces to remove debris. |
| 7 | Install the new friction components into the bracket. |
| 8 | Reattach the caliper over the rotor, ensuring a proper fit. |
| 9 | Secure the caliper with the retaining bolts, tightening them to specifications. |
| 10 | Reinstall the wheel and lower the vehicle to the ground. |
After completing the replacement, it is advisable to test the system to ensure proper function. A short drive can help verify that everything is working smoothly. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of friction materials can significantly enhance safety and performance.
Signs of Worn Brake Components
Recognizing the signs of degraded stopping mechanisms is crucial for maintaining vehicle safety and performance. Neglecting these indicators can lead to more severe issues and increased repair costs. Here are common symptoms that suggest the need for inspection and potential replacement of the essential components.
Common Symptoms
- Unusual noises: Squeaking, grinding, or clicking sounds when engaging the stopping system may indicate excessive wear.
- Vibration or pulsation: Feeling vibrations in the pedal while stopping can signify uneven wear or damage to the mechanisms.
- Soft or spongy pedal: A pedal that feels less firm or sinks closer to the floor may point to air in the hydraulic system or worn components.
Visual Indicators
- Thickness inspection: Measure the thickness of the friction material; it should meet manufacturer specifications.
- Check for cracks: Look for visible cracks or damage on the surfaces of the components.
- Corrosion signs: Rust or corrosion can compromise the functionality and longevity of the mechanisms.
Addressing these signs promptly can enhance the vehicle’s stopping efficiency and ensure safe driving conditions.
Upgrading Brake Parts for Performance

Enhancing the stopping capabilities of a vehicle is essential for both safety and handling. By focusing on the various components of the stopping system, enthusiasts can significantly improve performance, responsiveness, and overall driving experience. Upgrading to high-quality materials and advanced technologies can make a noticeable difference in how the vehicle handles on the road.
Key Components to Consider
- Rotors: Opt for slotted or drilled versions to improve heat dissipation.
- Pads: Choose performance-oriented compounds that provide better friction and fade resistance.
- Calipers: Consider upgrading to multi-piston designs for increased clamping force.
- Hoses: Use braided stainless steel lines for improved pedal feel and durability.
Benefits of Upgrading

- Improved stopping power and shorter distances.
- Enhanced resistance to brake fade during heavy use.
- Better heat management for consistent performance.
- Increased driver confidence in handling and stability.
Understanding Fluid Types
In the realm of hydraulic systems, the choice of fluid plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and safety. Different formulations offer distinct properties, affecting how effectively the system operates under various conditions. This section delves into the various categories of hydraulic fluids, highlighting their characteristics and appropriate applications.
There are several primary categories of hydraulic fluids, each designed to meet specific operational demands:
- Mineral Oil-Based Fluids: These fluids are derived from refined crude oil and are the most commonly used type. They provide good lubricating properties and corrosion protection.
- Water-Based Fluids: Comprising a mixture of water and other additives, these fluids are less flammable and often used in applications requiring lower temperatures.
- Synthetic Fluids: Engineered from chemical compounds, these fluids offer superior thermal stability, lubrication, and resistance to fire, making them ideal for high-performance scenarios.
- Biodegradable Fluids: Formulated from renewable resources, these fluids minimize environmental impact and are suitable for applications where leaks could occur in sensitive areas.
When selecting the appropriate fluid for a hydraulic system, consider the following factors:
- Operating Temperature: Ensure the fluid can withstand the temperature range of the application.
- Viscosity: The fluid’s thickness impacts its flow characteristics and efficiency.
- Compatibility: Verify that the fluid is compatible with system components to prevent degradation.
- Environmental Impact: Opt for eco-friendly options if the application is in a sensitive environment.
Understanding these types and factors is essential for maintaining hydraulic systems effectively and ensuring their longevity and reliability.