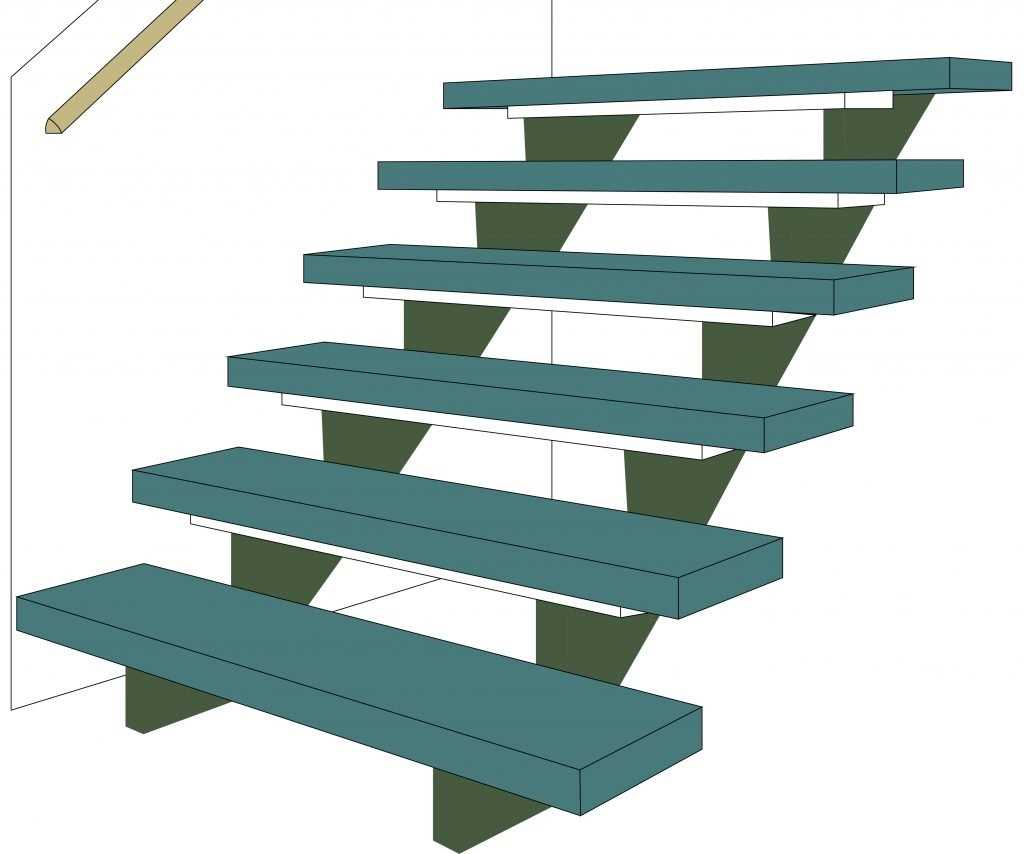
Creating an inviting and functional ascent involves various crucial elements that contribute to both aesthetics and safety. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring stability while enhancing the overall design. By exploring these individual elements, one can appreciate the craftsmanship involved in constructing an effective solution for elevation.
From the supportive bases to the connecting structures, understanding their interrelationships is essential for anyone looking to delve deeper into architectural design. The ultimate goal is to create a seamless experience for users while adhering to safety standards and visual harmony.
In this exploration, we will dissect the key elements that contribute to the functionality and beauty of these structures. With a focus on their characteristics and purposes, readers will gain insight into how each piece contributes to a cohesive whole.
Understanding Staircase Components
Exploring the various elements involved in the structure of an ascending or descending formation is essential for both design and functionality. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring safety, comfort, and aesthetic appeal.
Key Elements to Consider

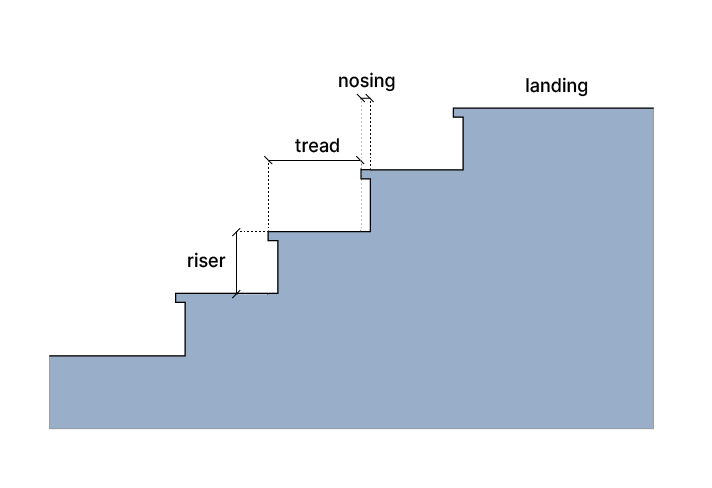
- Rise and Run: The vertical and horizontal measurements that determine the incline.
- Handrails: Essential for safety, providing support and stability.
- Treads and Risers: The surfaces on which one steps and the vertical sections that connect them.
Functional Aspects
- Safety regulations often dictate specific dimensions.
- Material choices influence durability and maintenance.
- Aesthetic considerations can enhance the overall design of the space.
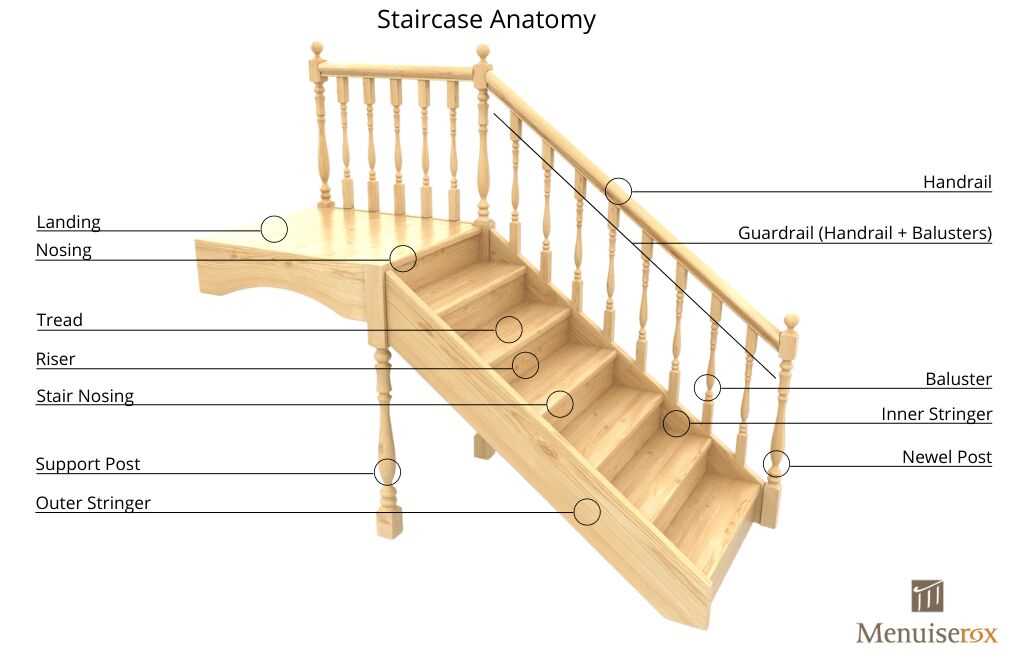
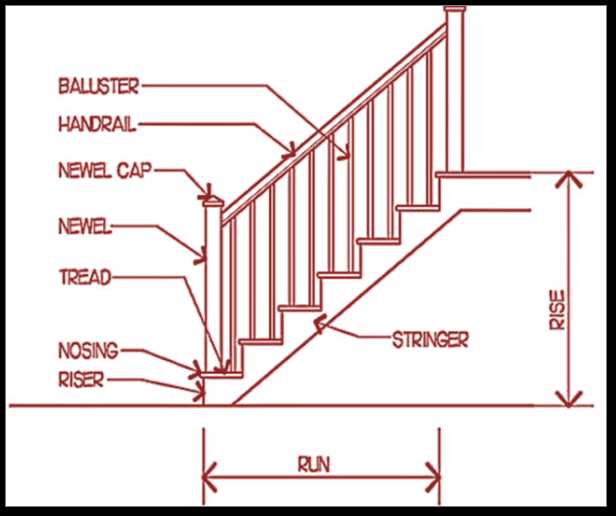
Essential Parts of a Staircase
Understanding the crucial components of a flight of steps is vital for both design and functionality. Each element plays a significant role in ensuring safety, accessibility, and aesthetic appeal. A comprehensive knowledge of these structures can aid in making informed decisions during construction or renovation.
Treads are the horizontal surfaces on which individuals step. Their width and depth are essential for comfort and stability. A well-designed tread not only supports weight but also enhances the overall visual appeal.
Risings, or the vertical sections between each tread, provide the necessary height to each level. The height of these elements is critical for ensuring a comfortable ascent or descent, contributing to a smooth flow of movement.
Handrails offer support and guidance, making navigation safer, especially for those with mobility challenges. Their placement and design must adhere to safety standards while also complementing the aesthetic of the surrounding space.
Newels act as the main vertical posts at the ends of a flight. They provide structural stability and can serve as decorative focal points, enhancing the overall design of the area.
Bullnose features, typically found at the landing, soften the transition and add an element of elegance. These rounded edges help prevent trips and enhance safety.
Each of these elements contributes to the overall function and beauty of the ascent, highlighting the importance of thoughtful design in creating a harmonious and safe environment.
Types of Staircases Explained
Exploring the various forms of elevated pathways reveals a fascinating array of designs, each tailored to specific architectural needs and aesthetic preferences. From the classic to the modern, these constructions can transform spaces while serving practical functions.
| Design | Description |
|---|---|
| Straight | A simple and straightforward configuration, ideal for limited spaces and easy access. |
| L-shaped | Featuring a turn, this style maximizes corner space and offers a dynamic transition between levels. |
| U-shaped | Characterized by two parallel flights, this design provides a graceful curve and can enhance visibility. |
| Spiral | A compact option that utilizes a circular pattern, perfect for tight areas while adding an artistic touch. |
| Curved | Similar to spiral but often more expansive, this type adds elegance and fluidity to interiors. |
Materials Used in Stair Construction
The choice of materials for creating elevation access systems significantly impacts their durability, aesthetic appeal, and safety. Various substances can be employed, each offering unique characteristics that cater to specific needs and preferences. Understanding the available options is essential for making informed decisions in construction projects.
Common Materials
- Wood: Known for its natural beauty and warmth, wood is a popular choice. It can be easily customized and offers various finishes.
- Concrete: Renowned for its strength and longevity, concrete provides excellent structural support and is often used in modern designs.
- Metal: Steel and aluminum are frequently utilized for their robustness and modern aesthetic. They are ideal for contemporary settings.
- Composite Materials: Combining various elements, these materials offer enhanced durability and reduced maintenance, making them a versatile option.
Factors Influencing Material Selection
- Safety: The slip resistance and structural integrity of the material are paramount to ensure user safety.
- Cost: Budget constraints often dictate the choice of materials, with some options being more affordable than others.
- Aesthetic Appeal: The visual impact of the materials contributes to the overall design and can enhance the ambiance of the space.
- Maintenance: Different materials require varying levels of upkeep, which can affect long-term costs and effort.
Importance of Staircase Safety Features
Ensuring the well-being of individuals navigating elevated surfaces is paramount in both residential and commercial environments. Thoughtful design and implementation of protective elements can significantly reduce the risk of accidents, fostering a secure atmosphere for users of all ages.
Risk Mitigation
Incorporating safety mechanisms can greatly lower the likelihood of falls and injuries. Features such as handrails, non-slip surfaces, and proper lighting play crucial roles in creating a safer environment. By addressing common hazards, these enhancements contribute to a more reliable structure that instills confidence in users.
Accessibility Considerations
Furthermore, safety attributes are vital for accommodating diverse needs. Ensuring that individuals with mobility challenges can navigate these structures easily not only complies with regulations but also promotes inclusivity. The addition of ramps, wider paths, and clear markings are essential for creating an accessible experience for everyone.
In conclusion, prioritizing safety features is essential for any elevated structure. By recognizing their significance, we can enhance both functionality and security, making these spaces more welcoming and user-friendly.
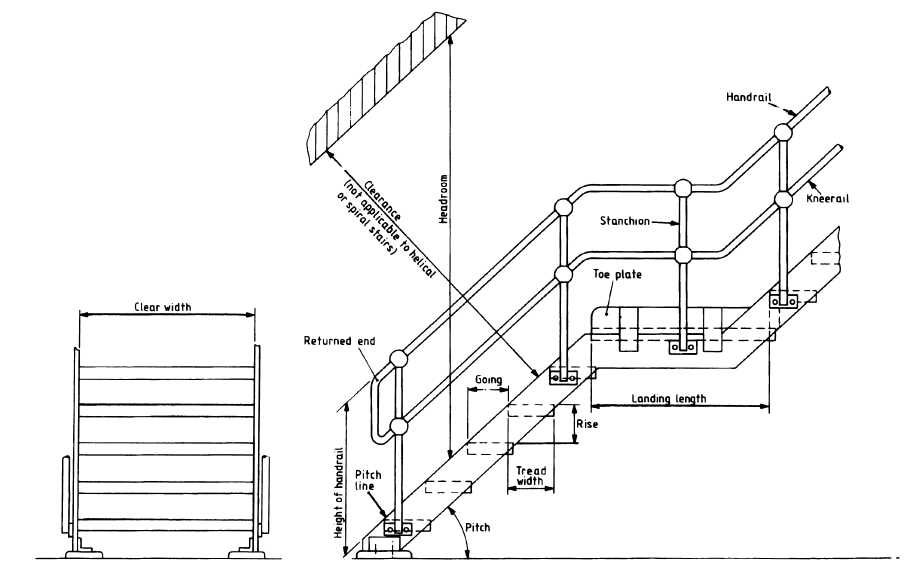
How to Read a Stair Diagram
Understanding the layout of a set of steps can greatly enhance your ability to visualize and execute your project. Familiarizing yourself with the symbols and measurements is essential for effective interpretation.
To effectively interpret the visual representation, consider the following key elements:
- Symbols: Different shapes often represent various components, such as risers, treads, and landings. Recognizing these will help you piece together the entire structure.
- Measurements: Dimensions are typically indicated in feet and inches or millimeters. Pay close attention to these numbers to ensure accurate construction.
- Angles: The inclination of the steps may be represented with angles or sloped lines. Understanding these can assist in maintaining proper safety standards.
Here are some tips to improve your comprehension:
- Study each element: Break down the image by focusing on one aspect at a time. This can prevent confusion and help in retaining information.
- Cross-reference: Use accompanying notes or legends that explain the symbols and measurements, providing additional context.
- Practice: The more you engage with these visual aids, the more intuitive reading them will become.
By mastering these elements, you will enhance your ability to construct and analyze designs effectively.
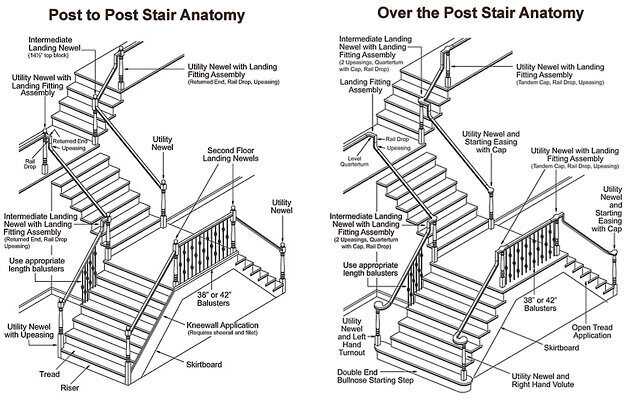
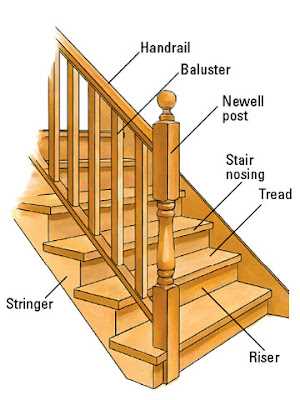
Common Staircase Design Terminology
Understanding the terminology related to the structure and design of elevated access systems is essential for anyone involved in construction or architecture. Familiarity with these terms enhances communication and ensures that designs are executed with precision. Below is a compilation of commonly used terms that provide clarity in discussions about various elements of these architectural features.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Tread | The horizontal part of the step where one places their foot. |
| Riser | The vertical component that connects one tread to the next. |
| Landing | A flat area at the top or bottom of a flight, providing a transition between levels. |
| Stringer | The supporting framework that holds the treads and risers in place. |
| Balustrade | A protective railing along the edge of a flight or landing, often featuring vertical posts. |
| Newel Post | A sturdy post that anchors the end of a railing or marks the turn of a staircase. |
| Handrail | A rail that provides support for individuals using the elevated access system. |
| Rise and Run | Measurements referring to the height and depth of each step, essential for comfort and safety. |
Measuring for Staircase Construction
Accurate measurements are crucial for creating a safe and functional ascent. Whether you’re embarking on a new project or renovating an existing structure, understanding how to properly gauge dimensions can significantly impact the final outcome.
To ensure precision, follow these essential steps:
- Determine the total height from the lower to the upper level.
- Decide on the rise and run of each individual step.
- Calculate the number of steps needed by dividing the total height by the rise.
- Measure the width of the stairway to accommodate foot traffic comfortably.
- Account for headroom clearance to avoid obstructions.
Using these guidelines will help you create a well-structured ascent that meets safety standards and suits your design preferences.
Staircase Assembly Process Overview
The construction of a multi-tiered structure involves a systematic approach that ensures stability and aesthetic appeal. Each phase is critical to achieving the ultimate design and functionality desired.
Preparation is the initial step, where precise measurements and material selection set the foundation for a successful build. Ensuring the right dimensions and quality of resources is essential.
Next comes the framework assembly, which involves connecting the main support elements. This stage requires careful alignment to provide the necessary strength for the overall structure.
Once the framework is established, the installation of the treads and risers occurs. This step enhances both safety and comfort, as these elements must be securely attached to withstand regular use.
Finally, finishing touches are applied, such as handrails and protective coatings. This not only contributes to the visual appeal but also ensures longevity and safety in everyday use.
Maintenance Tips for Stair Components
Regular upkeep of the various elements that form a flight of steps is essential for safety and longevity. Proper attention not only enhances the aesthetic appeal but also ensures that each element functions optimally. Here are some practical tips to maintain these crucial features effectively.
1. Inspect Regularly: Conduct routine checks for signs of wear, damage, or instability. Look for loose treads, cracked risers, or unstable railings. Early detection of issues can prevent accidents and costly repairs.
2. Clean Thoroughly: Keep surfaces free from dust, debris, and spills. Use appropriate cleaners for different materials. For wooden surfaces, a damp cloth followed by a dry one is often sufficient. For metal components, ensure to use non-corrosive cleaners.
3. Address Moisture: Excessive humidity can lead to warping or mold growth. Ensure good ventilation in the area to mitigate moisture problems. In particularly damp environments, consider using a dehumidifier.
4. Tighten Fasteners: Periodically check and tighten screws, bolts, and other fasteners. Loose fittings can lead to instability and may compromise safety.
5. Apply Protective Finishes: For wooden elements, consider applying a sealant or varnish to protect against wear and environmental factors. For metal components, a rust-inhibiting spray can help prolong their lifespan.
6. Replace Worn Elements: If any components show significant wear or damage, replace them promptly. Ignoring this can lead to more severe issues down the line.
By following these maintenance tips, you can ensure that all the features contributing to a well-structured ascent remain in excellent condition, enhancing both safety and aesthetic value.
Building Codes and Regulations for Stairs
Understanding the framework of standards and guidelines is crucial for ensuring safety and functionality in any elevated structure. Compliance with these rules not only enhances security but also promotes accessibility and usability for all individuals.
Key Requirements
Essential regulations typically address dimensions, load-bearing capacities, and materials. For instance, tread and riser specifications are designed to prevent accidents, while handrail height and spacing are established to assist users. Local building codes often dictate these parameters, ensuring that they meet community safety expectations.
Accessibility Considerations
Incorporating universal design principles is vital in making elevated structures accessible to everyone. Regulations may require features such as wider pathways and appropriately designed ramps. Adhering to these accessibility standards not only fulfills legal obligations but also enhances overall usability.
Creative Design Ideas for Stairs
Innovative approaches to elevating the look and functionality of ascent structures can transform a space dramatically. From unique materials to unexpected shapes, the possibilities are endless. Incorporating creativity not only enhances aesthetics but also adds personal flair to any home or building.
Material Choices
Utilizing a mix of materials can create stunning visual contrasts. Wood paired with metal or glass introduces a modern edge, while stone adds a touch of elegance. Explore the ultimate combinations that resonate with your style.
Lighting Solutions
Incorporating lighting can make a significant impact. Under-stair LED strips or decorative sconces illuminate the path and highlight design features. This not only enhances safety but also creates a warm ambiance, inviting everyone to explore.