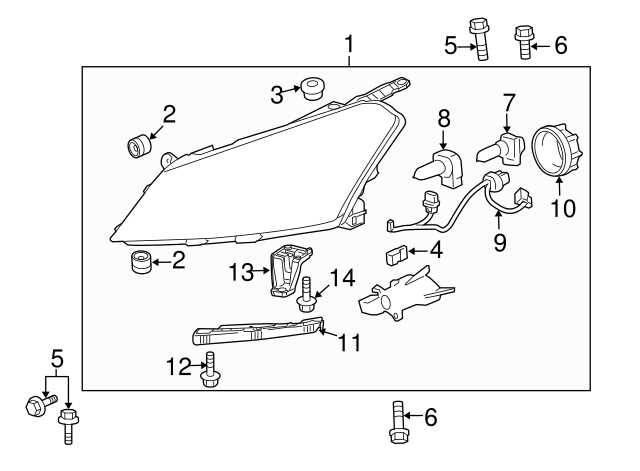
Understanding the configuration of essential vehicle elements is crucial for maintenance and repair. A well-structured representation provides valuable insights into how various components interconnect and function together. This knowledge is indispensable for both enthusiasts and professionals in the automotive field.
In this section, we delve into the intricate arrangement of a specific model’s features, highlighting their locations and roles within the assembly. Familiarizing oneself with these layouts can significantly enhance diagnostic accuracy and streamline the repair process.
By exploring the specific arrangement of each segment, individuals can make informed decisions regarding upgrades, replacements, and overall vehicle performance. This exploration serves not only to educate but also to empower vehicle owners and technicians alike in their endeavors to maintain and enhance their automobiles.
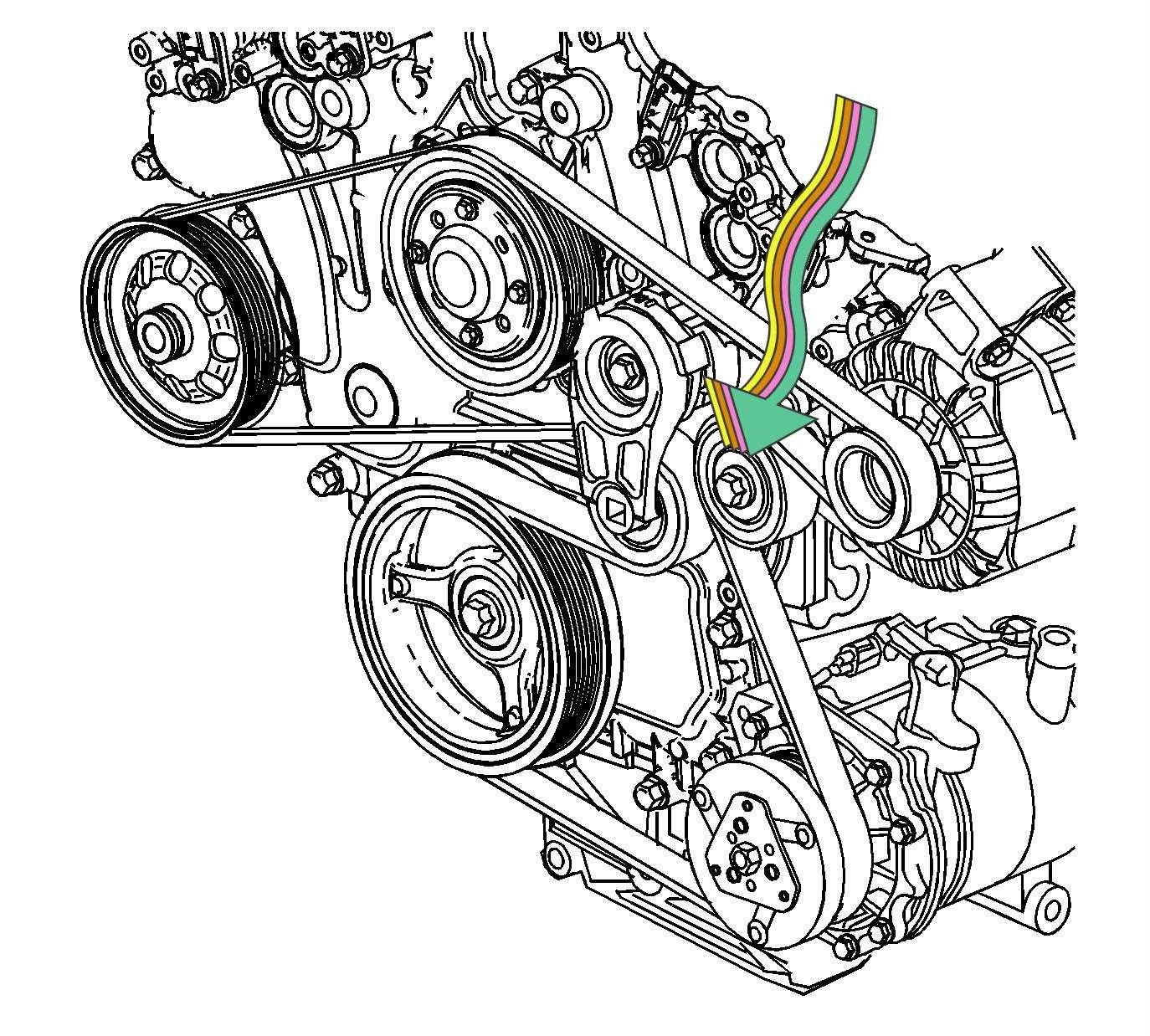
The transmission system plays a critical role in the overall performance and efficiency of a vehicle. This component is responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring smooth acceleration and deceleration. Understanding the intricacies of this system can provide valuable insights into its functioning and maintenance requirements.
Key Components of the Transmission System
- Torque Converter: Converts engine power into hydraulic energy, allowing for smooth gear shifts.
- Transmission Fluid: Lubricates and cools the internal parts, essential for optimal operation.
- Clutch Packs: Facilitate engagement and disengagement of gears during shifting.
- Valve Body: Directs fluid flow to various components, controlling gear changes.
- Transmission Control Module: An electronic unit that manages shifting based on driving conditions.
Specifications and Performance Metrics
- Gear Ratios: The varying ratios determine the power delivery and efficiency across different speeds.
- Fluid Capacity: Ensures that the system operates within optimal ranges for cooling and lubrication.
- Weight: Affects the overall mass of the vehicle, influencing fuel efficiency and handling.
- Torque Handling: The maximum torque capacity defines the performance limits of the transmission.
- Service Intervals: Regular maintenance is crucial to prevent wear and ensure longevity.
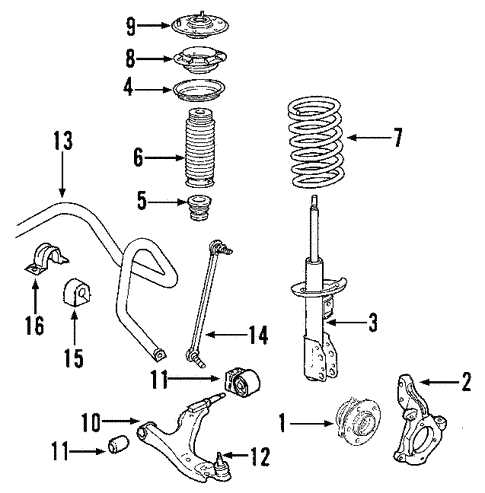
Suspension Setup and Key Parts

The suspension system plays a crucial role in the overall performance and comfort of a vehicle. It is designed to absorb shocks from the road, maintain tire contact, and enhance handling. Understanding the various components involved in this system is essential for ensuring optimal functionality and ride quality.
Essential Components

The main elements of the suspension assembly include shock absorbers, struts, and springs. Each component contributes to the vehicle’s ability to manage road imperfections and support the weight of the vehicle. Shock absorbers work to dampen the motion caused by uneven surfaces, while struts provide structural support and alignment for the wheels. Springs are responsible for supporting the vehicle’s weight and determining its ride height.
Adjustment and Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the suspension system is vital for safety and performance. Checking for signs of wear, such as leaking fluid from shock absorbers or unusual noises when navigating bumps, can prevent more significant issues down the line. Proper alignment and adjustments help maintain optimal handling and extend the lifespan of suspension components. Ensuring these elements are in good condition not only improves driving comfort but also enhances overall vehicle stability.
Brake System Configuration and Components
The braking mechanism of a vehicle is a crucial system that ensures safety by allowing effective deceleration and stopping. It is composed of several key elements that work together to provide optimal performance under various driving conditions. Understanding the layout and functionality of these components can aid in maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key components of the braking assembly include:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Brake Pedal | The interface for the driver to initiate braking by applying pressure. |
| Master Cylinder | Converts the force from the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure. |
| Brake Lines | Transport hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders. |
| Brake Calipers | Holds the brake pads and exerts pressure to clamp onto the brake disc, creating friction. |
| Brake Pads | Friction material that presses against the brake disc to slow down or stop the vehicle. |
| Brake Discs | Rotating elements that provide a surface for the brake pads to grip during braking. |
| Brake Fluid | A hydraulic fluid that transmits force and enables the brake system to function. |
Proper functioning of these components is vital for ensuring effective stopping power and overall vehicle safety. Regular inspection and maintenance can prevent premature wear and enhance the reliability of the braking system.
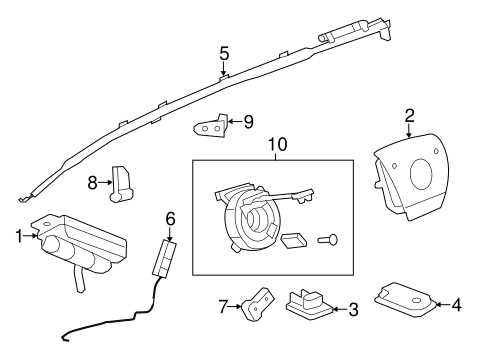
Electrical System Wiring and Layout
The intricate wiring and layout of the electrical framework play a crucial role in ensuring the optimal functionality of the vehicle’s systems. This section delves into the organization and connections of the various components, highlighting the significance of a well-structured electrical architecture.
At the core of the electrical system lies a network of wires and connectors that facilitate communication between different parts. This enables the efficient operation of crucial elements such as lighting, infotainment, and safety systems. Understanding the configuration is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance tasks.
| Component | Description | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Battery | Stores electrical energy for the vehicle. | Engine compartment |
| Fuses | Protects circuits from overload. | Fuse box under the dashboard |
| Wiring Harness | Bundle of wires that connects electrical components. | Throughout the vehicle |
| Control Modules | Processes signals from sensors and commands actions. | Under the dashboard |
| Ground Connections | Provides a return path for electrical current. | Various locations, typically near components |
A comprehensive understanding of this layout aids in identifying potential issues and facilitates efficient repairs. By maintaining the integrity of the electrical connections, vehicle performance can be optimized, ensuring a seamless driving experience.
Cooling System Components Explained
The efficient operation of a vehicle’s thermal management system is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance and longevity. This intricate system consists of various elements working together to regulate temperature and prevent overheating. Understanding these components is essential for effective maintenance and repair.
Radiator: The radiator serves as the primary heat exchanger, allowing coolant to dissipate heat absorbed from the engine. It consists of a network of tubes and fins that maximize surface area, facilitating efficient cooling as air flows through.
Water Pump: This component circulates coolant throughout the system, ensuring that it flows through the engine and radiator effectively. A properly functioning water pump is vital for maintaining consistent temperature levels.
Thermostat: The thermostat regulates coolant flow based on the engine’s temperature. It remains closed during cold starts, allowing the engine to warm up quickly, and opens when the desired temperature is reached, enabling proper circulation.
Cooling Fans: These fans assist in drawing air through the radiator when the vehicle is stationary or moving slowly. They help maintain optimal airflow, particularly in high-temperature conditions or during heavy engine loads.
Hoses: Various hoses connect different components within the cooling system, transporting coolant to and from the engine, radiator, and heater core. These flexible conduits must be regularly inspected for wear and leaks to ensure efficient operation.
Understanding the individual functions of each component allows for better diagnostics and maintenance practices, ultimately contributing to a vehicle’s reliability and performance.
Fuel System Architecture and Parts
The fuel system is a crucial component of any vehicle, designed to store and deliver the necessary energy for efficient operation. This intricate assembly consists of various elements working in harmony to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Understanding the structure and function of each component can aid in diagnosing issues and enhancing maintenance practices.
Components of the Fuel System include the fuel tank, which acts as a reservoir, ensuring a steady supply of gasoline or diesel. The fuel pump is responsible for transferring the fuel from the tank to the engine, while the fuel filter ensures that impurities are removed before entering the engine’s combustion chamber. Additionally, fuel injectors play a vital role in atomizing the fuel for efficient combustion, allowing for better fuel economy and reduced emissions.
Understanding the overall architecture of the fuel delivery mechanism is essential for effective troubleshooting and repair. Regular maintenance of these components can prevent performance degradation and extend the life of the engine, ensuring that the vehicle operates smoothly and efficiently.
Interior Layout and Essential Features
The design of the interior space emphasizes comfort and functionality, catering to the diverse needs of occupants. The arrangement facilitates easy access to controls and ensures a welcoming atmosphere. Thoughtful design choices enhance the overall experience, making it suitable for both daily commutes and long journeys.
Seating Configuration and Comfort
The seating arrangement accommodates up to seven individuals, providing ample space for passengers and cargo. Ergonomically designed seats ensure comfort during extended travel, while adjustable features allow for personalized positioning. The availability of premium materials enhances the overall aesthetic, contributing to a refined ambiance.
Technology and Connectivity
Modern technological advancements are seamlessly integrated into the cabin, offering various connectivity options. An intuitive infotainment system provides easy access to navigation, audio, and communication features. Multiple USB ports and Bluetooth capabilities enable passengers to stay connected, ensuring an enjoyable and convenient journey.
Exterior Elements and Body Parts
The exterior design of a vehicle plays a vital role in its overall aesthetic and functionality. This section will explore the various components that contribute to the vehicle’s outer appearance and structural integrity, highlighting their significance in both style and performance.
Key Components
- Bumpers: Essential for absorbing impact during minor collisions, they also enhance the visual appeal.
- Fenders: These elements protect the wheels and house vital components while providing a sleek look.
- Hoods: Serving as a cover for the engine, they are designed for ease of access during maintenance.
- Doors: Not only do they provide entry and exit, but they also contribute significantly to the overall shape of the vehicle.
- Windows: Designed for visibility and safety, they can also enhance the vehicle’s style.
Material Considerations
Many exterior elements are crafted from materials such as steel, aluminum, and plastic. Each material has unique properties affecting durability, weight, and cost:
- Steel: Known for its strength, it provides excellent protection but can add weight.
- Aluminum: Lighter than steel, it offers good corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice for various components.
- Plastic: Often used for trim and panels, it can be molded into intricate shapes, allowing for creative designs.
Diagnostic Tools for Parts Inspection
Assessing the integrity of vehicle components requires specialized instruments that provide precise evaluations. These tools enable technicians to detect issues, verify functionality, and ensure optimal performance. Understanding the various options available can streamline the inspection process and enhance reliability.
- Multimeters: Essential for measuring voltage, current, and resistance. They are invaluable for diagnosing electrical systems.
- OBD-II Scanners: Devices that connect to the onboard diagnostics system to retrieve error codes, helping to identify malfunctions.
- Pressure Gauges: Useful for assessing fluid pressure in systems like fuel and oil, crucial for maintaining performance standards.
- Thermal Imaging Cameras: These allow for non-invasive inspections by identifying hot spots and thermal variations in components.
Each of these instruments plays a vital role in ensuring the various systems operate smoothly. By employing a combination of these tools, technicians can achieve a thorough understanding of component conditions.
- Choose the appropriate tool based on the specific system being inspected.
- Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for usage to avoid damaging components.
- Document findings to track performance trends over time.
Investing in high-quality diagnostic instruments ultimately leads to more effective maintenance strategies and increased vehicle longevity.
Common Repairs and Replacement Guidelines
Understanding typical maintenance tasks and component exchanges can greatly enhance the longevity and performance of your vehicle. Identifying frequent issues allows for proactive measures, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing unexpected breakdowns.
When addressing repairs or substitutions, it is essential to follow certain protocols to guarantee safety and effectiveness. Here are some common interventions to consider:
| Component | Symptoms | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Brake Pads | Squeaking or grinding noises, reduced braking efficiency | Inspect and replace if worn |
| Battery | Dimming lights, difficulty starting | Test and replace if needed |
| Oil Filter | Engine noise, oil leaks | Replace during routine oil changes |
| Air Filter | Decreased fuel efficiency, poor acceleration | Inspect and replace as necessary |
| Wiper Blades | Streaking or skipping during use | Replace for optimal visibility |
Regular inspections and timely replacements of these components contribute to the overall reliability of your vehicle. Following manufacturer guidelines and consulting with a professional can further ensure proper handling and maintenance.