
The intricate world of mechanical devices often fascinates enthusiasts and professionals alike. Within this realm, a comprehensive grasp of the various elements that contribute to functionality is essential. This knowledge not only aids in effective maintenance but also enhances the overall performance of these tools.
Exploring the composition of a specific equipment reveals a network of interconnected segments. Each component plays a pivotal role, influencing efficiency and durability. By delving into the arrangement and operation of these elements, users can better appreciate the engineering behind them.
Furthermore, visual aids can significantly enhance the understanding of these complex systems. Utilizing detailed illustrations to represent each segment’s position and function provides clarity, making it easier for individuals to navigate and troubleshoot potential issues. This approach fosters a deeper connection with the machinery, encouraging more informed use and care.
Understanding Chinese Chainsaw Parts
This section aims to clarify the components that play a vital role in the functionality of cutting machinery. Familiarity with these elements enhances maintenance and performance, ensuring efficiency in operation.
Main Components
- Engine: The powerhouse that drives the entire mechanism.
- Guide Bar: Provides support and directs the cutting tool.
- Cutting Tool: The sharp element responsible for severing material.
- Chain: Connects the cutting tool and moves it around the guide bar.
- Handle: Offers control and maneuverability during use.
Importance of Each Element
Understanding the role of each element is crucial for effective usage and repair. Knowledge of how these components interact allows users to:
- Perform regular maintenance.
- Identify issues quickly.
- Enhance operational safety.
Importance of Diagrams in Repairs
Visual representations play a crucial role in the maintenance and restoration of machinery. They provide a clear outline of components and their interrelations, making complex systems more manageable for technicians. Understanding these illustrations enhances the efficiency and accuracy of repair tasks, allowing for quicker identification of issues and effective solutions.
Enhancing Understanding
Illustrative guides serve to demystify intricate structures. By breaking down each element into a visual format, users can gain insights into how various parts function together. This understanding is essential for diagnosing problems and performing repairs with confidence.
Streamlining the Repair Process
When engaging in maintenance activities, having a visual reference significantly reduces the time spent searching for information. Technicians can quickly locate the necessary components and follow step-by-step instructions, minimizing the risk of errors. As a result, this leads to improved productivity and a higher quality of work.
Common Components of Chainsaws
Understanding the essential elements of cutting machines is crucial for anyone interested in their operation and maintenance. Each machine consists of various integral parts that work together to ensure efficiency and safety during use. By familiarizing oneself with these components, users can enhance their experience and prolong the lifespan of the equipment.
Power Unit: The heart of any cutting machine, the power unit generates the necessary energy to drive the entire mechanism. It can vary in type, including gas or electric models, each offering unique advantages.
Guide Bar: This elongated metal piece serves as a track for the cutting chain. Its length and design directly influence the machine’s cutting capacity and maneuverability, making it a critical aspect of performance.
Cutting Chain: Composed of linked segments, this chain is responsible for executing the cutting action. The sharpness and configuration of the teeth on the chain determine its effectiveness and the type of material it can handle.
Drive Sprocket: This small yet vital component connects the power unit to the cutting chain, transferring energy and facilitating motion. A well-functioning sprocket ensures smooth operation and prevents wear on the chain.
Clutch: Acting as a connector between the power unit and the drive mechanism, the clutch engages and disengages the chain as needed. This feature enhances safety, allowing users to stop the chain while maintaining engine power.
Air Filter: Essential for maintaining engine performance, the air filter prevents debris from entering the combustion chamber. A clean filter is crucial for optimal airflow and efficient operation.
Fuel System: Comprising the fuel tank, lines, and carburetor, this system manages the delivery of fuel to the power unit. Proper maintenance of the fuel system is necessary to ensure reliable starting and consistent performance.
By understanding these fundamental components, users can make informed decisions about maintenance and repairs, ultimately leading to more effective use of their equipment.
How to Read a Parts Diagram
Understanding a schematic can greatly enhance your ability to identify and manage components within machinery. This process involves familiarizing yourself with symbols, labels, and organization of elements represented visually.
- Familiarize with Symbols: Recognize common icons that denote specific components.
- Study the Legend: Many visuals include a key explaining the symbols used.
- Identify Sections: Components are often grouped by function; learn how these sections are organized.
- Trace Connections: Follow lines that indicate how different pieces interact or connect.
By applying these strategies, you can confidently navigate any schematic and understand its ultimate purpose in maintenance or assembly.
Identifying Essential Chainsaw Parts
Understanding the fundamental components of a cutting tool is crucial for effective maintenance and operation. Familiarity with each element enhances performance and prolongs the lifespan of the equipment. This section delves into the primary sections of a cutting device, emphasizing their roles and significance.
Main Components Overview
Each segment of the equipment plays a vital role in its functionality. Recognizing these sections enables operators to troubleshoot issues and perform necessary repairs efficiently.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Engine | Drives the tool and provides the necessary power for operation. |
| Bar | Supports the cutting chain and guides it during use. |
| Chain | Consists of sharp links that cut through material. |
| Handle | Provides grip and control for the operator. |
| Fuel System | Stores and supplies fuel to the engine for combustion. |
| Safety Features | Includes mechanisms to prevent accidents and ensure user safety. |
Regular inspection and upkeep of these components are essential for optimal performance. Neglecting any section can lead to inefficiencies or even hazardous situations. Awareness and knowledge empower users to maintain their equipment properly.
Tools Needed for Chainsaw Maintenance
Proper upkeep of power tools is essential for ensuring their longevity and efficiency. Regular maintenance requires a specific set of implements that facilitate effective cleaning, adjustment, and repair. Understanding which tools are necessary can help you perform routine tasks with ease and precision.
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Wrench Set | For tightening and loosening bolts and nuts |
| Screwdriver | To adjust screws on various components |
| File | For sharpening blades and improving cutting performance |
| Brush | To remove debris and dirt from the machine |
| Protective Gear | For safety during maintenance activities |
| Oil Can | To lubricate moving parts and prevent wear |
Replacing Worn Chainsaw Parts
Maintaining optimal performance of your tool requires timely substitution of components that have lost their effectiveness. Over time, certain elements may degrade, affecting functionality and safety. Regular inspection and replacement ensure longevity and efficiency.
Identifying Signs of Wear
Look for indicators such as decreased performance, unusual noises, or visible damage. Regular checks can help pinpoint which components need attention before they lead to more significant issues.
Choosing Quality Replacements
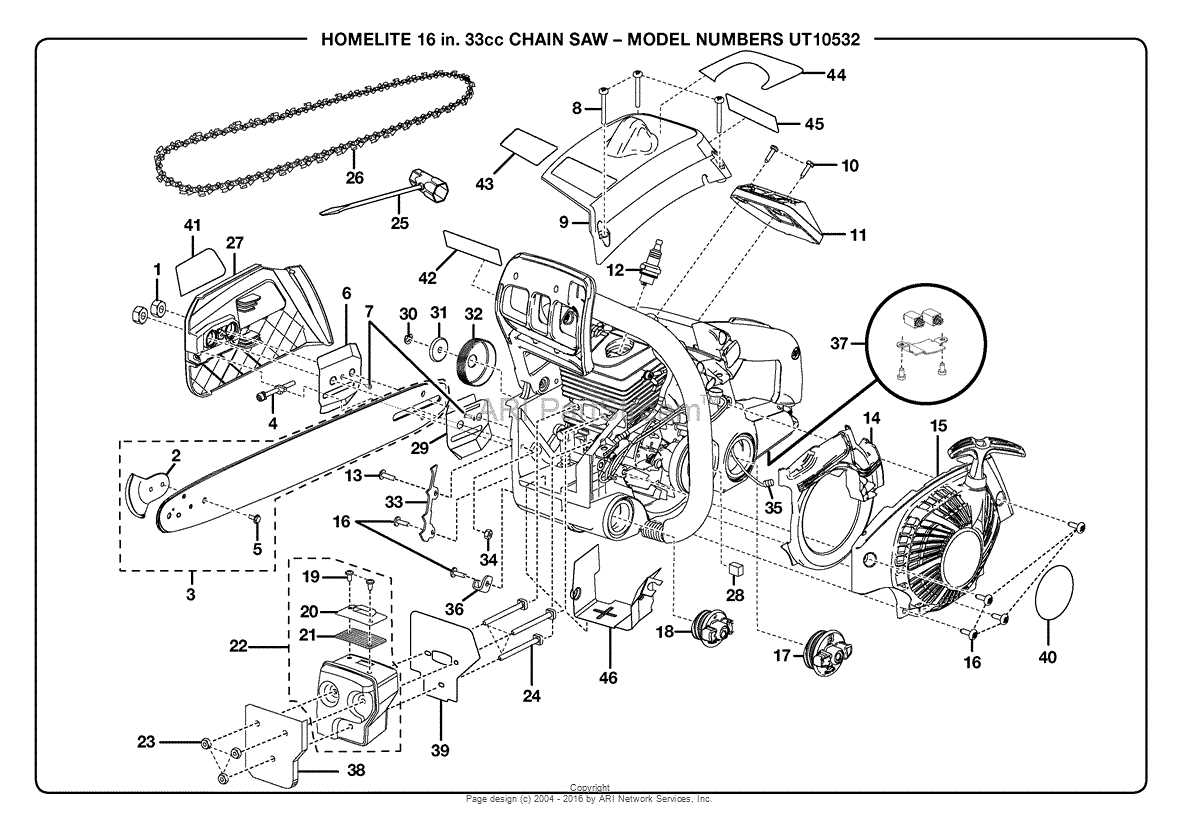
When selecting new components, prioritize durability and compatibility. Investing in high-quality replacements can enhance your tool’s performance and extend its lifespan significantly.
Safety Precautions During Repairs
Engaging in maintenance tasks can be rewarding, but it is essential to prioritize safety to prevent accidents and injuries. Understanding the potential hazards and taking necessary precautions can significantly enhance the repair experience.
Always Wear Protective Gear: Equip yourself with appropriate safety equipment. This includes gloves, goggles, and sturdy footwear. Protective clothing helps minimize the risk of cuts, abrasions, and exposure to hazardous materials.
Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Ensure that your workspace is adequately ventilated, especially when using solvents or chemicals. Proper airflow reduces the risk of inhaling harmful fumes, promoting a safer environment.
Disconnect Power Sources: Before beginning any repairs, always disconnect the power source. This prevents accidental activation of the machinery, reducing the chance of injury while working on it.
Organize Your Workspace: Maintain a clean and organized area to work in. Clutter can lead to accidents, so keep tools and materials in designated spots to avoid tripping or misplacing items.
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for repair procedures. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that repairs are performed correctly and safely, minimizing the likelihood of mistakes.
Be Mindful of Your Surroundings: Pay attention to your environment while working. Ensure that no one else is in close proximity to the equipment, as unexpected movements can lead to injuries.
By incorporating these safety measures, you can create a safer repair experience, allowing you to focus on the task at hand while minimizing risks.
Where to Find Quality Diagrams
Locating high-quality illustrations can significantly enhance your understanding of mechanical systems. These visual aids serve as essential resources for maintenance and assembly, allowing users to navigate complexities with ease.
Online Resources
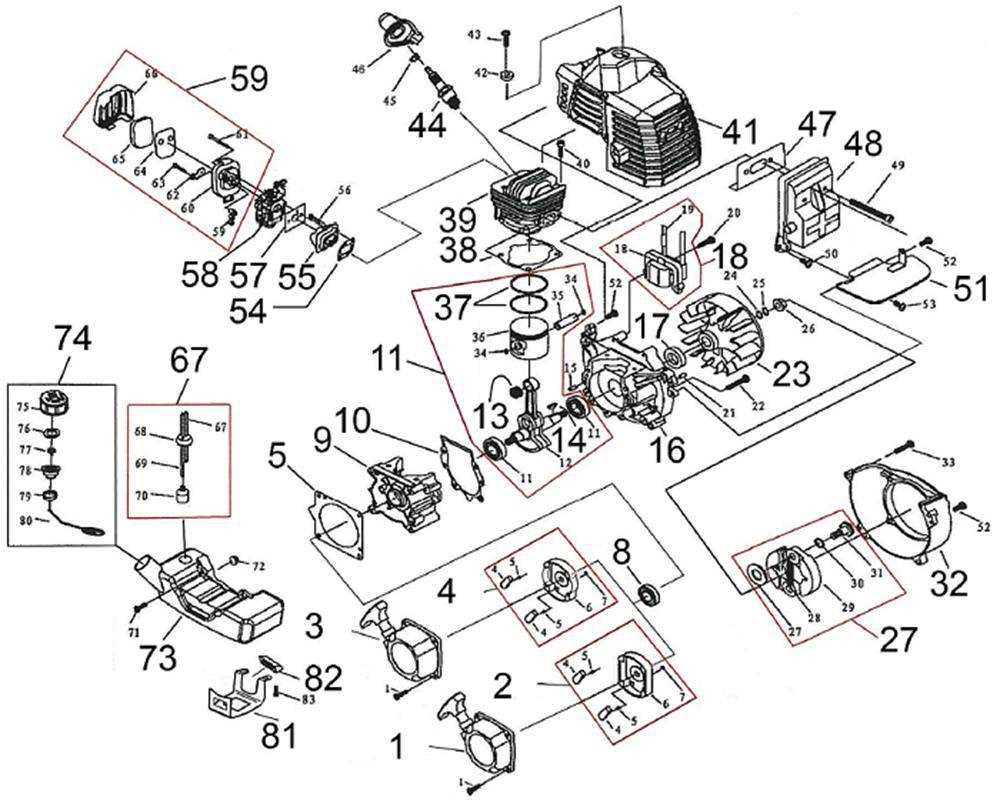
The internet offers a plethora of platforms where detailed schematics can be accessed. Websites dedicated to repair guides often provide downloadable content, while forums and communities share valuable insights and links to reputable sources.
Local Stores and Libraries
Physical locations, such as hardware stores and public libraries, can be excellent places to find printed manuals and illustrations. Engaging with knowledgeable staff may lead you to discover resources that are not readily available online.
Tips for Troubleshooting Issues
When facing operational difficulties with your equipment, it’s essential to approach the problem methodically. Identifying the root cause can save time and ensure efficient performance. Here are some strategies to help you diagnose common challenges effectively.
Common Symptoms and Solutions
- Engine Won’t Start:
- Check fuel levels and quality.
- Inspect the spark plug for wear.
- Ensure the ignition system is functioning properly.
- Unusual Noises:
- Listen for any grinding or knocking sounds.
- Examine moving parts for proper lubrication.
- Look for loose components that may need tightening.
Maintenance Tips
- Regularly clean the air filter to enhance airflow.
- Change the oil according to the manufacturer’s schedule.
- Keep all connections secure and free of debris.
Benefits of Using OEM Parts
Utilizing original equipment manufacturer components ensures optimal performance and longevity for your machinery. These items are designed specifically for compatibility and efficiency, minimizing the risk of malfunction and enhancing the overall user experience.
Quality Assurance

OEM components are manufactured to meet strict industry standards, ensuring durability and reliability. By choosing these items, you invest in quality that can withstand rigorous use over time.
Seamless Integration
Using original components guarantees seamless integration with your equipment. This compatibility reduces the likelihood of operational issues, allowing you to maintain peak performance without unnecessary disruptions.
Comparing Brands: Quality and Performance
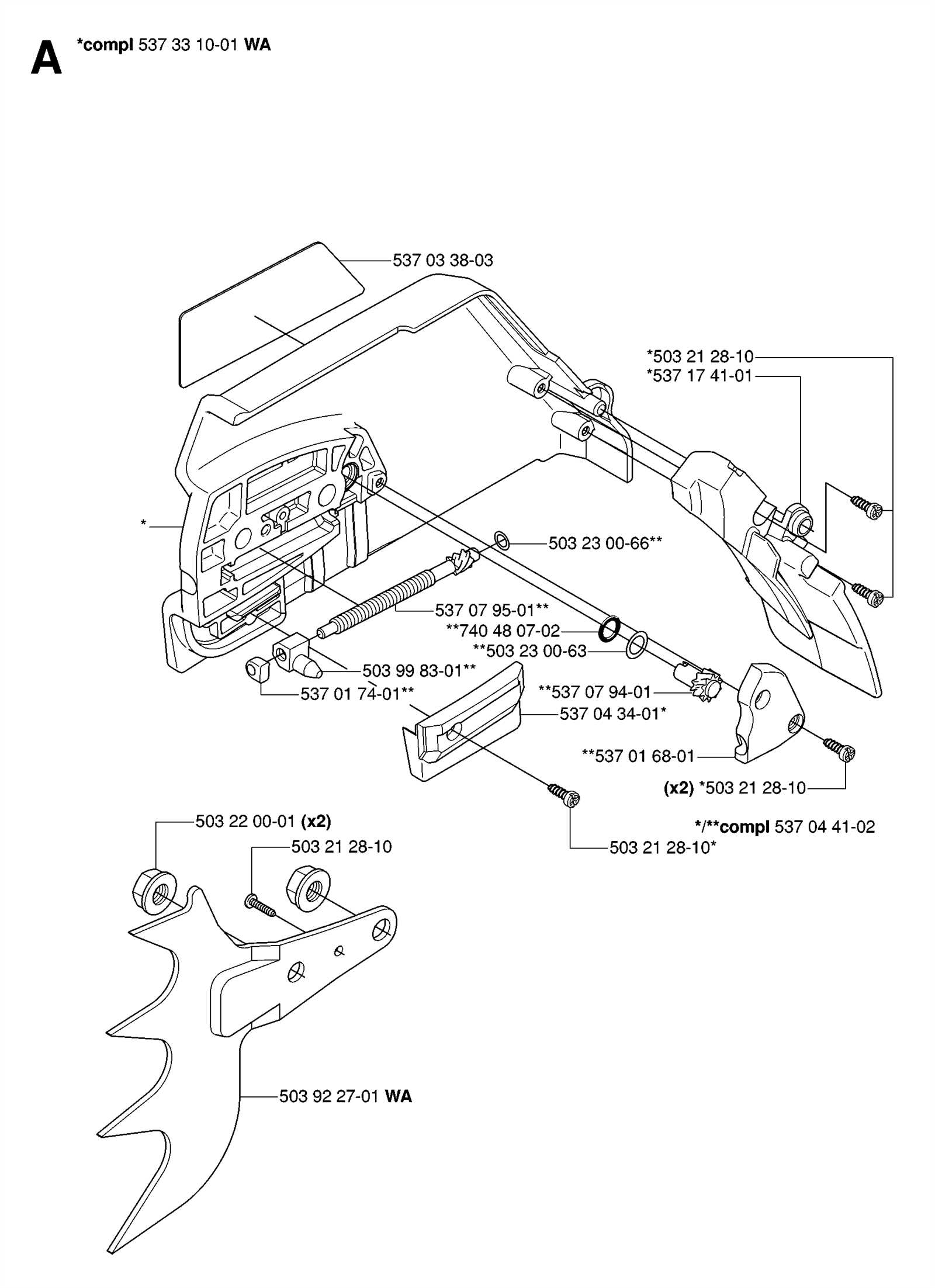
When evaluating various manufacturers in the cutting tool market, it’s essential to examine both the durability and efficiency of their offerings. Different brands exhibit distinct characteristics that can significantly affect user experience and satisfaction. By analyzing these factors, we can determine which options stand out in terms of reliability and functionality.
| Brand | Quality Rating | Performance Score |
|---|---|---|
| Brand A | 8/10 | 9/10 |
| Brand B | 7/10 | 8/10 |
| Brand C | 9/10 | 9/10 |
This comparison highlights the strengths and weaknesses of each manufacturer, guiding consumers towards informed choices that align with their specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Chainsaws
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the functioning, maintenance, and selection of power tools designed for cutting wood. Whether you are a novice or an experienced user, understanding these aspects can enhance your experience and ensure safety while operating.
General Information
Powerful cutting tools come in various models and styles. Users often wonder about the best practices for handling these machines, the types of fuel and oils required, and essential safety measures to keep in mind. Below are some frequently asked questions.
Maintenance Tips
Proper upkeep is crucial for the longevity of your tool. Regular maintenance can prevent malfunction and improve efficiency. Here is a quick reference table to guide you:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Clean Air Filter | Every 5 uses | Remove debris to ensure optimal airflow. |
| Check Chain Tension | Before each use | Ensure proper tension to avoid wear or accidents. |
| Sharpen Chain | Every 3-5 hours of use | Maintain sharpness for efficient cutting. |
| Inspect Fuel System | Every month | Check for leaks or blockages in the fuel lines. |