
Exploring the intricate workings of antique crafting devices reveals a fascinating interplay of components that contribute to their functionality. Each element plays a vital role, working harmoniously to create a seamless experience for users. Understanding these mechanisms not only enhances appreciation for the craftsmanship but also provides valuable insights for maintenance and restoration.
Visual representations of these mechanisms are essential for anyone interested in delving deeper into the history and operation of these classic tools. By examining the configuration of various segments, one can gain a clearer understanding of how these instruments operate. This knowledge is particularly beneficial for enthusiasts and collectors aiming to preserve the integrity of their treasures.
Furthermore, appreciating the design and arrangement of these components allows for a greater recognition of the ingenuity behind their creation. Each piece, from the smallest lever to the largest frame, has a purpose that contributes to the overall function. As we explore these relationships, we uncover the artistry and engineering that have stood the test of time.
Understanding Treadle Sewing Machines
This section explores the fascinating world of foot-powered fabric construction devices, delving into their functionality and components. These historical tools blend craftsmanship with mechanical ingenuity, representing a significant advancement in textile creation.
Components of the Device
- Foot Pedal: Controls the movement through manual power.
- Needle Holder: Secures the needle for stitching.
- Bobbin Case: Houses the thread spool for upper and lower threads.
- Feed Dogs: Move the fabric forward during operation.
How They Work
- Pressing the foot pedal initiates motion.
- The needle moves up and down, piercing the fabric.
- Thread tension is adjusted for even stitching.
- The feed dogs advance the fabric for continuous work.
History of Treadle Machines
The evolution of foot-operated devices has significantly shaped the landscape of textile production. These innovations emerged in the 19th century, revolutionizing the way fabrics were crafted and paving the way for mass production. Their impact extended beyond mere functionality, influencing social structures and economic practices.
Initially, these devices offered an accessible alternative to hand stitching, allowing individuals to create garments and household items with greater efficiency. The simplicity of their design made them popular among both amateur and professional users, enhancing productivity.
As time progressed, manufacturers refined these tools, introducing various enhancements that improved their usability and durability. This period saw a surge in domestic manufacturing, as households embraced these innovations, leading to a more self-sufficient lifestyle. The legacy of these devices continues to be felt, as they symbolize a crucial turning point in the history of craftsmanship.
Key Components of Treadle Models
This section explores the essential elements that contribute to the functionality and efficiency of these vintage devices. Understanding these components enhances appreciation for their craftsmanship and operation.
- Base: The sturdy foundation providing stability and support.
- Flywheel: A critical element that maintains momentum during use.
- Foot Pedal: The mechanism allowing manual control for operation.
- Needle Holder: Secures the needle in place for precise stitching.
- Bobbin Case: Houses the bobbin, essential for thread management.
- Stitch Regulator: Controls the length and type of stitch produced.
Each of these components plays a pivotal role, working in harmony to create an ultimate user experience.
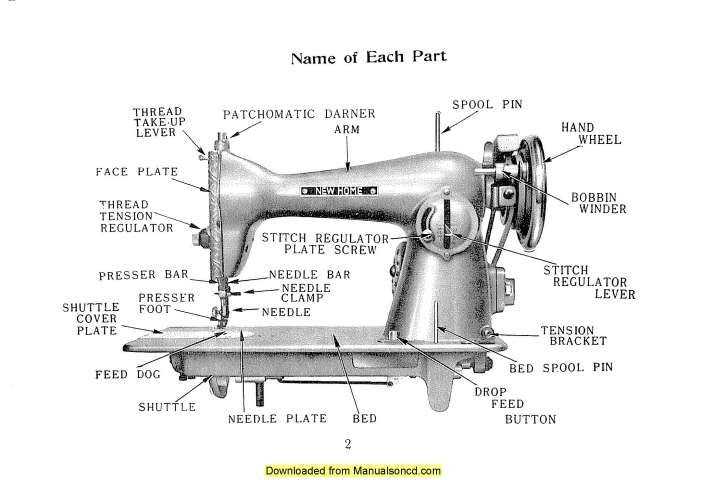
Identifying Machine Parts Easily
Understanding the various components of a mechanical device can significantly enhance your maintenance skills and troubleshooting abilities. Familiarity with each element allows for a smoother workflow and better overall performance.
- Start with the basic framework.
- Recognize the operational elements that drive functionality.
- Identify the supporting features that assist in operation.
To effectively pinpoint each section:
- Consult manuals or online resources for reference.
- Use clear images or visual aids for better comprehension.
- Label components for quick recognition during repairs.
By taking these steps, you’ll ultimately gain confidence in identifying and understanding each crucial element. This knowledge fosters a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of the device.
Common Issues with Treadle Machines
Older pedal-powered devices often face certain recurring challenges due to wear and tear over time. These issues can range from mechanical malfunctions to difficulties with regular operation, affecting the smoothness and efficiency of the work.
Here are some typical problems and their potential causes:
- Difficulty moving the mechanism: One common issue involves the pedal or flywheel becoming stiff or stuck, often due to insufficient lubrication or dust buildup in critical areas.
- Loose or broken belts: The driving belt can wear out, stretch, or snap, leading to inefficient movement or complete halting of the device’s functions.
- Inconsistent motion: Wobbling or jerky movements during operation are often caused by imbalanced parts or improper alignment.
- Noise during use: Creaking or grinding sounds can indicate parts rubbing together incorrectly or the need for cleaning and oiling.
Regular maintenance and timely replacements are key to avoiding these problems and ensuring that these mechanical devices continue to function as intended.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring the durability of your device requires regular upkeep. Proper care not only extends its lifespan but also enhances its overall performance, reducing the need for frequent repairs. Consistent attention to detail can prevent minor issues from turning into costly problems.
One of the key strategies is to regularly clean all moving components to prevent buildup of debris. Lubrication is another essential practice to keep the mechanism running smoothly. Applying the right oil to the appropriate areas minimizes wear and tear over time. Additionally, it is important to check the alignment and tension of various parts to ensure smooth operation and avoid any potential strain on the mechanism.
Lastly, store your device in a dry and clean environment, away from humidity and dust, which could lead to corrosion or mechanical issues. By following these basic steps, you can ensure your device remains functional and efficient for years to come.
How to Repair Treadle Components
When mechanical systems experience wear or malfunction, timely maintenance can ensure smooth functionality. Understanding the underlying mechanics and addressing issues promptly will help extend the lifespan of individual elements and prevent further complications.
Identifying Common Issues
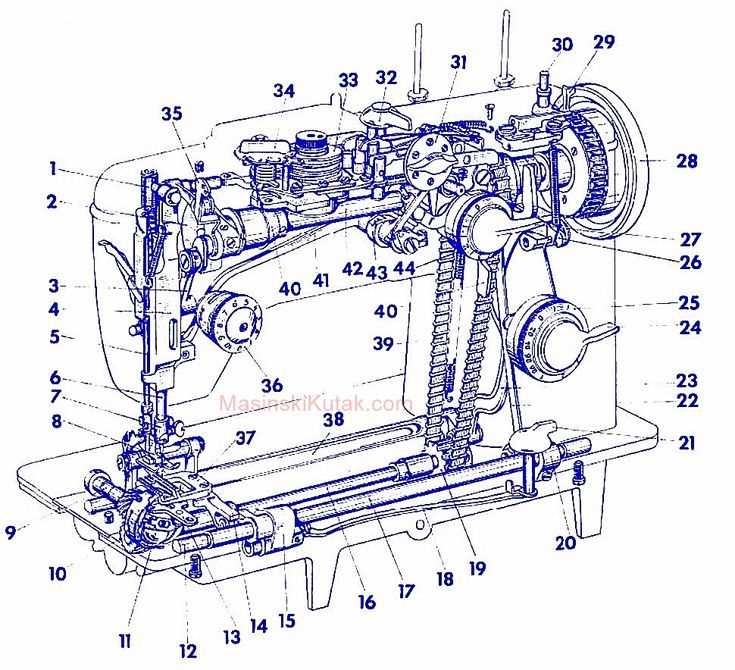
Start by examining areas prone to frequent use and friction. Look for signs of rust, loosening connections, or irregular motion. If any parts appear worn or damaged, disassemble the affected section for cleaning and lubrication. Regular oiling can prevent the build-up of residue and reduce mechanical strain.
Restoring Functionality
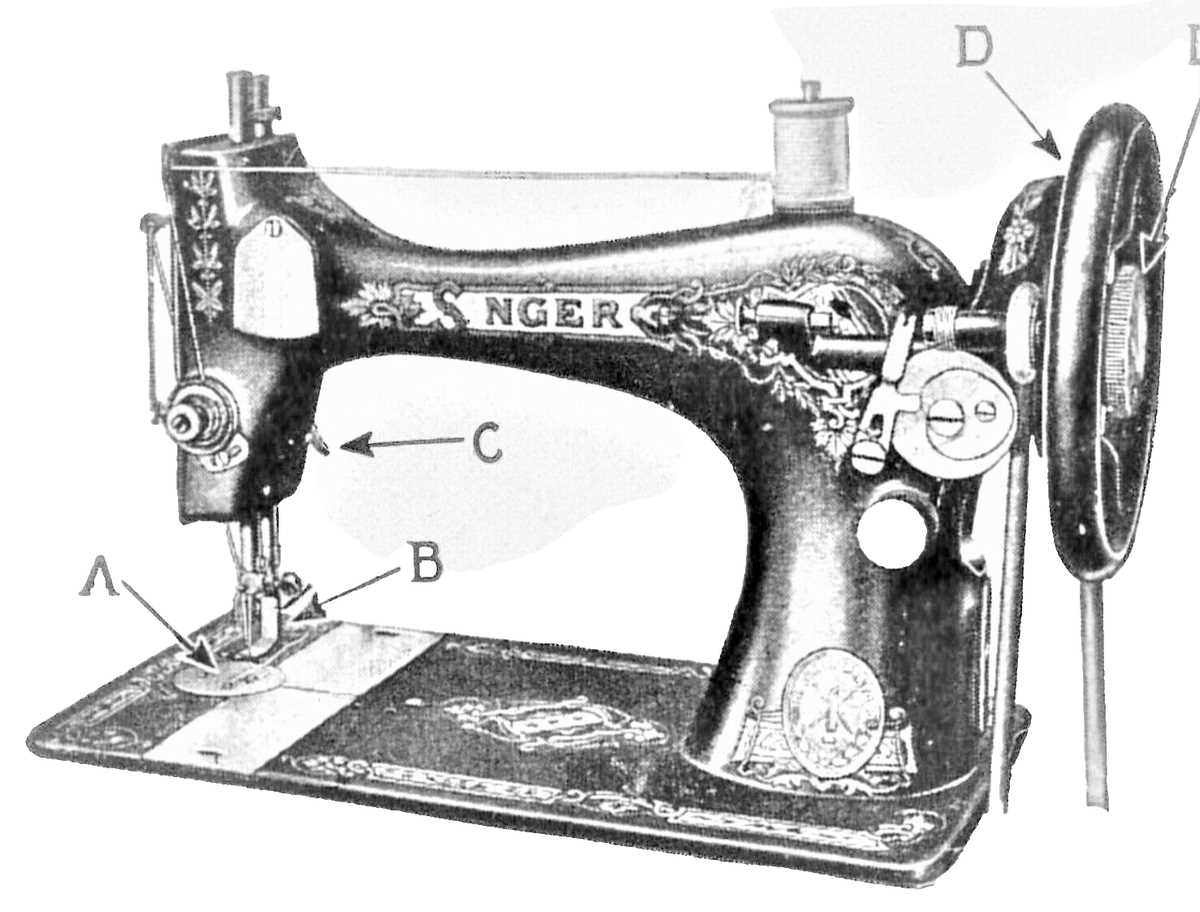
For parts that no longer function smoothly, it may be necessary to replace or realign them. Tighten any bolts or screws that have become loose over time. If certain elements no longer move as they should, inspect the connectors and hinges to ensure they are properly aligned and secure. Correct adjustments can restore optimal performance.
Upgrading Your Treadle Sewing Machine
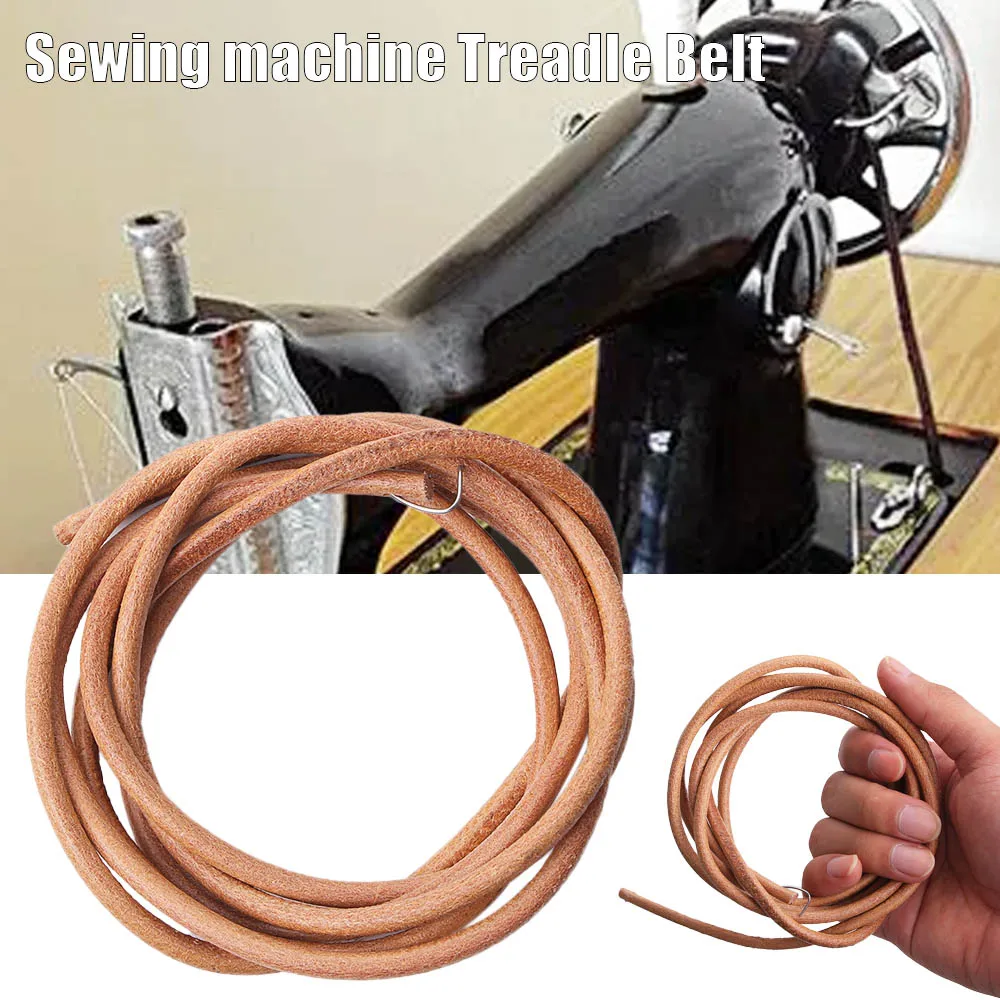

Enhancing your vintage apparatus can significantly improve its functionality and adaptability for modern projects. Whether you aim for smoother operation or additional features, updating this timeless tool offers both practical benefits and a renewed sense of satisfaction in its use.
Key Areas for Improvement
There are several components and aspects that can be upgraded to improve the overall performance. Focusing on the mechanics, ease of use, and versatility will ensure that your unit remains efficient while keeping its original charm intact.
| Upgrade Area | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Drive System | Smoother motion, less manual effort required |
| Stitching Mechanism | More consistent stitches, adaptability to modern materials |
| Accessories | Enhanced versatility, new functionalities |
Modern Adaptations
Consider integrating contemporary features like electric motors or improved lighting to make your experience more convenient without altering the aesthetic. These upgrades allow for seamless transitions between traditional and advanced techniques, catering to modern-day needs.
Safety Features in Treadle Models

Older hand-powered devices may seem simple, but they often include various protective elements designed to ensure safe and reliable operation. These innovations are crucial in preventing accidents during manual use, providing additional security and peace of mind.
Common Protection Mechanisms
Manual-driven systems typically come with mechanical safeguards to limit the risk of injury. These include finger guards, adjustable speed regulators, and automatic disengagement mechanisms. Each of these components plays a key role in making the process safer.
Durability and User-Friendly Design
Another important aspect is the robust construction of these devices. Sturdy frames and smooth-operating foot pedals contribute to a safer experience by reducing the likelihood of malfunction. Additionally, user-friendly layouts with easy-to-reach controls ensure minimal effort in everyday handling.
| Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| Finger Guard | Prevents accidental contact with moving parts. |
| Speed Regulator | Controls the pace of the device to avoid sudden movements. |
| Automatic Disengagement | Stops operation when not actively used to prevent unintended actions. |
Choosing Fabrics for Treadle Sewing
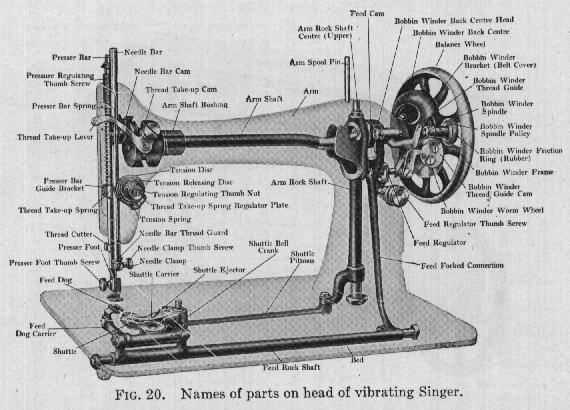
Selecting the right textiles is crucial for successful hand-powered crafting. The texture, thickness, and durability of materials greatly affect the ease and outcome of your project. It’s important to consider the type of fabric based on the final purpose of the item, ensuring that it suits both the technique and the desired look.
Lightweight Options for Beginners
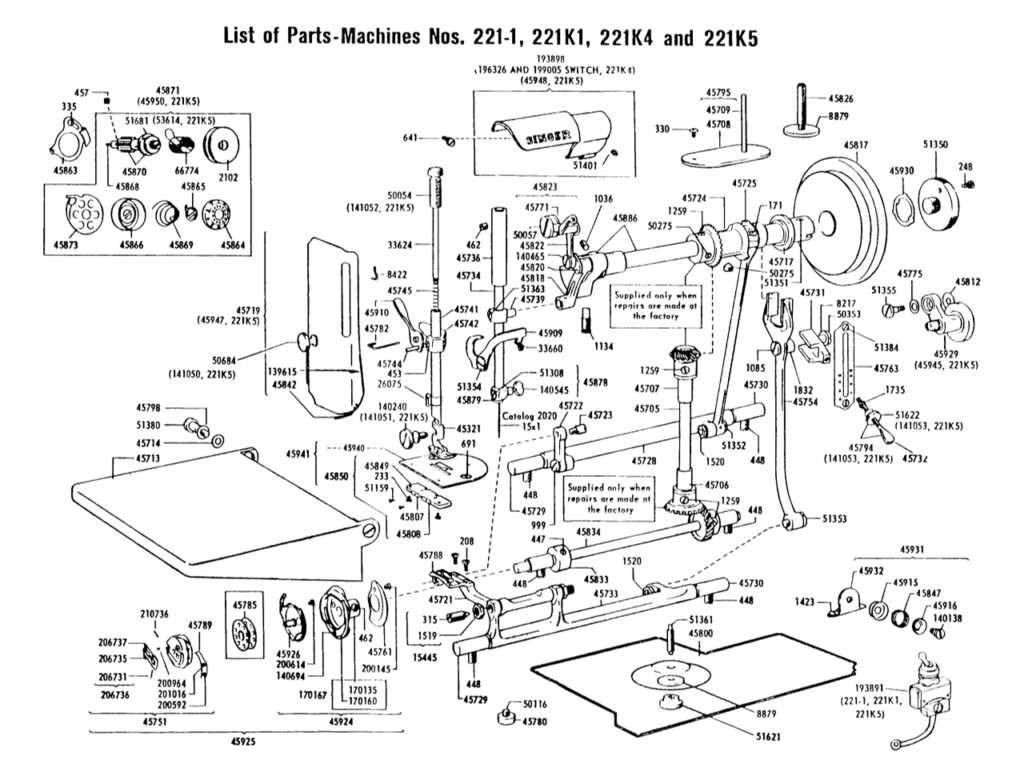
For those starting with basic projects, lightweight materials such as cotton or linen are easier to handle. They offer flexibility and are forgiving when adjusting tension. These fabrics also provide smooth seams, making them ideal for simple creations like clothing or home accessories.
Heavy Fabrics for Durability
When working on projects that require longevity, choosing denser fabrics like denim or canvas ensures strength and durability. These materials demand greater control but reward with sturdy, long-lasting results. Perfect for items needing extra toughness, like bags or upholstery, these textiles can enhance both form and function.
Stitch Techniques for Treadle Users
Mastering various methods of forming stitches is essential for those working with manually operated devices. By understanding different approaches, you can achieve better control over the fabric and produce more refined results. Below are some of the most useful techniques to enhance the precision and variety of your stitching.
- Backstitch: This method provides strong seams and is ideal for areas that require extra durability. It involves stitching backward to secure the thread.
- Chain Stitch: Known for its flexibility, this approach creates a looped pattern, which is great for decorative edges or seams that need to stretch slightly.
- Running Stitch: A basic but versatile option, this method works well for light fabrics and quick seams. It can be adjusted for both straight lines and gentle curves.
- Whipstitch: This method is perfect for joining two layers of material together, particularly in situations where you want to avoid visible stitches on one side.
Experimenting with these techniques will allow for greater versatility and finer detailing in your projects, ensuring a professional finish every time.
Resources for Treadle Enthusiasts

For those passionate about restoring and maintaining vintage mechanisms, there are numerous avenues to explore for guidance and supplies. Whether you’re looking for technical advice or rare components, a variety of platforms cater to enthusiasts eager to keep these historic devices in working order.
- Online forums: Dedicated communities offer insights, tips, and shared experiences. These platforms are invaluable for troubleshooting and exchanging knowledge.
- Specialized retailers: Some shops focus specifically on spare components and accessories for older mechanical devices, providing hard-to-find items for restoration projects.
- Instructional videos: Video tutorials can guide hobbyists through intricate repairs and adjustments, making even complex tasks accessible to beginners.
- Workshops and clubs: Local groups often organize events where enthusiasts gather to share techniques, tools, and advice, helping each other with hands-on projects.
- Historical references: Books and manuals offer detailed descriptions and step-by-step instructions, preserving the knowledge needed to maintain these timeless mechanisms.
Restoration Projects: A Guide
Restoring vintage equipment offers a rewarding way to bring historical pieces back to life, preserving their charm and functionality. With careful attention to detail and proper techniques, anyone can breathe new life into old tools, making them both functional and aesthetically pleasing. Whether it’s furniture, mechanical devices, or household tools, restoration requires patience, the right materials, and knowledge of traditional methods.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Preparation | Start by carefully inspecting the object, identifying areas of damage or wear, and gathering the tools necessary for the restoration process. |
| Cleaning | Thoroughly clean the surfaces, removing dust, rust, and old finishes. Use appropriate solvents and brushes to preserve delicate elements. |
| Repair | Replace broken or worn components, ensuring compatibility with the original structure. Traditional repair techniques often require specialized skills and tools. |
| Finishing | Once the repairs are complete, apply protective finishes to prevent future damage and enhance the appearance of the object. |