
Home appliances are designed with precision, where each component plays a vital role in ensuring the device functions smoothly. Recognizing the different elements that make up these systems helps users maintain, troubleshoot, and optimize the performance of their equipment. By examining the structure and purpose of each piece, it’s easier to address any operational concerns.
When you dive into the technical design of a GE cooling unit, you uncover a complex arrangement of mechanical and electrical elements. Each has a specific function, working together to maintain a balanced and efficient cooling process. Knowing how these elements interact allows users to make informed decisions about upkeep or necessary adjustments.
In this guide, we will explore various components that ensure your unit operates at peak efficiency. From key cooling mechanisms to supportive features, we will break down the essential details that help keep everything running smoothly, offering a clear perspective on how to approach repairs or maintenance.
Understanding the Main Components of a GE Refrigerator

Every cooling system is designed with specific elements that ensure efficient operation and long-term functionality. To fully grasp how your unit operates, it’s essential to know the key mechanisms that work together to maintain the ideal environment inside. These elements not only manage the cooling process but also play a role in energy efficiency and temperature control.
The compressor is the heart of the system, responsible for circulating the refrigerant and initiating the cooling process. It compresses the refrigerant, turning it into a high-pressure gas that flows through the system, starting the cooling cycle.
Another critical element is the evaporator coil, where the refrigerant absorbs heat from the inside, effectively cooling down the interior. This coil is strategically placed to maximize heat absorption and ensure even temperature distribution.
The condenser coil works in conjunction with the evaporator to release the absorbed heat to the surrounding air. Located on the back or bottom, it plays a crucial role in maintaining efficiency by expelling the excess heat generated during the cooling cycle.
To ensure consistent operation, a thermostat regulates the internal climate by monitoring and adjusting the temperature settings as needed. It acts as a control mechanism, activating or deactivating the compressor based on the temperature requirements.
The defrost system is another vital component, preventing frost buildup on the evaporator coil. This system activates periodically to melt any accumulated ice, ensuring the smooth functioning of the cooling process and optimal airflow.
How to Identify the Cooling System Parts

Understanding the components that regulate temperature within a cooling unit is essential for diagnosing issues and maintaining efficiency. The cooling mechanism consists of various elements working together to control airflow, dissipate heat, and circulate coolant. By recognizing these individual components, you can pinpoint potential areas of malfunction or wear.
Main Temperature Control Components
At the heart of the cooling system is the compressor, which pressurizes the refrigerant and pushes it through the entire system. Working closely with it, the condenser coils release heat absorbed during the cooling process. These coils are often located at the back or bottom, and they play a key role in transferring heat out of the unit.
Coolant Circulation and Airflow
The evaporator coils are equally important, located inside the unit, typically behind a panel. These coils absorb heat from the interior and convert the refrigerant into a gas. Fans then circulate the cold air, ensuring consistent temperature distribution. Lastly, temperature sensors monitor and maintain desired levels, ensuring the system runs efficiently.
Guide to the Electrical Components in GE Refrigerators
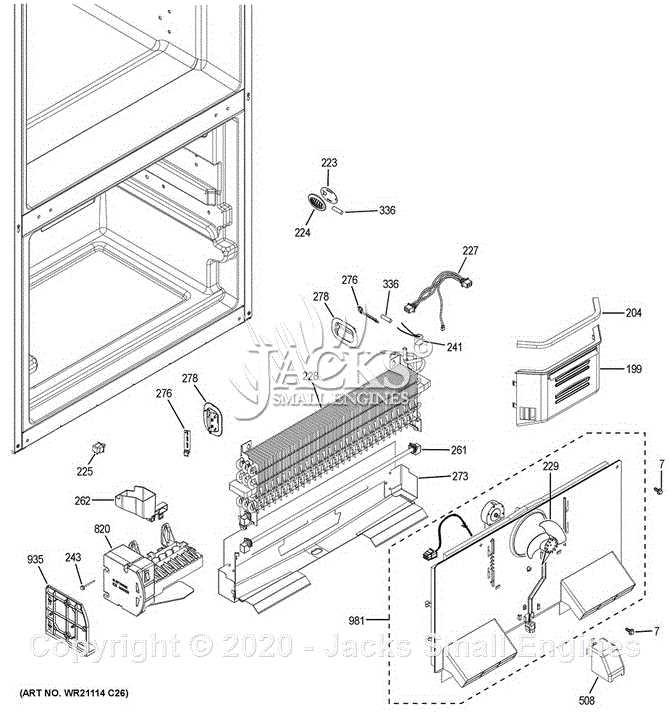
The electrical system in modern GE appliances plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient cooling and smooth operation. Understanding the core elements responsible for electrical functions helps users troubleshoot issues and maintain optimal performance. These components work together to regulate power distribution, manage temperature control, and maintain safety features. Proper knowledge of these electrical elements can greatly aid in diagnosing problems or performing routine maintenance.
One of the most critical units is the compressor, which relies on electrical input to operate. It’s responsible for driving the coolant through the system. Working alongside the compressor is the start relay, which helps to engage the motor at startup. Without a functioning relay, the cooling process would not initiate properly.
Thermostats and sensors act as the brain of the cooling unit, monitoring temperatures and adjusting settings as needed. These systems rely on electrical impulses to activate heating elements or compressors when temperatures fluctuate, ensuring a steady environment inside the cooling space.
In addition, defrost timers and heaters are crucial for preventing frost buildup. The timer periodically sends signals to the heater, ensuring that any excess ice is melted at regular intervals. This system helps maintain efficiency and prevents internal obstructions caused by ice accumulation.
Fans and motors, which are also powered electrically, ensure proper air circulation throughout the unit. This constant flow of air is vital for maintaining an even cooling environment. If these components fail, uneven temperatures or poor performance may result.
Lastly, various control boards and circuit breakers
Exploring the Water Filtration System
The water filtration system plays a crucial role in ensuring that the water used within the appliance is clean, safe, and tastes great. It helps remove impurities, contaminants, and undesirable elements from the water, providing a better experience for users. Understanding how this system operates can offer insights into maintaining both efficiency and water quality over time.
Main Components
The filtration system typically consists of several essential elements that work together to purify the water. Each component has a specific function, contributing to the overall process of filtration.
- Filter housing: The compartment where the filter is securely installed, allowing water to flow through it effectively.
- Water inlet: The point where water enters the filtration system, directed through the filtering process.
- Cartridge or filter: The core element responsible for removing impurities such as chlorine, lead, and sediments.
How It Works
Water flows into the filtration system through the inlet, passing through the filter media inside the cartridge. This media is designed to capture contaminants, ensuring only clean water passes through. After filtration, the purified water is directed towards the point of use, ready for consumption or other uses.
- Water enters through the designated inlet.
- It passes through the filter, which traps various particles and chemicals.
- Clean water exits the system, ready for consumption.
Regular maintenance of the system is essential for optimal performance. Replacing the cartridge at recommended intervals ensures continued filtration efficiency and preserves the quality of the water.
Commonly Replaced Parts in GE Refrigerators
Over time, many components in cooling appliances may require attention or replacement due to wear and tear, especially in models that have been in use for several years. These essential elements are vital to ensuring that your appliance runs smoothly, maintaining efficiency and extending its lifespan.
Door Gaskets: The seals around the door can lose their ability to close tightly, leading to energy inefficiency. Regularly inspecting and replacing these can prevent cold air from escaping, ensuring the appliance operates at optimal performance.
Water Filters: For models equipped with a water dispenser, the filtration system needs periodic replacement to maintain water quality and flow. Ignoring this maintenance can result in reduced water clarity and flow rate.
Thermostats: These regulate the internal temperature, and when malfunctioning, they can cause cooling issues or overcooling. A faulty regulator should be replaced to keep the internal environment consistent.
Defrost Heaters: If the unit begins to accumulate frost excessively, the defrost system might be at fault. The heating element responsible for clearing ice buildup can wear out and will need replacing to avoid frost buildup in the cooling compartment.
Evaporator Fans: These fans circulate cold air throughout the cooling and freezing sections. If airflow is reduced or stops, replacing the fan can restore even cooling and improve the overall function of the unit.
Condensers: The condenser helps in the heat exchange process. When dust or debris accumulates or if the unit is damaged, this element may need cleaning or replacement to prevent overheating and ensure efficient energy use.
Compressor Function and Location Explained
The compressor plays a vital role in the cooling system, ensuring efficient temperature regulation and optimal performance. This component is responsible for compressing the refrigerant, raising its pressure and temperature, and facilitating the movement of the cooling substance through the system. Understanding its function and placement is crucial for anyone looking to comprehend the mechanics of refrigeration technology.
Function of the Compressor
The primary function of the compressor can be broken down into several key processes:
- Compression: The compressor takes in low-pressure refrigerant vapor and compresses it into a high-pressure gas.
- Heat Transfer: As the refrigerant is compressed, its temperature increases, allowing it to release heat when it moves to the condenser.
- Circulation: The compressor facilitates the continuous circulation of refrigerant throughout the system, enabling effective cooling.
Location of the Compressor
The placement of the compressor is strategically chosen for optimal efficiency and accessibility. Typically, you can find it in the following locations:
- At the Back: Many cooling units position the compressor at the rear, allowing for efficient airflow and easy access during maintenance.
- Underneath: Some models feature a bottom-mounted compressor to save space and improve aesthetics.
- In Side Compartments: Advanced designs may incorporate the compressor in side compartments to enhance the unit’s overall performance.
Knowing both the function and the typical locations of the compressor enhances one’s understanding of how cooling systems operate, leading to better maintenance and troubleshooting practices.
Where to Find the Evaporator Fan in Your GE Unit

The evaporator fan plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal temperatures within your cooling appliance by circulating air. Locating this component can be essential for troubleshooting any airflow issues you may encounter. This guide will help you identify the specific area where the fan is situated in your GE model, enabling you to perform maintenance or repairs effectively.
Accessing the Interior Compartment
To locate the evaporator fan, you first need to open the unit and access the interior compartment. Typically, this fan is positioned at the back or side of the cooling area, hidden behind a cover panel. Carefully remove the screws or fasteners securing the panel to reveal the fan assembly.
Identifying the Fan
Once the cover is removed, you will notice the fan attached to the evaporator coil. It usually features a distinct shape with blades designed for optimal airflow. Ensure the unit is unplugged before touching any components. If you are unsure about the location, refer to the user manual for your specific GE model, which often includes diagrams for guidance.
Overview of the GE Refrigerator Door Components

The door of any cooling appliance is an essential element that not only provides access to the interior but also plays a critical role in maintaining optimal temperatures. Understanding the various elements that comprise this structure can enhance maintenance practices and ensure longevity.
Each component serves a specific function, contributing to both efficiency and user convenience. From seals that prevent air exchange to shelves that facilitate organization, these features are designed to work in harmony. Below is a table outlining key components and their respective functions:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Gasket | A flexible seal that ensures a tight closure, minimizing temperature fluctuations. |
| Shelves | Removable platforms that allow for the storage of various items, promoting efficient use of space. |
| Hinges | Mechanisms that facilitate smooth opening and closing of the door, ensuring durability over time. |
| Handle | An ergonomic feature designed for ease of access while providing a secure grip. |
| Door Liner | The interior surface that helps with insulation and supports other components. |
By familiarizing oneself with these elements, users can better appreciate the design and functionality of their cooling appliance, leading to informed decisions regarding care and upkeep.
Temperature Control Parts and Their Functions
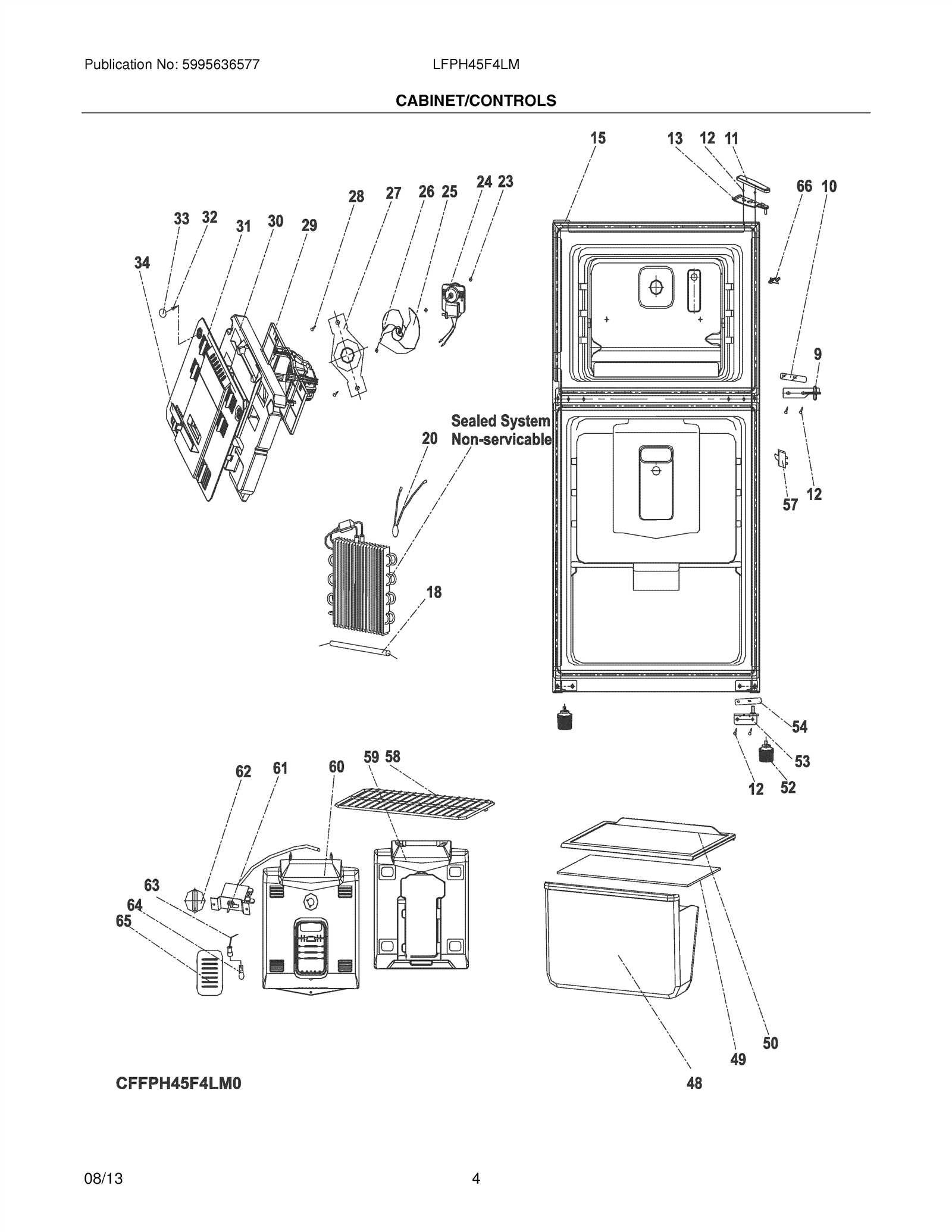
Effective regulation of temperature within a cooling appliance is essential for optimal food preservation and energy efficiency. This section explores various components responsible for maintaining desired temperature levels, ensuring that the internal environment remains conducive for storage. Each element plays a pivotal role in the functionality and reliability of the entire system.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Thermostat | Monitors and adjusts the internal temperature by turning the cooling mechanism on or off. |
| Temperature Sensor | Detects the current temperature within the unit, providing real-time data to the control system. |
| Control Board | Interprets signals from the thermostat and sensor, managing the operation of the compressor and fans. |
| Compressor | Circulates refrigerant throughout the system, facilitating heat exchange to lower internal temperatures. |
| Condenser Fan | Enhances airflow around the condenser coil, promoting efficient heat dissipation. |
| Evaporator Coil | Absorbs heat from the interior, playing a crucial role in cooling the air within. |
Troubleshooting the Defrost System Components

Understanding the intricacies of the defrost system is essential for maintaining optimal performance and efficiency in cooling appliances. A malfunction in this system can lead to frost buildup, reduced cooling efficiency, and even potential failures. This section provides guidance on identifying issues within the defrost mechanism and offers steps to resolve them effectively.
Common Issues and Symptoms
- Excessive frost accumulation on the evaporator coils.
- Inconsistent temperatures within the storage compartments.
- Unusual noises during the defrost cycle.
- Failure of the heating element to activate.
Steps for Diagnosis
- Inspect the Timer: Verify if the defrost timer is functioning correctly. Set it to test mode and listen for a click indicating the transition to defrost mode.
- Examine the Heating Element: Check for continuity using a multimeter. If there is no continuity, the element may need replacement.
- Check the Termination Thermostat: Ensure that this component is operational. It should close when the temperature is low and open when defrosting is complete.
- Inspect Drain Lines: Make sure the drain path is clear. Clogs can prevent proper water drainage during the defrost cycle.
By following these troubleshooting steps, one can effectively identify and rectify issues within the defrost system, ensuring smooth operation and longevity of the cooling unit.