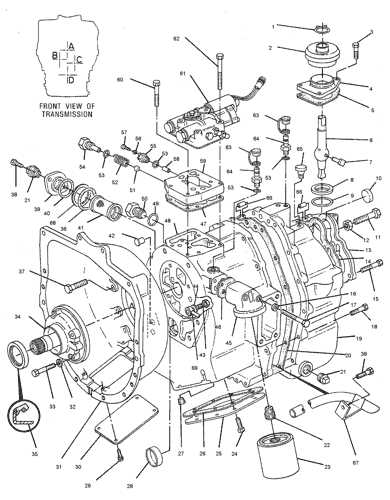
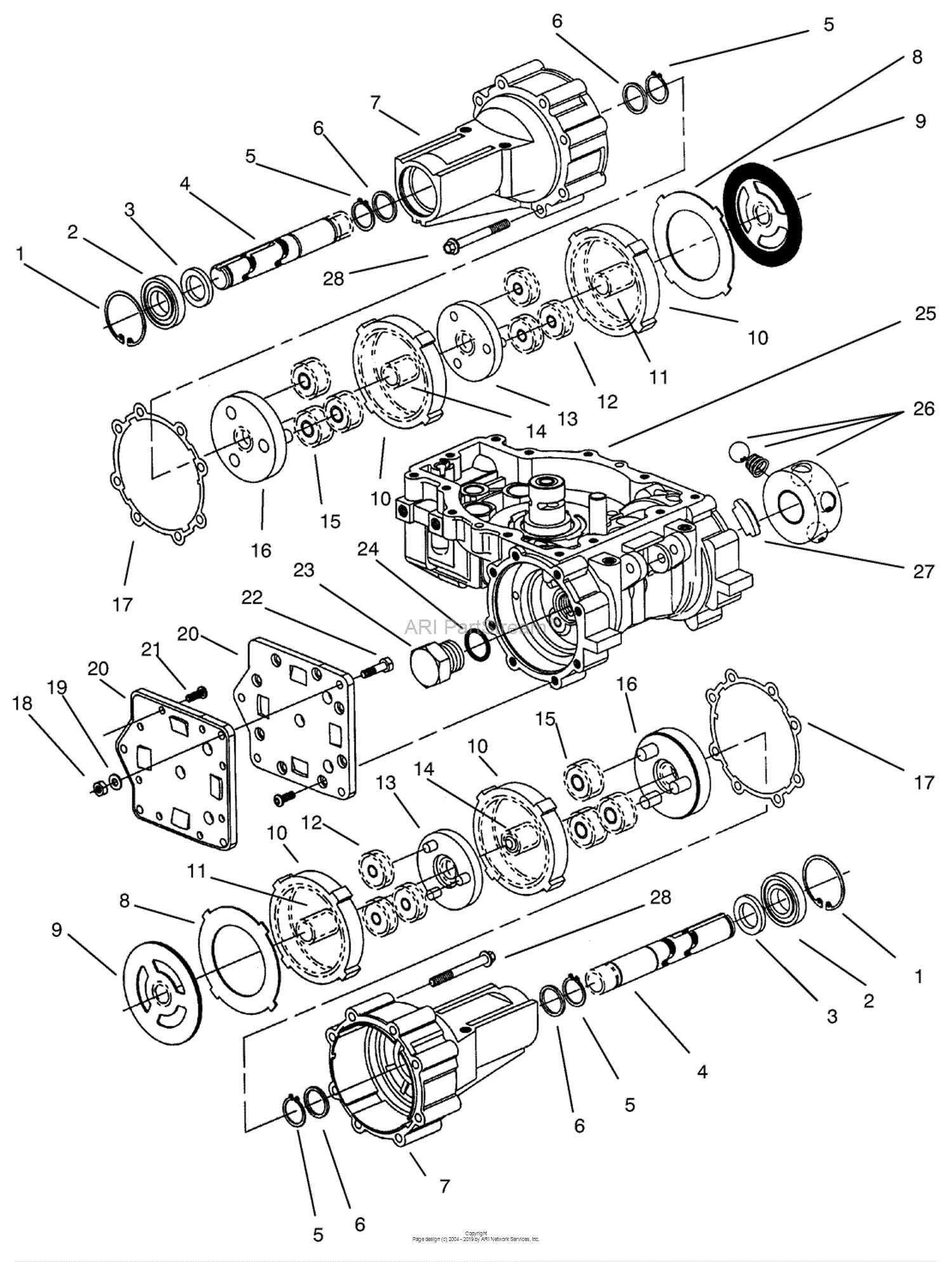
The structure of a modern gearbox can be quite intricate, with numerous elements working together to ensure efficient vehicle operation. Each section plays a vital role in maintaining proper performance, and understanding their layout is essential for both maintenance and troubleshooting.
In this guide, we’ll explore the layout of various elements within this complex mechanical system, focusing on how each part interacts with the others. By gaining insight into the specific arrangement and function of these components, you’ll have a clearer picture of how the entire system operates smoothly.
Whether you’re performing repairs or conducting routine checks, having a clear understanding of the internal setup is key. This breakdown will help ensure that each component is in optimal condition, contributing to the overall functionality and longevity of the machinery.
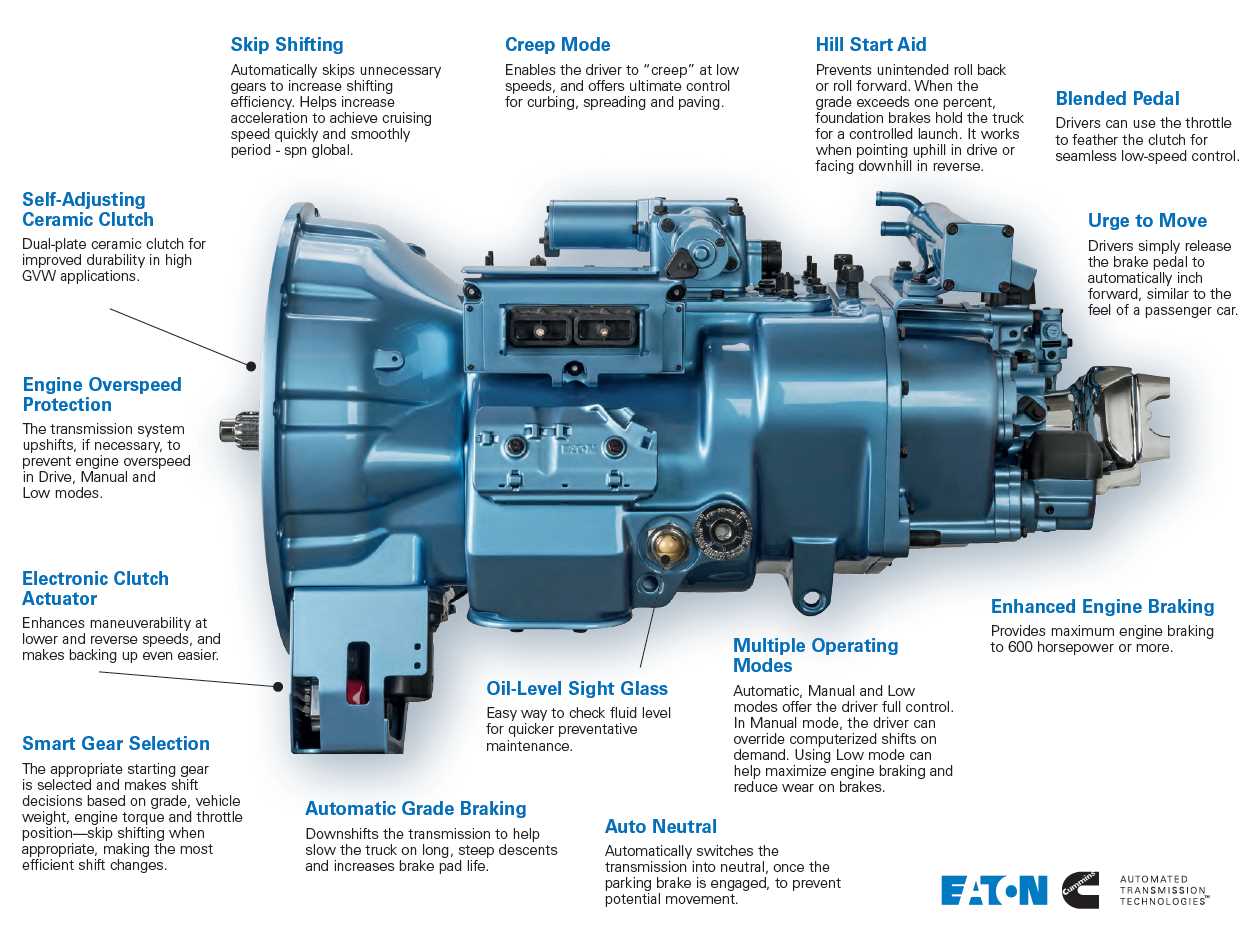
Eaton Fuller 18-Speed Transmission Overview
This section provides a comprehensive understanding of the advanced gear mechanism commonly used in heavy-duty vehicles. It is designed to manage significant loads and demanding conditions, offering smooth and efficient operation across various terrains.
Main Functions and Benefits

- Enables precise control for drivers handling challenging driving scenarios.
- Designed for maximum durability and long-term performance under heavy loads.
- Optimizes fuel efficiency by providing a wide range of gear options.
Key Features
- Multiple gear ratios to ensure adaptability to different road conditions.
- Enhanced torque distribution for better vehicle control and smoother transitions.
- Integration with modern truck systems for easier operation and maintenance.
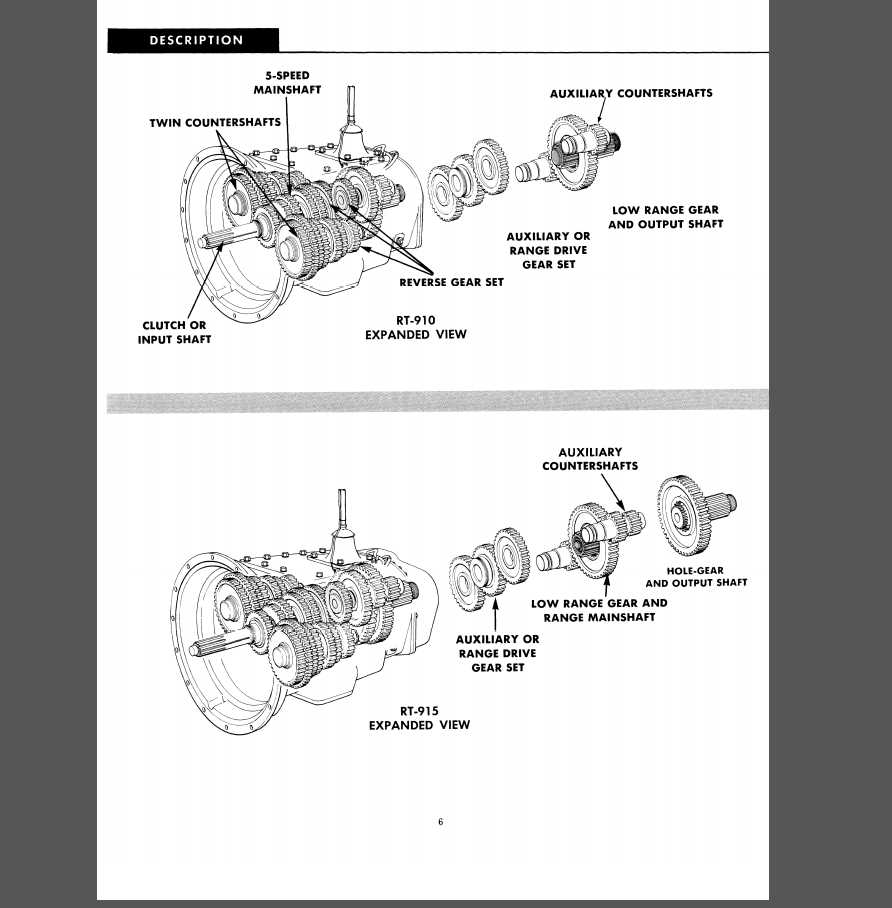
Main Components of the 18-Speed Transmission
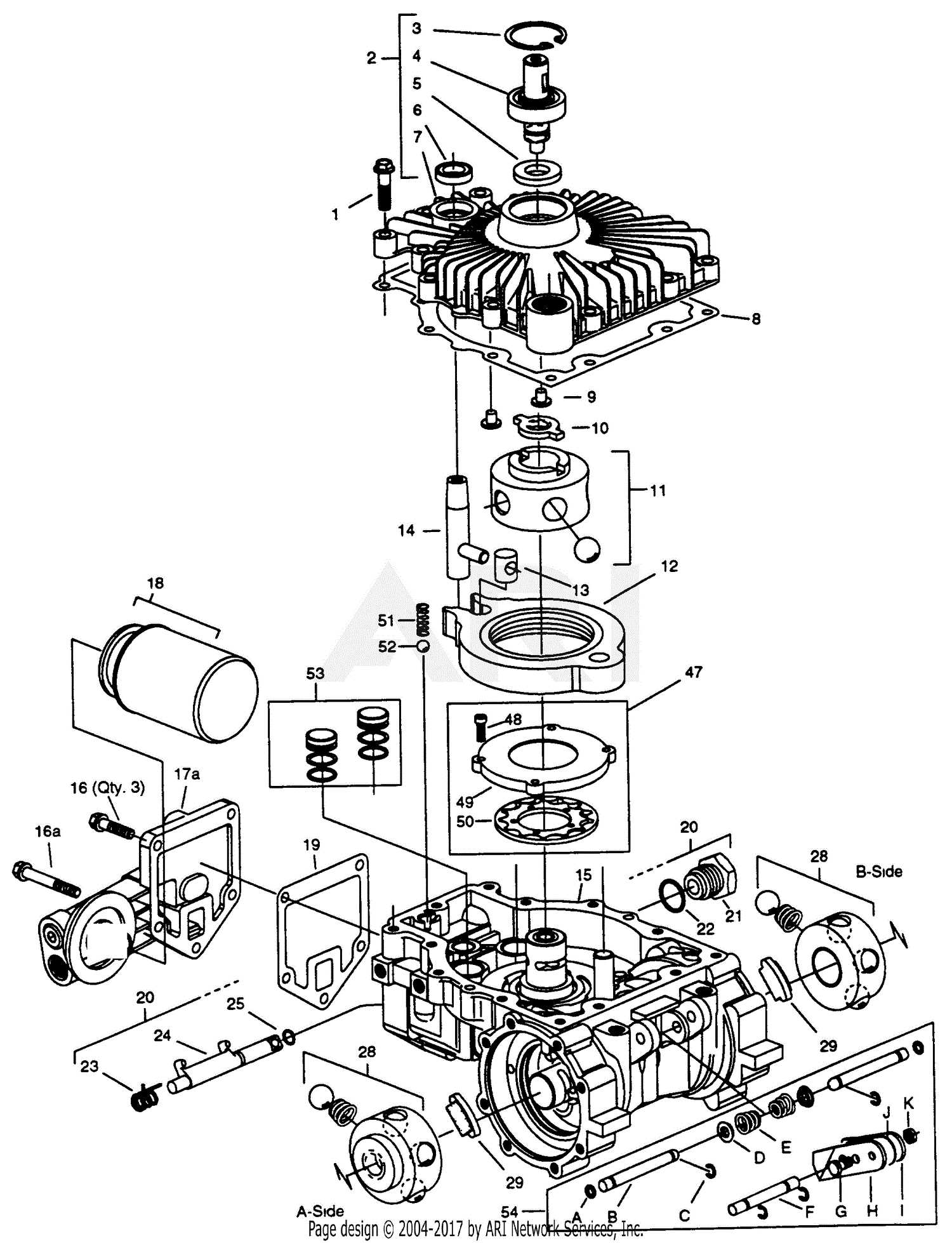
The complex gearbox system includes multiple essential elements that work together to ensure smooth and efficient power delivery. Each component is designed to interact with the others, enabling precise control over shifting and optimal performance under varying conditions.
Key Elements of the Gear Mechanism
- Main Shafts: These are the central axes that transfer rotational energy through the system, connecting different sections of the mechanism.
- Gear Sets: Different sets of gears are used to manage varying torque and speed ratios, ensuring smooth transitions between driving modes.
- Synchronizers: These components allow seamless engagement between different gears, reducing friction and wear during shifts.
Supportive Components
- Clutch Assembly: The clutch system helps to engage and disengage the driving force, making it easier to shift between different modes.
- Bearings: Bearings reduce friction between moving parts, improving the
Function of the Gear Selector Mechanism
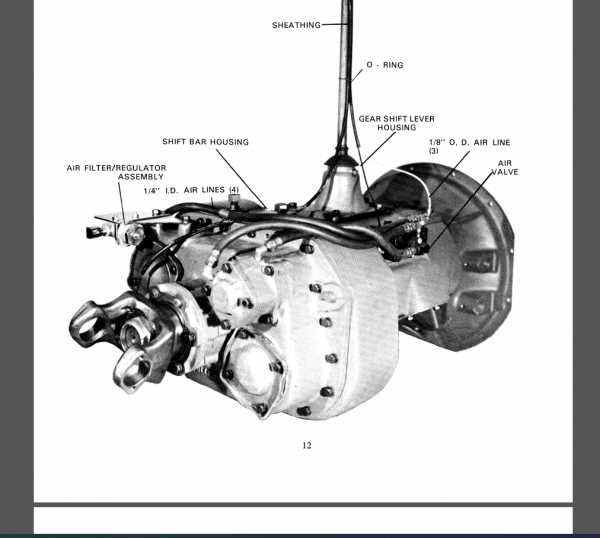
The gear selector mechanism plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth transitions between various gears within a vehicle’s drive system. This component is responsible for accurately determining and engaging the appropriate gear based on driver input, making it an essential element of the shifting process. By effectively managing the interaction between different moving parts, the selector helps maintain optimal performance and control during operation.
When the driver moves the lever, the selector mechanism coordinates the linkage, allowing precise engagement with the desired gear range. This coordination is vital for preventing mechanical stress and ensuring the longevity of the vehicle’s drive components. Additionally, the mechanism enables efficient transitions, reducing wear on internal components and contributing to a smoother driving experience.
Synchronizer Design and Operation in Eaton Fuller
The synchronizer plays a critical role in ensuring smooth gear transitions by matching the rotational speeds of gears before engagement. This mechanism is fundamental for enhancing efficiency and reducing wear within the gearbox, allowing for more precise control during shifts.
Key Components of the Synchronizer
- Friction Cone: This part ensures that gear speeds are aligned, reducing gear clash during shifts.
- Hub Sleeve: Facilitates the engagement of different gears by sliding between them.
- Blocking Ring: Works with the friction cone to prevent gear engagement until synchronization is achieved.
Operational Process
When a shift is initiated, the synchronizer first engages the friction cone, which adjusts the rotational speed of the target gear. Once the speeds are matched, the blocking ring allows the hub sleeve to lock the gears together, completing the shift without grinding or resistance.
Understanding the Shift Pattern Layout

The shift pattern layout is a crucial aspect that helps drivers navigate through different gears smoothly and efficiently. Understanding the arrangement of gear positions allows for better control of the vehicle, improving both performance and safety.
Typically, the pattern follows a logical sequence, enabling the driver to move through various ranges and gears with ease. Let’s take a closer look at how the layout is structured:
- Gears are arranged in a grid-like structure, often spanning multiple positions horizontally and vertically.
- The layout is divided into different ranges, with a designated low and high range for adapting to different driving conditions.
- Each gear is selected by moving the lever into specific slots within the layout, ensuring a smooth transition between shifts.
Understanding this layout is essential for mastering gear changes, ensuring a balanced and efficient driving experience.
Key Differences Between Range and Splitter Sections
The functionality of various mechanical systems can be significantly enhanced by understanding the distinctions between different components. In this context, two critical sections often found in complex gear arrangements are the range and splitter sections. Each plays a unique role in optimizing performance and adapting to various operational conditions.
Here are some of the main differences:
- Purpose: The range section primarily facilitates shifting between different sets of gear ratios, allowing for broader adaptability in speed and torque. In contrast, the splitter section enhances the number of available gear ratios within a given range, providing finer adjustments for performance.
- Operation: The range section typically involves a more straightforward operation, while the splitter section may require additional mechanisms to engage or disengage, leading to a more complex user experience.
- Gear Ratios: Gear ratios in the range section are designed to cover a wide spectrum of applications, while the splitter section focuses on providing incremental variations for enhanced control.
- Efficiency: While both sections contribute to overall efficiency, the range section is crucial for transitioning between high and low power demands, whereas the splitter section fine-tunes performance for specific driving conditions.
Understanding these differences aids in the selection and maintenance of systems that rely on sophisticated gearing mechanisms, ensuring optimal performance in various scenarios.
Torque Converter Role in Transmission Efficiency
The torque converter is a crucial component in optimizing the functionality of a vehicle’s drivetrain. It plays a vital role in enhancing performance by facilitating smooth power transfer from the engine to the wheels, ultimately affecting overall efficiency. Understanding its function helps in appreciating how power delivery is managed during operation.
One of the primary purposes of a torque converter is to multiply the engine’s torque. This amplification occurs through fluid dynamics, allowing for greater power availability under various driving conditions. As a result, vehicles can achieve better acceleration without requiring excessive engine speed. This efficiency can lead to improved fuel consumption and lower emissions.
Key advantages of a torque converter include:
- Smooth Power Transfer: It provides a seamless transition between engine output and wheel movement, reducing the likelihood of stalling.
- Enhanced Acceleration: By allowing the engine to operate in its optimal power band, it ensures responsive acceleration when needed.
- Reduced Wear and Tear: The converter absorbs shocks and vibrations, protecting other components from excessive stress and prolonging their lifespan.
In summary, the torque converter significantly contributes to the efficiency of a vehicle’s drivetrain. Its ability to enhance torque, facilitate smooth transitions, and protect against wear makes it an indispensable part of modern automotive design.
Lubrication and Cooling System for Gearbox Longevity
Ensuring optimal performance and durability of a gearbox heavily relies on effective lubrication and cooling mechanisms. These systems play a crucial role in minimizing friction between moving components, thereby reducing wear and tear over time. Proper maintenance of these systems is essential to prolong the lifespan of the gearbox and enhance its operational efficiency.
Lubrication is vital for maintaining smooth interactions among gears and other internal elements. High-quality lubricants not only reduce friction but also help in dissipating heat generated during operation. It is important to regularly check lubricant levels and replace them as needed to avoid potential damage.
The cooling system complements the lubrication process by managing heat levels within the gearbox. Efficient cooling prevents overheating, which can lead to component failure. Various cooling methods, such as oil coolers or dedicated cooling circuits, can be employed to ensure that the temperature remains within safe limits. Regular inspections and maintenance of both lubrication and cooling systems will greatly contribute to the longevity and reliability of the gearbox.
Common Wear Parts and Their Maintenance
In heavy-duty machinery, several components are subject to regular wear due to their crucial roles in performance. Understanding these elements and ensuring their upkeep is essential for the longevity and efficiency of the equipment. This section highlights frequently encountered wear items and best practices for their maintenance.
Identifying Key Components
Several critical components are typically affected by wear over time. Regular inspections can help identify signs of damage, allowing for timely replacements and maintenance. The following table outlines these components along with their specific maintenance requirements:
Component Signs of Wear Maintenance Tips Seals Leaking fluids Check for leaks regularly and replace worn seals promptly. Gears Chattering or grinding noises Inspect for wear patterns and lubricate as needed. Bearings Excessive play or noise Regularly check and replace bearings that show signs of wear. Filters Reduced performance Change filters according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Best Practices for Maintenance
To ensure the longevity of essential components, adhering to a regular maintenance schedule is vital. Implementing systematic inspections and timely replacements can significantly enhance the efficiency and reliability of the machinery.
Clutch and Input Shaft Assembly Diagram

This section provides an overview of the assembly that connects the power source to the drivetrain, focusing on the mechanism responsible for engaging and disengaging the driving force. Understanding the configuration and function of these components is crucial for maintenance and troubleshooting.
The assembly primarily consists of the following key elements:
- Clutch Plate: A critical component that facilitates the connection between the engine and the transmission.
- Pressure Plate: This element applies pressure to the clutch plate, ensuring effective engagement when activated.
- Input Shaft: This shaft transfers rotational power from the engine to the subsequent components within the assembly.
- Release Bearing: This part allows for smooth disengagement of the clutch by pushing against the pressure plate.
- Fork: A lever mechanism that moves the release bearing to engage or disengage the clutch.
Proper alignment and functioning of these components are vital for seamless operation, ensuring efficient power transmission and overall vehicle performance.
Transmission Housing and Support Brackets Overview
The structure that encases the internal mechanisms of a vehicle’s gear system plays a vital role in ensuring optimal performance. This casing not only houses the essential components but also provides stability and protection against external elements. Understanding the significance of this structure and its accompanying support elements is crucial for maintaining the functionality of the entire system.
Support brackets are integral to the overall assembly, serving as anchors that secure the housing to the chassis. These brackets are designed to withstand the vibrations and stresses encountered during operation, contributing to the longevity of the entire mechanism. Proper alignment and durability of these components are essential to prevent misalignment and potential damage.
Regular inspections of the casing and support elements can help identify wear and tear early, ensuring that any issues are addressed promptly. Maintaining the integrity of these components is essential for the reliable operation of the gear system, enhancing both safety and efficiency on the road.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Eaton Fuller 18-Speed
When operating heavy machinery, it is essential to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Various challenges can arise during use, impacting the overall functionality of the system. Identifying and addressing these issues promptly can prevent further complications and ensure smooth operation.
Here are some common problems you may encounter along with suggested solutions:
- Shifting Difficulties:
- Check for any obstructions in the linkage that may impede movement.
- Inspect the fluid levels and condition, ensuring they meet specifications.
- Examine the synchronizers for wear or damage.
- Unusual Noises:
- Listen for grinding sounds, which may indicate worn gears.
- Check for loose components that could cause rattling noises.
- Investigate the bearings for signs of deterioration.
- Overheating:
- Ensure proper cooling systems are functioning effectively.
- Monitor fluid temperatures to avoid excessive heat buildup.
- Inspect for any leaks that may lead to fluid loss.
- Fluid Leaks:
- Identify the source of the leak by checking seals and gaskets.
- Replace any damaged components to prevent further leakage.
- Regularly monitor fluid levels to detect any changes promptly.
By regularly inspecting these areas and addressing any issues, operators can maintain the reliability of their machinery, ensuring effective performance and longevity.
Transmission Upgrade Options and Compatibility
When considering enhancements for your vehicle’s shifting system, it is essential to evaluate various upgrade alternatives and their compatibility with your existing setup. Upgrading can lead to improved performance, better fuel efficiency, and enhanced driving experience.
Identifying Suitable Upgrades: Various upgrades are available, ranging from aftermarket solutions to factory enhancements. It is crucial to select components that align with your vehicle’s specifications to ensure optimal functionality and longevity. Upgrading clutches, gears, and associated components can provide significant benefits.
Compatibility Factors: Always verify the compatibility of new components with your vehicle model and configuration. Compatibility ensures that the new parts will work seamlessly with your current setup, minimizing the risk of issues during installation and operation. Consulting with professionals or utilizing detailed guides can assist in making informed decisions.