Maintaining the essential elements of a vehicle’s motion control system is crucial for both safety and performance. Proper upkeep and a thorough understanding of the critical mechanisms involved in the stopping power of a car can prevent accidents and enhance driving efficiency. Each component works together in harmony, ensuring smooth and reliable control, even in the most challenging conditions.
These mechanisms play a pivotal role in distributing force and managing the overall movement. By knowing how these parts interact and contribute to the overall function, you can better address any potential issues before they escalate. A detailed understanding of this area can aid in identifying wear and tear, improving overall maintenance, and ensuring a longer lifespan for your vehicle.
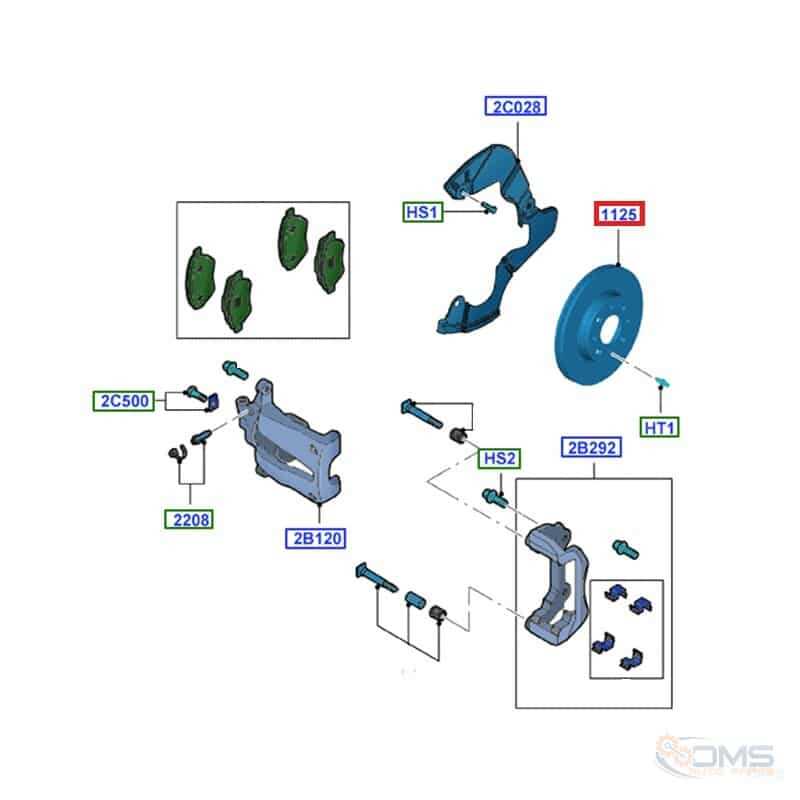
Understanding the Front Brake Assembly
The stopping system of a vehicle is essential for ensuring safety on the road. It involves several interconnected components that work together to slow down or stop the motion. These elements must function harmoniously to provide effective performance, translating the driver’s input into physical action. Each part plays a critical role in converting kinetic energy into controlled deceleration, ensuring smooth operation during use.
Main Components and Their Functions
The system includes various key sections, each designed with specific tasks in mind. They operate through the application of pressure and friction, enabling the vehicle to reduce speed. The seamless interaction between these sections ensures that the energy is dissipated evenly, preventing overheating or wear.
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Caliper | Applies pressure to the necessary areas for deceleration. |
| Disc | Receives friction to help reduce the movement. |
| Pads | Provides the friction surface needed for slowing down the vehicle. |
Interaction and Maintenance
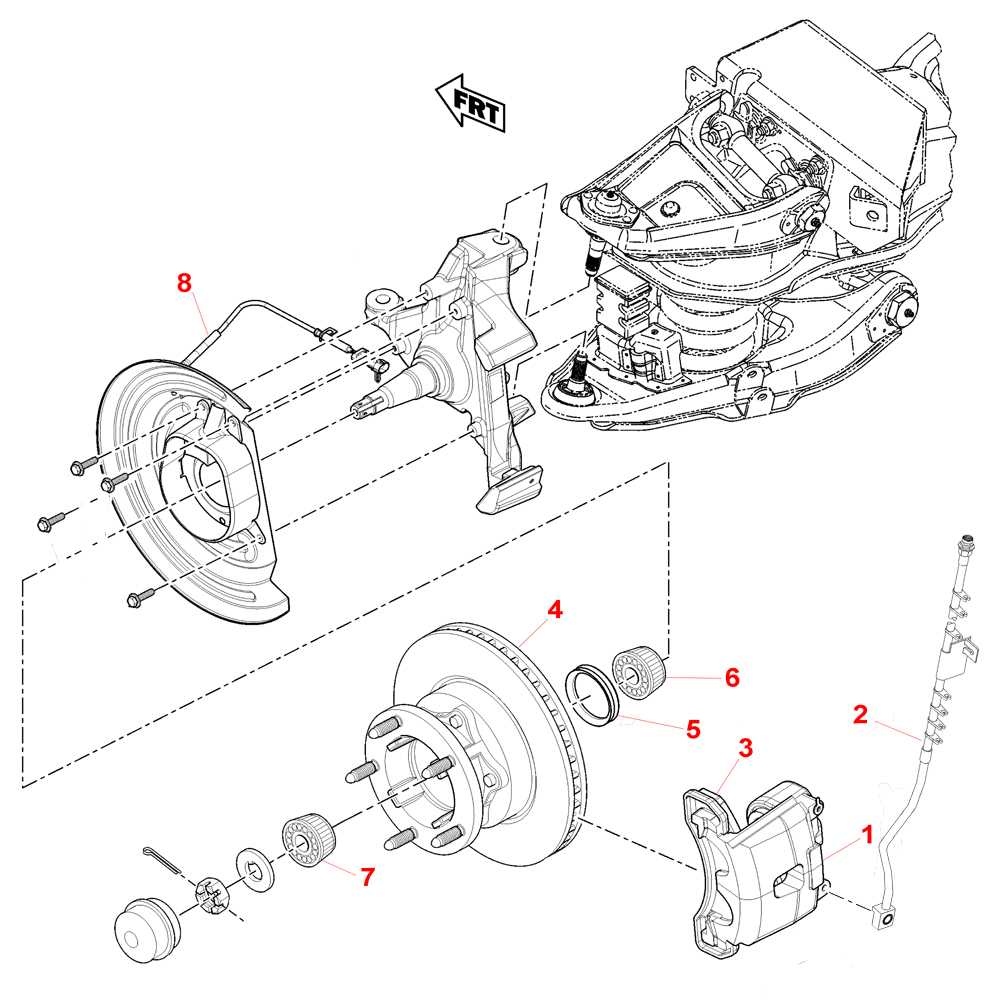
Proper care of the entire assembly is crucial for long-term reliability. Regular checks can prevent issues caused by excessive wear or improper contact. Ensuring the components remain in good condition guarantees that the system performs as expected when it is most needed.
Common Front Brake Components Explained
Vehicles rely on a well-coordinated set of elements to ensure a smooth deceleration process. These elements work together to bring a moving object to a stop efficiently. While each component has a specific function, they must harmonize for optimal performance and safety.
Rotating Discs play a critical role in this system by interacting with other mechanisms to create the necessary friction. As the discs spin, another set of moving parts makes contact, slowing down the motion.
Pads, designed to press against the discs, generate the needed resistance. Over time, they may wear down and require replacement to maintain proper function.
The calipers, which house these pads, ensure that pressure is applied evenly on both sides, allowing the system to work consistently. Proper maintenance of these units helps prevent uneven wear and promotes durability.
Finally, the overall setup relies on a fluid-driven system to transfer the necessary force. Keeping this system in good working order is essential for effective deceleration, as any issues with fluid levels or pressure can affect the entire operation.
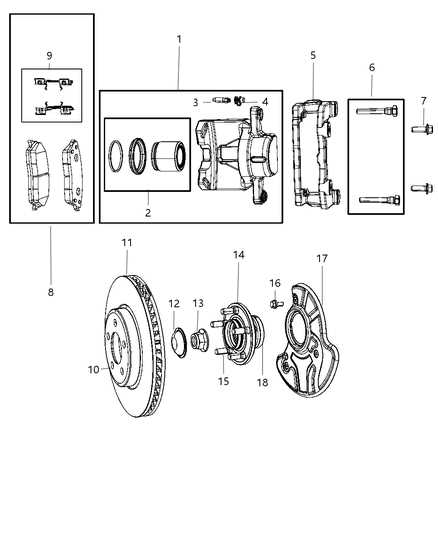
How Disc Brakes Work on the Front Wheels
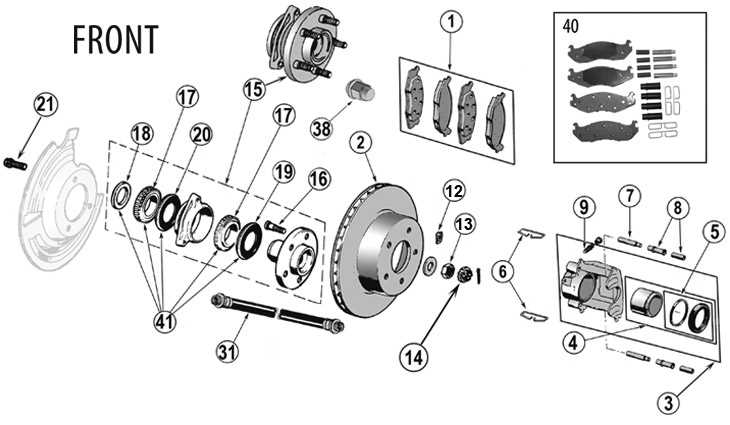
In vehicles, the stopping system uses a mechanism that relies on friction to slow down or halt movement. This setup includes various elements that interact to convert the vehicle’s momentum into heat energy, which is then dissipated, reducing speed. The system ensures a smooth deceleration when pressure is applied by the driver.
Main Components of the Stopping Mechanism
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Caliper | Holds and controls the movement of key elements that apply pressure. |
| Rotors | Spin along with the wheels and provide the surface for the pressure application. |
| Pads | Make contact with the spinning surface, creating the necessary resistance to reduce speed. |
These components work together to ensure a reliable and efficient deceleration proces
Front Brake Caliper: Function and Maintenance
The caliper is essential for ensuring smooth and controlled deceleration. It plays a key role in pressing the pads against the rotating discs, creating the necessary friction to reduce speed. Without proper function, this component can cause uneven stopping and affect overall safety. Therefore, regular checks are important to prevent potential issues.
Proper upkeep of the caliper ensures consistent performance over time. Cleaning, inspecting for wear, and lubricating moving parts can extend its lifespan. Below is an outline of key maintenance steps:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Inspection | Check for leaks, wear, and damage. |
| Cleaning | Remove dirt and debris to avoid malfunction. |
| Lubrication | Apply appropriate grease to moving areas for smooth operation. |
| Replacement | If damaged, replace the caliper to maintain safety and performance. |
Identifying the Brake Pads on Your Diagram
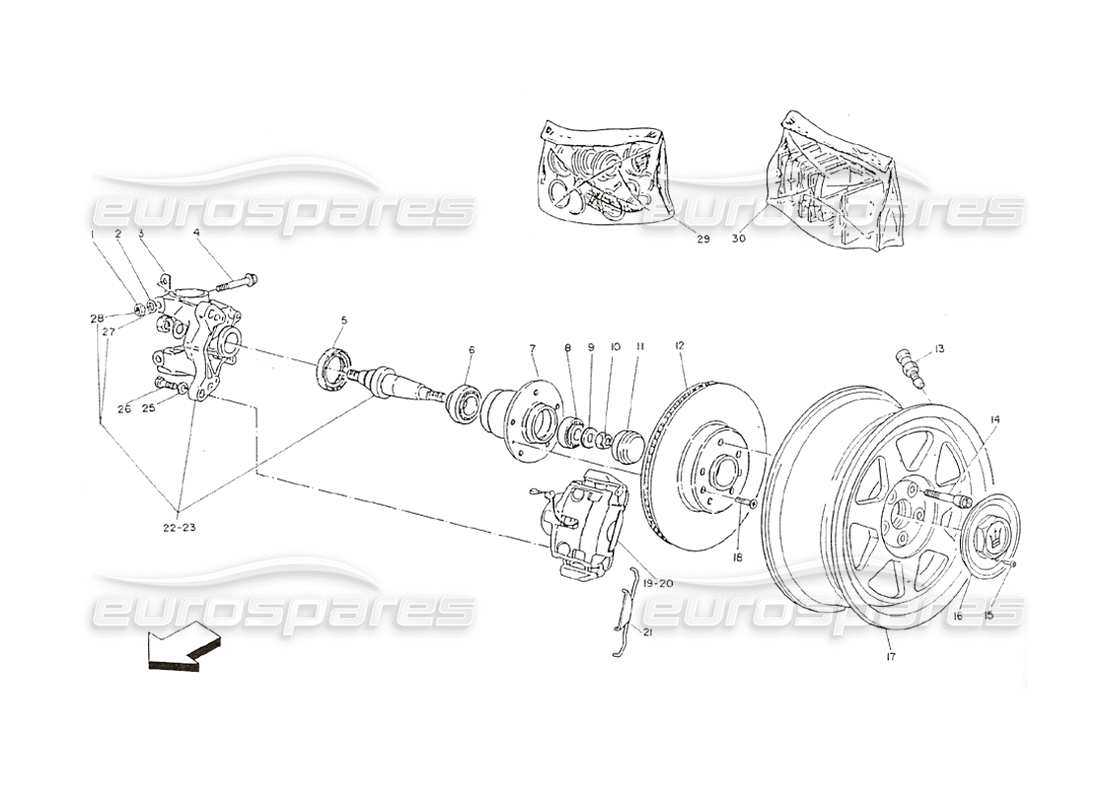
When analyzing the layout of your vehicle’s stopping system, one crucial component stands out due to its vital role in controlling motion. These elements are responsible for applying pressure that helps reduce speed or bring your vehicle to a halt. Recognizing these key parts in the system is essential for maintenance and replacements.
Shape and Position
Typically, these parts are rectangular and located near the rotating discs. Their strategic placement allows them to press against the rotating components to create the necessary friction. Understanding their exact shape and position will help you easily identify them in your layout.
Material Characteristics

These components are designed to withstand high levels of heat and stress. They are made from materials specifically chosen for durability and performance. Paying attention to the material properties in your layout will also assist in distinguishing them from other system components.
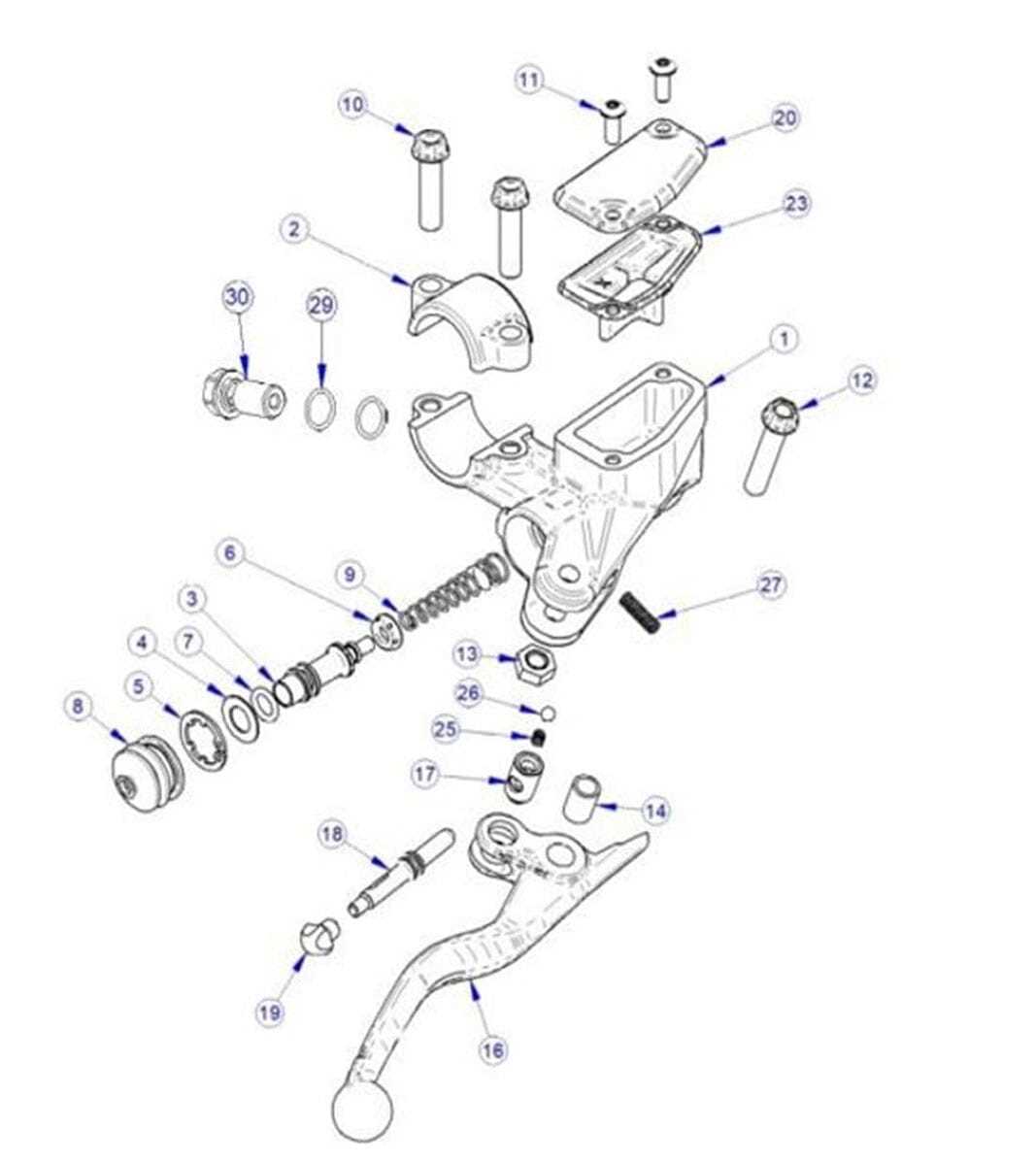
Master Cylinder and Its Connection to Front Brakes
The master cylinder is a vital component in the hydraulic system responsible for initiating the stopping mechanism of a vehicle. It plays a crucial role in generating the necessary pressure to activate the stopping system. Understanding its function and relationship with the overall mechanism is essential for effective maintenance and performance.
This component is typically connected to various elements, which work in harmony to ensure efficient operation. The following points highlight the key connections and functions:
- Hydraulic Fluid Reservoir: The master cylinder houses the hydraulic fluid reservoir, supplying fluid to the system.
- Piston Action: When the driver engages the stopping mechanism, the piston within the master cylinder compresses the fluid.
- Pressure Transfer: The generated pressure is transmitted through the fluid to other components, enabling them to respond appropriately.
- Seals and Gaskets: Proper sealing is crucial to prevent leaks, ensuring efficient pressure maintenance throughout the system.
Regular inspection and maintenance of the master cylinder and its connections are necessary to guarantee optimal functionality and safety during operation. Understanding this component’s role is essential for anyone involved in vehicle maintenance and repair.
Brake Rotors: Importance in Front Braking
The elements responsible for slowing down a vehicle play a crucial role in overall safety and performance. Among these components, the discs are vital for effective deceleration, ensuring that the wheels can slow or stop smoothly when needed. Their condition directly impacts driving dynamics and control.
Optimal performance of the discs ensures consistent friction, allowing the system to respond promptly to driver inputs. High-quality materials and proper maintenance can enhance their durability and efficiency. Additionally, the design and thickness of these components can influence heat dissipation, which is essential to prevent fading during extended use.
Regular inspection is necessary to identify signs of wear or damage, such as warping or cracking. Neglecting these elements can lead to decreased effectiveness, resulting in longer stopping distances and potential safety hazards. Prioritizing the integrity of these components is essential for a reliable and safe driving experience.
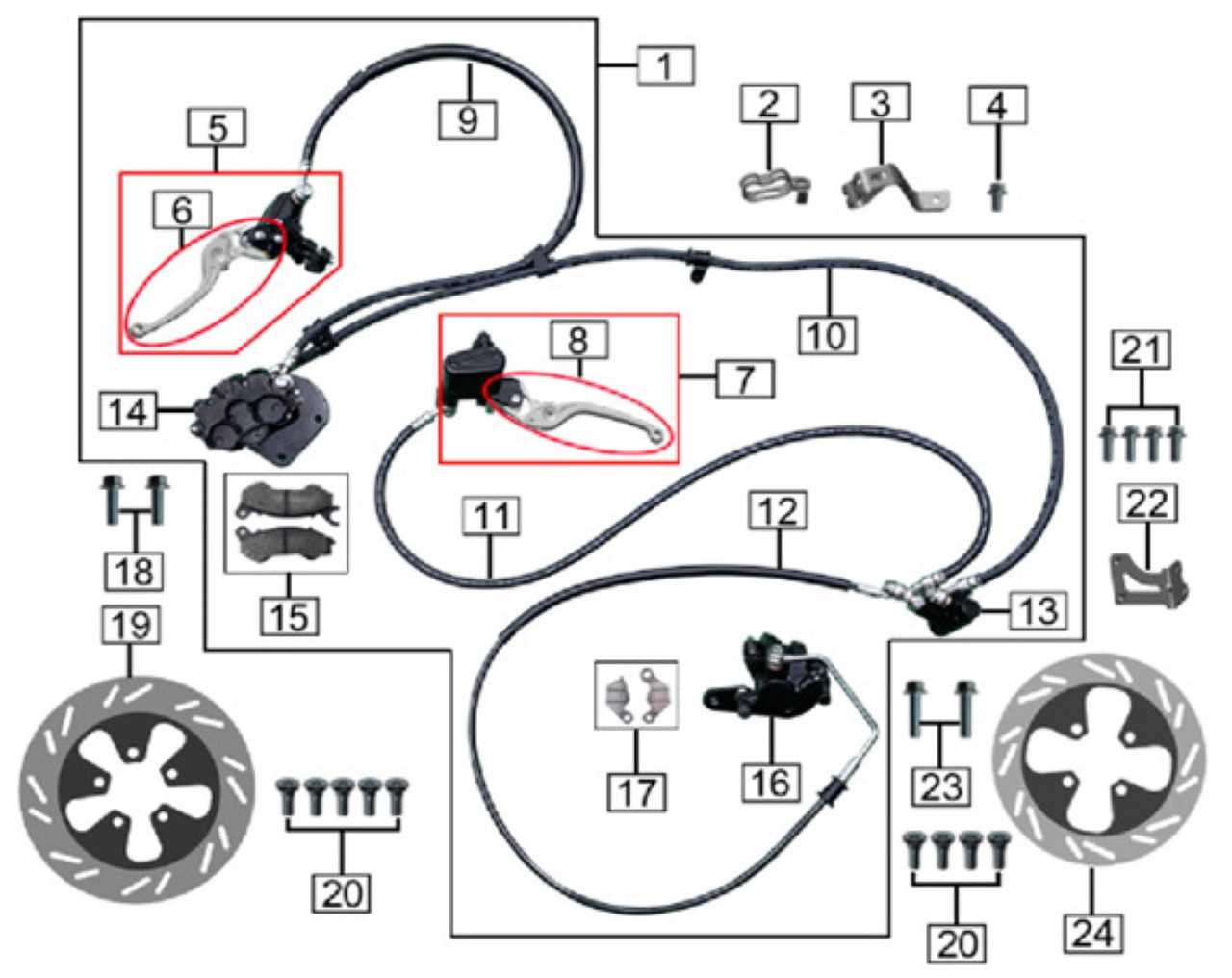
Diagnosing Issues with Front Brake Lines
Identifying problems within the hydraulic system of a vehicle is essential for ensuring safe and effective stopping power. These challenges can arise from various factors, including wear and tear, leaks, or obstructions. Properly diagnosing these issues is crucial to maintaining optimal functionality and safety on the road.
Common Symptoms of Hydraulic System Issues

Recognizing the signs of trouble is the first step in addressing any concerns. Common symptoms that may indicate problems include:
- Inconsistent stopping power
- Unusual noises when applying pressure
- Visible fluid leaks around connection points
- Soft or spongy feel in the pedal
- Warning lights on the dashboard
Steps for Troubleshooting
When issues arise, following a systematic approach can help pinpoint the source of the problem:
- Inspect for visible leaks and damages in hoses and connections.
- Check fluid levels and quality, replacing any contaminated fluid.
- Test the function of the master cylinder and calipers.
- Examine the alignment and condition of all related components.
- Conduct a pressure test to identify any weak points.
By methodically evaluating these aspects, drivers can effectively address any complications and ensure their vehicle remains in optimal condition.
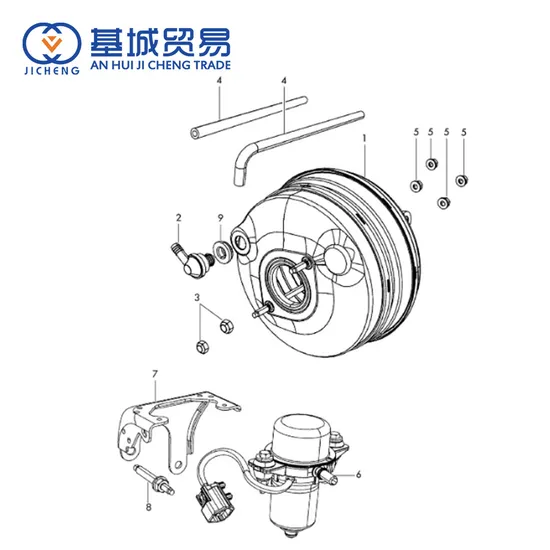
Exploring the Front Brake Booster’s Role
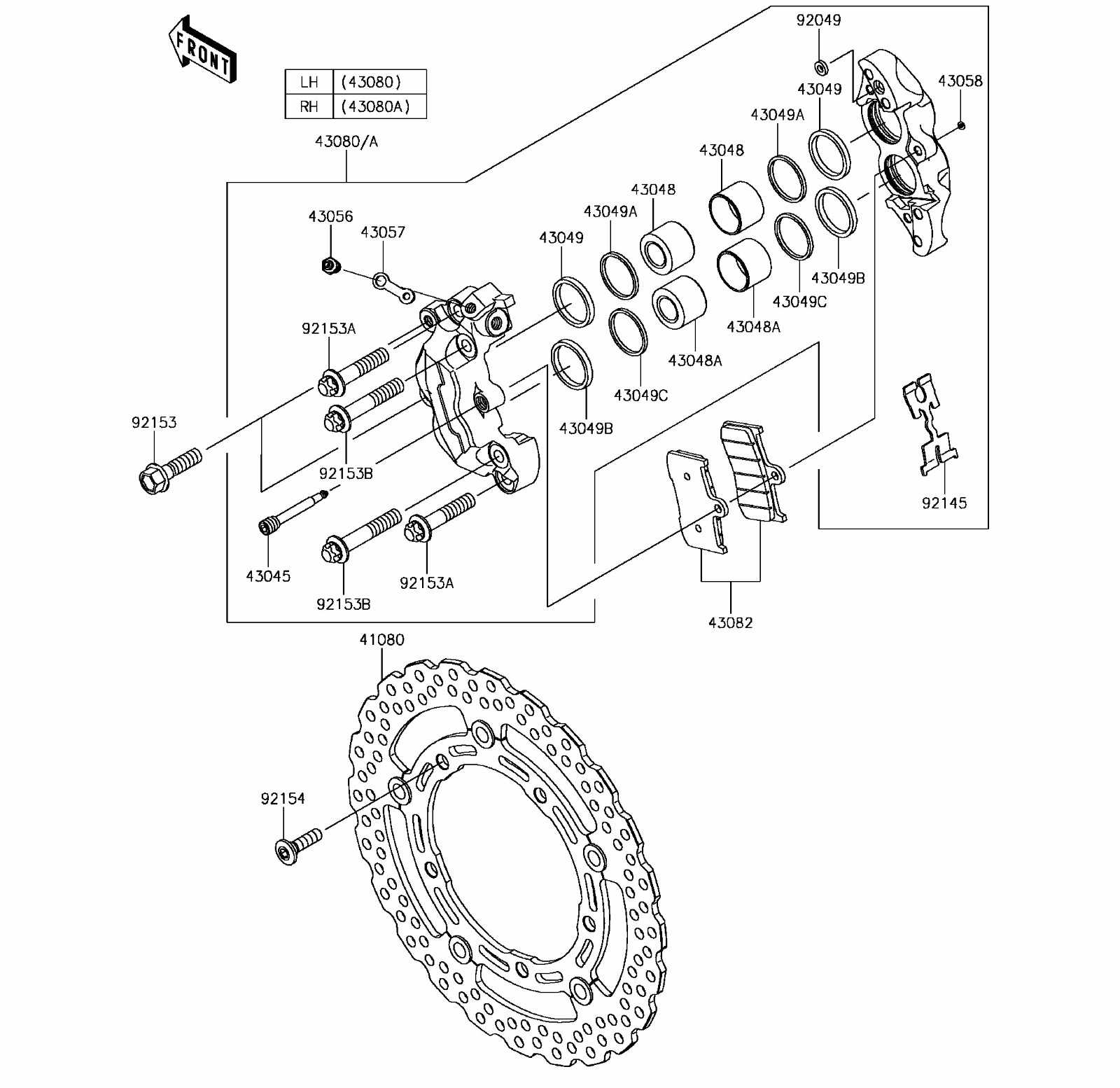
The mechanism responsible for enhancing stopping power is crucial for vehicle safety. Understanding its function and importance can help in appreciating the overall efficiency of the stopping system.
This component operates by amplifying the force applied to the pedal, ensuring that even minimal pressure translates into significant stopping power. This enhancement is vital for effective deceleration, especially under various driving conditions.
Key functions of this mechanism include:
- Improving responsiveness: It allows for a more immediate reaction from the stopping system, contributing to quicker stopping times.
- Reducing effort: Drivers experience less physical strain when engaging the stopping mechanism, enhancing comfort during operation.
- Maintaining control: Increased force translates into better stability, particularly during sudden stops or emergencies.
Regular inspection and maintenance of this mechanism are essential for ensuring optimal performance. Potential issues, such as leaks or mechanical failures, can significantly impair its effectiveness, leading to compromised safety.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of this component’s function underscores its importance in the overall performance of the vehicle’s stopping capabilities. Ensuring its proper operation is paramount for driving safety and efficiency.
Maintaining Your Front Brake System for Safety
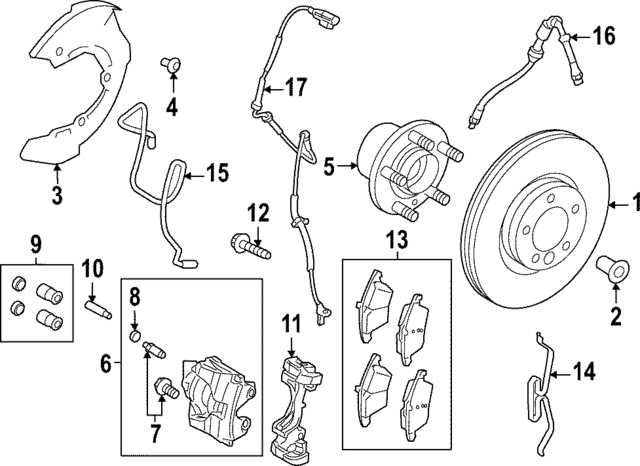
Ensuring the functionality of your vehicle’s stopping mechanism is crucial for safe operation. Regular upkeep of this system not only enhances performance but also significantly reduces the risk of accidents. Understanding how to care for this vital component will contribute to both your safety and the longevity of your vehicle.
Key Maintenance Practices
Implementing the following practices can help keep your stopping system in optimal condition:
- Regularly inspect components for wear and tear.
- Replace worn elements promptly to avoid further damage.
- Keep the system clean to prevent debris buildup.
- Check fluid levels and ensure they are at the appropriate mark.
Signs of Potential Issues
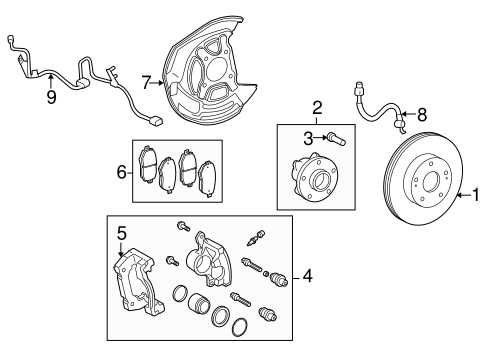
Being aware of warning signs can help you identify problems early:
- Unusual noises during operation, such as grinding or squeaking.
- Vibrations felt in the pedal when engaging.
- A noticeable decrease in stopping power.
- Fluid leaks beneath the vehicle.
By adhering to these guidelines and remaining vigilant, you can ensure the reliability of your vehicle’s stopping system, promoting a safer driving experience for yourself and others on the road.