When it comes to large vehicles, the mechanisms that ensure safe and effective deceleration are of paramount importance. These systems are intricate, featuring various elements that work harmoniously to achieve the ultimate goal of safety on the road. A comprehensive understanding of these components is essential for both operators and maintenance personnel.
In this section, we will delve into the different elements that contribute to the functionality of stopping mechanisms in heavy machinery. From the primary units to the auxiliary features, each part plays a crucial role in enhancing performance and reliability. Grasping how these components interact can significantly impact the longevity and efficiency of the overall system.
By exploring the arrangement and operation of these vital elements, readers will gain insights that could prove invaluable for troubleshooting and maintenance. Ultimately, knowledge of these systems can lead to improved safety practices and informed decision-making in vehicle management.
Understanding Truck Brake Systems
This section explores the critical components that contribute to the stopping mechanism of heavy vehicles, ensuring safety and reliability on the road.
Key elements of these systems include:
- Friction materials that provide the necessary stopping force.
- Hydraulic systems that transmit force from the driver’s input.
- Air systems that enhance performance in larger models.
Common types of mechanisms found in these systems are:
- Disc mechanisms for effective heat dissipation.
- Drum mechanisms for durability and strength.
Understanding these components is essential for maintenance and performance enhancement, ensuring optimal functionality in demanding conditions.
Components of Brake Assembly
This section explores the essential elements that contribute to the effective functioning of a stopping mechanism. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring safety and reliability during operation.
Caliper: The caliper houses the friction material and is responsible for applying pressure to create the necessary force for slowing down. Its design influences the overall efficiency and responsiveness.
Pads: These materials make direct contact with the rotating surface, providing the friction needed to decelerate. The quality and composition of the pads are crucial for optimal performance.
Rotors: Rotors are the circular discs that interact with the pads. Their durability and heat dissipation properties are vital for maintaining consistent operation under various conditions.
Lines: Hydraulic lines transport fluid from the master cylinder to the caliper, allowing for effective force transfer. The integrity of these lines is essential for preventing leaks and ensuring responsiveness.
Master Cylinder: This component generates hydraulic pressure to engage the calipers. Its reliability is critical for the overall functionality of the entire system.
Understanding these elements provides insights into their collective impact on performance and safety, allowing for informed decisions regarding maintenance and upgrades.
Types of Truck Brake Parts
Understanding the various components involved in the deceleration system is essential for optimal performance and safety. Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring reliable stopping power and vehicle control. Here, we will explore the different categories of these essential components.
- Friction Materials:
- Linings
- Pads
- Shoes
- Hydraulic Components:
- Cylinders
- Hoses
- Master Cylinder
- Mechanical Assemblies:
- Drums
- Rotors
- Calipers
- Actuation Systems:
- Levers
- Push Rods
- Actuators
- Support Structures:
- Brackets
- Backing Plates
- Mounting Hardware
Each of these categories contains specific elements that contribute to the overall functionality of the system, ensuring effective operation in various driving conditions.
How Braking Systems Operate

The efficiency of halting vehicles relies on a complex interplay of components that work in unison to create the necessary force. Understanding this system provides insights into how safety and control are maintained while in motion.
At the core of the operation are a few key elements that function together to ensure effective deceleration:
- Control Mechanism: The initial action often begins with a control input from the operator, typically through a lever or pedal.
- Fluid Dynamics: A hydraulic or pneumatic system transmits the force applied to the control mechanism, converting it into pressure that acts on other components.
- Friction Generators: The components responsible for slowing down are designed to create friction, effectively converting kinetic energy into heat.
- Heat Dissipation: As energy transforms, it’s crucial for the system to manage the heat produced to avoid degradation of performance.
- Feedback Mechanism: Systems often include sensors that provide information back to the operator, enhancing responsiveness and safety.
By recognizing how these elements interact, one can appreciate the engineering behind effective stopping systems and their vital role in vehicle safety and efficiency.
Common Brake Part Materials
Understanding the various materials utilized in essential stopping components is crucial for performance and safety. Each material offers distinct advantages, contributing to efficiency and durability under diverse operating conditions.
Metals
Steel is the most prevalent choice due to its strength and resistance to wear. Aluminum, while lighter, provides excellent heat dissipation, enhancing overall functionality. Other alloys may also be incorporated to balance weight and strength effectively.
Composite Materials
Fiberglass and carbon composites are increasingly popular, offering reduced weight while maintaining structural integrity. These materials are particularly valued for their ability to withstand extreme conditions without compromising performance.
Maintenance of Brake Components
Regular upkeep of crucial components is essential for optimal performance and safety. Neglecting this aspect can lead to diminished efficiency and increased risk of failure. A systematic approach to maintenance not only extends the lifespan of these elements but also ensures smooth operation during use.
Inspection is a fundamental step, allowing for the identification of wear and potential issues before they escalate. Regular checks can reveal cracks, leaks, or any signs of fatigue that may compromise functionality.
Additionally, cleaning these components is vital to prevent the buildup of dirt and debris, which can hinder performance. Using appropriate solvents and tools can enhance their durability.
Finally, lubrication of moving parts plays a crucial role in maintaining efficiency. Selecting the right type of lubricant is key, as it reduces friction and helps prevent premature wear.
Signs of Worn Brake Parts
Recognizing the indicators of deterioration is crucial for maintaining vehicle safety. Certain symptoms can suggest that components are no longer performing optimally, which may lead to severe consequences if neglected.
Common Indicators
- Noisy operation, such as squeaking or grinding sounds.
- Increased stopping distance, requiring more pressure on the pedal.
- Vibrations felt through the steering wheel when slowing down.
- Visible wear, such as cracking or discoloration on visible components.
What to Monitor
- Inspect for fluid leaks around the assembly.
- Check for dashboard warning lights signaling issues.
- Assess performance changes during routine driving.
Brake Diagram Overview
This section provides a comprehensive look at the components involved in the stopping mechanism of heavy vehicles. Understanding the arrangement and functionality of these elements is crucial for ensuring safety and optimal performance. A well-structured layout reveals how each unit contributes to the overall operation, allowing for better maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components
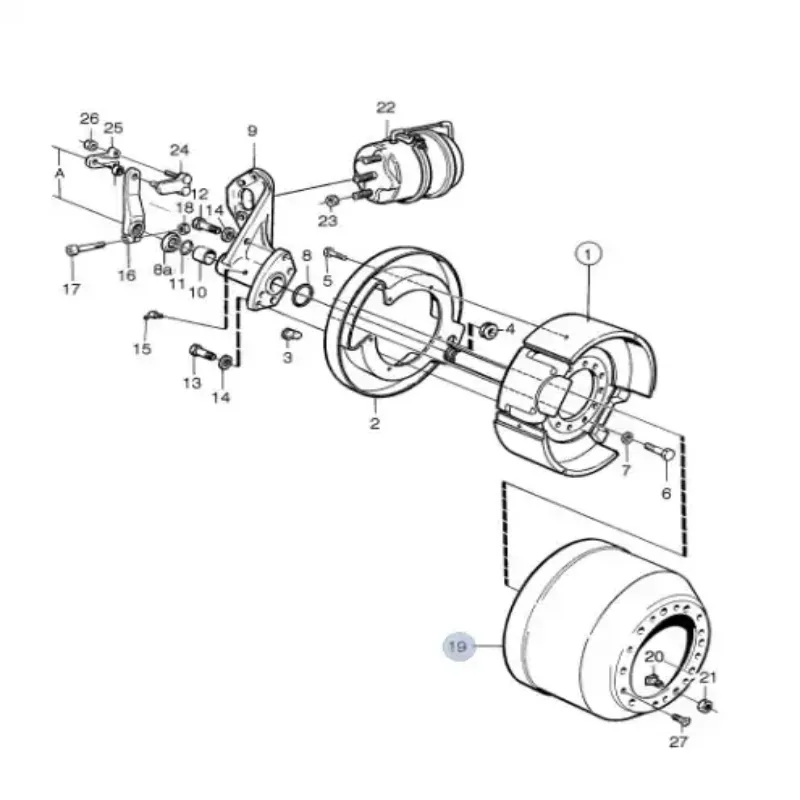
At the core of the stopping system are various essential elements that work in harmony. These include friction materials, hydraulic systems, and electronic controls. Each of these plays a vital role, from generating stopping force to regulating pressure and response times.
Operational Insights
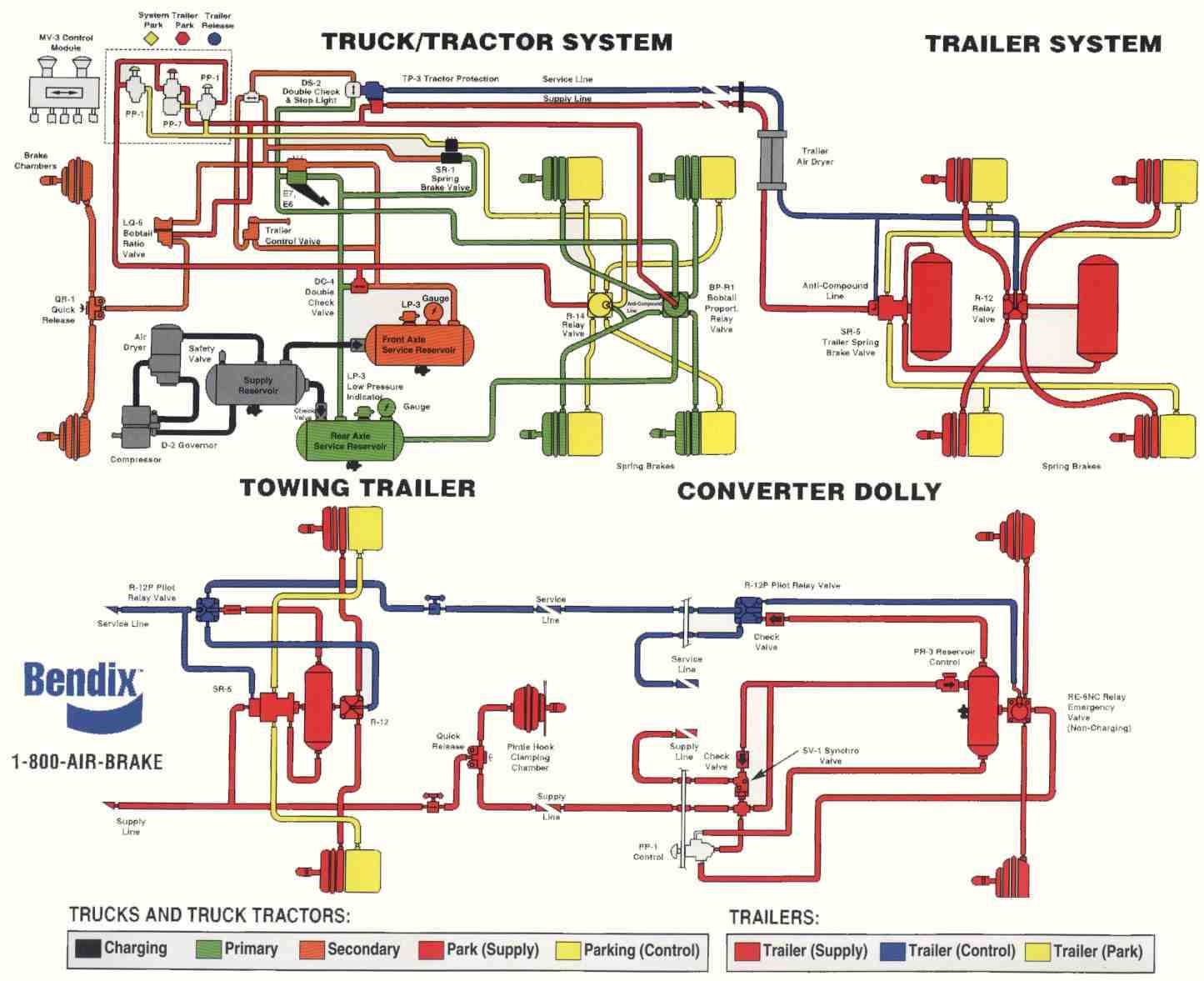
Grasping the relationships between these units enhances comprehension of how the entire mechanism reacts under different conditions. Regular inspection and maintenance are necessary to ensure that all components function correctly and efficiently, ultimately leading to improved vehicle safety and reliability.
Replacing Truck Brake Parts
Maintaining optimal performance in heavy vehicles is essential for safety and efficiency. Regular replacement of critical components ensures that these machines operate smoothly and reduces the risk of failures during operation. Understanding the process of changing these components is crucial for every operator.
Preparation Steps
Before beginning the replacement procedure, it’s important to gather the necessary tools and materials. Follow these steps:
- Ensure the vehicle is parked on a level surface.
- Gather tools: wrenches, sockets, and a jack.
- Purchase high-quality replacement components suited for your vehicle model.
- Review the vehicle manual for specific instructions.
Replacement Process
Follow this systematic approach for replacing the components:
- Lift the vehicle using a jack and secure it with jack stands.
- Remove the wheel to access the necessary components.
- Detach the old components by unscrewing or unbolting them carefully.
- Install the new components, ensuring they are properly aligned and secured.
- Reattach the wheel and lower the vehicle back to the ground.
- Test the new components by performing a brief operational check.
Regularly replacing these essential components not only enhances safety but also extends the lifespan of the vehicle. Proper maintenance practices are vital for ensuring reliability and performance on the road.
Importance of Regular Inspections
Ensuring optimal performance and safety of vehicles requires consistent evaluation of critical components. Regular examinations help identify potential issues before they escalate into significant problems, thereby enhancing reliability and extending the lifespan of essential systems.
Preventative maintenance plays a vital role in maintaining operational efficiency. By routinely checking vital elements, one can detect wear and tear, ensuring that replacements are made in a timely manner. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of unexpected failures.
Moreover, frequent assessments contribute to overall safety on the road. Addressing minor concerns early can prevent hazardous situations, protecting not only the vehicle operator but also other road users. Investing time in inspections ultimately leads to peace of mind and confidence in vehicle reliability.
Upgrading Brake Systems for Safety
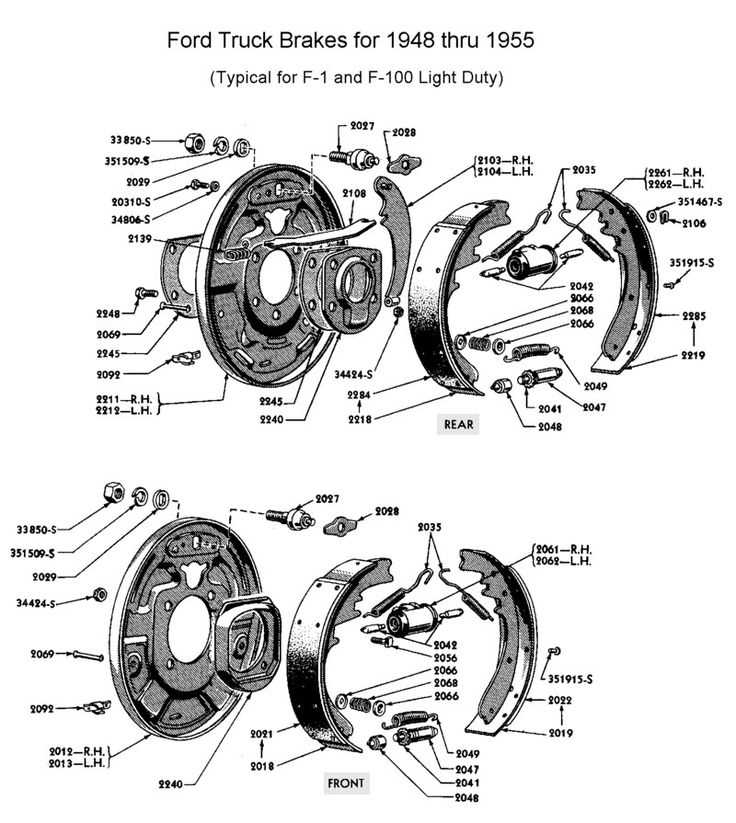
Enhancing the stopping mechanisms of heavy vehicles is crucial for ensuring the highest levels of safety on the road. As advancements in technology emerge, it becomes essential for operators to consider the latest innovations that provide improved responsiveness and reliability. Investing in superior components not only boosts performance but also enhances overall vehicle safety, which is paramount for drivers and their cargo.
Importance of Quality Components
Utilizing high-quality materials in the stopping systems significantly reduces wear and tear, leading to longer-lasting functionality. Choosing reputable brands ensures that the components can withstand rigorous conditions, thereby reducing the risk of failure in critical situations. Reliability is the ultimate goal when upgrading, as it directly impacts the safety of all road users.
Regular Maintenance and Upgrades
Incorporating a routine maintenance schedule along with periodic enhancements can greatly extend the lifespan of the system. Regular inspections help identify any potential issues before they escalate, while timely upgrades introduce the latest safety features. Ultimately, staying proactive about enhancements contributes to a more secure driving experience.
Regulatory Standards for Brake Systems
Ensuring the safety and efficiency of stopping mechanisms is crucial in various vehicles. These standards establish guidelines that manufacturers must adhere to, promoting reliability and minimizing risks on the road.
- Performance Criteria: Specifications regarding stopping distance, response time, and overall effectiveness.
- Material Safety: Regulations concerning the materials used, ensuring they can withstand heat and wear.
- Testing Procedures: Protocols for assessing system performance under different conditions.
Compliance with these regulations is monitored by relevant authorities to ensure that all vehicles meet essential safety benchmarks.
- Regular inspections and maintenance are required to uphold standards.
- Documentation of compliance is necessary for manufacturers and vehicle operators.
Ultimately, these measures aim to safeguard lives and enhance operational efficiency across the transportation sector.