
When dealing with intricate mechanical systems, understanding the individual elements and how they fit together is crucial for both maintenance and repair. Each component serves a vital role, ensuring smooth operation and long-term efficiency. A well-organized layout of these elements helps users quickly identify areas that need attention, ensuring a streamlined approach to troubleshooting.
The layout of a machine’s internal components not only assists in identifying specific issues but also provides valuable insight into the system’s overall design. Recognizing how different elements connect and interact allows for better decision-making when it comes to replacements or upgrades. By visualizing these connections, one can efficiently manage repairs and avoid unnecessary
Understanding the Kubota L3430 Structure

The overall framework of this agricultural vehicle is designed to provide efficiency, durability, and versatility in various field operations. Its layout is structured to optimize performance while ensuring ease of use and maintenance for operators.
Key components are strategically arranged to enhance functionality. Below is
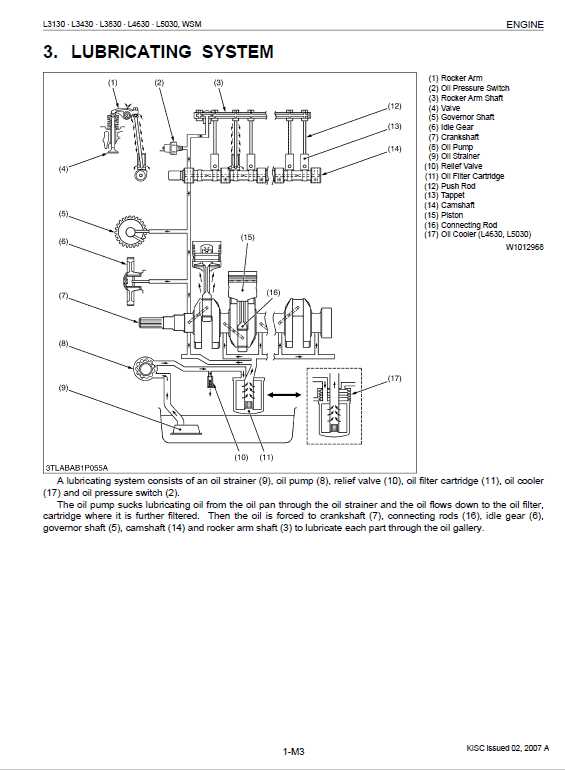
Key Engine Components and Functions
The internal structure of an engine is designed to perform a variety of tasks that work in unison to ensure smooth and efficient operation. Understanding the core elements that drive this system is essential for maintaining and troubleshooting performance.
Cylinder and Piston Operation
The cylinder is the central chamber where fuel combustion occurs, driving the piston. The piston moves up and down within the cylinder, converting the force from combustion into mechanical energy. This energy is then transferred to other components, allowing the system to generate power.
Crankshaft and Valve Timing
The crank
Hydraulic System Overview and Parts
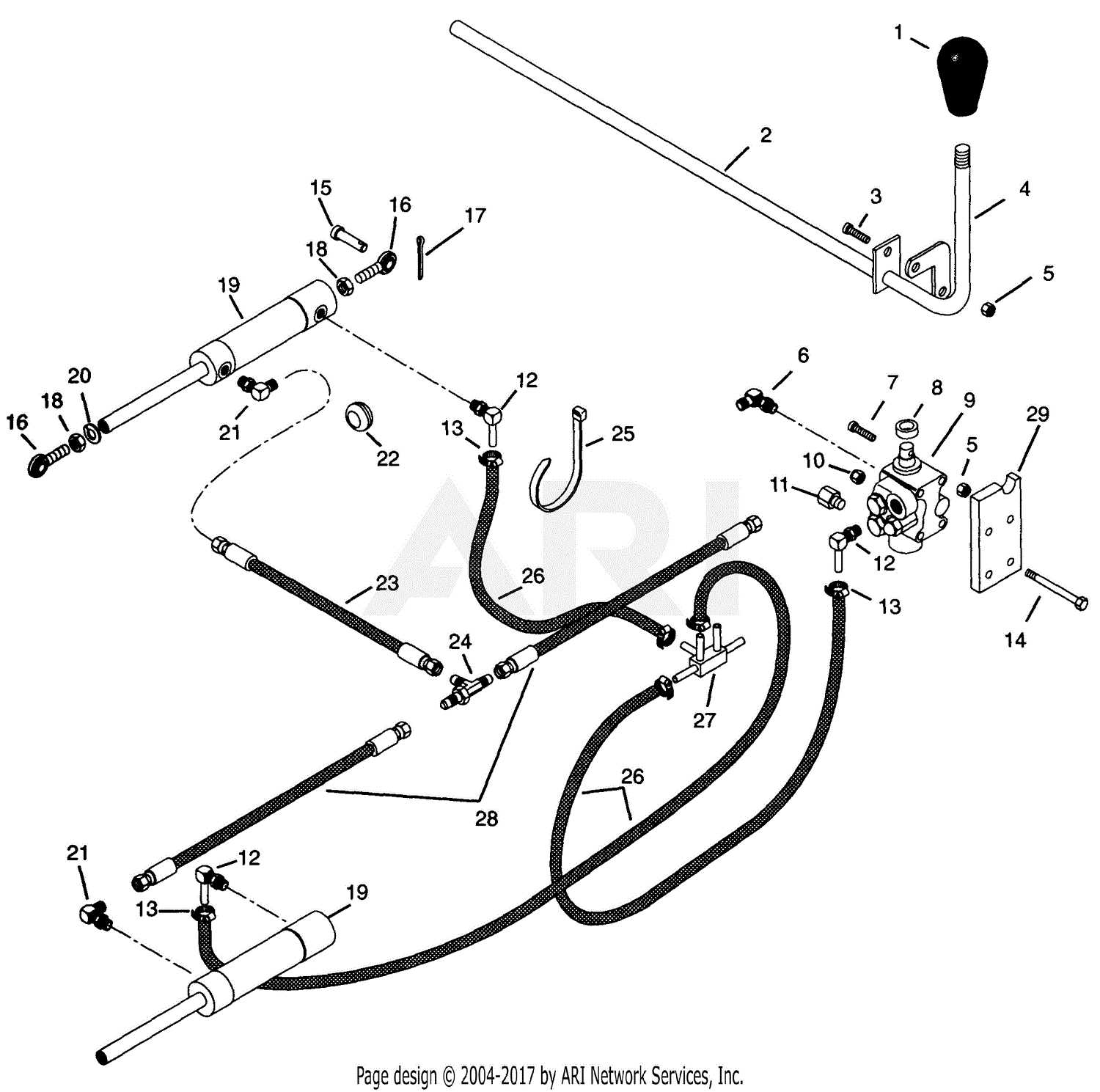
The hydraulic mechanism is a critical component in the operation of modern agricultural machinery. This system facilitates the movement of various elements by transferring fluid power through pressurized liquid. By utilizing this method, the equipment achieves precise control and smooth functioning in a wide range of applications.
Key elements of this mechanism include the pump, which generates the necessary fluid flow, cylinders that convert hydraulic energy into mechanical force, and valves that regulate the pressure
Exploring the Transmission Assembly
The transmission assembly plays a crucial role in ensuring that power generated by the engine is properly transferred to the wheels, enabling smooth operation and control. Understanding its components and how they work together is essential for efficient maintenance and repair.
Main Components of the Assembly
This assembly consists of several interconnected elements that work in harmony. Each piece has a specific function, contributing to the overall performance of the vehicle.
- Fuel Tank: The reservoir that stores the fuel before it is delivered to the engine.
- Fuel Pump: Responsible for transferring fuel from the tank to the engine at the correct pressure.
- Fuel Filter: Ensures that contaminants are removed from the fuel, protecting the engine from potential damage.
- Fuel Injectors: Precisely spray the fuel into the combustion chamber, ensuring the correct mixture for efficient ignition.
- Fuel Lines: These pipes transport fuel between the tank, pump, and injectors, maintaining a secure flow without leaks.
- Brake Pads: These create friction against the rotating surface to slow down the machinery.
- Brake Discs: The discs work in tandem with the pads, providing the necessary surface for friction.
- Calipers: These house the brake pads and apply pressure during braking.
- Hydraulic Lines: Responsible for transmitting pressure from the pedal to the calipers, facilitating smooth operation.
- Inspecting brake pads for wear and tear.
- Checking hydraulic fluid levels to ensure proper function.
- Cleaning components to prevent debris accumulation.
- Unusual noises during operation
- Inconsistent performance or power loss
- Leaking fluids
- Excessive vibration
Electrical System and Wiring Layout
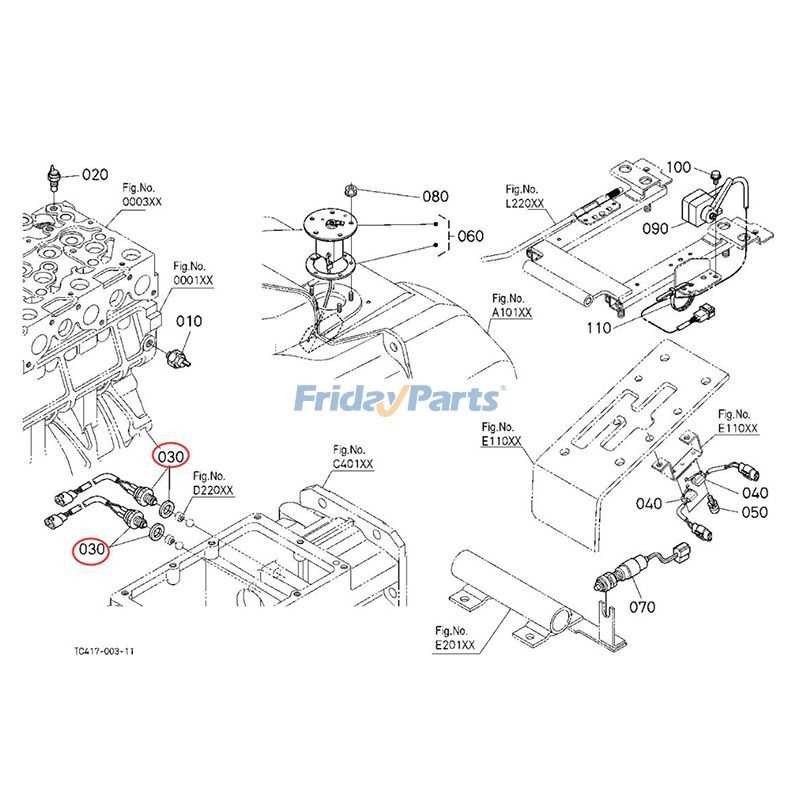
The electrical framework of modern machinery plays a vital role in ensuring all components function harmoniously. Understanding the connections and pathways between various electrical elements is essential for troubleshooting, repairs, or modifications.
Key Components Overview
The system consists of several essential elements that work together to distribute power effectively. These include a power source, a control unit, and various sensors that monitor operations. The wiring layout is crucial in connecting these parts, ensuring that signals are transmitted without interruption.
Wiring Layout and Connections
Wiring diagrams typically show the arrangement of electrical cables
Front Axle and Steering Components
The front axle and steering components play a vital role in ensuring the maneuverability and stability of agricultural machinery. These elements work together to facilitate smooth handling and support the weight of the vehicle, providing both durability and reliability in various working conditions.
Understanding the configuration and function of these components is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Below is a summary of the key elements that comprise the front axle and steering assembly:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Axle Housing | Encases the axle and supports the weight of the front end. |
| Spindle | Connects the wheel assembly to the axle, allowing for rotation. |
| Steering Knuckle | Facilitates the turning motion of the wheels. |
| Control Arm | Connects the steering knuckle to the chassis, providing stability. |
| Steering Gearbox | Converts the steering wheel motion into wheel movement. |
Fuel System Breakdown and Function
The efficiency and reliability of an engine heavily depend on its fuel delivery mechanism. Understanding how this system operates is crucial for maintenance and troubleshooting. A well-designed fuel system ensures optimal performance by managing the flow and pressure of the fuel necessary for combustion.
In essence, the fuel system consists of several key components, each playing a vital role in the overall function:
Each of these components works in harmony to provide the necessary fuel for the engine’s operation. Regular inspection and maintenance of the fuel system are essential to prevent performance issues and extend the lifespan of the engine.
Maintenance Tips for Cooling Systems
Proper upkeep of cooling systems is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of machinery. Regular attention to these components not only prevents overheating but also enhances overall efficiency. This section outlines key practices that can help maintain these vital systems in peak condition.
Regular Inspection and Cleaning

Frequent examination of the cooling components is crucial. Check for any debris or buildup that may hinder airflow. Cleaning radiators, fans, and hoses will promote better heat dissipation. Ensure that all connections are secure and free from leaks, as even minor issues can lead to significant problems over time.
Monitoring Fluid Levels and Quality
Maintaining appropriate levels of coolant is vital for effective thermal regulation. Regularly inspect the fluid levels and top off as necessary. Additionally, monitor the quality of the coolant; it should be free of contaminants and not exhibit signs of corrosion. Replacing the coolant at recommended intervals will help prevent system failures and extend the lifespan of cooling components.
Understanding the Brake Assembly
The brake assembly is a crucial component in any machinery, ensuring safety and control during operation. This system works by creating friction, allowing for the effective slowing and stopping of equipment. A thorough understanding of its parts and functionality can enhance maintenance practices and prolong the lifespan of the equipment.
Components of the Brake System
Key elements of the brake assembly include the following:
Maintenance Tips
Regular inspection and maintenance of the brake assembly are essential for optimal performance. Key maintenance practices include:
Troubleshooting Common Mechanical Issues
Understanding how to identify and resolve prevalent mechanical problems is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of machinery. This section provides insights into typical issues that operators may encounter and offers practical solutions to address them.
Identifying Symptoms

Recognizing the signs of mechanical malfunctions is the first step in troubleshooting. Common symptoms include:
Common Solutions
Once symptoms are identified, addressing the root causes can help restore functionality. Consider the following solutions:
- Inspect Fluid Levels: Ensure all fluids are at optimal levels to prevent overheating and maintain proper lubrication.
- Check for Loose Connections: Tighten any loose bolts or fasteners that may contribute to vibrations or instability.
- Replace Worn Components: Identify and replace any worn or damaged parts to enhance overall performance.
- Regular Maintenance: Schedule routine inspections and maintenance to catch potential issues before they escalate.
How to Identify
Recognizing specific components within machinery can significantly enhance repair and maintenance efforts. This section outlines essential strategies for distinguishing various elements, ensuring efficient identification and optimal performance of the equipment.
Visual Inspection
Begin by conducting a thorough visual examination of the machinery. Look for unique characteristics that can help in recognizing components:
- Color and texture variations
- Size and shape differences
- Labels or markings indicating specifications
- Any signs of wear or damage
Referencing Manuals
Consulting operational manuals can provide valuable insights into component identification. Manuals often include:
- Illustrations and descriptions
- Part numbers and specifications
- Assembly guidelines
- Maintenance tips for various elements