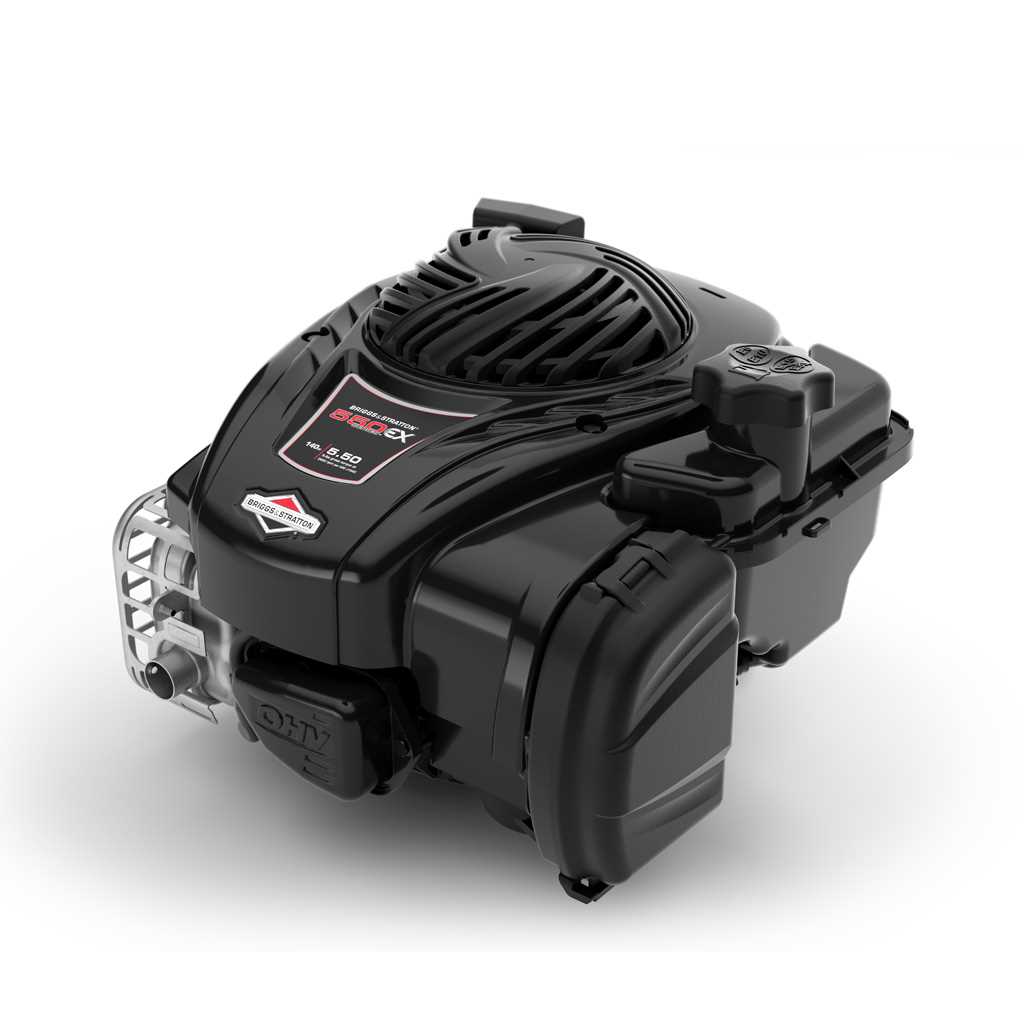

Understanding the various elements that constitute a small engine is essential for effective maintenance and repair. Each engine comprises multiple components that work together to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Familiarity with these elements aids in troubleshooting and enhances the longevity of the equipment.
In this section, we will explore a detailed breakdown of the specific components utilized in various engine models. This comprehensive overview will provide insights into their functions, interconnections, and the overall assembly. By gaining a clearer perspective on these features, users can better navigate the complexities of engine upkeep.
Whether you are a seasoned technician or a novice enthusiast, having access to a visual representation of the engine’s structure can significantly simplify the process of identifying and sourcing replacement components. This guide aims to serve as a valuable resource for anyone looking to deepen their understanding of engine mechanics.
This section aims to explore the essential elements of a specific power unit, focusing on their functions and interrelationships. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of these components, users can better maintain and troubleshoot their equipment, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Core Elements of the Power Unit
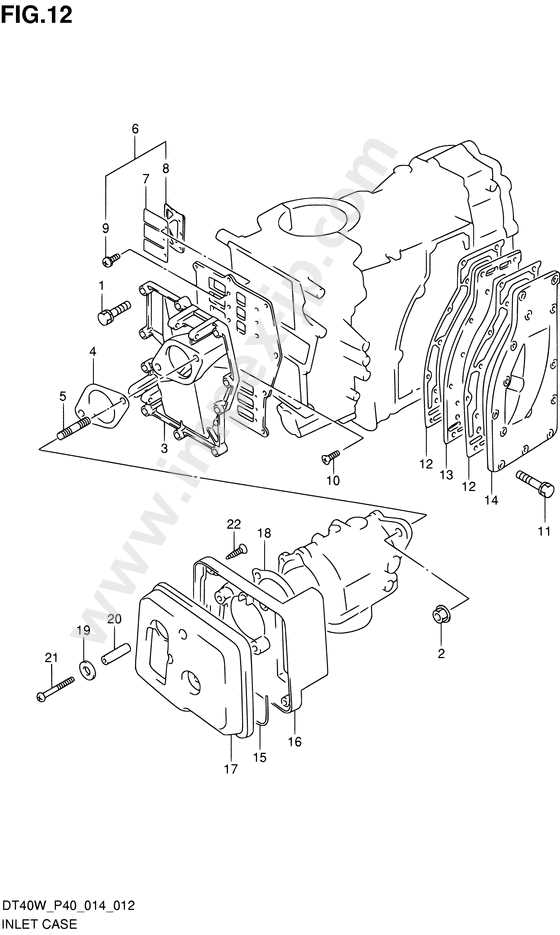
The primary elements that constitute this engine play a crucial role in its functionality. Familiarizing oneself with these components enhances the overall operational knowledge, making it easier to identify any issues that may arise.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Cylinder | Houses the piston, facilitating combustion. |
| Piston | Converts the combustion pressure into mechanical energy. |
| Crankshaft | Transforms linear motion of the piston into rotational motion. |
| Camshaft | Controls the timing of the intake and exhaust valves. |
| Fuel System | Delivers fuel to the combustion chamber for ignition. |
| Ignition System | Generates a spark to ignite the fuel-air mixture. |
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
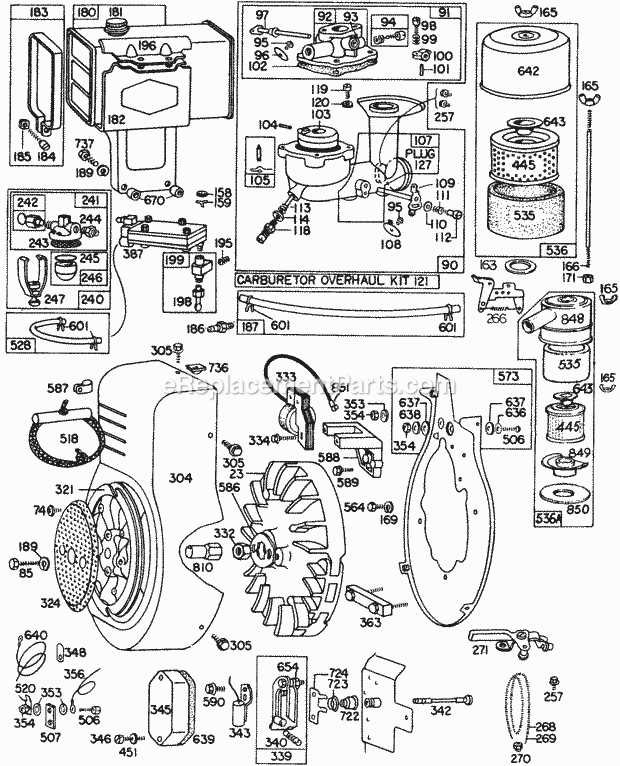
Regular maintenance of the essential components can significantly enhance the efficiency and lifespan of the engine. Simple tasks, such as cleaning filters and checking fluid levels, are crucial for maintaining peak performance.
Key Features of 850 Series
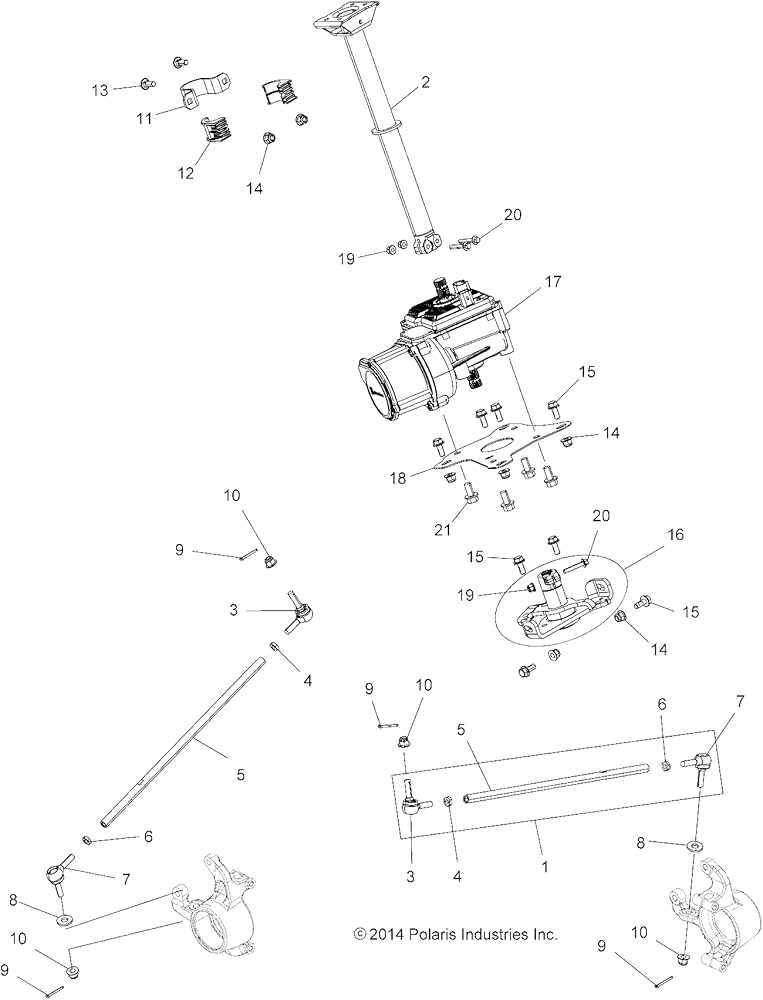
The 850 line is designed to deliver exceptional performance and reliability, catering to various outdoor power equipment needs. Its innovative design incorporates advanced technologies that enhance efficiency and ease of use, making it suitable for both residential and commercial applications.
Power and Efficiency
This model boasts a powerful engine that ensures optimal output, allowing for smooth operation across diverse tasks. Its fuel-efficient design not only reduces consumption but also minimizes emissions, contributing to a greener environment.
Durability and Maintenance
Constructed with high-quality materials, this engine is built to withstand challenging conditions. Regular maintenance is straightforward, thanks to accessible components, ensuring longevity and consistent performance over time.
Parts Identification Guide
This section provides an overview of how to recognize various components within a specific model of small engines. Understanding the function and appearance of each element is crucial for maintenance and repair tasks, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Essential Components Overview
- Engine Block: The core housing that contains the internal parts.
- Cylinder Head: This component covers the top of the cylinder and houses the valves.
- Crankshaft: Responsible for converting the linear motion of the pistons into rotational energy.
- Piston: Moves up and down within the cylinder, creating compression.
- Carburetor: Mixtures air and fuel for combustion.
Identification Tips
- Refer to the manual for a labeled illustration of each element.
- Look for part numbers stamped or printed on each component for easy reference.
- Familiarize yourself with the general shape and function of each part to ease identification.
- Use online resources or forums for additional visual aids and descriptions.
Common Issues and Solutions
This section addresses frequent challenges encountered with small engines, focusing on typical malfunctions and practical remedies. Understanding these issues can enhance performance and prolong the lifespan of your equipment.
- Engine Won’t Start:
- Check the fuel level and quality; stale fuel can cause starting problems.
- Inspect the spark plug for wear or damage; replacing it may resolve ignition issues.
- Ensure the air filter is clean and unobstructed to allow proper airflow.
- Unusual Noises:
- Listen for rattling sounds, which could indicate loose components; tighten as needed.
- Grinding noises may suggest that internal parts are worn; a professional inspection may be necessary.
- Overheating:
- Check the oil level; low oil can lead to overheating and damage.
- Ensure that cooling fins are clean and free of debris to facilitate heat dissipation.
- Poor Performance:
- Examine the fuel filter; a clogged filter can restrict fuel flow.
- Adjust the carburetor settings if the engine is running rich or lean.
By regularly maintaining and addressing these common issues, users can optimize engine functionality and ensure reliable operation.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
To ensure the prolonged efficiency of your equipment, regular upkeep is essential. Implementing effective maintenance practices can enhance performance, minimize wear, and extend the lifespan of the engine. This section outlines vital strategies for optimal care and functionality.
Regular Inspections
- Check fluid levels frequently, including oil and fuel.
- Inspect air filters for cleanliness and replace when necessary.
- Examine the spark plug for wear and proper functionality.
- Look for signs of wear on belts and hoses, replacing them as needed.
Seasonal Maintenance
- At the start of each season, perform a comprehensive cleaning of the exterior to remove dirt and debris.
- Change the oil and oil filter to keep the engine running smoothly.
- Sharpen or replace blades to ensure effective cutting performance.
- Store the equipment in a dry, sheltered area during off-seasons to prevent rust and damage.
Replacement Procedures for Critical Parts
Maintaining the functionality of essential components in small engines is crucial for optimal performance. Understanding the procedures for replacing these vital elements ensures longevity and efficiency. This section outlines the necessary steps for handling replacements effectively.
Identifying Components for Replacement
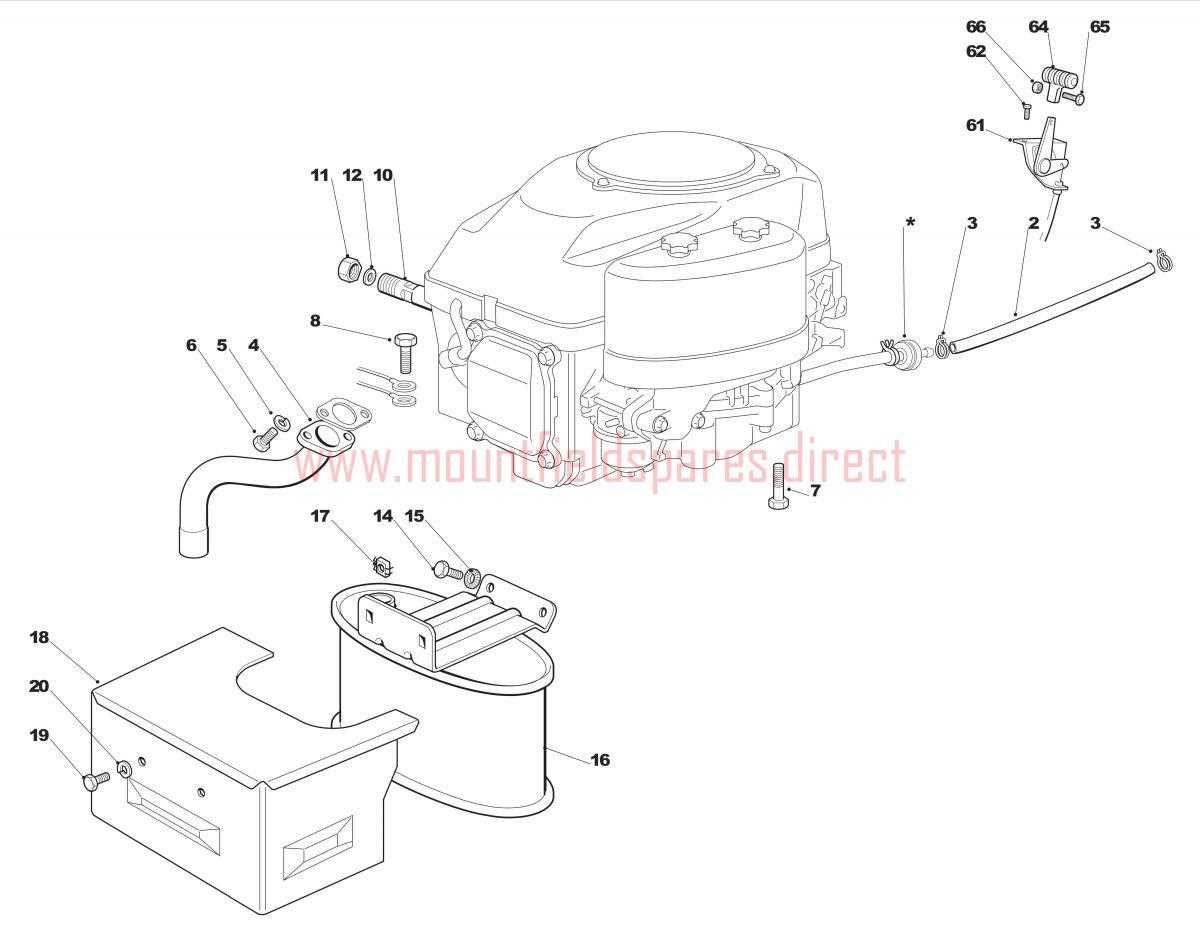
Before initiating the replacement process, it is important to accurately identify the components that require attention. Regular inspections can help detect signs of wear or damage. Look for indicators such as unusual noises, leaks, or decreased performance, which may suggest that specific components need to be replaced.
Replacement Steps
Once the components have been identified, follow these guidelines for a smooth replacement process:
- Gather Tools: Ensure that you have all the necessary tools, including wrenches, screwdrivers, and replacement components.
- Disconnect Power: Safety is paramount. Disconnect the power source to prevent any accidental starts during the process.
- Remove the Old Component: Carefully detach the worn or damaged part, taking note of its orientation and connections.
- Install the New Component: Position the new part in place, ensuring it aligns correctly with the existing setup.
- Reassemble: Once the new component is secured, reattach any covers or shields that were removed.
- Test Functionality: Reconnect the power and conduct a test run to ensure everything operates smoothly.
By following these procedures, users can effectively replace critical components, thereby enhancing the performance and reliability of their equipment.
Understanding the Parts Diagram
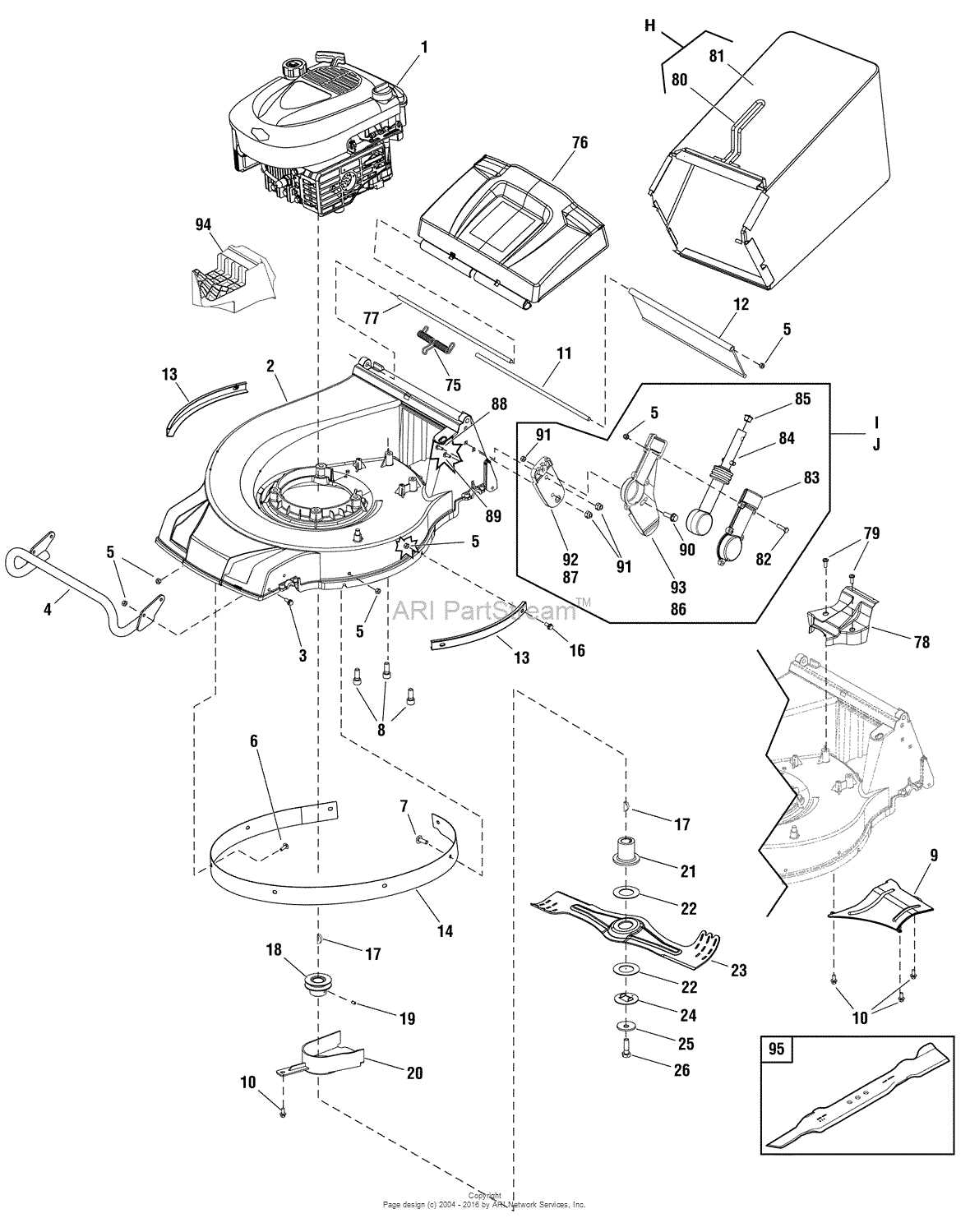
The visual representation of components is essential for anyone looking to comprehend the intricacies of a machine. This illustration serves as a guide, highlighting each element’s position and function, facilitating easier maintenance and repairs.
Importance of the Visual Representation
Grasping the layout of the components allows users to:
- Identify individual elements quickly.
- Understand how different parts interact.
- Streamline the repair process by knowing what to look for.
Interpreting the Illustration
When examining the graphic, pay attention to:
- Labels: Each item is typically marked for easy identification.
- Connections: Observe how various components link together; this is crucial for troubleshooting.
- Ordering Parts: The visual guide aids in determining the correct replacement items needed.
By mastering the layout and function of each element, users can enhance their understanding and efficiency when working with machinery.
Tools Required for Assembly
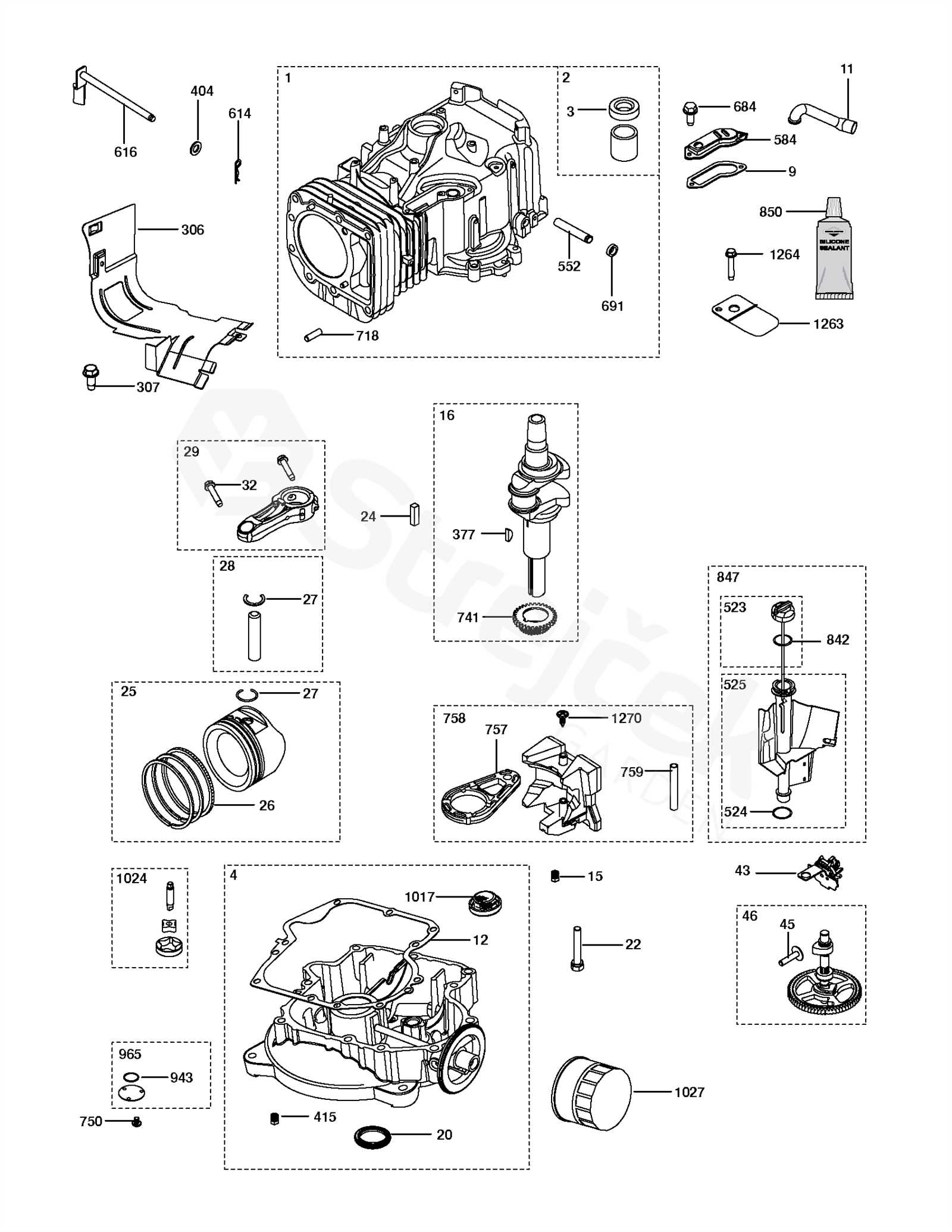
Assembling machinery components necessitates specific instruments to ensure proper functionality and efficiency. Utilizing the right tools simplifies the process, minimizes errors, and enhances overall performance.
Here is a list of essential tools that will aid in the assembly process:
- Screwdriver Set: A variety of sizes and types are needed to accommodate different fasteners.
- Wrench Set: Both open-end and socket wrenches will provide the necessary grip for tightening and loosening bolts.
- Pliers: Useful for gripping, bending, and cutting wires and small components.
- Torque Wrench: Ensures that fasteners are tightened to the specified torque levels, preventing damage.
- Utility Knife: Ideal for cutting through packaging and any excess materials.
- Measuring Tape: Essential for ensuring accurate dimensions during assembly.
Having these tools on hand will facilitate a smooth assembly experience, allowing for efficient and effective construction of the unit.
Safety Precautions During Repairs

When performing maintenance on outdoor equipment, it is essential to prioritize safety to prevent accidents and injuries. Taking the right precautions ensures that both the technician and the machinery remain unharmed throughout the repair process.
Before starting any work, always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and sturdy footwear. These items shield against potential hazards, including sharp components and harmful substances.
Ensure that the device is powered off and disconnected from any electrical source to eliminate the risk of accidental starts. Additionally, allow the engine to cool completely before beginning any repairs to avoid burns or other injuries.
Maintain a tidy workspace by organizing tools and components to reduce the likelihood of tripping or misplacing items. Having everything in its proper place promotes efficiency and safety.
Lastly, familiarize yourself with the manufacturer’s safety guidelines and recommendations specific to the equipment being serviced. Following these protocols will enhance overall safety during maintenance tasks.
Where to Find Genuine Parts
Locating authentic components for your equipment is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and longevity. Reliable sources ensure that you receive high-quality items that match the specifications of your machine, preventing issues that can arise from using substandard alternatives.
Authorized Dealers
One of the best places to find original components is through authorized distributors. These dealers are officially recognized and offer a wide range of genuine items that meet the manufacturer’s standards.
Online Retailers
Numerous reputable online platforms specialize in selling original equipment. These sites often provide detailed descriptions and compatibility information, making it easier to identify the correct items for your specific model.
| Source Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Authorized Dealers | Guaranteed authenticity and support |
| Online Retailers | Convenient shopping and wide selection |
| Manufacturer’s Website | Direct access to the latest offerings |
Comparing with Other Series Models
This section explores the distinctions and similarities between various engine models, highlighting their unique features and functional capabilities. By analyzing these differences, users can make informed decisions about which engine best suits their specific needs.
Key Differences
- Power Output: Each model offers a different power range, affecting the overall performance in various applications.
- Fuel Efficiency: Variations in fuel consumption can influence operational costs and runtime.
- Maintenance Requirements: Some engines may require more frequent servicing or specific parts, impacting long-term usability.
Similarities Across Models
- Design Philosophy: Many models share a commitment to durability and reliability, making them suitable for demanding tasks.
- Common Components: Certain elements, such as air filters and spark plugs, are interchangeable among different models, simplifying repairs.
- User-Friendly Features: Most engines are designed with ease of use in mind, ensuring accessibility for a wide range of users.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section aims to address common inquiries related to engine components and their functionalities. Understanding these aspects can help users navigate issues and enhance their experience with various mechanical systems.
What should I do if my engine won’t start?
If your engine fails to ignite, check the fuel supply, ensure the spark plug is functioning correctly, and examine the battery for sufficient charge. Additionally, look for any blockages in the air intake.
How can I identify the correct replacement components?
To find the right replacement items, consult the user manual or an online resource that provides detailed specifications for your particular model. Cross-referencing part numbers can also be beneficial.
What maintenance tasks are essential for optimal performance?
Regular maintenance tasks include changing the oil, replacing the air filter, inspecting the spark plug, and cleaning or replacing the fuel filter. Following a routine schedule can prolong the lifespan of your engine.
How do I troubleshoot issues with the starting system?
Begin by examining the ignition switch, checking for loose connections or corroded terminals. Testing the battery voltage and ensuring the starter motor operates correctly are also crucial steps in diagnosing starting system problems.
Are there any specific tools required for repairs?
Basic tools such as wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers are typically sufficient for most repairs. However, specialized tools may be necessary for more complex tasks. Always refer to the user manual for specific tool recommendations.