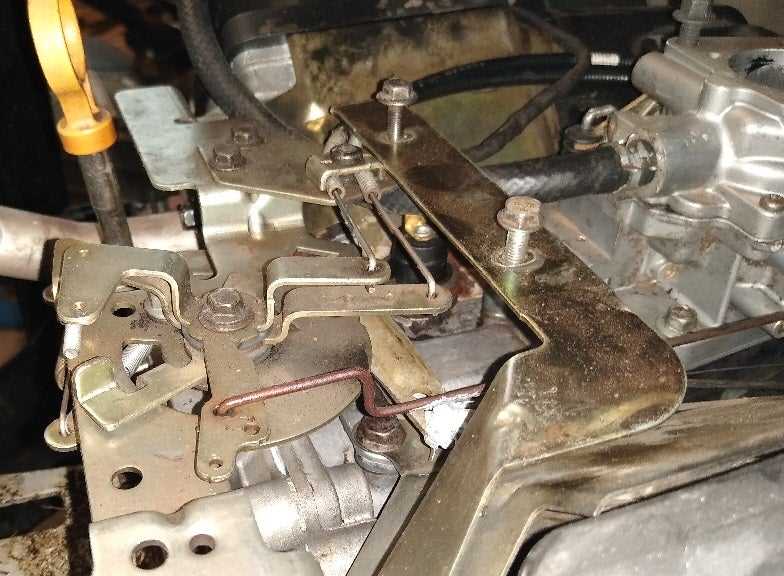

When dealing with the inner workings of an engine, it’s crucial to have a clear view of how all its individual elements interact. This knowledge not only aids in the smooth functioning of the system but also ensures effective troubleshooting and maintenance. Every component plays a vital role, and understanding their layout and connections can significantly reduce the complexity when dealing with mechanical issues.
In this section, we will explore the various parts of an engine, focusing on their structure and how each part supports the overall performance. Through detailed visual aids, we aim to break down the complexities of engine design and provide insight into the organization of key elements.
By examining the mechanical relationships between these components, it becomes easier to identify where issues may arise and how to address them. Whether you’re replacing a worn-out part or performing routine maintenance, knowing the placement and function of each piece is essential to ensure the engine continues to operate at its best.
Exploring the Kohler CH25S Engine
This section delves into the essential components and mechanisms behind a popular small engine model, known for its durability and performance in various equipment. Understanding the layout and function of these systems is crucial for maintenance and repair, ensuring optimal functioning throughout its lifecycle.
Key Features and Functionality
At the heart of this engine is a finely tuned assembly designed to deliver consistent power across demanding tasks. Key elements, such as the ignition system, fuel delivery, and air intake, work together to provide efficiency and reliability. Regular inspection of these systems can prevent common issues, enhancing the longevity of the engine.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
To maintain the engine’s peak performance, regular servicing is required. Pay special attention to components like the fuel system and valve operation, which are critical for smooth operation. Troubleshooting may involve simple adjustments or part replacements, ensuring minimal downtime during use. Proper care and understanding of the engine’s assembly are vital for seamless functionality.
Understanding the Main Components
Every engine is made up of a series of key elements that ensure its efficient operation. These parts work together to create the power necessary for the machine’s performance. Each component plays a crucial role in maintaining the smooth running of the system, and understanding their functions helps in better maintenance and troubleshooting.
Core Engine Elements
The engine’s core consists of multiple interconnected units, each responsible for specific tasks. From the combustion chamber to the lubrication system, each part has a vital function that supports the engine’s overall effectiveness. Regular inspection of these components can prevent many common issues and extend the engine’s life.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Crankshaft | Translates linear force into rotational motion to drive the machine. |
| Cylinder | Houses the piston and facilitates the combustion process. |
| Fuel System | Delivers the correct amount of fuel to the engine for combustion. |
| Ignition System | Ignites the fuel mixture within the combustion chamber to initiate power production. |
| Cooling System | Maintains optimal operating temperature by regulating the heat generated during combustion. |
Maintenance Considerations
Regular maintenance of these vital components ensures the engine performs at its peak. Preventive measures such as checking fluid levels, replacing worn-out parts, and cleaning the components can help avoid costly repairs and improve overall functionality.
Engine Assembly Overview

The engine assembly is a complex structure that brings together various components, each playing a crucial role in the proper functioning of the machine. Understanding the layout and interaction of these parts is essential for ensuring the smooth operation and longevity of the engine. This section provides an in-depth look at the key elements involved in engine construction.
The primary components of the engine include:
- Crankcase: The central housing where key components are mounted, including the crankshaft.
- Pistons: Vital elements that move up and down within the cylinders, transferring energy from combustion to mechanical motion.
- Valves: Control the intake of fuel and air and the expulsion of exhaust gases, ensuring efficient engine performance.
- Cylinders: The chambers in which pistons move, facilitating the combustion process that powers the engine.
- Camshaft: A rotating shaft responsible for controlling the opening and closing of the valves.
Each part of the assembly must be precisely aligned and well-maintained for optimal performance. Proper understanding of the engine’s construction is essential for both maintenance and repair work, helping to identify and address potential issues before they become major problems.
Key Parts for Maintenance
Regular upkeep of machinery is essential for ensuring longevity and optimal performance. Understanding the critical components that require attention can significantly reduce the risk of failure and improve efficiency. Identifying these elements is a crucial step in the process of servicing and maintaining mechanical systems.
Essential Components for Routine Care
Among the various elements that contribute to the smooth operation of the engine, a few stand out as particularly vital for maintenance. Regular checks and servicing of these components can prevent wear and tear, extending the lifespan of the equipment. The following list highlights some of the most important parts:
- Fuel Filter: Keeps the fuel system clean, preventing contaminants from reaching the engine.
- Air Filter: Ensures that the air entering the engine is free from debris, promoting efficient combustion.
- Oil Filter: Protects the engine by trapping dirt and particles from the oil, maintaining proper lubrication.
- Spark Plug: Vital for ignition; it should be inspected periodically for wear and proper gap.
- Carburetor: Plays a critical role in mixing fuel and air to ensure optimal engine performance.
Maintenance Schedule and Best Practices
Sticking to a consistent maintenance schedule for these components helps avoid unexpected failures. Below are some key practices to follow:
- Change the oil and replace the oil filter regularly to maintain lubrication efficiency.
- Inspect and clean the air filter to prevent clogging and ensure adequate airflow.
- Check the spark plug and replace it if it shows signs of wear or carbon buildup.
- Keep the fuel system clean by replacing the fuel filter and checking for leaks.
- Monitor the carburetor for proper adjustment and cleanliness to ensure smooth fuel delivery.
Cooling System and Its Role
The cooling mechanism plays a critical role in maintaining engine performance by regulating temperature levels. Excessive heat can damage engine components, leading to reduced efficiency and premature wear. By dissipating heat, the system ensures the longevity of the engine and prevents potential malfunctions.
Key functions of an effective cooling system include:
- Preventing overheating by maintaining optimal operational temperature.
- Protecting engine parts from thermal stress, ensuring smooth performance.
- Improving fuel efficiency by stabilizing engine conditions.
- Enhancing the durability of internal components by reducing wear and tear.
Regular maintenance of the cooling system ensures consistent performance and avoids costly repairs. Components like the radiator, fan, and coolant are essential for effective heat management, and ensuring their proper function is vital for the engine’s health.
Fuel Delivery Mechanisms
Effective fuel delivery is essential for the smooth operation of any internal combustion engine. The system responsible for transporting and managing fuel ensures that the engine receives the correct amount of fuel at the appropriate time. Without a precise mechanism in place, performance can be compromised, leading to inefficiency or failure to start.
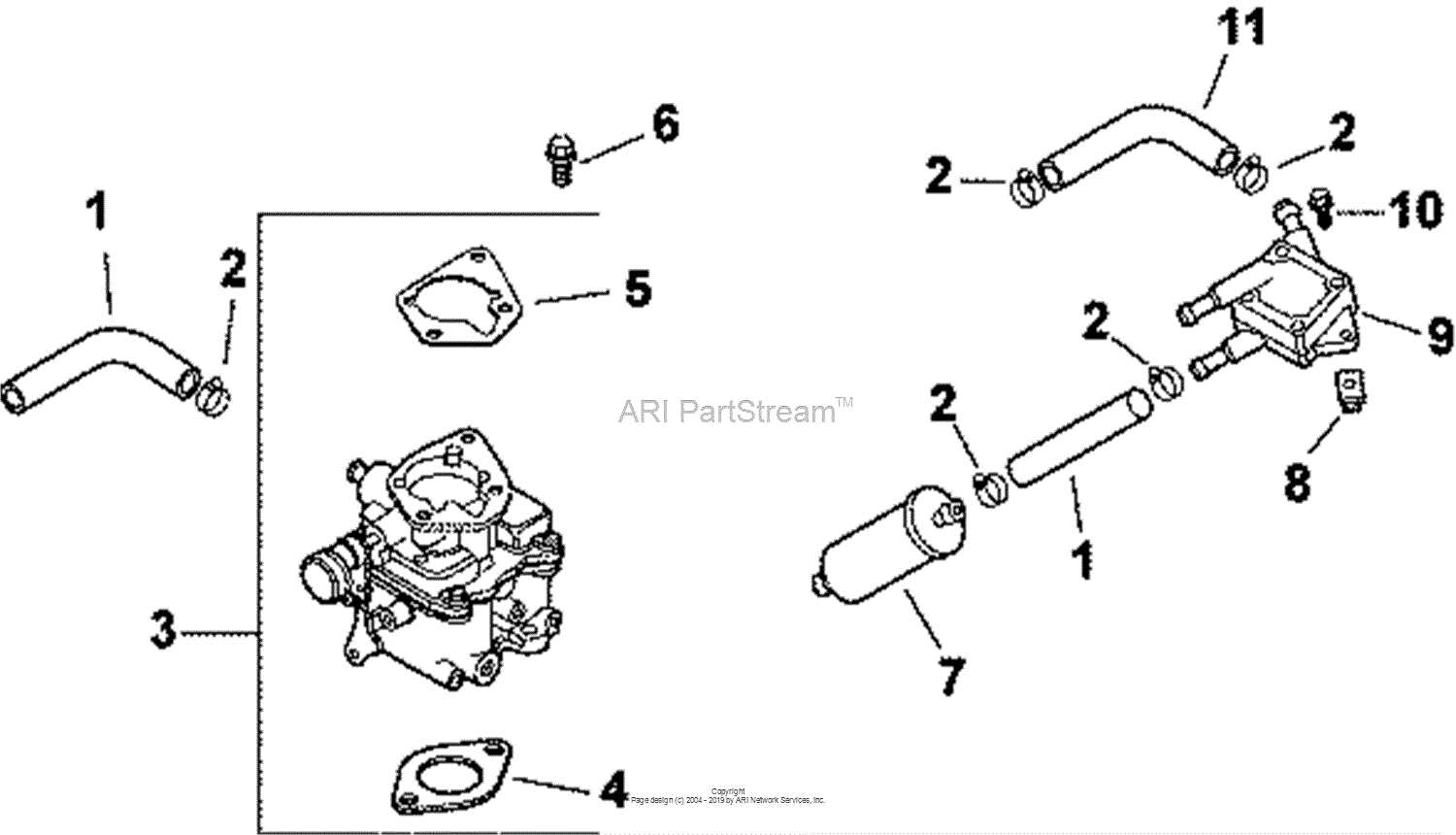
Components Involved in Fuel Transfer
The fuel delivery system typically consists of a series of components that work together to transport fuel from the tank to the engine. These include fuel lines, pumps, filters, and injectors, each playing a crucial role in ensuring that fuel is delivered cleanly and reliably. Fuel pumps provide the necessary pressure, while filters ensure that contaminants are kept out of the system.
Fuel Regulation and Timing
Fuel regulation is controlled by systems that manage the timing and flow of fuel, ensuring optimal combustion. This regulation is key to maintaining efficiency and preventing damage to the engine. Components like fuel regulators adjust the fuel pressure, while sophisticated systems in modern engines fine-tune the timing of fuel injection to match the demands of the engine at any given moment.
Ignition System Breakdown
The ignition system plays a crucial role in ensuring that the engine starts and operates smoothly. This system is responsible for igniting the air-fuel mixture within the engine’s combustion chamber, creating the power needed for movement. A reliable ignition system is essential for efficient engine performance and longevity.
Key Components
The ignition system consists of several key elements, including the spark plug, ignition coil, and flywheel magnet. These parts work together to produce the spark necessary for combustion. The spark plug receives the electrical charge from the coil, which is activated by the movement of the flywheel magnet. Proper synchronization of these components is vital to prevent misfires or engine failure.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Over time, components such as the ignition coil or spark plugs may wear out, leading to starting problems or inefficient performance. Common issues include weak or inconsistent sparks, which can result in misfiring, poor fuel efficiency, or difficulty starting the engine. Regular inspection and replacement of worn-out parts help maintain optimal ignition system function.
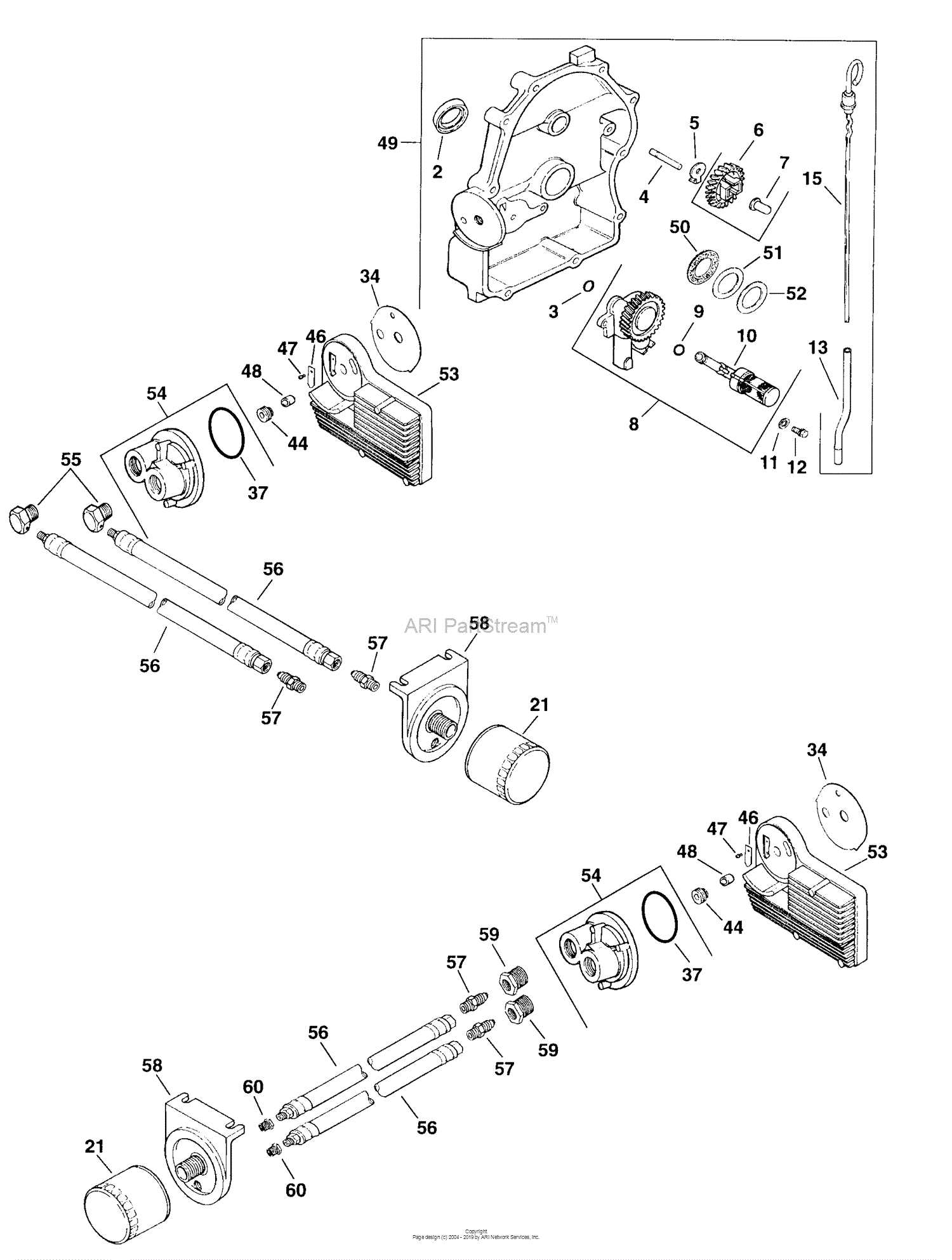
Lubrication and Oil Circulation
Efficient lubrication is essential for the proper functioning of an engine, ensuring smooth operation and preventing wear. The circulation of oil plays a critical role in reducing friction between moving parts, thereby enhancing longevity and performance. In this system, oil is continuously pumped through the engine to maintain optimal performance and to cool various components.
- The oil pump, powered by the engine, draws in oil from the sump and delivers it to key areas that require lubrication.
- The oil is filtered to remove contaminants before it circulates through the engine’s internal components.
- Critical engine parts such as the crankshaft, camshaft, and valve lifters benefit from this constant flow of oil, which minimizes wear and tear.
- Oil also acts as a coolant, absorbing heat generated by the engine and transferring it to the oil cooler, helping maintain safe operating temperatures.
Regular maintenance and proper oil levels are crucial for ensuring the oil circulation system functions efficiently. Lack of proper lubrication can lead to severe damage, causing overheating or mechanical failure.
Understanding the Crankshaft Function

The crankshaft is a central component in converting the linear energy of a piston into rotational force, which powers various mechanical systems. Its smooth operation is essential for the efficiency and longevity of the engine, as it supports the dynamic motion and synchronizes the engine’s power cycle.
Role in Engine Operation
Located at the heart of the engine, the crankshaft plays a crucial role in transforming the up-and-down movement of the piston into rotational motion. This rotational force is then transmitted to the rest of the engine components, enabling the vehicle or machinery to operate effectively. Here’s how the crankshaft operates within the engine:
- The piston moves in a linear motion due to the combustion process.
- This linear motion is transferred to the crankshaft through a connecting rod.
- The crankshaft rotates, delivering power to the drive mechanisms like the transmission or alternator.
Importance for Engine Balance
The balance of the crankshaft is integral to the smooth functioning of the engine. An unbalanced crankshaft can lead to vibrations, reducing efficiency and increasing wear. Proper engineering ensures the crankshaft is finely tuned, allowing it to absorb and distribute forces evenly during operation.
Transmission and Gear Interaction
The mechanism that transmits power between various components is vital for ensuring smooth operation. This system, composed of several interdependent parts, facilitates the transfer of energy to the driven elements. Understanding the interaction between these parts is essential for efficient performance and longevity.
The main components of the system are the transmission and the gear assemblies. These elements work together to regulate the flow of power, allowing the engine to operate under different load conditions. Proper alignment and synchronization are crucial for preventing wear and ensuring effective functioning.
- Transmission: It serves as the conduit for power transfer from the engine to the drive components, using various internal mechanisms to adjust output speed and torque.
- Gears: These are the precise elements that mesh to control the direction and efficiency of the power flow, contributing to the overall speed and force exerted by the system.
- Interaction: The interaction between the gears and transmission ensures the power is evenly distributed, adjusting to various operating conditions without excessive strain on any individual part.
Regular maintenance and checks are necessary to keep these components in good condition. Ensuring the gears are properly lubricated and the transmission system is free from blockages will promote smoother engagement and reduce the risk of failure.
Air Intake and Exhaust Systems
The air intake and exhaust mechanisms play a crucial role in engine performance by regulating airflow. These systems are designed to ensure efficient combustion and optimal engine operation. Proper airflow influences fuel efficiency, engine power, and emissions, making these components essential for long-term engine health and functionality.
The intake system is responsible for drawing in air, filtering out debris, and directing it to the engine’s combustion chamber. A clean and efficient intake ensures a steady flow of oxygen, which is necessary for the combustion process. Meanwhile, the exhaust system expels the gases created by combustion, helping to reduce backpressure and maintain engine efficiency. Both systems must be properly maintained to avoid damage and to ensure that the engine runs smoothly at all times.
Common Troubleshooting Tips
When dealing with mechanical systems, it’s important to know how to approach issues that may arise. Understanding how to identify common problems can save time and prevent unnecessary repairs. The following tips cover some of the most frequent challenges users encounter and provide guidance on resolving them effectively.
Engine Fails to Start
If the engine is not starting, ensure that the fuel supply is adequate and clean. Check the ignition system for potential faults such as worn spark plugs or a faulty ignition coil. Also, inspect the air filter and ensure there is no blockage preventing airflow.
Excessive Vibration
Excessive shaking or vibration can indicate loose components or imbalanced parts. Make sure all mounting bolts are securely fastened and check for any signs of wear or damage on rotating components. Balancing the moving parts may help reduce the vibrations significantly.
Proactive maintenance and timely inspections can help maintain optimal performance and extend the lifespan of the system.