
In a world filled with complexity, understanding how different concepts interact can be challenging. This visual representation serves as a powerful means of illustrating the overlaps and distinctions between various sets of ideas. By examining these relationships, we gain insights that can enhance our comprehension and decision-making.
The tool showcases three distinct groups, each contributing unique characteristics to the collective understanding. As we delve into their intersections, we can identify shared traits and explore how these elements influence one another. This analytical approach not only clarifies our thought processes but also fosters deeper connections between seemingly disparate notions.
Utilizing this graphical method allows for an engaging exploration of relationships, facilitating discussions and collaborative efforts. Whether in academia, business, or everyday life, such representations can unveil patterns and guide us toward more informed conclusions. Embracing this technique opens the door to innovative thinking and enriched perspectives.
Understanding the 3-Part Venn Diagram
This visual representation illustrates the relationships and intersections between three distinct sets, helping to clarify how they interact with each other. By examining the shared and unique attributes of each group, one can gain deeper insights into complex ideas and identify patterns that may not be immediately obvious.
Applications in Various Fields
This tool is widely utilized across multiple disciplines, including mathematics, logic, and data analysis. In educational settings, it aids students in grasping the concept of set theory, while in business, it helps teams visualize market segments or product features. Such representations encourage critical thinking and facilitate discussions around overlapping concepts.
Benefits of Using This Visual Tool
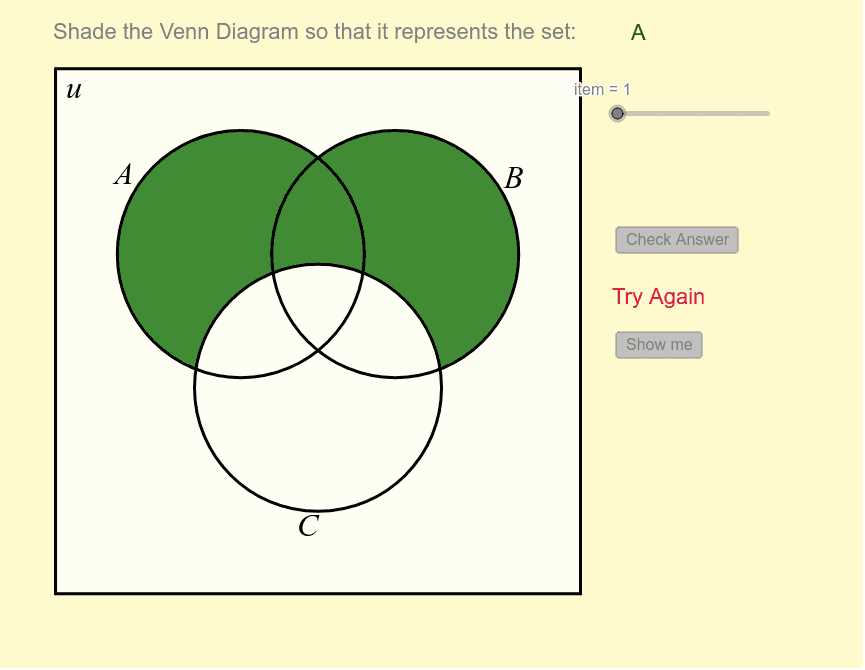
Utilizing this visual format fosters clarity and enhances comprehension. It allows individuals to quickly assess similarities and differences, promoting effective decision-making. Furthermore, it serves as an engaging way to present information, making complex relationships more accessible and memorable for the audience.
Origins and Historical Context
The concept explored here has roots that trace back through various intellectual traditions, reflecting the intersections of different fields of thought. This approach allows for a multifaceted analysis, bridging disciplines and revealing how interconnected ideas can enhance our understanding of complex subjects.
Historical Development
Throughout history, thinkers have sought to visualize relationships between concepts to facilitate deeper comprehension. This method emerged as a tool for educators and philosophers, serving to clarify and emphasize the connections among disparate ideas. Notable figures contributed to its evolution, adapting it to their respective contexts and needs.
Applications Across Disciplines
The versatility of this analytical framework has led to its adoption in various domains, including science, mathematics, and social studies. Each field has utilized this approach to illustrate relationships, drawing unique insights from the overlapping areas of knowledge. Below is a summary of its application across different areas:
| Field | Usage |
|---|---|
| Science | Visualizing relationships between species or chemical compounds. |
| Mathematics | Exploring set theory and logical relationships. |
| Social Studies | Examining cultural intersections and historical events. |
Key Components of the Diagram
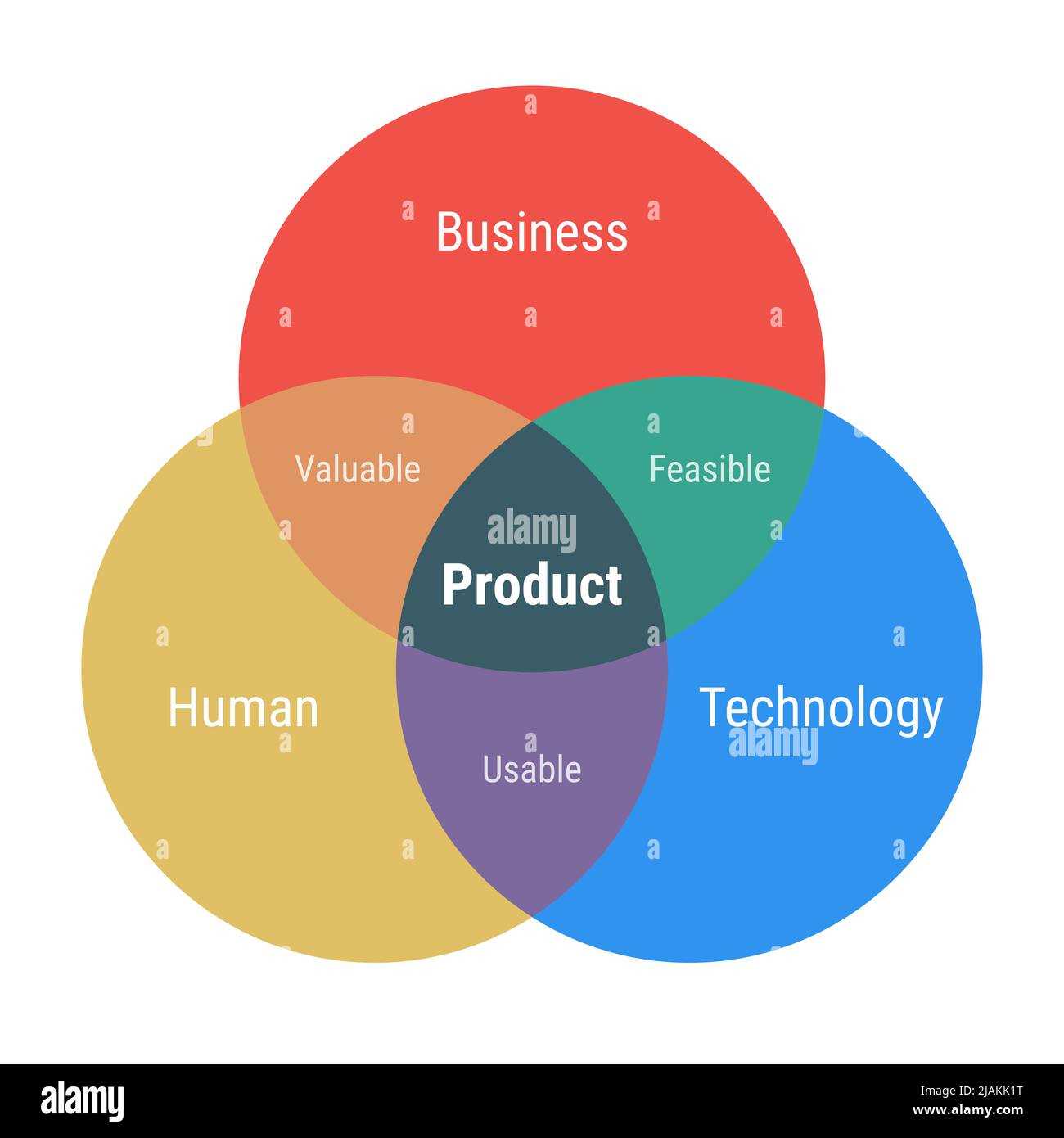
Understanding the essential elements of this visual representation is crucial for effective analysis and communication. Each section plays a significant role in illustrating the relationships and intersections between different concepts or groups, helping to highlight both similarities and differences.
Core Areas
The primary regions of the visual are where the individual categories reside. Each area signifies a unique concept, showcasing its distinct characteristics. These segments provide a clear foundation for comparison, allowing viewers to easily discern what makes each category unique.
Intersections

The overlapping zones between the areas are pivotal. They reveal the shared attributes or connections among the categories, emphasizing the importance of collaboration or commonality. This interplay not only enhances understanding but also encourages deeper insights into the relationships at hand.
Applications in Education and Learning
The intersection of various educational concepts fosters a deeper understanding of complex subjects. By exploring the connections between different disciplines, learners can gain a holistic view that enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This multifaceted approach not only enriches knowledge but also encourages collaboration among students and educators alike.
Interdisciplinary Learning
Integrating diverse fields of study allows students to see relationships between subjects, promoting creativity and innovation. For example, blending science with art can lead to unique projects that highlight the importance of both areas, encouraging students to think outside the box.
Collaborative Projects
Group activities that draw on multiple areas of expertise enable students to learn from one another. This collaboration cultivates a sense of community and prepares learners for real-world scenarios where teamwork and diverse perspectives are essential.
Using Venn Diagrams in Data Analysis
Visual representations of relationships among different sets can enhance our understanding of complex data. By illustrating overlaps and distinctions, these tools facilitate a clearer interpretation of how various categories interact and influence one another.
Benefits of Visual Representations
- Clarifies relationships between datasets.
- Highlights similarities and differences.
- Enhances communication of findings.
Applications in Data Analysis
- Market research: Understanding customer segments.
- Survey analysis: Identifying common responses.
- Academic research: Comparing theoretical frameworks.
Visualizing Relationships Between Concepts

Understanding the connections between different ideas can significantly enhance our comprehension and retention of information. By employing visual representations, we can better identify similarities, differences, and intersections among various themes. This method not only aids in organizing thoughts but also fosters deeper insights into how distinct concepts interact with one another.
One effective way to illustrate these connections is through overlapping circles, where each circle represents a specific concept. The areas where the circles intersect highlight shared attributes or relationships, making it easier to grasp complex ideas. Such visuals encourage critical thinking, prompting us to explore the nuances and complexities inherent in various subjects.
Moreover, utilizing this technique allows for a dynamic exploration of ideas, facilitating discussions and collaborative learning. By visualizing the interplay of concepts, we can uncover patterns and trends that may not be immediately apparent, thus enriching our understanding and promoting a more holistic perspective.
Common Mistakes in Diagram Creation
Creating visual representations can often lead to misinterpretations if not approached carefully. Understanding the frequent pitfalls in this process is essential for producing clear and effective visuals that convey the intended message. This section explores typical errors that can undermine the clarity and impact of your graphical illustrations.
Overcomplicating the Design
A common error is cluttering the visual with excessive elements. When too many categories or details are included, the viewer may struggle to identify the main relationships. Striving for simplicity helps ensure that the core concepts are easily understood.
Neglecting Proper Labels
Another frequent mistake involves inadequate labeling. Labels serve as guides, clarifying the meaning behind each section. Without clear and concise labels, the viewer may misinterpret the connections, leading to confusion rather than insight.
Digital Tools for Diagram Design
Creating visual representations of complex ideas has become essential in various fields. Digital platforms now offer an array of functionalities that empower users to illustrate relationships and data effectively. These tools not only simplify the design process but also enhance clarity and engagement.
Popular software options include web-based applications and desktop programs, catering to different preferences and needs. Users can explore features like customizable shapes, color palettes, and collaborative functions, which foster teamwork and creativity.
For those seeking the ultimate experience, some platforms provide templates and guides to help beginners get started. Advanced users can delve into more sophisticated options, such as integrating interactive elements or exporting to various formats, ensuring their creations meet diverse presentation requirements.
Examples from Various Fields
This section explores the intersections of different domains, highlighting how diverse concepts can align and create new understanding. By examining these overlaps, we can appreciate the complexity and richness of knowledge across disciplines.
Science and Technology
In the realm of science and technology, the fusion of biology, chemistry, and physics has led to groundbreaking advancements. For instance, bioinformatics merges biology and computer science to analyze genetic data, facilitating significant discoveries in medicine.
Art and Business
The integration of artistic expression and business strategies has transformed creative industries. Designers and marketers often collaborate, merging visual communication with consumer insights to enhance brand identity and engagement.
| Field 1 | Field 2 | Intersection Example |
|---|---|---|
| Biology | Computer Science | Bioinformatics |
| Art | Business | Brand Design |
| Education | Technology | e-Learning Platforms |
Tips for Effective Presentations
Delivering a compelling presentation requires a blend of preparation, engagement, and clarity. By focusing on key elements, speakers can create an impactful experience that resonates with their audience.
Know Your Audience: Understanding the needs and interests of your listeners is crucial. Tailor your content to address their expectations and level of knowledge.
Practice Thoroughly: Rehearsing multiple times helps to refine your delivery and boosts confidence. Aim for a natural flow that enhances your message.
Use Visual Aids: Incorporating relevant visuals can enhance understanding and retention. Choose images, graphs, or slides that complement your points rather than overwhelm them.
Engage With Your Audience: Foster interaction by asking questions or encouraging feedback. This not only keeps attention but also makes the presentation more dynamic.
Maintain Clarity: Avoid jargon and overly complex language. Aim for simplicity to ensure your message is easily grasped by everyone.
Summarize Key Points: Conclude with a recap of the main ideas. This reinforces the message and helps to solidify what your audience has learned.
Enhancing Critical Thinking Skills
Developing the ability to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information is essential for effective problem-solving and decision-making. This process involves recognizing biases, questioning assumptions, and drawing connections between different concepts. By fostering a mindset geared towards inquiry and reflection, individuals can improve their cognitive abilities and apply them in various contexts.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Questioning | Encouraging open-ended questions to explore deeper insights. |
| Reflection | Taking time to consider experiences and outcomes critically. |
| Discussion | Engaging with diverse perspectives to broaden understanding. |
Comparing Venn Diagrams with Other Models
Exploring relationships among different sets can be approached through various conceptual frameworks. Each model offers unique strengths and weaknesses, influencing how we visualize intersections, unions, and differences among groups. This section delves into some alternative representations and highlights their distinctions from the standard three-circle approach.
Alternative Models for Set Relationships
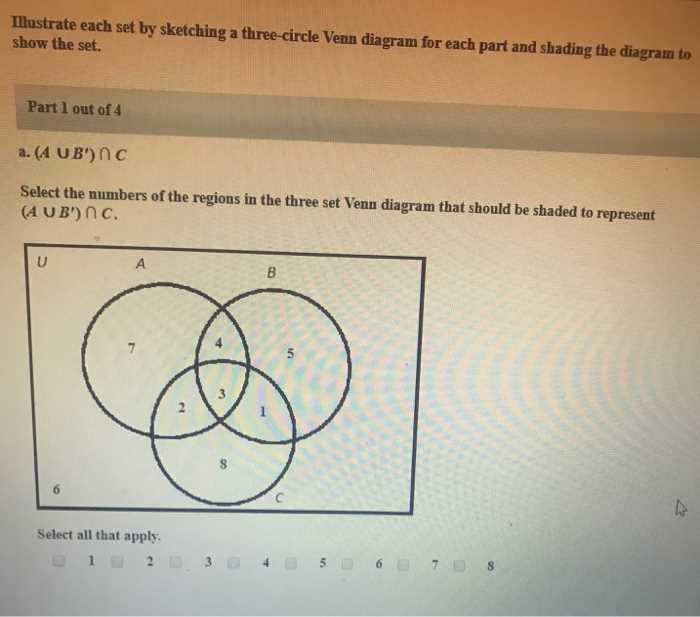
- Euler Circles: These shapes emphasize the connections between sets while allowing for more complex relationships. Unlike traditional structures, they can represent overlapping areas more fluidly, accommodating variations in set sizes.
- Bar Graphs: Useful for displaying quantitative comparisons, these visual aids focus on the magnitude of elements within each group rather than their relational aspects. They excel in providing clear, immediate insights into numerical data.
- Flowcharts: These models illustrate processes and sequences, making them ideal for depicting hierarchical relationships or decision-making paths. They can convey dynamics that static representations may overlook.
Strengths and Limitations
- Visual Clarity: Traditional shapes offer clear visual distinctions but may struggle with representing larger or more complex sets effectively.
- Flexibility: Alternative frameworks can adapt to varying data types and relationships, offering a more versatile approach to visualization.
- Complex Relationships: Some models excel in showing intricate connections, while others simplify relationships, which might obscure important details.
Understanding these differences allows for a more nuanced selection of visual tools tailored to specific analytical needs. By evaluating the effectiveness of each representation, we can enhance our capacity to convey information meaningfully.