In the realm of automotive maintenance and repair, comprehending the configuration of various components is essential for effective troubleshooting and replacement. A clear representation of each element within the assembly provides valuable insights, aiding both enthusiasts and professionals alike in their efforts to ensure optimal performance.
Detailed schematics serve as a crucial reference, highlighting the intricate relationships between different assemblies. By examining these visual guides, one can easily identify locations, functions, and potential points of failure, streamlining the diagnostic process.
Furthermore, such illustrations empower individuals to make informed decisions when sourcing replacements or upgrades. Whether embarking on a restoration project or simply conducting routine maintenance, having a thorough understanding of the arrangement enhances the overall experience and contributes to the longevity of the vehicle.

This section provides an overview of the essential elements found in a specific vehicle model, highlighting their functionality and arrangement. Understanding the intricate layout of these components can greatly assist in maintenance and repairs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
The following table outlines the major categories of elements typically found in the mentioned automobile, offering a comprehensive guide to their respective roles:
| Component Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Engine | The powerhouse of the vehicle, responsible for propulsion and overall performance. |
| Transmission | Facilitates gear shifts, providing the appropriate power to the wheels based on speed and load. |
| Suspension | Ensures a smooth ride by absorbing shocks and maintaining tire contact with the road. |
| Braking System | Critical for safety, this system slows down or stops the vehicle using hydraulic force. |
| Electrical System | Includes wiring, batteries, and electronic controls, powering various features and components. |
| Cooling System | Maintains optimal engine temperature, preventing overheating during operation. |
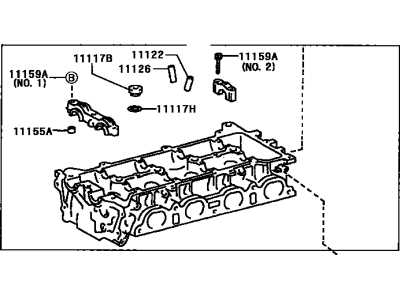
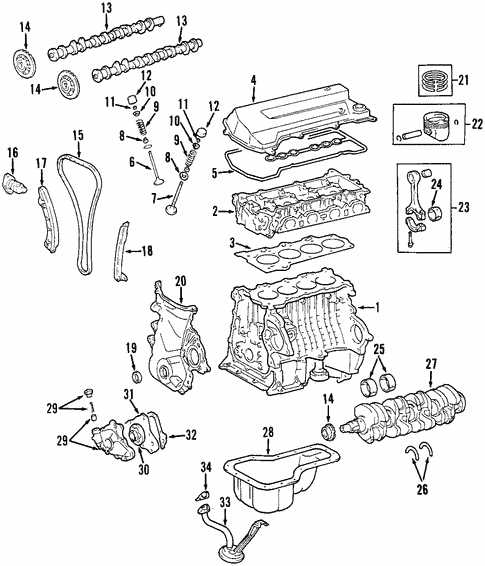
Engine Assembly Breakdown

The internal components of a vehicle’s propulsion system are crucial for its overall performance and efficiency. Understanding the various elements that constitute the engine assembly provides insights into how power is generated and transferred to the wheels. This section delves into the essential parts and their functions, highlighting the complexity and engineering behind a smoothly operating machine.
Main Components
The core of the engine assembly includes several key components, such as the crankshaft, camshaft, and pistons. The crankshaft converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, enabling the vehicle to move. Meanwhile, the camshaft regulates the timing of the intake and exhaust valves, ensuring optimal airflow and combustion efficiency. Each part plays a vital role in the engine’s performance and longevity.
In addition to the primary components, various supporting elements contribute to the overall functionality of the engine assembly. These include the timing belt or chain, which synchronizes the movement of the crankshaft and camshaft, and the oil pump, which lubricates moving parts to reduce friction. Understanding these auxiliary components is essential for grasping the intricacies of engine operation and maintenance.
Transmission System Features
The transmission system plays a crucial role in the overall performance of a vehicle, serving as the bridge between the engine and the wheels. It is responsible for transferring power efficiently while enabling smooth gear shifts, contributing significantly to the driving experience. Various elements within this system work together to optimize functionality and enhance vehicle responsiveness.
Key Components
At the heart of the transmission system are essential components such as the gearbox, torque converter, and clutch. The gearbox regulates the speed and torque delivered to the wheels, allowing for acceleration and deceleration as needed. Meanwhile, the torque converter facilitates a seamless transfer of power from the engine to the transmission, ensuring smooth transitions between gears. The clutch acts as a mechanism that engages and disengages the engine from the transmission, allowing for precise control during gear changes.
Advanced Technologies
Modern advancements have introduced several features that enhance the efficiency and reliability of the transmission system. Technologies such as adaptive transmission control and continuously variable transmissions (CVTs) are designed to improve fuel economy and driving dynamics. These innovations allow for better performance by automatically adjusting to driving conditions, ensuring that the vehicle operates at optimal levels under various circumstances.
Suspension System Details
The suspension system plays a crucial role in providing stability, comfort, and control to a vehicle. It is designed to absorb shocks from the road, ensuring a smooth ride while maintaining the integrity of the chassis. This system consists of several components working together to manage the vehicle’s dynamics effectively.
Main Components
- Shock Absorbers: These elements help control the oscillation of the springs, enhancing ride quality by dampening vibrations.
- Struts: Integrated with the coil springs, struts provide structural support and contribute to the vehicle’s handling characteristics.
- Springs: Springs support the weight of the vehicle and absorb energy from bumps, playing a vital role in ride height and comfort.
- Control Arms: These link the chassis to the wheel assemblies, allowing for controlled wheel movement and alignment.
- Stabilizer Bar: This component reduces body roll during cornering, contributing to improved handling and stability.
Maintenance Considerations
- Regular Inspections: Frequent checks can identify wear and damage, ensuring components function effectively.
- Fluid Checks: Monitoring shock absorber fluid levels helps maintain performance and prevent leaks.
- Alignment Adjustments: Proper alignment is essential for tire longevity and optimal handling.
- Spring Condition: Inspecting springs for signs of fatigue or corrosion can prevent failure and maintain safety.
Electrical System Layout
This section provides an overview of the configuration of the electrical components within the vehicle. Understanding the arrangement of these elements is essential for troubleshooting, maintenance, and upgrades. A clear structure helps in identifying the location and function of each component, ensuring optimal performance of the electrical system.
Key Components
The electrical system comprises various critical parts that work together to power and control the vehicle’s functions. Each element plays a significant role in the overall functionality.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Battery | Stores electrical energy for starting the engine and powering electrical accessories. |
| Alternator | Generates electricity to recharge the battery and power the vehicle’s electrical systems while the engine is running. |
| Fuse Box | Protects electrical circuits by interrupting the flow of electricity in case of a fault. |
| Wiring Harness | Connects various electrical components and facilitates the flow of electricity throughout the system. |
System Overview
The electrical system’s layout ensures a well-organized and efficient flow of energy. Each component is strategically placed to minimize interference and enhance accessibility during repairs or inspections.
Braking System Overview
The braking mechanism is a crucial component of any vehicle, responsible for ensuring safety and control during operation. It functions by converting kinetic energy into thermal energy, enabling the vehicle to decelerate or come to a complete stop when necessary. Understanding the elements involved in this system can enhance maintenance and performance, contributing to a safer driving experience.
Key Components
- Brake Pedal: The initial point of driver interaction that activates the braking process.
- Master Cylinder: Converts the force applied on the pedal into hydraulic pressure.
- Brake Lines: Transmit hydraulic fluid to the braking assemblies at each wheel.
- Brake Calipers: House the brake pads and utilize hydraulic pressure to clamp down on the rotors.
- Brake Rotors: Circular discs that provide a surface for the pads to grip, slowing the vehicle.
- Brake Pads: Friction materials that press against the rotors to create stopping power.
Types of Braking Systems

- Disc Brakes: Commonly used for their efficient heat dissipation and consistent performance.
- Drum Brakes: Typically found in rear applications, offering good stopping power but can overheat.
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): Prevents wheel lock-up during hard braking, enhancing control and stability.
- Regenerative Braking: Utilizes electric motors to recover energy during deceleration, commonly found in hybrid and electric vehicles.
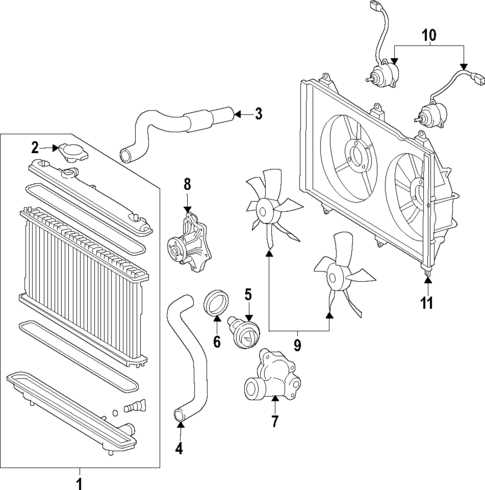
Cooling System Configuration
The arrangement of the cooling mechanism is crucial for maintaining optimal operating temperatures within the engine. This system plays a vital role in preventing overheating, thereby ensuring efficiency and longevity of the vehicle’s components. Proper circulation of coolant, along with the functioning of various parts, contributes to the overall effectiveness of this essential system.
Key Components
Several integral components work together to facilitate the cooling process. These parts ensure that the coolant flows seamlessly, transferring heat away from the engine and maintaining appropriate temperatures. Understanding their roles is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Radiator | Dissipates heat from the coolant as it circulates through the system. |
| Water Pump | Circulates coolant throughout the engine and radiator. |
| Thermostat | Regulates the flow of coolant based on temperature, ensuring efficient heating and cooling. |
| Coolant Reservoir | Holds excess coolant and allows for expansion and contraction during temperature changes. |
| Heater Core | Transfers heat from the coolant to the interior cabin, providing warmth during cold conditions. |
System Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of the cooling mechanism are vital to avoid potential issues such as leaks, clogs, or overheating. Ensuring proper levels of coolant, inspecting hoses for wear, and replacing the thermostat when necessary are all critical steps to keep this system functioning effectively.
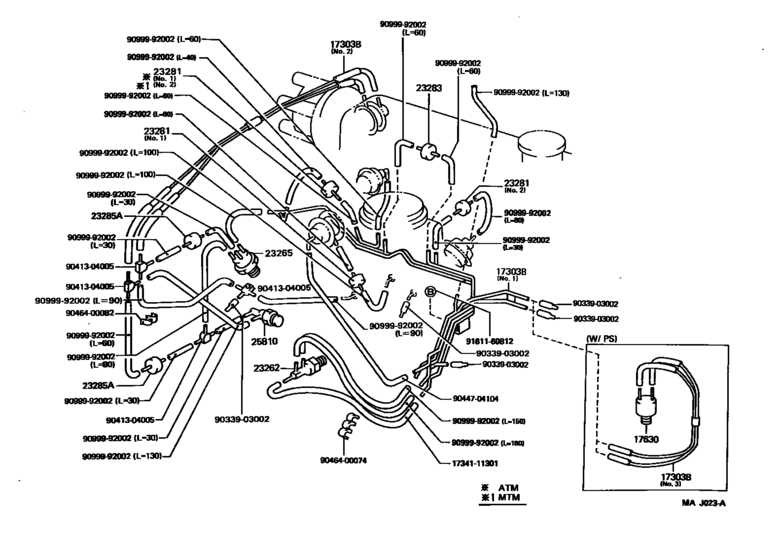
Fuel System Components
The fuel system plays a crucial role in the operation of a vehicle, ensuring that the engine receives the right amount of fuel for optimal performance. This system is designed to store, filter, and deliver fuel to the engine efficiently, contributing to overall functionality and efficiency.
Key elements of the fuel system include:
- Fuel Tank: Serves as the storage unit for fuel, allowing for safe containment and access.
- Fuel Pump: Responsible for transporting fuel from the tank to the engine, often operating under varying pressures.
- Fuel Filter: Ensures that impurities and debris are removed from the fuel before it reaches the engine, preventing potential damage.
- Fuel Injector: Delivers precise amounts of fuel into the combustion chamber, facilitating efficient combustion and performance.
- Fuel Lines: Connect various components, transporting fuel throughout the system while maintaining proper pressure.
- Pressure Regulator: Maintains consistent fuel pressure, adjusting flow as necessary to meet engine demands.
Understanding these components is essential for diagnosing issues and performing maintenance, as they collectively ensure the engine operates smoothly and efficiently.
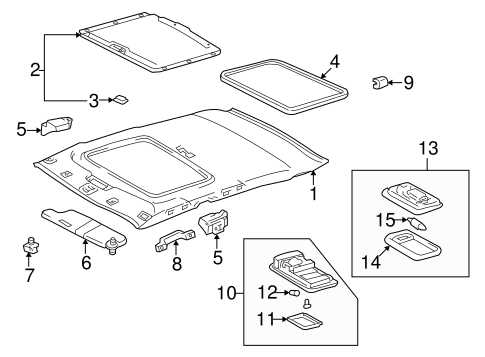
Interior Parts Arrangement
The layout of components within a vehicle cabin plays a crucial role in enhancing both functionality and comfort. Each element is meticulously positioned to ensure accessibility and ease of use, creating a harmonious environment for both the driver and passengers.
Central Console: This area serves as the hub for various controls and storage solutions. Featuring multimedia systems and climate control, it allows for seamless interaction while maintaining a tidy space.
Dashboard: The front panel, designed for visibility and clarity, houses essential instruments and indicators. Its ergonomic design ensures that crucial information is readily available without distracting the driver.
Seating Arrangement: Comfort is prioritized with carefully designed seating that supports long journeys. Each seat is positioned to provide ample legroom and access to controls, enhancing the overall driving experience.
Storage Compartments: Cleverly integrated storage options throughout the cabin, including glove boxes and door pockets, maximize space utilization while keeping essential items within easy reach.
Door Panels: These panels not only contribute to the aesthetic appeal but also incorporate handles and controls for windows and locks, ensuring convenient access for all passengers.
In summary, the thoughtful arrangement of cabin elements not only elevates the driving experience but also underscores the importance of design in automotive engineering.
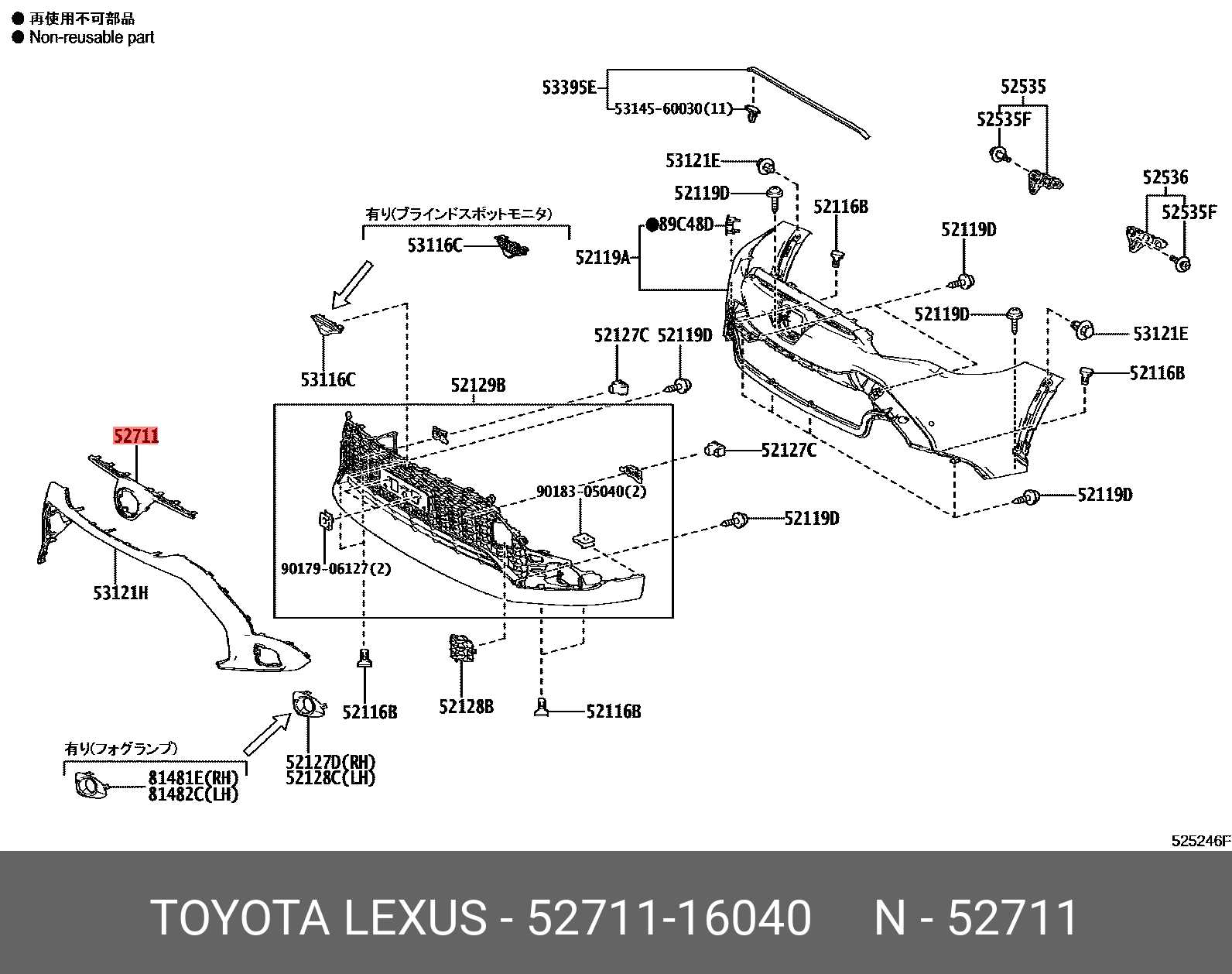
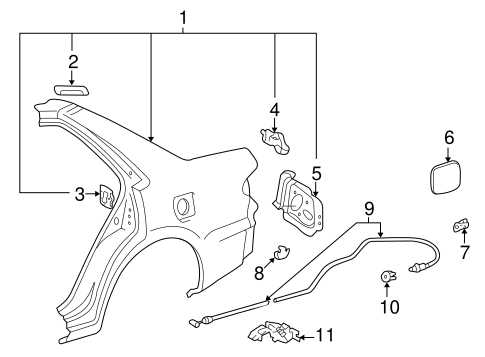
Exterior Features and Accessories
This section explores the various elements and enhancements that contribute to the visual appeal and functionality of the vehicle’s exterior. From protective elements to aesthetic upgrades, these features play a crucial role in defining the overall character of the automobile.
Body Panels: The outer shell is composed of several key panels, each designed to provide durability while enhancing the car’s sleek profile. These components are often engineered for optimal aerodynamics, ensuring both style and efficiency.
Lighting: High-quality illumination is essential for safety and aesthetics. The vehicle is equipped with advanced headlamps, tail lights, and turn signals that not only enhance visibility but also add a modern touch to the overall design.
Mirrors: Side mirrors are designed to provide excellent visibility while complementing the vehicle’s streamlined look. Many models feature integrated turn signals for added safety and convenience.
Wheels and Tires: The choice of wheels can dramatically alter the vehicle’s appearance. Stylish rims, paired with performance tires, contribute to improved handling and overall driving experience.
Accessories: Various enhancements, such as spoilers, roof racks, and custom trim, offer personalization options that allow owners to express their unique style. These additions not only enhance aesthetics but can also improve functionality.
Color Options: A range of vibrant hues and finishes allows for individuality and personal expression, making it easier for owners to find a vehicle that resonates with their preferences.