Understanding the relationships between components and their collective formation is essential in various fields. These visual tools serve to clarify how individual elements interconnect, creating a comprehensive picture of the subject at hand. By utilizing these illustrative methods, complex ideas can be simplified, enabling better grasp and retention.
Such representations are invaluable for learners and professionals alike. They facilitate a deeper exploration of structures, allowing one to dissect and analyze intricate systems. The ability to visualize how parts contribute to a larger entity enhances comprehension and promotes insightful discussions.
In educational contexts, these visuals empower students to engage more actively with material. They transform abstract concepts into tangible illustrations, aiding in the ultimate understanding of the content. By bridging gaps in knowledge, these tools support a more holistic learning experience.
Understanding Part Whole Diagrams
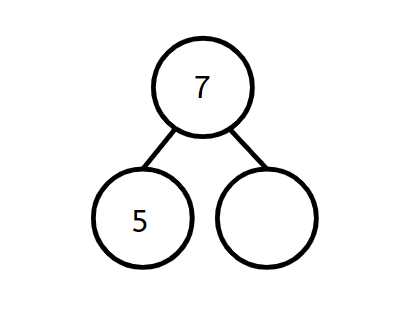
This section explores the concept of visual representations that illustrate relationships between components and their larger contexts. Such visual aids help to clarify how individual elements contribute to a complete system, enhancing comprehension and organization of information.
These illustrations serve as powerful tools for educators and learners alike, providing a clear framework for analyzing complex subjects. By breaking down intricate ideas into manageable segments, users can easily grasp the interconnectedness of various aspects.
Ultimately, utilizing these visual formats can foster deeper insights, allowing for more effective problem-solving and critical thinking. Understanding these structures can significantly enhance one’s ability to synthesize knowledge and communicate ideas clearly.
Definition and Key Concepts
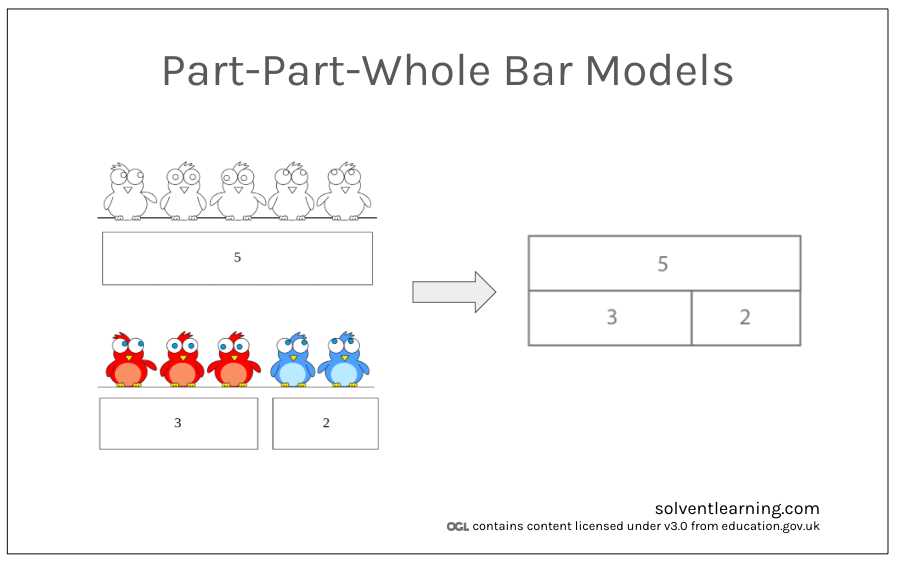
This section delves into the foundational ideas surrounding the visual representation of relationships between elements and their subsets. Understanding these concepts is essential for grasping how various entities are interconnected and how they can be organized into hierarchical structures.
At its core, the practice involves illustrating the connections and distinctions among different components. This can enhance comprehension and facilitate better communication of complex information. Here are some fundamental notions associated with this topic:
- Elements: The individual items or components that are being analyzed or represented.
- Subsets: Groups formed from larger collections, showcasing specific characteristics or qualities.
- Relationships: The connections that illustrate how elements interact or relate to one another.
- Hierarchy: The arrangement of components in levels of importance or inclusion, often depicted to clarify the structure.
- Visualization: The act of creating a graphical representation that aids in understanding complex information.
By familiarizing oneself with these key concepts, one can better appreciate the methodology behind these representations and their practical applications in various fields.
Historical Background and Development
The exploration of relationships between components and their aggregates has been an essential aspect of human understanding for centuries. This conceptual framework has evolved over time, adapting to various disciplines, from philosophy to mathematics, and has played a crucial role in how we visualize and interpret complex information.
Ancient Roots
In ancient civilizations, scholars and thinkers sought to categorize knowledge in a manner that reflected interconnectedness. Philosophers such as Aristotle laid the groundwork for understanding classification, while early mathematicians began to represent numerical relationships through rudimentary graphical methods. These early efforts set the stage for future advancements in visual representation.
Modern Developments
With the Renaissance came a surge in scientific inquiry and the systematic study of relationships. Thinkers like Descartes and Newton employed graphical methods to convey their ideas, emphasizing clarity and precision. The 20th century witnessed a significant transformation with the advent of information theory and graphic representation techniques, leading to the sophisticated visual tools we use today. As technology advanced, the ability to create intricate visuals for data analysis and educational purposes became more accessible, reflecting a continuous evolution in our approach to understanding interconnectedness.
Types of Part Whole Diagrams
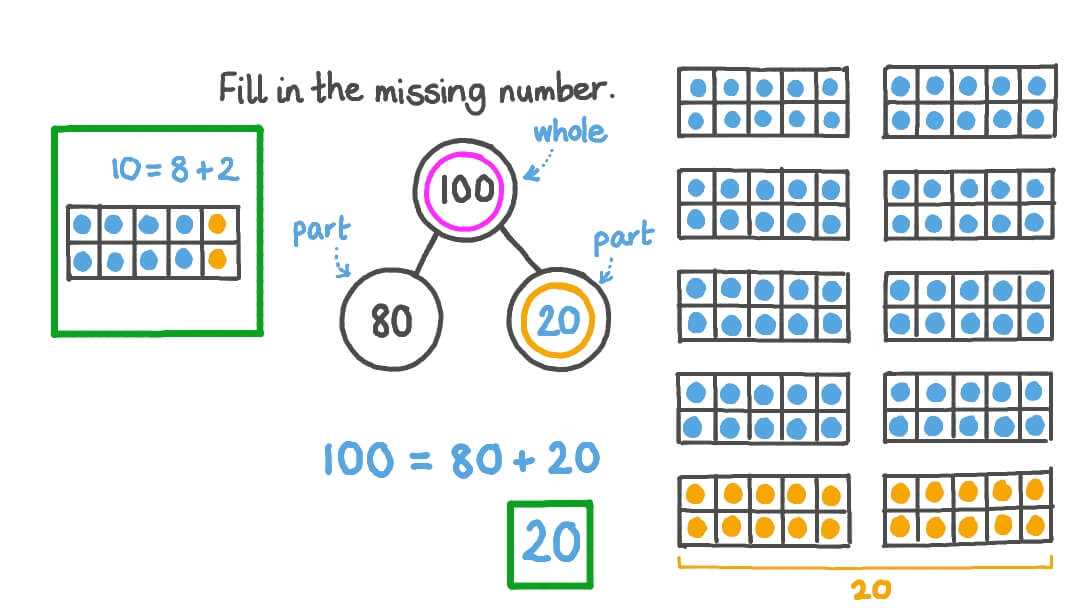
Exploring various representations that illustrate the relationship between components and their larger constructs reveals a rich diversity in approaches. Each format serves a unique purpose, allowing for a clearer understanding of how individual elements interact within a greater framework.
Hierarchical Models
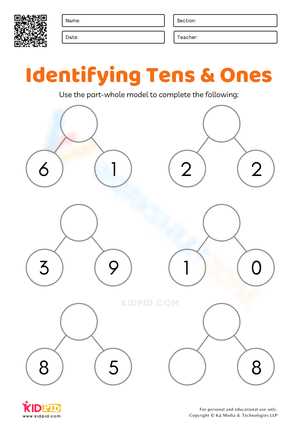
Hierarchical models depict a structured arrangement where elements are organized in levels, demonstrating the relationship between broader categories and their subcategories. This format is particularly useful in visualizing organizational structures or classification systems.
Venn Representations
Venn representations utilize overlapping circles to show how different groups intersect and share common attributes. This method effectively illustrates relationships among multiple sets, making it a powerful tool for comparing and contrasting distinct categories.
Applications in Education and Learning
Visual representations play a crucial role in the educational process, helping learners to grasp complex concepts and relationships. By organizing information in a clear and accessible manner, these tools facilitate deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. They encourage students to explore connections between ideas, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
In classrooms, these illustrations can be utilized to enhance lessons across various subjects, from science to literature. Educators often incorporate them to outline key themes, break down intricate systems, or illustrate historical events. This method not only supports diverse learning styles but also engages students, making the learning experience more interactive and enjoyable.
Moreover, such visual tools are effective for collaborative learning. They enable groups to brainstorm and visualize their thoughts collectively, promoting teamwork and communication. As students work together to create and interpret these illustrations, they develop essential social skills while enhancing their understanding of the material.
In digital learning environments, the versatility of these visual aids is further amplified. Online platforms allow for dynamic and interactive representations, which can adapt to individual learner needs. This flexibility ensures that all students can benefit, regardless of their starting point or preferred learning style.
Ultimately, the integration of these visual strategies in education not only enriches the curriculum but also empowers learners to take charge of their educational journey, making connections that will last beyond the classroom.
Benefits of Using Diagrams
Visual representations serve as powerful tools for conveying complex information in an accessible manner. They enable clearer understanding and enhance communication by simplifying intricate concepts.
- Enhanced Clarity: Visual aids break down complicated ideas into digestible parts, making it easier to grasp essential points.
- Improved Retention: People often remember visual content better than text alone, leading to stronger recall of information.
- Facilitated Problem Solving: These representations help identify relationships and patterns, streamlining the decision-making process.
- Engagement: Visual formats capture attention, encouraging active participation and interaction among viewers.
Incorporating such visuals in presentations or educational materials ultimately fosters a deeper understanding and promotes effective learning experiences.
How to Create Effective Diagrams
Crafting clear and informative visual representations is essential for conveying complex information. A well-structured illustration can simplify intricate concepts, making them accessible to a wider audience. Here are some key strategies to ensure your visuals communicate effectively.
- Define Your Purpose: Before you start, clarify what you want to achieve. Consider the message you wish to convey and the audience’s needs.
- Choose the Right Type: Select the appropriate format for your illustration, such as flowcharts, trees, or matrices, based on the information structure.
- Simplify the Content: Avoid clutter. Use concise labels and limit the number of elements to maintain focus on the main idea.
- Establish a Logical Flow: Organize information in a way that guides viewers through the content naturally, ensuring a clear path from one point to another.
- Use Color Strategically: Implement color to differentiate elements or highlight important parts, but ensure it enhances rather than distracts.
Additionally, consider the following techniques to further enhance your visual representations:
- Incorporate Symbols and Icons: Utilize universally recognized symbols to convey meaning quickly and reduce text reliance.
- Ensure Consistency: Maintain a uniform style in terms of fonts, colors, and shapes to create a cohesive look.
- Gather Feedback: Share your illustration with peers for constructive criticism and make necessary adjustments based on their insights.
- Iterate and Improve: Don’t hesitate to revise your work. Continuous refinement leads to better clarity and effectiveness.
By applying these principles, you can create visuals that not only inform but also engage your audience effectively.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
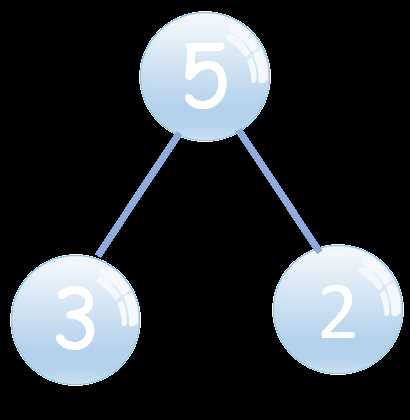
When creating visual representations to illustrate relationships and components, it’s crucial to steer clear of frequent pitfalls that can obscure understanding. These errors can lead to confusion and misinterpretation, undermining the ultimate goal of clarity.
One major mistake is overcrowding the representation with excessive details, which can overwhelm the viewer. It’s essential to maintain simplicity and focus on the primary elements to enhance comprehension.
Another common issue is inconsistent labeling. Using varied terminology for similar concepts can create ambiguity. Consistency is key to ensuring that the audience easily grasps the connections being depicted.
Failing to establish clear hierarchies can also hinder understanding. Properly organizing elements by importance or relevance helps convey the relationships more effectively, guiding the viewer through the information.
Finally, neglecting to review for visual balance can detract from the overall impact. An aesthetically pleasing arrangement can significantly enhance engagement and comprehension, making the information more accessible.
Software and Tools for Diagramming
Creating visual representations of complex information requires effective software and tools that facilitate clarity and organization. These applications help users translate abstract concepts into understandable formats, making communication more efficient across various fields. Choosing the right tool can significantly enhance productivity and collaboration.
Here is a table comparing some popular software options:
| Software | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Lucidchart | Real-time collaboration, templates, integrations | Teams and individuals |
| Microsoft Visio | Extensive shapes library, enterprise-level solutions | Corporate environments |
| Draw.io | Free, user-friendly, web-based | Personal and educational use |
| SmartDraw | Automated formatting, cloud storage | Business presentations |
| Canva | Design-focused, templates, easy to use | Marketing and creative projects |
Each option offers unique advantages, catering to different user needs and preferences. The ultimate choice depends on specific requirements and desired outcomes.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples

This section explores practical applications of visual representations in various fields, highlighting their effectiveness in conveying complex relationships. By examining real-world scenarios, we can understand how these tools facilitate comprehension and decision-making.
| Field | Example | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Education | Curriculum Planning | Improved clarity in course structure |
| Business | Project Management | Enhanced team collaboration |
| Healthcare | Patient Care Plans | Better treatment outcomes |
| Software Development | System Architecture | Streamlined development process |
These examples demonstrate the ultimate value of visual tools in fostering understanding and collaboration across diverse sectors.
Integrating Diagrams into Presentations
Incorporating visual representations into presentations can significantly enhance understanding and retention of information. These visual tools serve as effective means to simplify complex concepts, making them more accessible to the audience. By thoughtfully integrating these elements, presenters can convey their messages with greater clarity and impact.
Benefits of Using Visual Tools
- Enhanced Clarity: Visual elements help break down intricate information into digestible parts, facilitating easier comprehension.
- Improved Engagement: Audiences are often more engaged when presented with visual stimuli, leading to increased interest in the content.
- Memory Retention: Information paired with visuals is more likely to be remembered, making it a powerful tool for learning.
Tips for Effective Integration
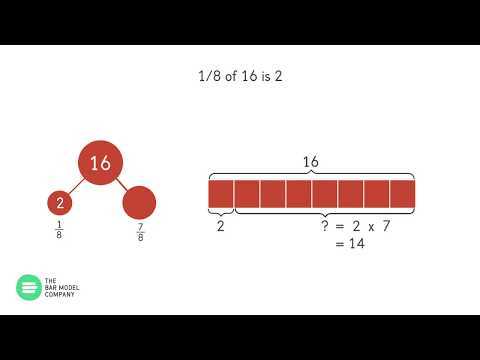
- Relevance: Ensure that each visual element directly supports the key messages of your presentation.
- Simplicity: Avoid clutter. Use clean and straightforward visuals to prevent overwhelming the audience.
- Consistency: Maintain a consistent style and color scheme throughout your visuals to create a cohesive look.
- Practice: Familiarize yourself with the visuals to enhance your delivery and ensure smooth transitions during the presentation.
Future Trends in Diagram Usage
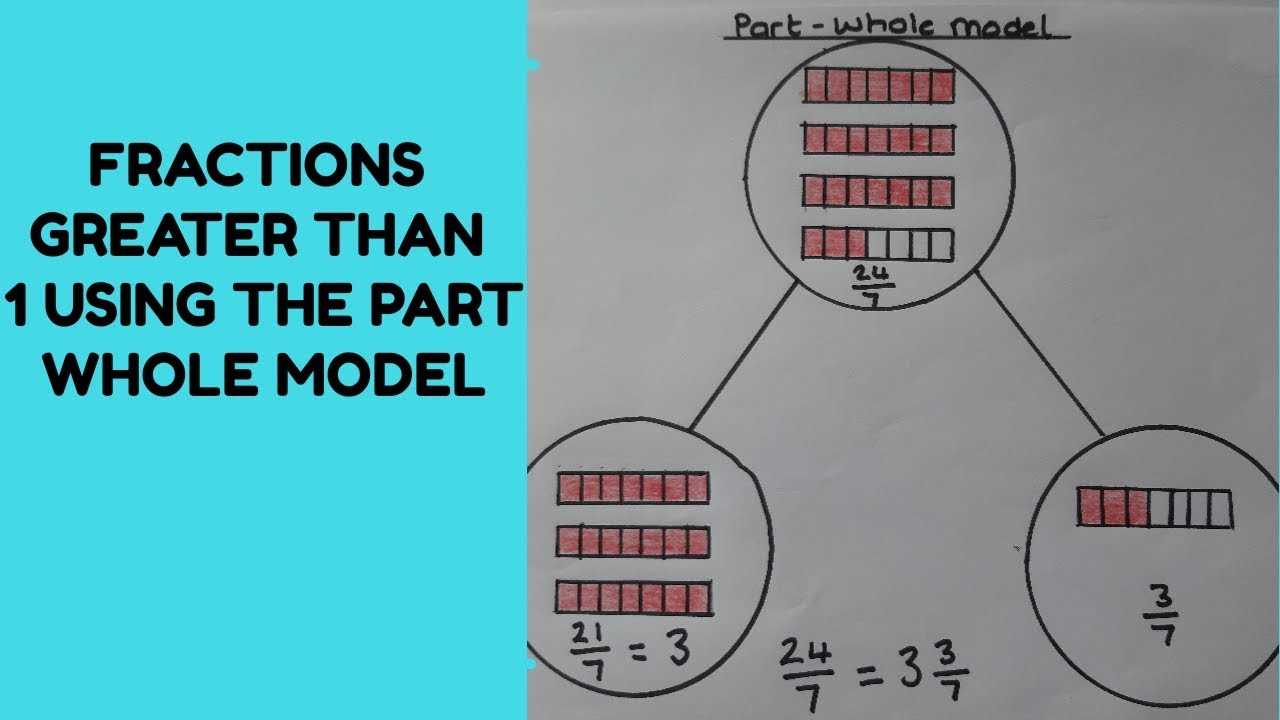
The evolution of visual representation techniques is poised to transform how information is conveyed and understood. As technology advances, innovative methods are emerging to enhance clarity and engagement, making complex data more accessible to diverse audiences.
One significant trend is the integration of interactive elements, allowing users to manipulate representations for deeper insights. This shift fosters a more immersive experience, enabling individuals to explore connections and relationships intuitively.
Additionally, the rise of artificial intelligence will likely streamline the creation process, automating design aspects and suggesting optimal layouts based on content. This could democratize access to high-quality visual tools, empowering users with varying skill levels.
Moreover, the increasing emphasis on storytelling through visuals will influence future designs. By prioritizing narrative flow, creators can guide viewers through information more effectively, enhancing comprehension and retention.
Finally, the move towards collaborative platforms will facilitate real-time sharing and editing, encouraging collective input and enhancing the richness of visual communication. These advancements indicate a future where representation tools are more dynamic, user-friendly, and interconnected.