Understanding the intricate details of a vehicle’s construction is essential for both owners and technicians alike. A comprehensive breakdown of each element ensures that repairs and maintenance are carried out with precision. From the engine to the interior, every section plays a pivotal role in the overall functionality of the machine.
To properly maintain and repair a car, it’s crucial to have access to clear and accurate information about the different systems that make up the vehicle. This information aids in identifying specific parts, their placement, and how they interact with other components. Knowing the arrangement of these parts helps in diagnosing issues and determining what replacements or adjustments might be necessary.
Whether you’re a professional mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, familiarizing yourself with the structure and layout of these systems is fundamental. It allows for more efficient troubleshooting and can prevent costly mistakes during the repair process. With this guide, you will gain a better understanding of the vehicle’s inner workings and improve your maintenance efforts.
Engine Components of the 2009 Toyota Camry
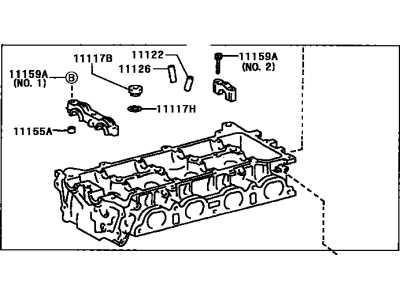
Understanding the key elements of an automobile’s powertrain is essential for anyone looking to maintain or repair it. The internal combustion engine of this model is a complex assembly that relies on various components to function efficiently. Each part plays a crucial role in ensuring the engine operates smoothly, delivering power, and maintaining fuel efficiency.
Main Engine Elements
- Engine Block: The main framework that houses several crucial parts of the engine, including cylinders, pistons, and the crankshaft.
- Cylinders: The chambers where fuel combustion occurs, pushing the pistons to generate power.
- Pistons: Move up and down within the cylinders to convert fuel combustion into mechanical energy.
- Crankshaft: Transforms the up-and-down motion of the pistons into rotational motion that powers the vehicle.
- Camshaft: Controls the timing of the engine’s intake and exhaust valves, ensuring efficient air-fuel mixture flow.
Supporting Systems
- Timing Belt: Ensures synchronization between the crankshaft and camshaft, allowing the engine to function properly.
- Valves: Regulate the intake of air-fuel mixture and the expulsion of exhaust gases.
- Oil Pump: Circulates oil throughout the engine to lubricate moving parts, reducing friction and preventing overheating.
- Water Pump: Helps in cooling the engine by circulating coolant through the engine block and radiator.
By maintaining these key components, the engine remains in optimal condition, ensuring smooth operation and reliability over time.
Detailed Overview of Transmission Parts

The transmission system is crucial for the smooth operation of a vehicle, as it facilitates the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. This complex assembly consists of multiple components working in harmony to ensure that the vehicle shifts efficiently through various gears, optimizing performance and fuel economy.
Main Components of the Transmission System

- Gearbox: The primary structure where gears are engaged to control speed and torque output.
- Clutch: The mechanism that engages or disengages the engine from the drivetrain, allowing for smooth transitions between gears.
- Torque Converter: A fluid coupling that allows the engine to continue running while the vehicle is stationary, transmitting power when engaged.
- Flywheel: A large rotating component that helps maintain engine momentum during gear changes.
- Transmission Fluid: A special lubricant that ensures proper function and cooling of the moving parts within the transmission.
Additional Transmission Elements
- Synchronizers: Devices that assist in matching the speed of gears during shifting, preventing grinding.
- Shift Forks: Mechanical components responsible for moving gears into the correct position during a shift.
- Valve Body: The control center that directs transmission fluid flow to the various valves for smooth gear operation.
Understanding the Suspension System
The suspension system is a crucial component of any vehicle, ensuring a smooth and stable ride. It connects the wheels to the car’s frame, absorbing shocks from the road and maintaining traction. The system consists of various elements that work together to control how the vehicle handles bumps, turns, and overall driving conditions. A well-designed suspension not only improves comfort but also enhances vehicle safety by improving control and stability.
In most vehicles, the suspension system can be broken down into several key components. Each part plays a specific role in ensuring that the car moves efficiently, while minimizing the impact of rough terrains. Below is a breakdown of the main elements found in most suspension systems:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Shock Absorbers | These dampen the movement of the springs, preventing excessive bouncing and providing better control. |
| Springs | Springs bear the weight of the vehicle and absorb the impact of uneven surfaces. |
| Control Arms | These connect the wheel hubs to the vehicle’s chassis and allow controlled movement in response to the road conditions. |
| Struts | Struts combine the shock absorber and spring into a single unit, helping to stabilize the ride. |
| Sway Bars | They reduce body roll during turns by distributing the force evenly between the wheels. |
Each component must function optimally for the suspension system to provide the best balance between comfort and handling. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of worn-out parts help maintain the vehicle’s performance and safety on the road.
Key Electrical Elements in the Vehicle

The electrical system in modern vehicles plays a vital role in ensuring smooth and efficient operation. From providing power to essential components to supporting advanced features, the electrical system consists of several key elements that work together harmoniously. Understanding these components is crucial for diagnosing issues and performing maintenance.
Battery
The battery is the heart of a vehicle’s electrical system, storing and supplying electrical energy to power up various systems when the engine is off. It ensures that the vehicle starts and powers essential electronics like lights and entertainment systems when the engine is not running.
Alternator

The alternator works in conjunction with the battery by generating electrical power while the engine is running. It recharges the battery and ensures that all electrical components, including lights, air conditioning, and the onboard computer, receive the necessary power during operation.
Fuses and Relays

- Fuses: These small devices protect the electrical circuits from overloading by breaking the connection when a fault occurs.
- Relays: Relays control the flow of electricity to various parts of the vehicle by acting as switches, allowing low-power circuits to control high-power components like the starter motor and headlights.
Wiring Harness
The wiring harness is an intricate network of electrical cables that connects all the vehicle’s electrical components. It ensures that power is delivered to where it is needed, from the lights to the control modules. Proper maintenance of the wiring harness is essential for avoiding electrical faults.
Braking System Breakdown
The braking system is a crucial component for ensuring vehicle safety and smooth operation. Understanding how this system functions and recognizing its key elements can help diagnose issues effectively. From the master cylinder to the brake pads, each part plays a role in stopping the vehicle when necessary. A well-maintained braking system ensures optimal performance and reduces the risk of accidents.
Key Components
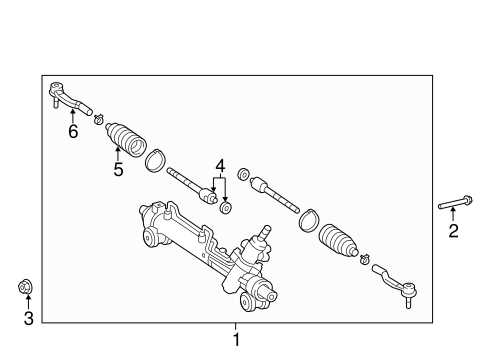
The braking system consists of several interdependent components that work together to slow down and stop the vehicle. The brake master cylinder is the heart of the system, converting the force from the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure. This pressure is transmitted through the brake lines to the brake calipers, which then apply friction to the brake discs. The brake pads create the necessary friction to reduce the speed of the wheels and bring the vehicle to a halt.
Common Issues and Maintenance
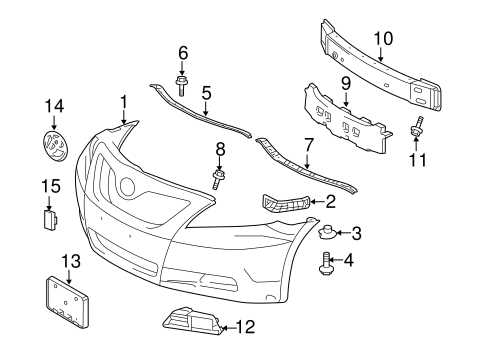
Several issues can arise within the braking system, from worn brake pads to air in the hydraulic lines. Regular maintenance is crucial to keep the system functioning properly. Inspecting the brake fluid levels, checking for leaks, and replacing worn-out pads can prevent more serious issues. Neglecting these tasks can lead to decreased stopping power and compromised safety.
Insight into Fuel System Design
The fuel system is a critical component of any vehicle, ensuring efficient fuel delivery and combustion processes. The design of this system plays an essential role in performance, fuel economy, and emissions control. At its core, the fuel system consists of several interconnected parts working harmoniously to store, filter, and deliver fuel to the engine. Understanding the complexity of these components and their design principles helps in appreciating how they contribute to a smooth driving experience.
At the heart of the system lies the fuel tank, which serves as the reservoir for the fuel. From there, fuel is transported through fuel lines and passes through a fuel pump, which pressurizes the system for proper flow. Additionally, a fuel filter is employed to remove impurities and debris before the fuel enters the engine. The fuel injectors then precisely meter the fuel into the combustion chambers for efficient combustion. The entire system is controlled by an electronic control unit (ECU), which ensures the optimal air-fuel mixture and adapts to varying driving conditions.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | Holds the fuel until it is needed for combustion. |
| Fuel Pump | Pressurizes and transports fuel from the tank to the engine. |
| Fuel Filter | Removes contaminants and particles from the fuel before it enters the engine. |
| Fuel Injectors | Meter and inject fuel into the combustion chambers for efficient combustion. |
| Electronic Control Unit (ECU) | Monitors and adjusts fuel delivery and air-fuel mixture based on engine conditions. |
In conclusion, the design of the fuel system is a complex and finely tuned process. Each component works together to ensure that the engine receives the right amount of fuel at the right time, leading to optimal performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control.
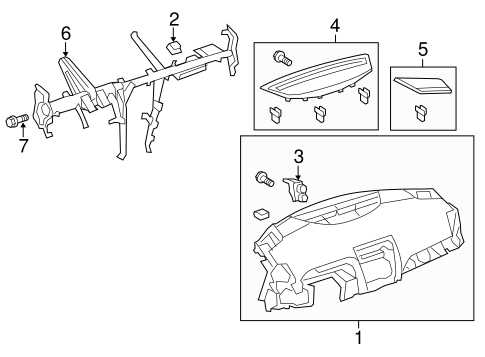
Interior and Dashboard Components
The interior of a vehicle is carefully designed to enhance both functionality and comfort. A key element of this design is the dashboard, which serves as the control center of the cabin. It houses various elements essential for driving, navigation, and convenience. Each component in this area contributes to a seamless driving experience by allowing the driver to monitor and operate the car efficiently.
Below is a breakdown of some essential components typically found in the dashboard and interior space, providing an overview of their functions and locations:
| Component | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Steering Wheel | Front center of the dashboard | Controls vehicle direction and contains buttons for various functions |
| Instrument Cluster | Behind the steering wheel | Displays speed, fuel level, engine status, and other vital information |
| Center Console | Middle section of the dashboard | Holds climate control, entertainment system, and storage compartments |
| Infotainment System | Center of the dashboard | Provides audio, navigation, and connectivity functions |
| Climate Control Panel | Below the infotainment system | Adjusts the temperature and airflow within the cabin |
| Air Vents | Located on the dashboard | Directs airflow for heating, cooling, or ventilation |
| Gear Shift | Front section of the center console | Controls the vehicle’s transmission settings (park, reverse, drive, etc.) |
Each of these elements plays a critical role in ensuring an efficient, comfortable, and safe driving experience, contributing to the overall functionality of the vehicle’s interior layout.
Essential Cooling and Heating Parts

Maintaining optimal engine performance requires efficient regulation of temperature within the vehicle. The cooling and heating systems play a crucial role in ensuring that the engine operates within the ideal temperature range. These components are designed to prevent overheating and ensure proper cabin comfort by regulating airflow and heat distribution.
Cooling System Components
- Radiator – Transfers heat from the coolant to the surrounding air, preventing the engine from overheating.
- Water Pump – Circulates coolant throughout the engine and radiator, maintaining proper temperature balance.
- Thermostat – Controls the flow of coolant to regulate the engine’s temperature based on its heat level.
- Cooling Fans – Pull air through the radiator to help dissipate heat from the coolant when the vehicle is stationary or moving slowly.
- Coolant Reservoir – Stores additional coolant that is used when the system needs more fluid during operation.
Heating System Components
- Heater Core – Works as a small radiator inside the cabin, using engine heat to warm the interior of the vehicle.
- Blower Motor – Pushes air through the heater core and into the cabin to provide warmth.
- HVAC Controls – Allow the driver to adjust the temperature inside the vehicle by controlling the flow of air through the heating system.
- Defrost Vents – Direct warm air to the windshield and side windows to remove condensation and improve visibility.
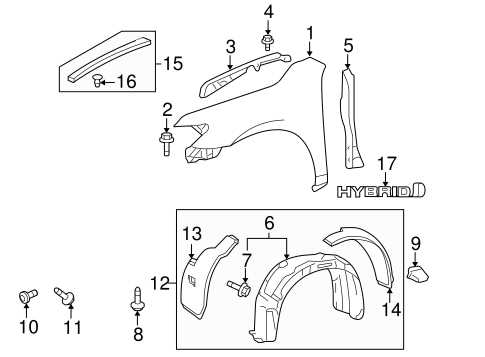
Exterior Body and Frame Elements
The exterior structure of a vehicle consists of various components that provide both aesthetic appeal and functional protection. These elements are designed to ensure the vehicle’s durability, safety, and resistance to environmental factors. The body panels and the underlying frame are crucial in maintaining the integrity of the vehicle, while also contributing to its aerodynamic properties and overall design.
Frame Components
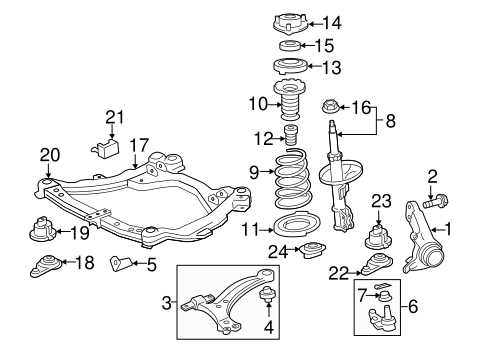
The frame serves as the foundational support system of the vehicle. It is responsible for holding all the major mechanical and structural parts in place, including the engine, transmission, and suspension. Made from high-strength materials, it is designed to absorb and distribute impact energy during collisions, thereby protecting the occupants and enhancing the safety of the ride. Additionally, the frame offers support for the exterior panels and the roof structure.
Body Panels and Exterior Features
The body panels, including the hood, doors, and fenders, form the outer skin of the vehicle. These elements play a key role in enhancing the vehicle’s appearance while offering protection from physical damage and weathering. Panels are often crafted from materials such as steel, aluminum, or composite substances to balance strength with weight efficiency. Exterior features like bumpers and side mirrors also contribute to the vehicle’s functionality and safety, improving visibility and protection during maneuvering.
Exhaust System Configuration
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in controlling emissions and improving engine efficiency. It is designed to channel harmful gases away from the engine, reduce noise levels, and maintain optimal performance. This system typically consists of various components that work together to achieve these goals, each serving a specific function in the overall operation.
Key Components of the Exhaust System
The configuration of the exhaust system involves a series of interconnected parts that ensure proper gas flow and reduce pollution. The primary elements include the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe. Each part serves a specific purpose in managing the output of gases and minimizing their environmental impact.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Exhaust Manifold | Collects gases from the engine’s cylinders and directs them toward the catalytic converter. |
| Catalytic Converter | Converts harmful gases like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides into less harmful emissions. |
| Muffler | Reduces engine noise by using internal baffles to control sound waves. |
| Tailpipe | Channels the treated gases out of the system and away from the vehicle. |
Performance and Efficiency Considerations
An optimized exhaust system is essential for balancing engine performance and environmental responsibility. The design of the system can significantly influence power output, fuel efficiency, and noise reduction. Regular maintenance of the exhaust system is necessary to ensure its components function efficiently and meet emission standards.