Exploring the intricate world of bicycle shifting systems reveals a fascinating interplay of various elements that work in harmony to ensure smooth transitions between gears. These mechanisms play a crucial role in enhancing the cycling experience, allowing riders to adapt effortlessly to changing terrains and conditions.
Each element within the shifting assembly has a unique function, contributing to the overall efficiency and performance of the bike. By examining these components, enthusiasts can gain valuable insights into how to maintain and optimize their gear-shifting capabilities.
In this section, we will delve into the essential constituents of these systems, providing a comprehensive overview that highlights their significance and interconnectivity. Understanding these elements is the ultimate key to achieving a more enjoyable and effective ride.
Understanding the Front Derailleur
This section explores the essential mechanism responsible for shifting gears on a bicycle, enhancing the riding experience through precise chain movement. Understanding its functionality is crucial for optimal performance and maintenance.
Functionality of the Mechanism
The device operates by guiding the chain between different rings on the crankset, enabling smooth transitions and adaptability to various terrains. Its design allows for efficient energy transfer, critical for achieving speed and control.
Maintenance Tips
Components of a Front Derailleur
This section explores the essential elements that contribute to the effective functioning of the shifting mechanism, ensuring smooth transitions between gear levels. Each component plays a crucial role in achieving optimal performance and reliability.
- Cage: This part holds the chain and guides it onto the desired gear.
- Arm: The lever that moves the cage to shift the chain.
- Spring: Provides the necessary tension for returning the arm to its original position.
- Mounting Bracket: Connects the assembly to the bike frame securely.
- Adjustment Screws: Allow for precise tuning of the shifting action.
Understanding these components helps in maintaining and optimizing gear shifting performance.
How the Front Derailleur Works
The mechanism responsible for shifting gears at the front of a bicycle plays a crucial role in optimizing performance and efficiency. It allows riders to switch between different chainrings, ensuring smooth transitions and adapting to varying terrains. Understanding its functionality reveals the intricacies involved in seamless gear changes.
Mechanism of Action
This device operates through a combination of cable tension and pivot points. When the rider shifts the gear lever, the cable pulls or releases tension, prompting the mechanism to move laterally. This lateral movement guides the chain from one chainring to another, facilitating smooth transitions during rides.
Importance of Adjustment
Proper alignment and tuning of this mechanism are essential for optimal performance. Misalignment can lead to inefficient shifting, causing delays and potential chain issues. Regular maintenance ensures reliability, allowing cyclists to fully utilize the benefits of their gearing system.
Types of Front Derailleurs Explained
Understanding the various mechanisms for shifting gears is essential for any cycling enthusiast. Each variant offers unique features and advantages, catering to different riding styles and preferences. Below are the main categories of these shifting systems.
- Traditional Models
These are the classic versions, typically found on standard bicycles. They are known for their simplicity and reliability.
- Compact Variants
Designed for efficiency, compact types allow for smoother transitions and are often favored by road cyclists.
- Electromechanical Options
Incorporating technology, these systems provide precise shifting with minimal effort, often used in high-performance setups.
- Mountain Models
Built to withstand rugged conditions, these are robust and offer enhanced functionality for off-road adventures.
- Hybrid Designs
These integrate features from various models, aiming to deliver versatility and cater to diverse riding scenarios.
Choosing the right mechanism depends on individual needs, riding conditions, and personal preferences, making it important to consider all available options before making a decision.
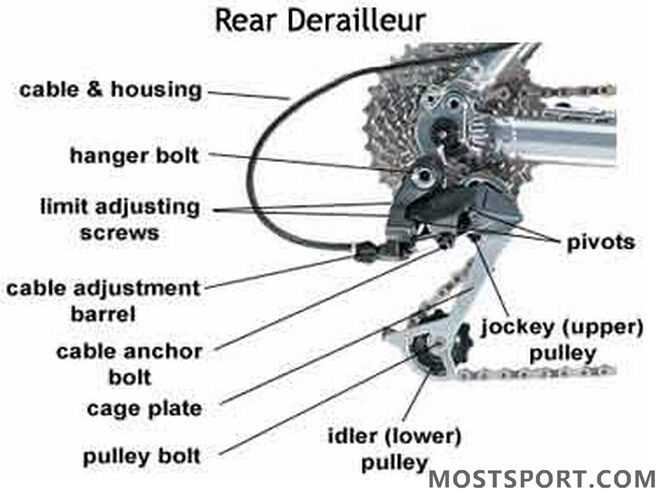
Identifying Key Parts on Diagrams
Understanding the components illustrated in technical representations is essential for effective maintenance and repair. Each element plays a specific role in the overall functionality, and recognizing these features can greatly enhance one’s ability to troubleshoot and optimize performance.
Typically, these illustrations include a variety of labels and symbols that indicate the various components involved. By familiarizing oneself with these markings, one can quickly pinpoint areas that require attention or adjustment. It’s important to note that some components might be labeled differently based on the manufacturer, so cross-referencing with product manuals can provide additional clarity.
Furthermore, appreciating the relationship between the various components aids in understanding their collective operation. Many representations will show the arrangement and alignment of these features, which is critical for ensuring smooth performance and preventing issues during use. Overall, a thorough comprehension of these illustrations fosters confidence in handling maintenance tasks.
Common Issues with Front Derailleurs
Bicycles often encounter several challenges related to their shifting mechanisms, which can affect performance and rider experience. Understanding these issues can help cyclists maintain their equipment and ensure smooth gear transitions.
One frequent problem is misalignment, where the component does not sit correctly in relation to the chainrings. This can lead to poor shifting, causing the chain to skip or fail to engage with the desired gear. Regular adjustments are essential to prevent this from occurring.
Another common concern is the accumulation of dirt and debris. Over time, grime can build up, hindering the movement and responsiveness of the mechanism. Keeping the area clean and lubricated is vital for optimal function.
Additionally, cable tension can impact performance. If the cables are too loose or too tight, shifting can become difficult. Proper tension ensures that the mechanism responds accurately to the rider’s input.
Wear and tear on components can also lead to issues. Springs and pivots can degrade over time, affecting the ability to shift smoothly. Regular inspections and timely replacements can prevent these problems from escalating.
Lastly, compatibility between the shifting system and the bike’s drivetrain is crucial. Using mismatched components can result in ineffective shifting and increased wear. It’s important to ensure that all elements work harmoniously together.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring optimal performance and extending the lifespan of your cycling components. By implementing a few simple practices, you can significantly enhance durability and functionality over time.
Routine Inspection
- Check for wear and tear regularly.
- Inspect cables and housing for frays or damage.
- Ensure alignment is correct to prevent excessive strain.
Cleaning and Lubrication
- Clean components with a suitable degreaser.
- Apply lubricant sparingly to moving parts.
- Wipe off excess to avoid attracting dirt.
Adjusting Your Front Derailleur
Proper alignment and tuning of your shifting mechanism are crucial for seamless gear transitions. Ensuring that this component operates efficiently enhances overall riding experience and extends the lifespan of your bike’s drivetrain.
Initial Setup
Begin by checking the positioning of the mechanism in relation to the chainrings. It should be parallel to the largest chainring, with a small gap of about 1-2mm. This alignment is essential for accurate shifting and prevents chain rub.
Tuning the Limits
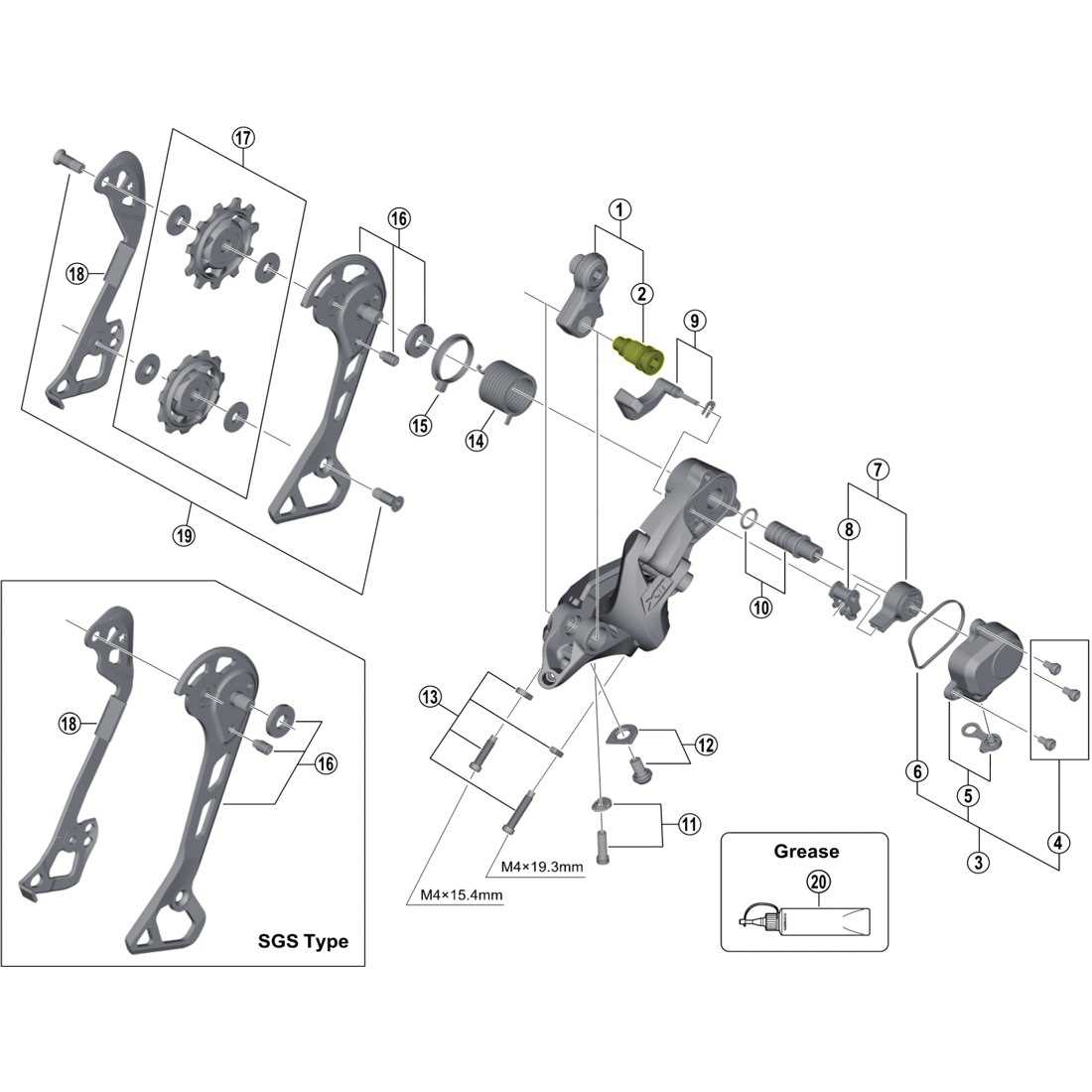
Next, adjust the limit screws to define the boundaries of the movement. The high limit screw prevents the chain from overshifting to the outer ring, while the low limit screw ensures it doesn’t fall off the inner ring. Fine-tuning these settings will provide ultimate reliability during rides.
Choosing the Right Derailleur for Your Bike
Finding the appropriate shifting mechanism for your bicycle is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring a smooth ride. With various options available, understanding your specific needs and the type of riding you intend to do is essential.
Factors to Consider
- Type of Riding: Consider whether you are commuting, racing, or mountain biking. Each style demands different features.
- Compatibility: Ensure the selected component matches your bike’s gearing system and frame design.
- Weight: Lighter models enhance speed and efficiency, while sturdier versions offer durability for rugged terrains.
- Budget: Prices can vary significantly. Determine your budget while keeping in mind the quality and longevity of the product.
Popular Options
- Standard Mechanisms: Suitable for everyday riding and general use.
- High-Performance Models: Ideal for competitive cyclists seeking precision and rapid shifts.
- Durable Alternatives: Perfect for off-road adventures and challenging conditions.
Ultimately, the right selection will enhance your cycling experience, ensuring reliability and enjoyment on every ride.
Installation Process for Beginners
This section will guide you through the fundamental steps necessary for setting up a specific component of your bicycle’s shifting system. With careful attention to detail and a bit of patience, even those new to bike maintenance can achieve a successful installation.
Tools You Will Need
Before starting, gather the following tools to ensure a smooth process:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Wrench | To tighten and adjust screws |
| Screwdriver | For precise adjustments |
| Hex Key | For securing bolts |
| Lubricant | To ensure smooth movement |
Step-by-Step Instructions
Begin by preparing your bicycle, ensuring it is stable. Position the component in the correct orientation and secure it using the appropriate tools. Make adjustments gradually to avoid misalignment. Finally, test the shifting mechanism to confirm optimal performance.
Front Derailleur vs. Rear Derailleur
The mechanisms responsible for shifting gears play a crucial role in enhancing cycling performance. Each component serves its purpose, contributing to a smooth transition between gear ratios, yet they operate in distinct ways tailored to their specific locations on the bike.
Functionality Comparison
One mechanism focuses on the gears located near the pedals, while the other handles those near the rear wheel. The former allows riders to efficiently change to larger chainrings, optimizing power for climbs, while the latter enables swift shifts to smaller sprockets, aiding speed on descents.
Design Considerations
The construction of these mechanisms varies significantly. The mechanism at the front typically features a simpler design, with fewer adjustments required. In contrast, the rear mechanism incorporates more intricate components to manage a broader range of gears, making it essential for high-performance bikes.
Future Trends in Derailleur Design
The evolution of shifting mechanisms is entering an exciting phase, driven by advancements in technology and changing rider preferences. Innovations are set to enhance performance, efficiency, and user experience, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in cycling gear.
Smart Technology Integration
Smart systems are increasingly becoming a focal point, offering real-time data and adaptive shifting capabilities. This technology promises to create a more intuitive connection between the rider and the machine, tailoring performance to individual needs.
Materials and Weight Reduction
Next-generation materials will play a crucial role in enhancing durability while minimizing weight. This trend is vital for competitive cyclists seeking every advantage on the road or trail.
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Smart Integration | Incorporating data-driven features for optimized performance. |
| Advanced Materials | Utilizing lighter, stronger materials for improved efficiency. |
| Customization | Offering tailored solutions to meet diverse riding styles. |