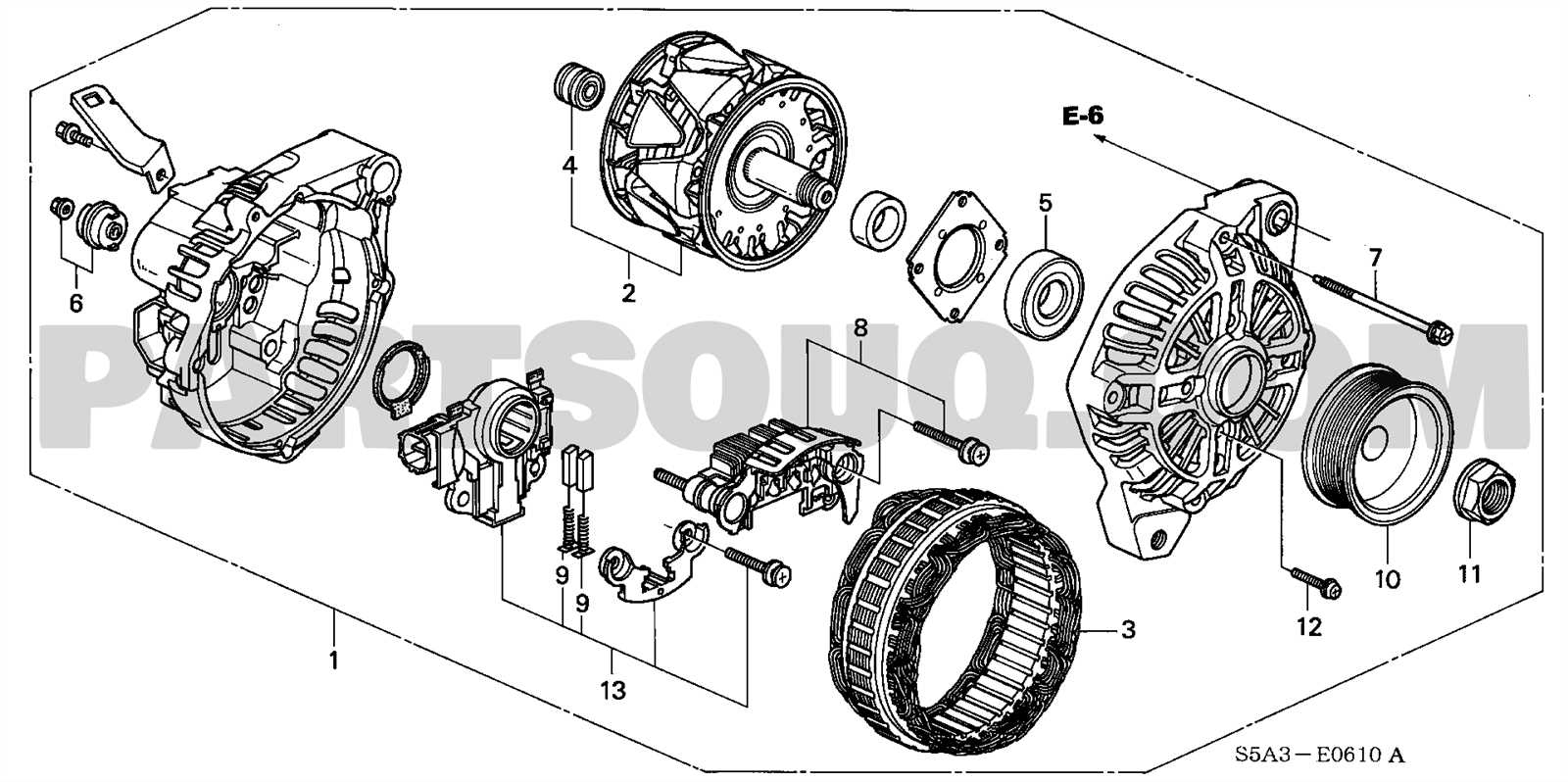
Exploring the intricate layout of a vehicle’s internal elements can provide valuable insights into its structure and functionality. Whether you’re an enthusiast or a professional, having a clear view of how various systems interconnect is crucial for both maintenance and upgrades. This knowledge helps in identifying key areas that may require attention or replacement over time.
By examining detailed illustrations that outline the connections and placements of mechanical and electrical units, you gain a comprehensive understanding of the inner workings of your automobile. This approach not only simplifies troubleshooting but also ensures that any modifications or repairs are executed with precision.
In this guide, we delve into the specifics of various assemblies, highlighting their roles and interactions within the larger framework of the vehicle. By focusing on these aspects, we aim to make your exploration of the automobile’s structure more intuitive and accessible.
The braking assembly is a crucial component in ensuring vehicle safety, providing the necessary control to manage deceleration effectively. This section explores the various elements that work together to bring the vehicle to a stop, emphasizing how each component plays a role in maintaining stability and control.
Main Components of the Braking Assembly
The structure of the braking setup involves several interconnected units that collaborate to deliver a smooth and responsive braking experience. Each element is designed to function in harmony, converting kinetic energy into heat energy, thus slowing down the vehicle efficiently.
Detailed Overview of Key Elements
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Brake Calipers | Responsible for applying pressure to the brake pads, which then create friction against the rotors to slow down the wheels. |
| Brake Pads | These are friction materials that press against the rotors, generating the force required to reduce wheel speed. |
| Rotors | Rotating discs that the brake pads clamp onto, converting motion into heat and enabling the deceleration process. |
| Brake Lines | Conduits that carry hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the braking components, ensuring consistent pressure delivery. |
Understanding the specific roles of these elements allows for better maintenance and troubleshooting of the braking system, ensuring that it functions optimally under various driving conditions.
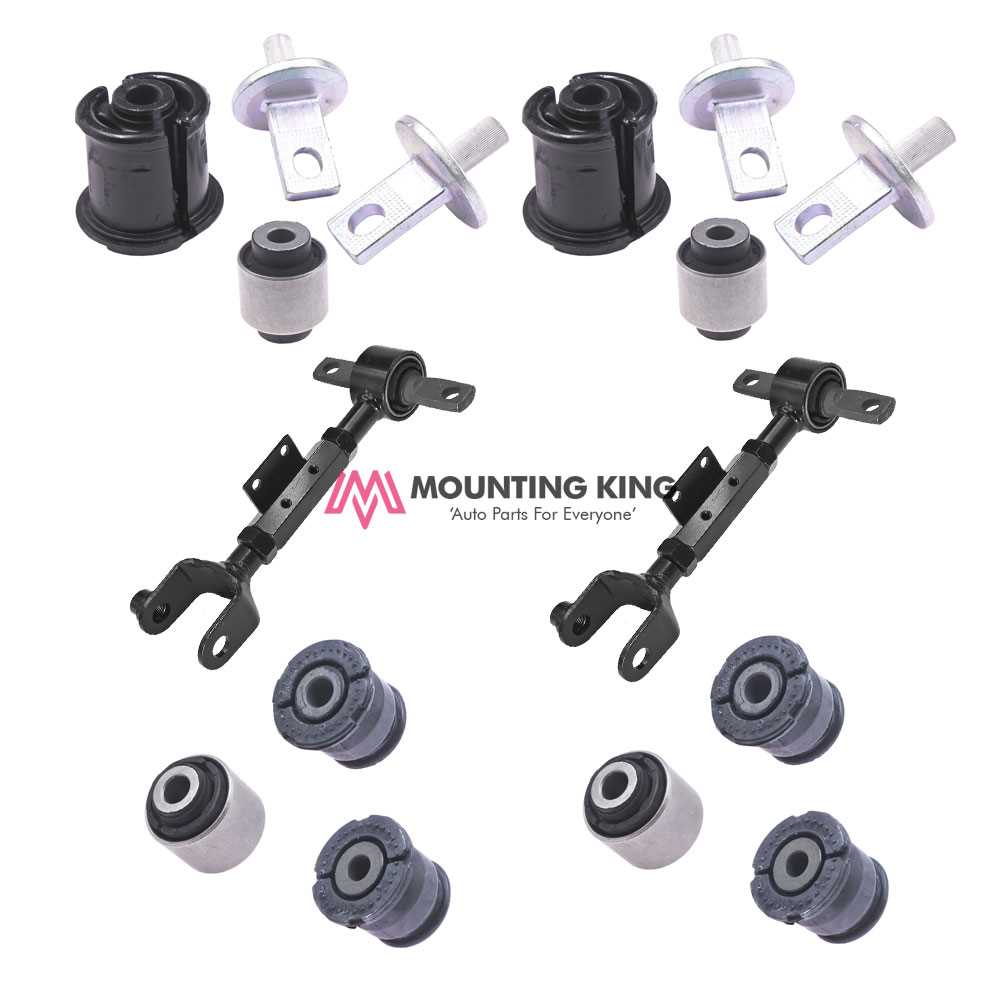
Exploring Suspension and Steering Components
The stability and control of any vehicle rely heavily on the intricate system that manages its movement and direction. This section delves into the essential elements that provide a smooth and responsive driving experience, focusing on the mechanisms that connect the wheels to the rest of the structure.
Key Elements in the Suspension System
One of the most crucial functions of the suspension is to absorb shocks and vibrations, ensuring comfort and control. This system incorporates various elements that work in unison to balance the vehicle’s weight and manage its contact with the road surface. Components like shock absorbers and springs play a vital role in maintaining stability, especially on uneven terrains.
Understanding Steering Dynamics
The steering assembly is designed to translate the driver’s input into precise wheel movement, providing accurate direction changes. It includes interconnected parts that adjust the angle of the tires to navigate curves efficiently. Proper alignment of these components is essential to prevent wear and enhance control, ensuring the vehicle responds accurately to the driver’s commands.
Body Frame Elements and Their Role
The structural framework of a vehicle is crucial to its overall durability and stability. Each component within this framework is meticulously designed to contribute to the integrity and functionality of the vehicle’s structure, ensuring both safety and performance. Understanding these elements helps in identifying how they interact to provide support and protection.
Main Structural Components
- Pillars: These vertical supports are key to the vehicle’s roof stability and passenger compartment protection. They play a significant role in minimizing impact during collisions.
- Side Beams: Positioned along the sides, these beams help distribute forces across the frame, enhancing the overall strength of the structure.
- Cross Members: These horizontal components connect various parts of the framework, providing additional rigidity and reducing flex under load.
Protective and Reinforcement Elements
Beyond the main frame, additional reinforcements are integrated to absorb energy and reduce deformation under stress. These elements work collectively to safeguard the vehicle’s core structure while maintaining its shape during dynamic movements.
- Crush Zones: Specially designed areas that deform in a controlled manner to absorb impact energy, reducing the force transferred to the cabin.
- Reinforced Rails: These are strategically placed to bolster the frame’s resistance against bending or twisting, crucial for maintaining vehicle alignment.
Cooling System Parts and Maintenance
The efficiency of a vehicle’s engine largely depends on its ability to regulate temperature. A well-maintained cooling mechanism prevents overheating and ensures optimal performance. Understanding the components involved and their upkeep is essential for longevity and reliability.
Key components of the cooling mechanism include:
- Radiator: Dissipates heat from the coolant.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant throughout the engine.
- Thermostat: Regulates the temperature of the coolant.
- Coolant Reservoir: Holds excess coolant and allows for expansion.
- Hoses: Transport coolant between components.
Proper maintenance practices are vital to ensure the cooling system operates effectively:
- Regular Inspection: Check hoses and connections for wear and leaks.
- Coolant Replacement: Change the coolant at recommended intervals to prevent corrosion and maintain efficiency.
- Radiator Flush: Periodically flush the radiator to remove sediment and debris.
- Thermostat Check: Test the thermostat to ensure it opens and closes properly.
- Monitor Temperature Gauge: Keep an eye on the engine temperature to catch any issues early.
By prioritizing these maintenance tasks, vehicle owners can ensure that their cooling system remains in peak condition, thereby enhancing overall engine performance.
Interior Controls and Dashboard Layout
The arrangement of operational elements within a vehicle’s cabin significantly influences user experience and functionality. A well-designed layout facilitates ease of access and enhances overall comfort for both the driver and passengers. Understanding the positioning and functionality of various controls is essential for effective utilization.
Control Features and Accessibility
The interface for managing in-car systems typically includes knobs, buttons, and touchscreens. Each component is strategically placed to ensure that essential functions, such as climate control and audio settings, are easily reachable. This thoughtful design promotes intuitive operation while driving, minimizing distractions.
Dashboard Configuration and Displays
The dashboard serves as the primary information hub, featuring gauges and indicators that convey crucial data about the vehicle’s status. An organized arrangement of these displays allows for quick comprehension of performance metrics, enhancing safety and awareness on the road. Clear visibility and ergonomic positioning are key factors that contribute to a driver-friendly environment.
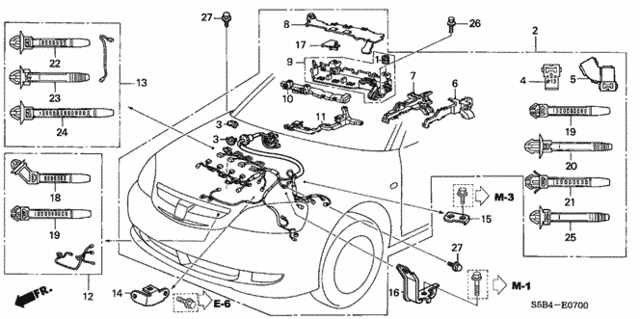
Electrical Wiring Essentials and Layout
The effective functioning of any vehicle relies heavily on its electrical system. Understanding the basics of wiring and layout is crucial for maintaining and troubleshooting these systems. Proper organization and knowledge of the electrical components enhance overall performance and safety.
Key aspects to consider when examining wiring essentials include:
- Color Coding: Familiarizing oneself with color codes used in wiring helps identify connections and ensures accurate installations.
- Component Locations: Knowing where essential electrical components are situated allows for efficient maintenance and quick troubleshooting.
- Wiring Schematics: Reviewing schematics aids in understanding the flow of electricity and the relationship between various components.
When planning the layout of the electrical system, consider the following:
- Access Points: Ensure that wiring is routed to allow easy access for repairs and inspections.
- Protection Against Damage: Use protective conduits and routing techniques to safeguard wiring from wear and environmental factors.
- Grounding Practices: Implement proper grounding methods to prevent electrical faults and enhance safety.
By adhering to these principles, one can effectively manage the electrical system, resulting in improved reliability and performance.
Fuel System Parts Overview
The fuel delivery system plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal engine performance and efficiency. This intricate network is designed to manage the storage, delivery, and combustion of fuel within the engine. Understanding the various components involved is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Fuel Tank: The storage unit responsible for holding the fuel until it is needed by the engine. It must be designed to withstand various environmental conditions and ensure safety.
Fuel Pump: This component is vital for transporting fuel from the tank to the engine. It generates the necessary pressure to ensure an adequate flow of fuel.
Fuel Filter: Acting as a barrier, this part ensures that impurities and contaminants are removed from the fuel before it reaches the engine. Regular replacement is essential to maintain system efficiency.
Fuel Injectors: These precision devices atomize the fuel, allowing it to mix with air for optimal combustion. Their performance directly affects engine efficiency and emissions.
Fuel Lines: These conduits are responsible for transporting fuel between the tank, pump, and engine. They must be durable and resistant to pressure fluctuations.
Each of these components works in harmony to deliver the fuel required for combustion, highlighting the importance of regular inspection and maintenance to prevent issues that could lead to performance decline.
Analyzing Exhaust Components and Setup
Understanding the arrangement and functionality of the exhaust system is crucial for optimizing vehicle performance. This system plays a significant role in controlling emissions and ensuring efficient engine operation. A detailed examination of the components involved can enhance overall effectiveness and reliability.
Key Components of the Exhaust System

- Exhaust Manifold: Directs exhaust gases from the engine cylinders to the rest of the system.
- Catalytic Converter: Reduces harmful emissions by converting exhaust gases into less harmful substances.
- Muffler: Dampens noise produced by the exhaust gases while allowing them to exit smoothly.
- Exhaust Pipes: Channels exhaust gases away from the engine and out of the vehicle.
Setup Considerations for Optimal Performance
- Ensure all connections are secure to prevent leaks, which can lead to reduced efficiency.
- Check for any signs of corrosion or damage, as these can hinder performance.
- Consider upgrading components for enhanced flow, which can improve engine output.
- Regular maintenance and inspections can help maintain the integrity of the entire system.