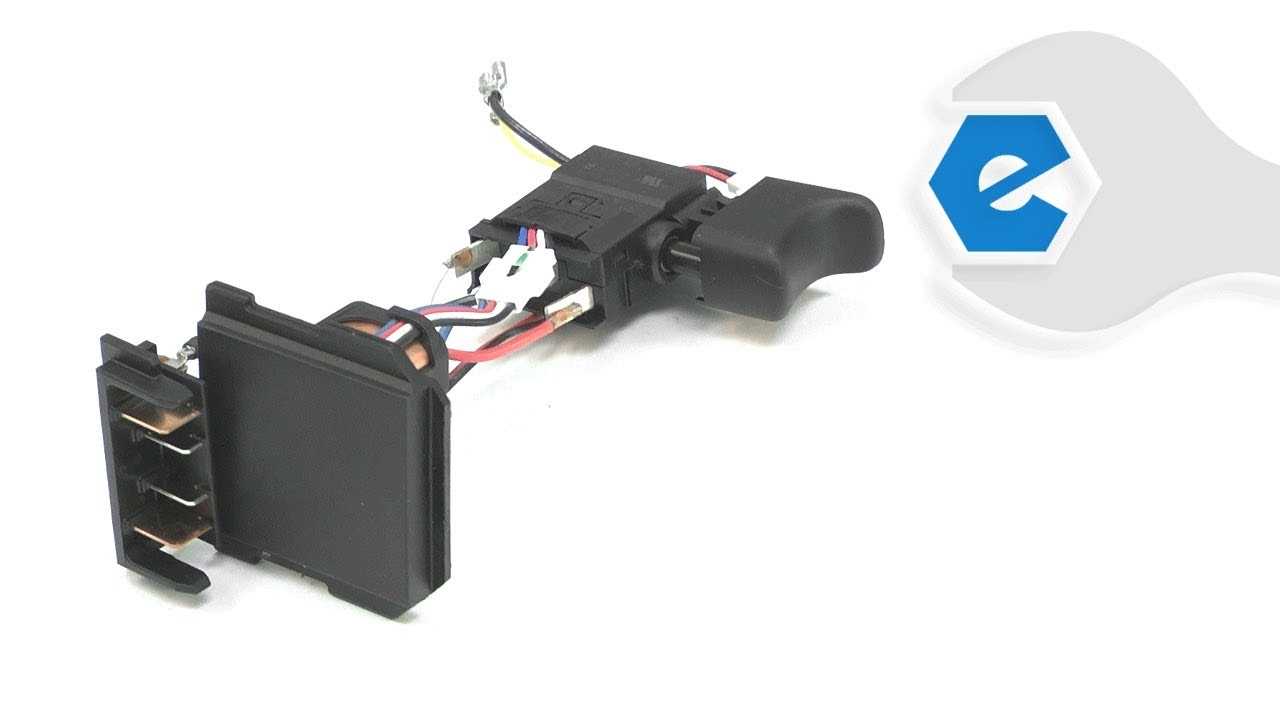

Understanding the intricate workings of a leading power tool model is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This section delves into the various components that make up this highly efficient device, shedding light on its construction and functionality. By gaining insight into each element, users can enhance their operational knowledge and ensure optimal performance.
In this exploration, we will examine the arrangement and role of each significant piece within the tool. A thorough grasp of how these elements interact can aid in identifying potential issues and facilitate smoother repairs or replacements. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a hobbyist, having access to a comprehensive overview of the tool’s configuration is invaluable.
This examination will provide a clear perspective on the overall structure, allowing users to familiarize themselves with the necessary components. Recognizing the distinct functions of each part contributes to a better understanding of the tool’s capabilities and limitations, ultimately empowering users to make informed decisions during usage and maintenance.
Dewalt DCF887 Parts Diagram Overview
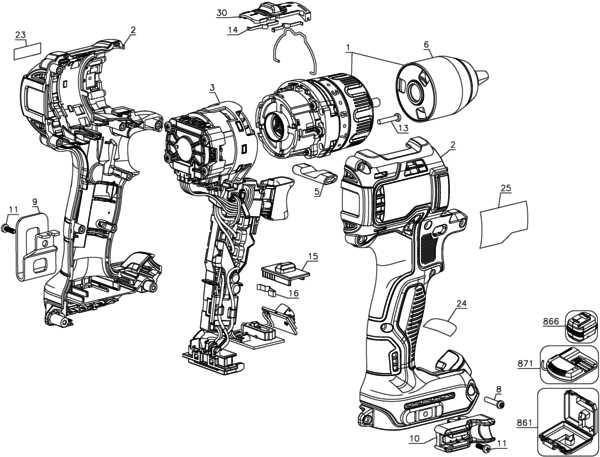
This section provides an in-depth look at the assembly and individual components of a high-performance power tool. Understanding each element’s role is crucial for effective maintenance, repair, and optimal usage. By familiarizing yourself with the layout and functionality, you can enhance the longevity and efficiency of your device.
Key Components
- Motor Assembly
- Gearbox
- Battery Housing
- Trigger Mechanism
- Chassis
- Control Switch
Functionality Insights
- The motor assembly is responsible for generating power.
- The gearbox transmits the motor’s energy to the output shaft.
- The battery housing stores energy, ensuring portability and ease of use.
- The trigger mechanism controls the operation, providing user-friendly engagement.
- The chassis provides structural integrity and houses all internal parts.
- The control switch allows for the management of power settings.
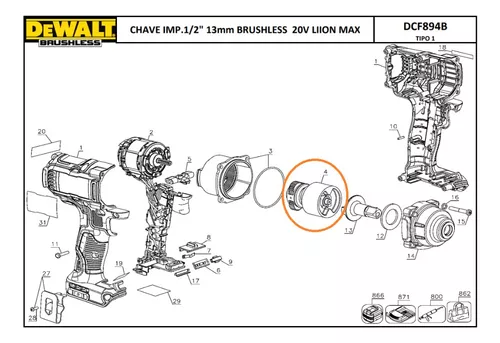
Understanding the Tool’s Components
Every power tool consists of various essential elements that work together to ensure efficient operation and durability. Recognizing these components is crucial for users who aim to maximize performance and maintain their equipment. By understanding the functionalities and interrelations of these parts, users can enhance their experience and ensure their tool remains in optimal condition.
Key Elements of the Tool
The core of any power tool is its motor, which drives the entire mechanism and determines its efficiency. Accompanying the motor are gears that facilitate the transfer of power, enabling different speed and torque settings. Additionally, the casing protects internal components from dust and damage, contributing to the longevity of the device.
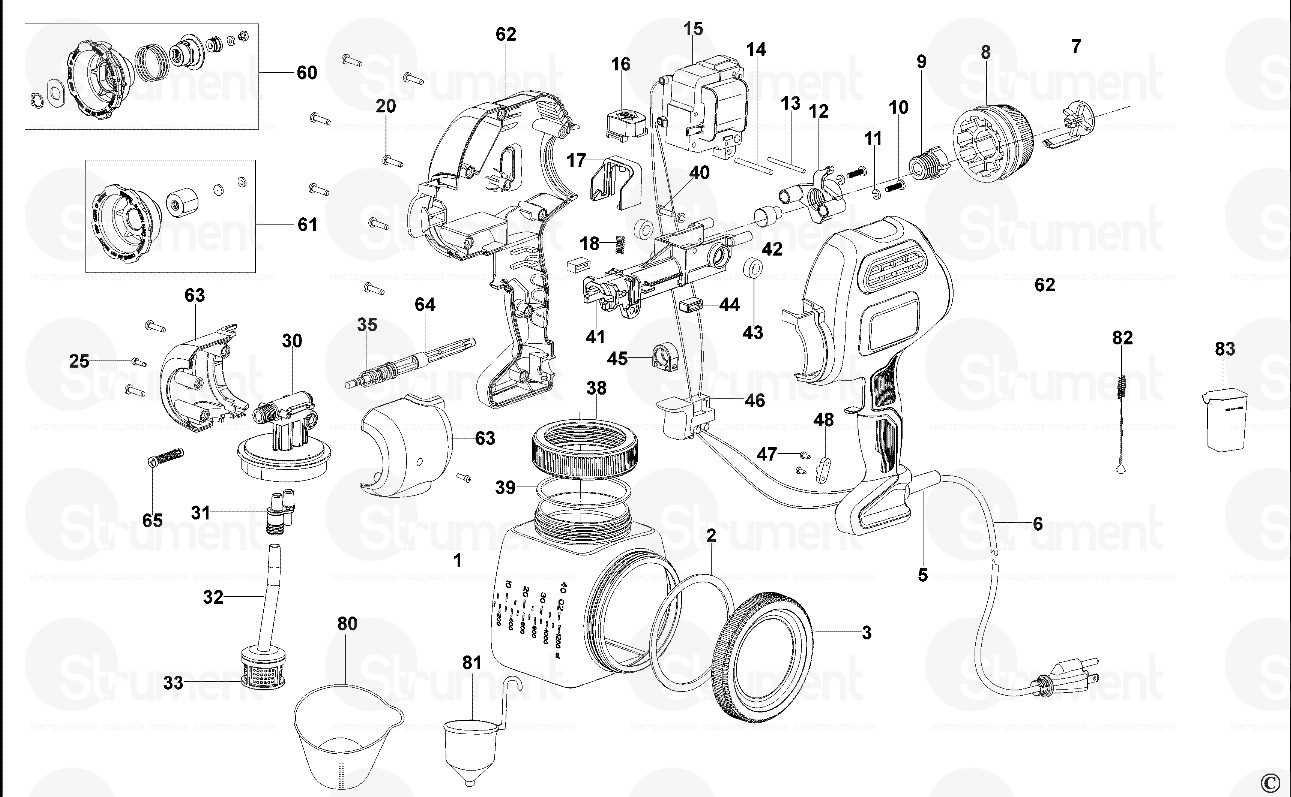
Maintenance and Upkeep
Regular maintenance is essential to prolong the lifespan of the equipment. Users should pay attention to the battery, ensuring it is charged correctly and stored safely when not in use. Furthermore, keeping the tool clean and free of debris will help prevent performance issues and maintain optimal functionality. Familiarity with these critical aspects will empower users to handle their devices with greater confidence.
Key Features of DCF887 Model
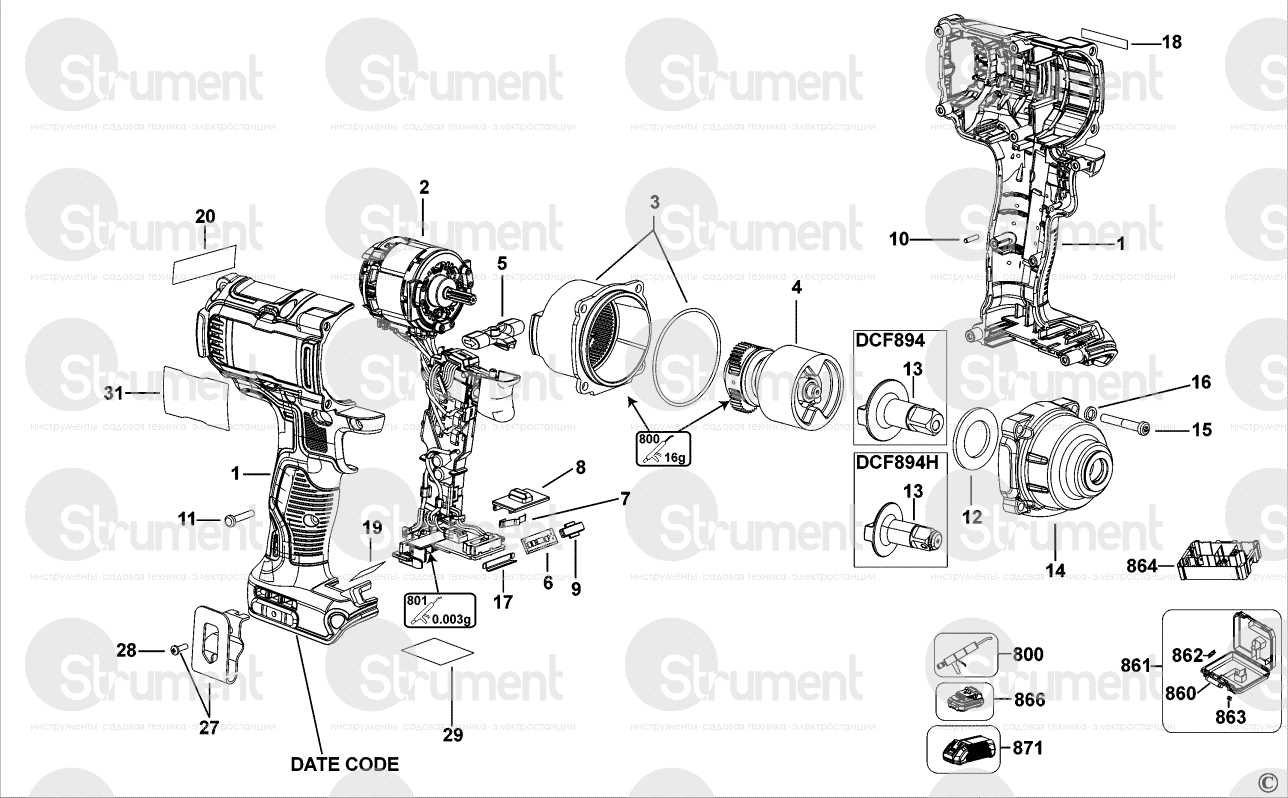
This model stands out due to its innovative design and advanced functionalities that cater to both professional and DIY enthusiasts. It is engineered to provide exceptional performance, ensuring efficiency and ease of use in a variety of tasks.
Performance and Power
- High Torque Output: Offers impressive torque levels that enable efficient fastening in tough materials.
- Brushless Motor: Incorporates a brushless motor for extended runtime and reduced maintenance.
- Compact Size: Designed for tight spaces, making it ideal for a range of applications.
User-Friendly Features
- Variable Speed Control: Allows users to adjust speed settings for greater control during operation.
- LED Light: Equipped with an integrated LED light that illuminates the workspace, enhancing visibility in dark areas.
- Ergonomic Grip: Features a comfortable handle that minimizes fatigue during prolonged use.
Identifying Major Parts and Functions
Understanding the key components of a tool is essential for effective use and maintenance. Each element plays a specific role in ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Recognizing these elements can greatly enhance your ability to troubleshoot issues and perform necessary repairs.
Power Source: This vital component provides the energy required for operation. It is crucial for ensuring the tool runs efficiently and consistently during tasks.
Motor: The heart of the device, the motor converts electrical energy into mechanical motion. Its efficiency determines the overall power and speed of the tool, making it a critical aspect to consider.
Gearbox: Responsible for transmitting power from the motor to the output shaft, the gearbox allows for adjustments in speed and torque. A well-designed gearbox enhances the tool’s versatility for various applications.
Chuck: This component holds the accessory in place securely. It enables quick changes between different attachments, ensuring convenience and efficiency during use.
Trigger: The trigger initiates operation and controls the speed of the tool. Its responsiveness is vital for precision and control, allowing users to adapt to various materials and tasks seamlessly.
By familiarizing yourself with these essential elements, you can better appreciate how they contribute to the overall functionality and effectiveness of the tool, leading to improved performance and user satisfaction.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
To ensure the durability and optimal performance of your power tools, regular upkeep is essential. Implementing a consistent maintenance routine not only extends the lifespan of the equipment but also enhances its efficiency and reliability during use.
Regular Cleaning: After each use, clean the exterior and interior components of the tool to remove dust, debris, and residue. This practice prevents buildup that can hinder functionality and performance.
Inspection: Periodically check all moving parts for signs of wear or damage. Look for any loose screws, cracked housing, or frayed cords. Early detection of issues can prevent more significant problems down the line.
Lubrication: Apply appropriate lubricants to moving parts to reduce friction and wear. Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for the correct type of lubricant and application frequency.
Battery Care: For battery-operated tools, ensure the batteries are charged correctly and stored in a cool, dry place. Avoid completely discharging the battery before recharging, as this can reduce its overall lifespan.
Proper Storage: Store tools in a designated area that is dry and free from extreme temperatures. Using a protective case or organizer can help prevent accidental damage and keep everything organized.
Follow Manufacturer Instructions: Always refer to the user manual for specific maintenance recommendations. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines ensures the tool operates as intended and maintains its warranty.
Common Issues with DCF887 Parts
When working with power tools, it’s essential to recognize potential problems that may arise with their components. Understanding these common challenges can help users maintain optimal functionality and extend the lifespan of their equipment. Various issues can occur due to wear and tear, improper handling, or lack of maintenance.
One frequent concern involves battery performance. Over time, rechargeable units may lose their ability to hold a charge, leading to reduced operational efficiency. Users should regularly inspect batteries for signs of swelling or leakage, which can indicate deterioration.
Another typical problem is related to the motor’s functionality. If the tool experiences inconsistent power or unusual noises, it may signal an internal malfunction. Regular cleaning and lubrication can prevent debris buildup, which often leads to overheating and subsequent failure.
Furthermore, fastening mechanisms can become unreliable if not properly maintained. Users may notice difficulty in engaging or disengaging bits, which can hinder performance. Ensuring that these components are clean and free of rust can significantly enhance their reliability.
Lastly, electrical connections may become loose or corroded over time, resulting in poor performance. Regular inspections can help identify these issues early, allowing for timely repairs and reducing the risk of complete failure. By being proactive and attentive to these common challenges, users can ensure their tools remain in excellent working condition.
How to Replace Worn Components
Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your tools in optimal condition. Over time, certain components may wear out due to frequent use, affecting performance and efficiency. This section provides a straightforward guide to identifying and replacing these worn parts to ensure your equipment continues to operate smoothly.
Step 1: Identify Worn Components
Begin by inspecting your tool for signs of wear. Look for any unusual noises, decreased power, or physical damage. Common areas to check include the motor, gears, and battery. Recognizing these issues early can prevent further damage and costly repairs.
Step 2: Gather Necessary Tools
Before starting the replacement process, assemble the required tools. You may need screwdrivers, pliers, and replacement components specific to your model. Having everything ready will streamline the process and save you time.
Step 3: Disassemble the Tool
Carefully disassemble the tool following the manufacturer’s guidelines. Take note of the order in which you remove parts, as this will aid in reassembly. Keep track of screws and small components to avoid losing them during the process.
Step 4: Replace Worn Parts
Once the tool is disassembled, replace the worn components with new ones. Ensure that the replacements are compatible with your specific model. Take your time to fit each part correctly to avoid future issues.
Step 5: Reassemble and Test
After replacing the necessary components, reassemble the tool. Make sure all parts are securely fastened and properly aligned. Finally, test the tool to confirm that it operates as intended, ensuring that the replacement was successful.
Tools Needed for Disassembly

Disassembling a power tool requires specific implements to ensure a smooth and efficient process. Having the right tools not only facilitates the task but also minimizes the risk of damage to the components. Below is a list of essential instruments needed for effective disassembly.
- Screwdrivers:
- Flathead screwdriver for removing screws with a straight, flat groove.
- Phillips screwdriver for screws with a cross-shaped slot.
- Socket Wrenches:
- Various sizes to accommodate different nuts and bolts.
- Ratchet wrench for quick turning and easier access to tight spaces.
- Pliers:
- Needle-nose pliers for gripping small parts and wires.
- Channel-lock pliers for larger components requiring extra leverage.
- Torx Drivers:
- For specialized screws that have a star-shaped socket.
- Hex Keys:
- Essential for screws with hexagonal recesses.
- Work Surface:
- A clean, flat area to lay out components and prevent loss.
- Magnetic tray to keep small parts organized and accessible.
Gathering these tools in advance will enhance the disassembly experience, making it safer and more efficient.
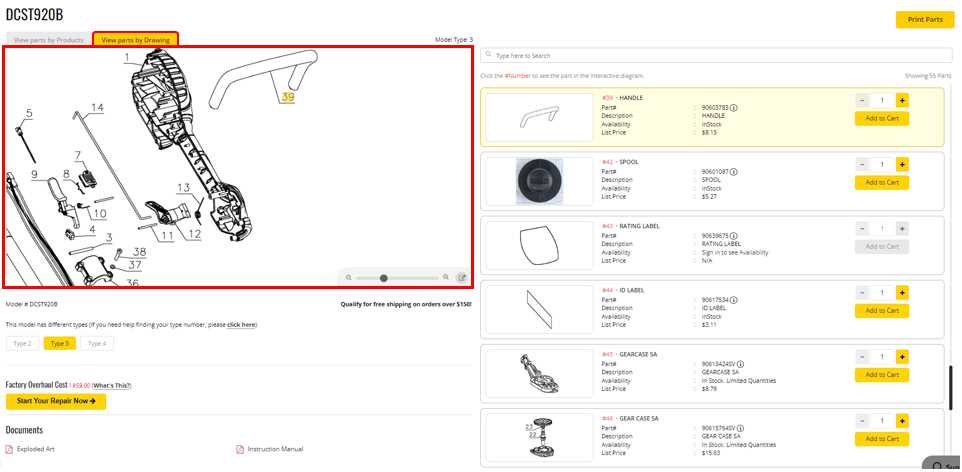
Visual Guide to Assembly Process
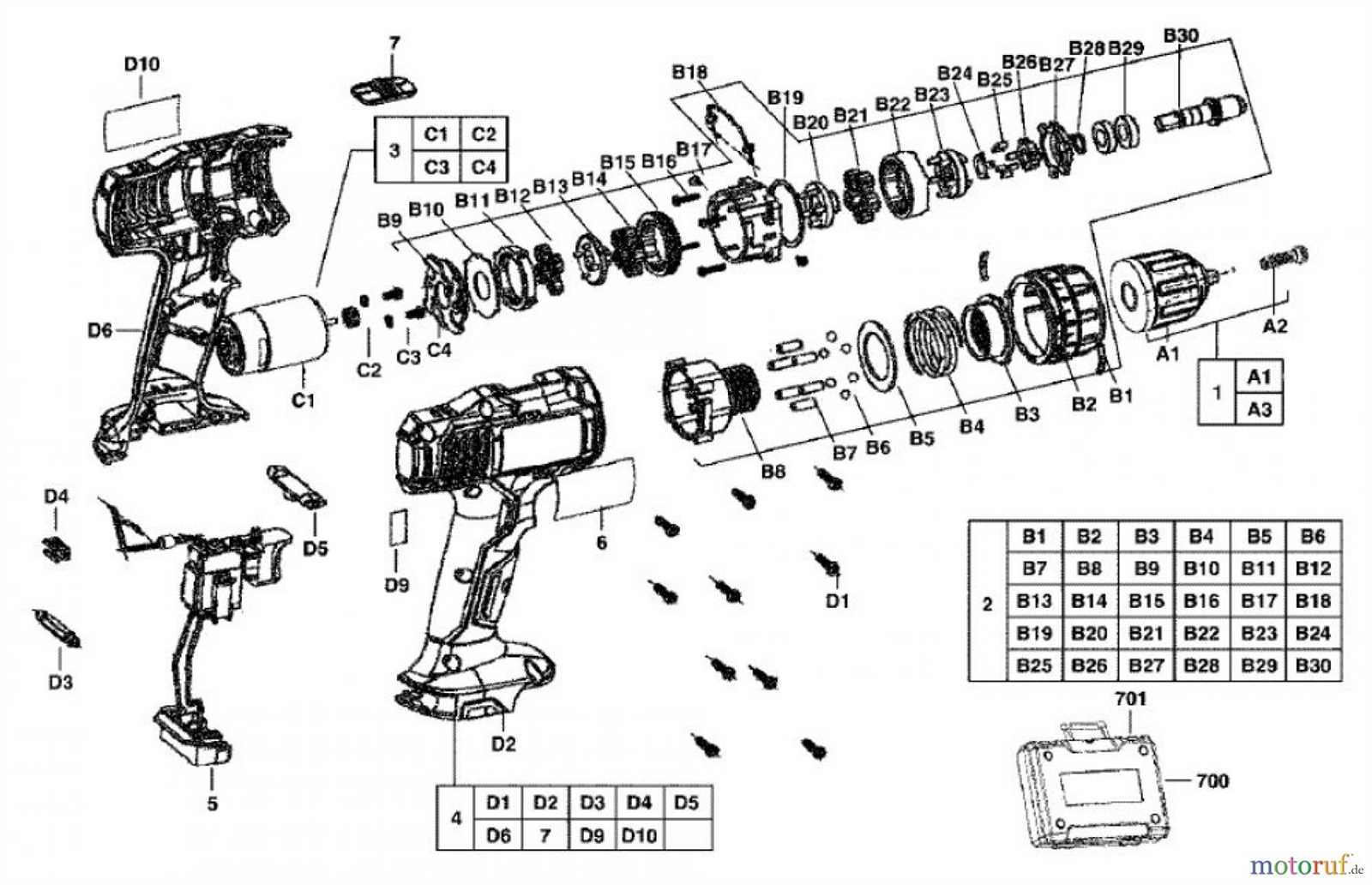
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the assembly procedure for a popular power tool model. Understanding the sequence of components and their interactions is crucial for efficient assembly and maintenance. A visual guide enhances comprehension and serves as a handy reference for users at various skill levels.
Begin by gathering all essential components, ensuring they are free from damage. Organizing the items will streamline the process. Pay close attention to each element’s placement and orientation, as incorrect assembly can lead to operational issues.
Next, follow a step-by-step approach, referring to illustrations that detail each stage of the process. Highlight the importance of securing connections firmly, using appropriate tools to avoid excessive wear. Additionally, ensure that safety features are installed correctly to promote user safety during operation.
As you progress, regularly check for alignment and proper fit of components. Adjustments may be necessary to achieve optimal performance. After completing the assembly, conduct a thorough inspection to confirm that all parts are assembled correctly and functioning as intended.
Finally, refer back to the visual guide for troubleshooting tips. This will aid in addressing any potential issues that may arise post-assembly, ensuring longevity and efficiency of the tool in use.
Compatibility with Other Dewalt Models
This section explores how a particular model integrates with various tools from the same brand. Understanding compatibility is crucial for users looking to expand their toolset without investing in entirely new equipment. Many devices share similar components, which can enhance functionality and provide users with a seamless experience.
Interchangeable Features
Several tools from this brand utilize interchangeable features, allowing users to swap accessories and batteries effortlessly. This compatibility enables users to maximize their investment by using existing resources across multiple devices. For instance, batteries designed for one model may function in another, reducing the need for additional purchases.
Shared Technology
Models often incorporate shared technology, resulting in improved performance and efficiency. By utilizing the same innovative designs and engineering principles, tools within the range can deliver similar power outputs and operational capabilities. This alignment ensures that users can achieve consistent results, regardless of the specific device they choose to operate.
Where to Find Replacement Parts

Finding the right components for your power tools can significantly extend their lifespan and maintain optimal performance. Numerous avenues exist for sourcing these essential elements, each offering various options depending on your needs and preferences.
Authorized Retailers are often the best first stop. These stores typically stock genuine components that are compatible with your equipment, ensuring a perfect fit and reliable functionality. Always check for a list of authorized dealers on the manufacturer’s website to avoid counterfeit items.
Online Marketplaces provide a vast selection of components, often at competitive prices. Websites like eBay, Amazon, and specialized tool retailers offer new and used options, allowing for flexibility in budgeting. Be sure to read customer reviews and product descriptions carefully to ensure quality.
Local Repair Shops can also be valuable resources. Many of these establishments not only sell components but also offer professional installation services. Engaging with local experts can provide insights into the best components for your specific tools.
Manufacturer’s Website is another reliable source. Most manufacturers maintain online catalogs where you can search for components specific to your model. This ensures that you are looking at the correct items that meet the required specifications.
In summary, a combination of authorized retailers, online platforms, local repair shops, and the manufacturer’s own site will equip you with the resources needed to keep your equipment in top shape.
Importance of Genuine Parts Usage
Utilizing authentic components in power tools is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Genuine replacements are specifically designed to fit seamlessly, maintaining the integrity and functionality of the equipment. This practice not only enhances efficiency but also safeguards the investment made in high-quality tools.
Reliability is a key factor when considering the use of original components. These items undergo rigorous testing and quality control, ensuring that they meet the manufacturer’s specifications. By opting for genuine replacements, users can avoid the risks associated with inferior alternatives that may compromise safety and effectiveness.
Moreover, compatibility is paramount. Authentic elements are engineered to work harmoniously with the overall design of the tool, reducing the likelihood of malfunctions. In contrast, non-genuine components can lead to improper functioning and potentially damage other integral parts.
In addition to functionality, using original components also supports warranty compliance. Many manufacturers stipulate that the use of non-genuine items can void warranties, leaving users unprotected against defects or failures. By adhering to manufacturer guidelines, users can ensure that they remain covered and can access support if needed.
In summary, the choice of utilizing authentic components significantly impacts performance, safety, and warranty coverage. Prioritizing quality not only enhances the user experience but also extends the lifespan of the equipment.
DIY Repair vs. Professional Service
When it comes to fixing tools or equipment, there are two main approaches: tackling the issue yourself or hiring an expert. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, making the decision dependent on various factors such as skill level, time availability, and complexity of the problem.
Opting for a do-it-yourself approach can be cost-effective and empowering. It allows individuals to learn and develop new skills while gaining a deeper understanding of their equipment. However, this route requires a certain level of expertise and access to the necessary tools. Mistakes made during the repair process can lead to further damage, which may ultimately increase costs.
On the other hand, choosing to seek professional assistance often ensures a reliable and efficient solution. Experienced technicians have the knowledge and tools to diagnose and resolve issues quickly, minimizing downtime. However, this option typically comes with a higher price tag and may involve waiting for an appointment or service visit.
Ultimately, the decision between DIY repair and professional service hinges on individual circumstances. Weighing the pros and cons of each method will help determine the most suitable path for addressing equipment issues effectively.