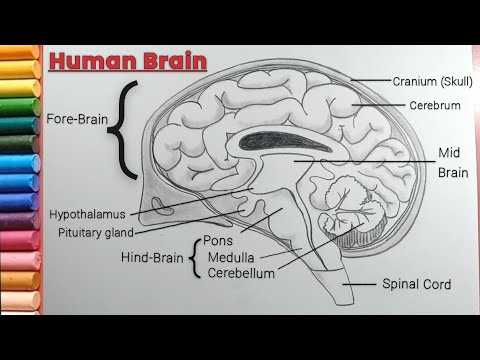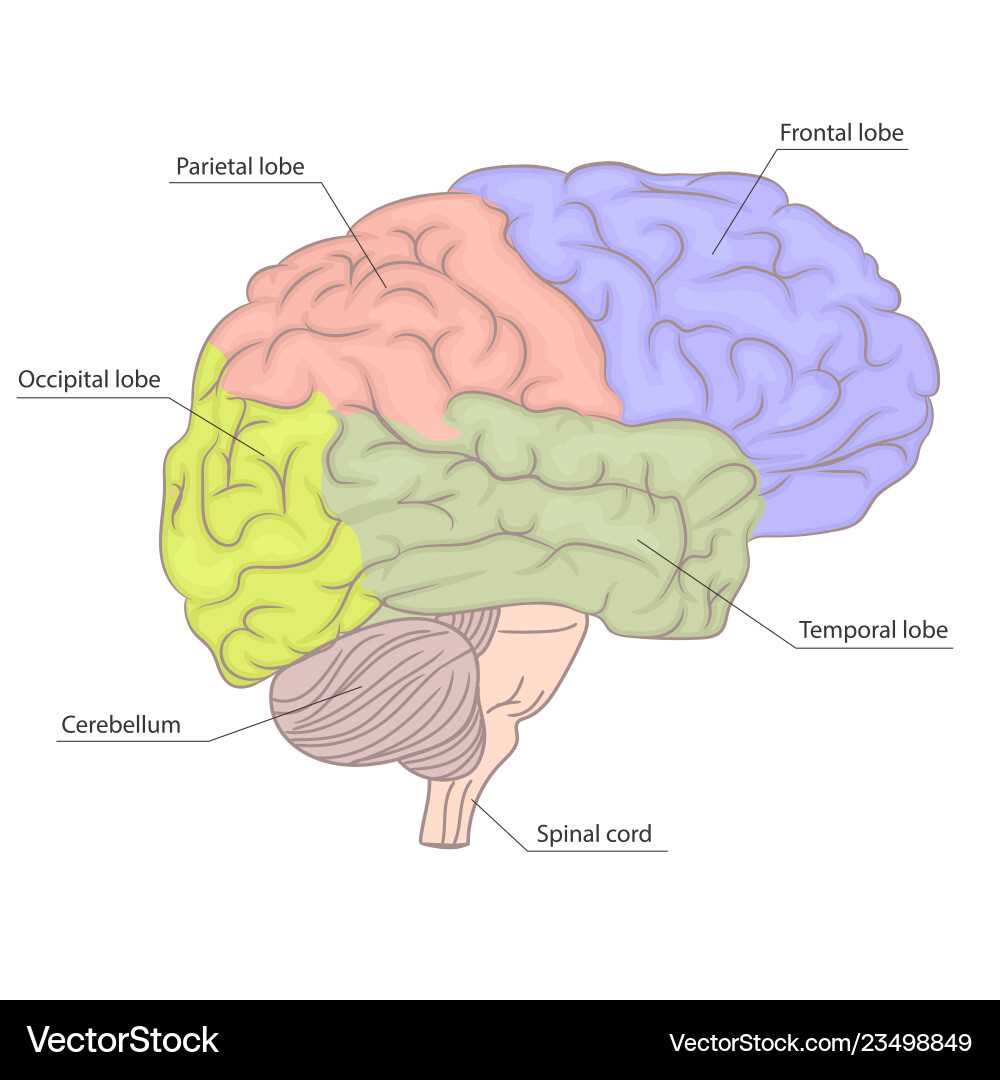
The intricate network governing thought, perception, and movement has captivated the attention of researchers for centuries. This complex structure is composed of interconnected regions, each responsible for distinct yet interconnected functions that maintain cognitive processes and bodily coordination. Exploring these regions unveils the fascinating ways in which they work together to process information and respond to the external world.
At the core of this system are key sections responsible for regulating essential activities such as memory retention, sensory interpretation, and voluntary movement. These areas communicate through neural pathways, ensuring swift responses and adaptive behavior. By examining the architecture of this organ, we can better understand how different zones interact to support everyday tasks and advanced intellectual capabilities.
This exploration delves into the specific areas that contribute to emotional regulation, logical reasoning, and physical coordination, revealing the harmonious operation of this vital organ. Each section plays a unique role, contributing to the overall function that keeps both the mind and body in sync.
Anatomy of the Human Brain
The structure of the central organ of our nervous system is intricate and fascinating. It comprises various sections, each responsible for specific functions, working together to maintain overall control of the body. Understanding the internal layout and connections provides valuable insights into how thoughts, movements, and vital processes are regulated.
Main Functional Areas
The central organ can be divided into different regions that handle distinct tasks. Some of these sections focus on processing sensory information, while others are involved in managing movement, emotions, and higher cognitive abilities. Each region plays an essential role in ensuring coordinated activity and response to the environment.
Connections and Roles
Multiple layers of tissue and connections form a complex network of pathways. These layers are responsible for everything from simple reflex actions to advanced reasoning. Understanding how these regions communicate and interact reveals the sophisticated nature of the organ’s operations.
| Section | Primary Function |
|---|
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Respiratory Control | Regulates breathing patterns and oxygen intake. |
| Region | Function |
|---|---|
| Dentate Gyrus | Involved in the formation of new memories and the processing of spatial information. |
| CA3 | Plays a role in pattern recognition and associative memory. |
| CA1 | Essential for the consolidation of memories and linking them to existing knowledge. |
| Subiculum | Acts as a relay between the hippocampus and other regions of the cerebral cortex. |
How the Cerebellum Controls Movement
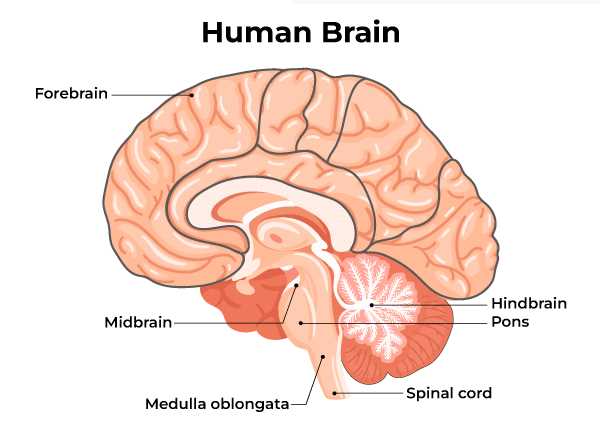
The cerebellum plays a crucial role in coordinating and fine-tuning physical activities. This structure is essential for maintaining balance, posture, and precise movements. It processes sensory information and integrates it with motor commands, ensuring that actions are smooth and accurate.
Coordination of Muscular Activities
This region enhances the efficiency of muscle contractions, allowing for fluid motion. By receiving input from various sensory pathways, it assesses the position and speed of limbs. This feedback enables the adjustment of movements in real-time, facilitating activities ranging from simple tasks to complex athletic performances.
Role in Learning and Adaptation
In addition to immediate control, the cerebellum is vital for motor learning. It helps in the development of skills through practice and repetition. As experiences are accumulated, this area adapts motor responses, leading to improved execution of tasks over time. Consequently, the cerebellum contributes significantly to the acquisition of new physical abilities.
Understanding the Limbic System
The limbic system serves as a critical center for emotions, memory processing, and various autonomic functions. It plays a vital role in influencing behaviors that are essential for survival, connecting emotional responses to physiological reactions. This complex network is not only responsible for emotional regulation but also integrates various sensory inputs, allowing individuals to experience a wide range of feelings and reactions.
Key Components
This intricate structure encompasses several significant components, each contributing uniquely to its overall function. Hippocampus is essential for memory formation and spatial navigation, while the amygdala is pivotal in processing emotions, particularly fear and pleasure. Together, these elements facilitate a deeper understanding of experiences and enhance learning capabilities.
Functions and Importance
Understanding the significance of this system extends to various aspects of mental health and emotional well-being. Its functionality influences behavior, motivation, and social interactions. Disruptions within this network can lead to emotional disorders, highlighting its importance in maintaining psychological balance. Recognizing the roles of each component can aid in developing strategies for therapeutic interventions and improving overall mental health.
The Role of the Thalamus in Sensory Processing
The thalamus serves as a critical hub for the relay and processing of information originating from various sensory modalities. Its intricate structure allows it to filter and transmit signals to specific regions, thereby influencing how sensory data is perceived and interpreted. This functionality plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the organism effectively responds to its environment.
Functions of the Thalamus in Sensory Modality
- Relay Station: The thalamus acts as a conduit for sensory information, channeling signals from the periphery to appropriate cortical areas.
- Processing Center: It not only transmits information but also processes it, refining and enhancing the signals before they reach their final destination.
- Integration of Sensory Inputs: The thalamus integrates inputs from multiple senses, allowing for a cohesive understanding of environmental stimuli.
Impact on Perception and Response
Through its regulatory functions, the thalamus significantly affects how stimuli are perceived. This can be observed in the following ways:
- Attention Regulation: The thalamus helps prioritize certain stimuli over others, allowing the organism to focus on relevant information.
- Timing of Responses: By controlling the flow of sensory information, it influences the timing and appropriateness of reactions to stimuli.
- Emotional Context: The thalamus also interacts with structures involved in emotional processing, thereby modulating how sensory experiences are interpreted based on context.
Overall, the thalamus plays an indispensable role in how sensory information is processed and understood, shaping the overall interaction with the surrounding world.
Functions of the Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and regulating various physiological processes. This small yet vital structure is involved in numerous functions that are essential for overall well-being.
One of the primary roles of the hypothalamus is to control the endocrine system by influencing the pituitary gland. This interaction allows for the regulation of hormone release, which affects growth, metabolism, and reproductive functions. Additionally, it orchestrates the body’s response to stress through the release of corticotropin-releasing hormone, promoting an appropriate response to challenging situations.
The hypothalamus also regulates essential behaviors such as hunger, thirst, and sleep. It monitors energy levels and nutrient availability, triggering sensations of hunger or satiety accordingly. Furthermore, this structure helps maintain body temperature by initiating responses like sweating or shivering, ensuring optimal functioning in varying environmental conditions.
Emotional responses are also influenced by the hypothalamus, as it is interconnected with the limbic system. This connection plays a significant role in how emotions are expressed and perceived, contributing to the overall emotional balance of an individual.
In summary, the hypothalamus serves as a critical hub for numerous regulatory processes, impacting everything from hormone production to emotional responses. Its multifaceted functions are vital for sustaining life and ensuring the body operates efficiently.
How the Brain Communicates with the Body
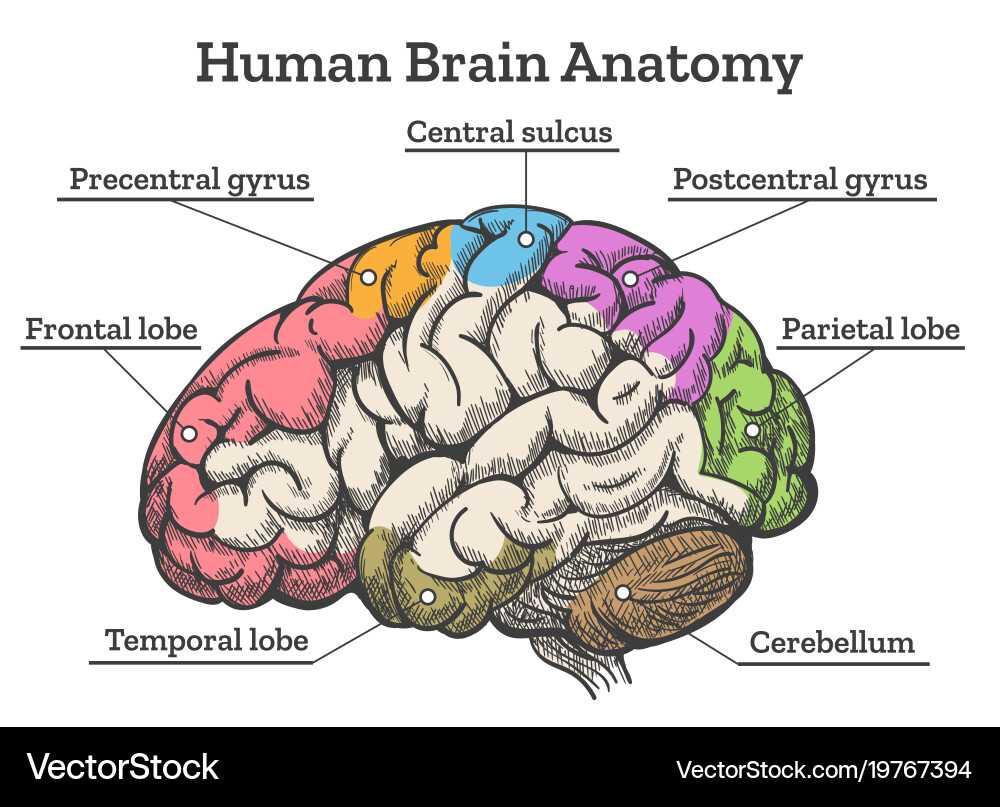
The central nervous system orchestrates an intricate dialogue between various systems, ensuring seamless functionality. This communication is essential for maintaining homeostasis and enabling responses to environmental stimuli.
The exchange of information occurs through a network of specialized cells and pathways, which can be categorized as follows:
- Neurons: These cells transmit signals through electrical impulses and chemical neurotransmitters.
- Synapses: Junctions where communication between neurons takes place, allowing for signal transmission and modulation.
- Glial cells: Supportive cells that maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and provide support and protection for neurons.
Information is relayed in a structured manner:
- Signal Generation: Sensory receptors detect stimuli and convert them into electrical signals.
- Signal Transmission: Neurons carry these signals along their axons towards the target areas.
- Signal Reception: Target cells, such as muscles or glands, receive the signals and execute appropriate responses.
This process allows the body to react swiftly to internal and external changes, facilitating movement, regulation of vital functions, and adaptation to new situations. Understanding this complex communication pathway enhances our appreciation of physiological processes and overall health.