When maintaining or upgrading your off-road motorbike, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of its essential elements. Every component plays a vital role in ensuring the performance and longevity of your vehicle. Whether it’s the engine, suspension, or braking system, each part needs attention to keep your bike running smoothly in tough terrain.
In this section, we’ll explore how the arrangement of different mechanical and electrical elements contributes to the overall function of an off-road two-wheeler. Proper knowledge of the
Comprehensive Guide to CRF 80 Components
Understanding the various elements of this off-road vehicle is essential for both maintenance and performance improvements. Each mechanical unit serves a unique purpose, contributing to the overall reliability and efficiency of the machine. This guide provides an in-depth look into the key mechanisms and their functions, helping enthusiasts and riders alike keep their bikes in optimal condition.
- Engine System: The core of the vehicle, driving the entire mechanism and powering all movements.
- Transmission: Responsible for adjusting speed and torque, ensuring smooth transitions between gears.
- Suspension: Vital for absorbing shocks
Exploring Key Engine Parts Layout
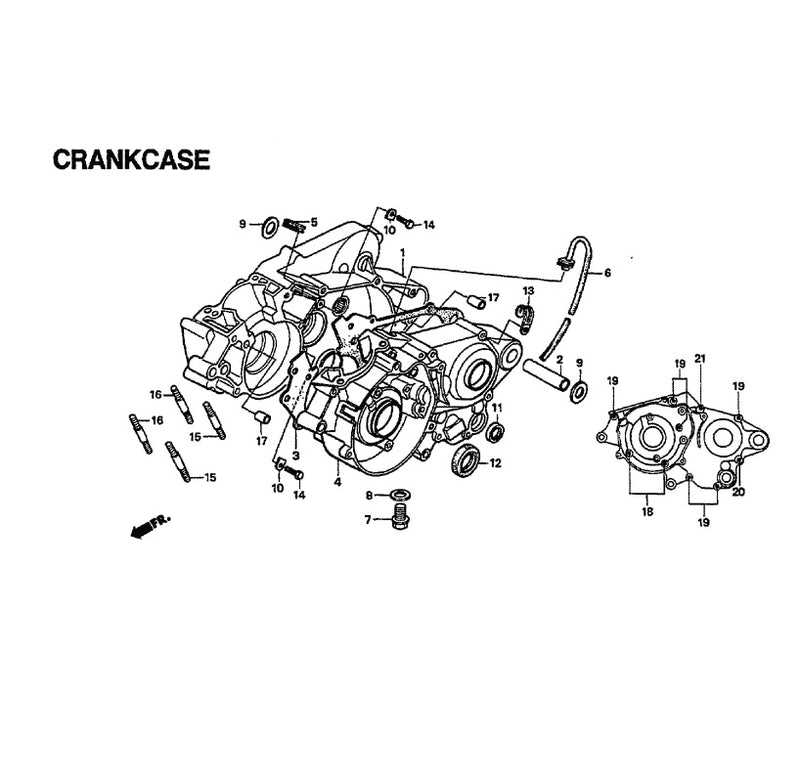
The arrangement of core components within the motor plays a crucial role in the overall performance and reliability of the machine. Understanding the spatial organization and how each element interacts with others is essential for ensuring efficient maintenance and troubleshooting.
Component Function Cylinder Head Houses valves and controls airflow into the combustion chamber. Understanding the Suspension System Configuration
The arrangement of the shock absorption components plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth rides over uneven terrain. This system is designed to absorb impact and maintain stability, providing both comfort and control to the rider. By carefully adjusting the structure of these elements, one can improve handling performance in a variety of environments.
Each element in this setup works in harmony to reduce the effects of rough surfaces. The combination of springs and dampers ensures that vibrations are minimized, while the frame remains balanced and responsive. Regular checks and fine-tuning are key to maintaining optimal function and safety.
Brake Assembly Breakdown and Functions
The brake system is an essential component responsible for ensuring the safe deceleration and stopping of a vehicle. Understanding how this system operates is crucial for maintaining performance and ensuring safety. Each element within the assembly plays a specific role, working together to provide reliable braking power.
Key Components of the Brake System
The braking mechanism is composed of several interconnected parts, including the pedal, lines, calipers, and discs. The pedal initiates the braking
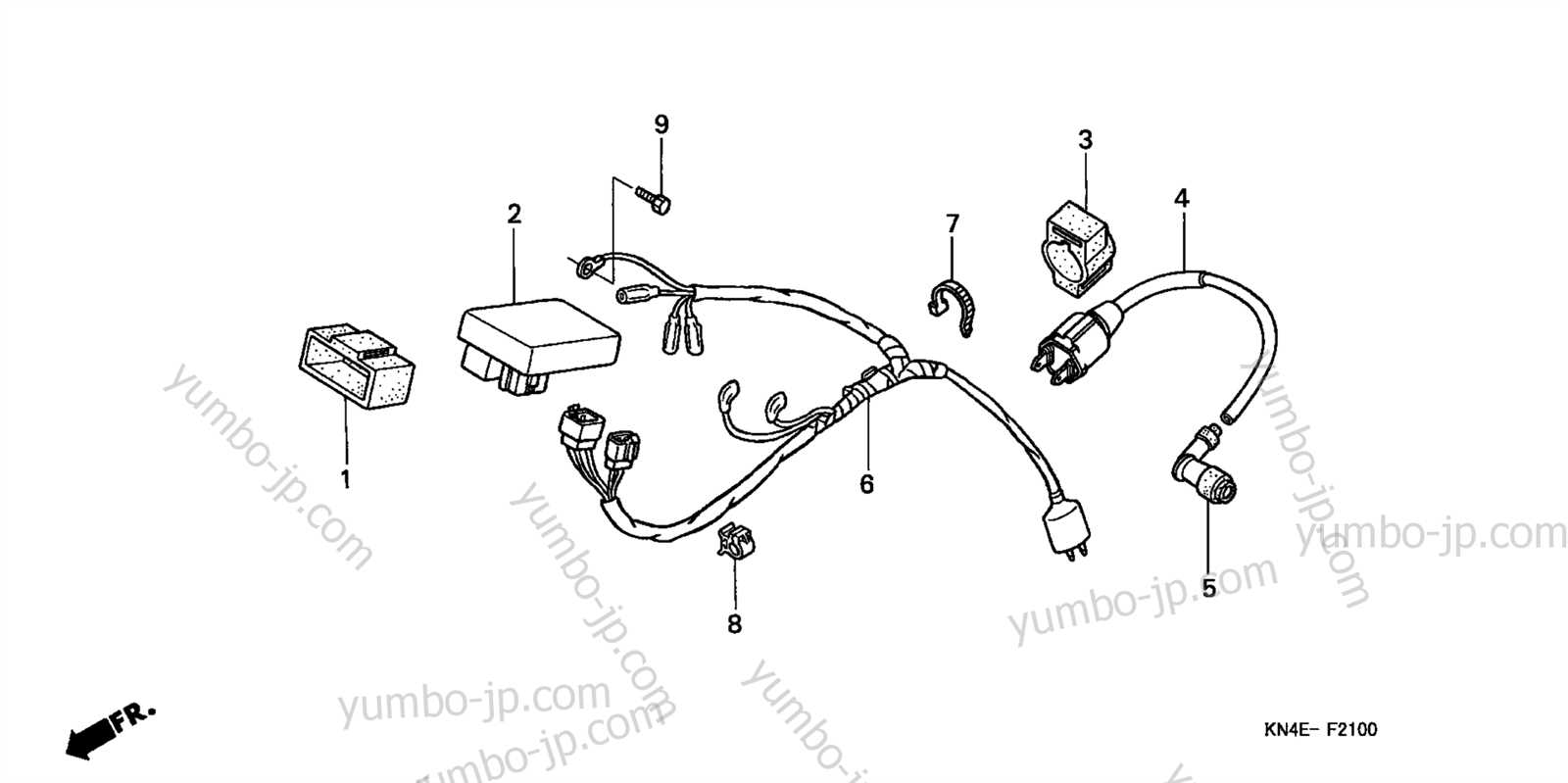
Analyzing the Electrical Wiring Diagram

The electrical layout of a motorbike provides a detailed overview of the connections and pathways essential for its operation. Understanding the organization of the wires and components helps ensure proper functionality and safety. By reviewing the wiring setup, you can better grasp how power flows through the system and what each connection contributes to the overall performance.
Key Components and Connections
Each wire is part of a larger network, linking critical elements such as the
Overview of the Fuel System Structure
The fuel system is a critical component in the operation of a motorcycle, playing a vital role in ensuring efficient combustion and overall performance. This system consists of several interconnected elements that work together to store, transport, and deliver fuel to the engine. Understanding its structure helps in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
Main Components of the Fuel System

The fuel system comprises various parts, each serving a specific function:
- Fuel Tank: Stores the fuel needed for operation.
- Fuel Pump: Transfers fuel from the tank to the engine.
- Fuel Filter: Cleans the fuel by removing impurities before it reaches the engine.
- Fuel Lines: Hoses that transport fuel between components.
- Carburetor or Fuel Injector: Mixes fuel with air to create a combustible mixture for the engine.
Functionality and Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the fuel system is essential for optimal performance. Here are some key practices:
- Inspect and replace the fuel filter periodically to ensure clean fuel supply.
- Check for leaks in fuel lines and connections to prevent fuel loss.
- Clean or replace the carburetor or fuel injectors as necessary to maintain efficient fuel delivery.
Understanding these elements contributes to the effective management and upkeep of the motorcycle’s fuel system.
Examining the Exhaust Components Setup
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in the overall performance and efficiency of any motorized vehicle. Understanding its configuration can help enthusiasts maintain optimal functionality and enhance the riding experience. This section explores the various elements of the exhaust assembly, detailing their functions and how they contribute to effective operation.
Key Components of the Exhaust Assembly

The following components are essential for the proper functioning of the exhaust setup:
- Muffler: Reduces noise produced by the engine and aids in the smooth exit of exhaust gases.
- Exhaust Pipe: Directs the flow of exhaust gases away from the engine, minimizing back pressure.
- Header: Connects the engine to the exhaust system, ensuring efficient gas flow.
- Gaskets: Provide a seal between components to prevent leaks and maintain pressure.
Importance of Regular Inspection
Routine checks of the exhaust components are vital for:
- Identifying wear and tear that may lead to performance issues.
- Ensuring compliance with environmental regulations by minimizing emissions.
- Enhancing engine efficiency and prolonging its lifespan.
Frame and Body Part Identification
Understanding the layout and function of the structural components of a vehicle is crucial for effective maintenance and repair. The framework and outer elements serve as the foundation for performance and stability, playing a vital role in the overall integrity of the machine. Proper identification of these segments is essential for both novices and experienced mechanics, ensuring a thorough approach to service and enhancements.
Key Structural Components
The primary components of the framework include the main chassis and subframes, which support the engine and suspension systems. These elements are designed to withstand various stresses while providing a stable platform for the vehicle. Identifying each segment allows for targeted inspections and modifications, improving performance and safety.
Outer Body Features
The external shell consists of panels and protective elements that not only enhance aesthetics but also contribute to aerodynamics and durability. Recognizing the distinct parts of the outer casing enables efficient repairs and replacements, ensuring the vehicle remains in optimal condition. Pay attention to specific markings and connections, as they provide essential information for assembly and disassembly.
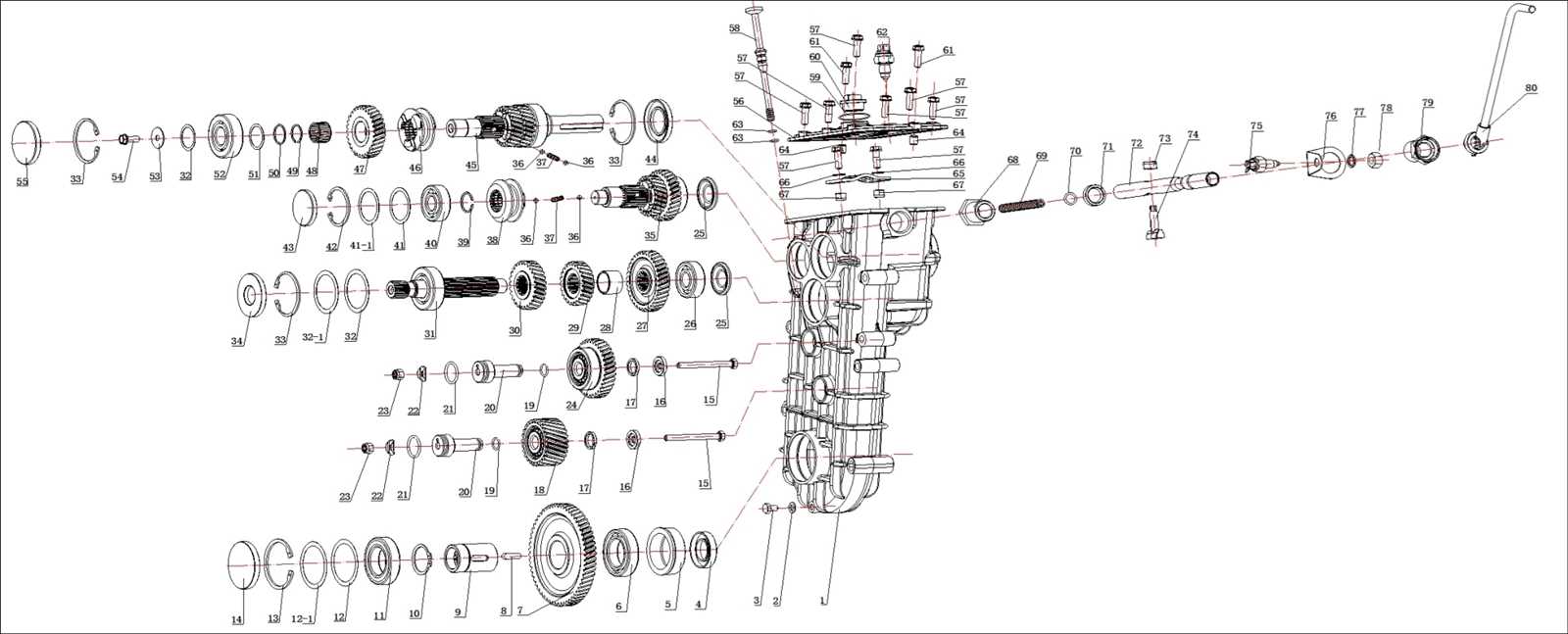
Transmission System Schematic and Overview
The transmission system in a motorcycle plays a crucial role in converting engine power into motion, ensuring efficient performance across various speeds. Understanding its layout and components is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the transmission architecture, highlighting its key elements and their functions.
Key Components of the transmission include gears, shafts, and clutch mechanisms. Each element works together to manage torque transfer from the engine to the wheels, allowing for smooth acceleration and deceleration. The arrangement of these components can significantly influence the vehicle’s responsiveness and overall riding experience.
In summary, a thorough understanding of the transmission layout is vital for any enthusiast or mechanic aiming to optimize performance and ensure longevity. Familiarity with the intricate connections within this system aids in diagnosing issues and implementing effective solutions.
Front and Rear Wheel Assembly Details
The wheel assembly is crucial for the overall performance and stability of a two-wheeled vehicle. Understanding the components involved in both the front and rear wheel assemblies helps in ensuring proper maintenance and functionality. Each part plays a significant role in the operation of the vehicle, contributing to both safety and efficiency.
Key components of the wheel assembly include:
- Rims: These provide the structural foundation for the tire and support the weight of the vehicle.
- Spokes: These connect the rim to the hub, allowing for flexibility and strength in the wheel.
- Hubs: Located at the center of the wheel, hubs facilitate rotation and house bearings.
- Tires: Essential for traction and handling, tires must be compatible with the rim size.
- Axles: These components support the wheel and allow it to rotate freely.
When assembling or disassembling the wheel, consider the following steps:
- Ensure the vehicle is securely positioned to prevent movement.
- Remove any fasteners holding the wheel in place.
- Carefully detach the wheel from the axle.
- Inspect all components for wear or damage.
- Reassemble by following the reverse order, ensuring all parts are securely fastened.
Regular inspection and maintenance of the wheel assembly not only enhance performance but also extend the lifespan of the vehicle.
Steering Mechanism and Control Layout
The steering mechanism is a crucial component in ensuring precise handling and control of the vehicle. This section will explore the layout and functionality of the controls associated with the steering system, highlighting how they contribute to the overall performance and safety.
The steering system typically consists of various elements that work together seamlessly. These components include:
- Handlebars: The primary interface for the rider, allowing for directional control.
- Steering Stem: Connects the handlebars to the front fork, providing stability and support.
- Fork Assembly: Supports the front wheel and absorbs shocks from the terrain.
- Throttle Control: Located on the handlebars, it regulates engine power and acceleration.
- Brake Lever: Provides immediate stopping power when engaged, ensuring rider safety.
Understanding the layout of these controls is essential for effective operation. Proper handling techniques can enhance the riding experience while minimizing the risk of accidents. Riders should familiarize themselves with the positioning and functionality of each component to ensure optimal performance.
In summary, a well-designed steering mechanism and control layout significantly impact maneuverability and rider confidence. Regular inspection and maintenance of these elements are vital for long-term reliability and safety.