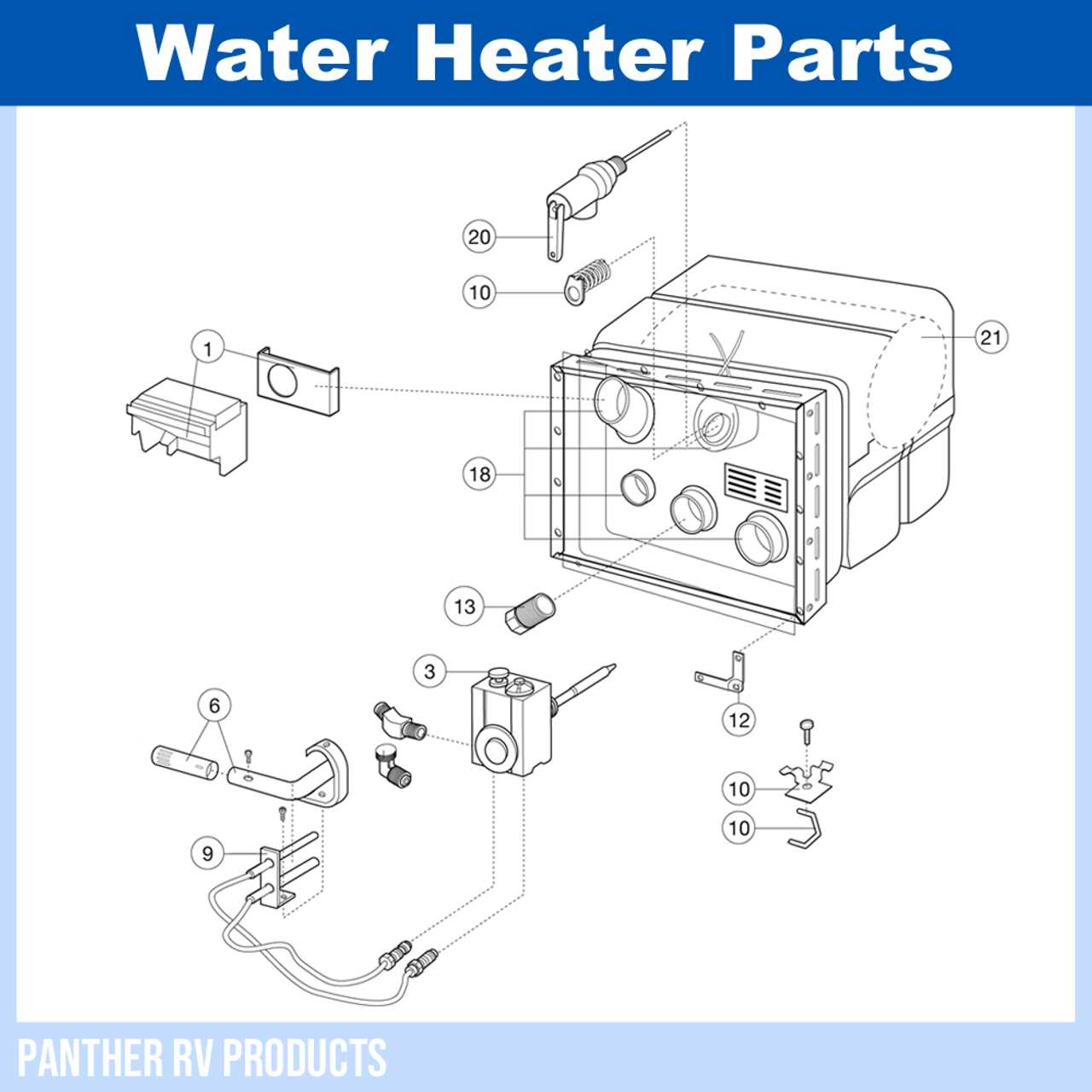
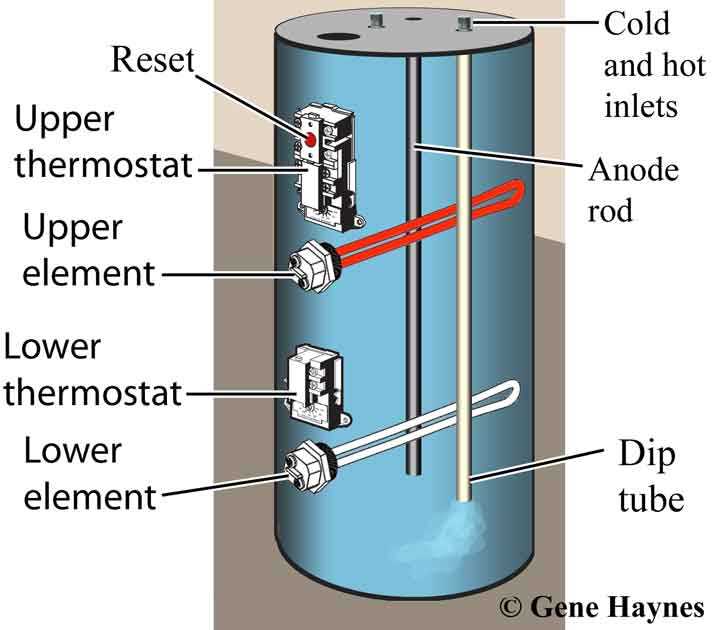
Thermostat Role in Temperature Control
The thermostat is a vital component in ensuring a consistent and desired temperature is maintained. It acts as the system’s regulator, allowing for precise management of warmth levels, ensuring comfort and efficiency. By continuously monitoring conditions, this device adjusts the heating process to avoid fluctuations and energy waste.
How it Works: The thermostat uses a sensor to detect the surrounding warmth. Once the desired threshold is reached, it sends a signal to halt the heating process. If the temperature drops below the set level, the device triggers the system to resume until balance is restored.
Common Materials in Heating Elements
The performance and efficiency of heating components largely depend on the materials used in their construction. Different substances possess unique properties that affect heat generation, conductivity, and durability. Understanding these materials is essential for selecting the appropriate element for specific applications.
Commonly Used Materials
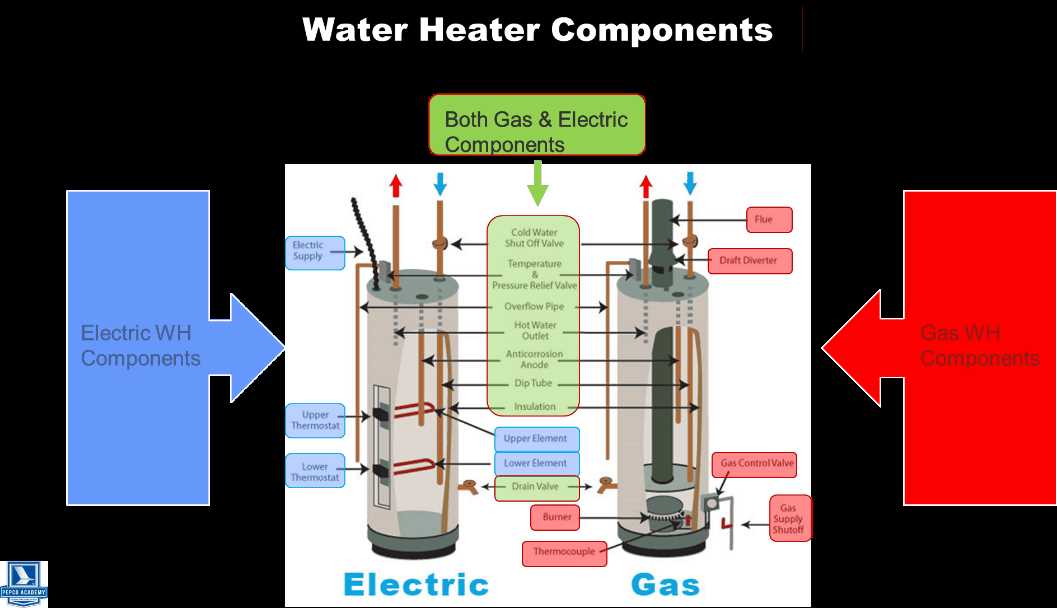
Among the most widely utilized materials are nickel-chromium alloys, known for their high resistance to oxidation and excellent thermal stability. These alloys can withstand elevated temperatures while providing efficient heating. Another popular choice is copper, valued for its outstanding electrical conductivity and thermal efficiency. However, it is often combined with other metals to enhance its resistance to corrosion.
Emerging Alternatives

In recent years, silicon carbide has gained popularity as a material for heating elements. Its ability to withstand extreme conditions and provide uniform heating makes it suitable for various high-temperature applications. Additionally, tungsten is becoming increasingly favored in specialized environments due to its remarkable melting point and durability.
Anode Rod: Purpose and Maintenance
The anode rod serves a critical function in prolonging the lifespan of a heating appliance. It acts as a sacrificial component that attracts corrosive elements, preventing damage to the inner lining of the storage unit. Regular attention to this element ensures optimal performance and durability of the system.
Functionality of the Anode Rod
This rod is primarily designed to counteract the corrosive effects of minerals present in the liquid. As it deteriorates over time, it helps to safeguard the internal surfaces from rust and degradation. By sacrificing itself, the rod allows the tank to maintain its integrity and efficiency.
Maintenance Recommendations
To ensure longevity, periodic inspections of the anode rod are essential. It is advisable to check its condition every one to three years, depending on the mineral content of the liquid. If significant corrosion is observed, replacement is necessary. Proper upkeep not only enhances the longevity of the unit but also promotes efficient operation.
Tank Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Proper insulation plays a crucial role in maintaining the temperature of stored fluids, significantly affecting overall performance and operational costs. By minimizing heat loss, effective thermal barriers ensure that less energy is required to maintain desired temperatures, ultimately leading to lower utility expenses and reduced environmental impact.
Insulation materials are vital in enhancing thermal retention. Commonly utilized substances include fiberglass, foam, and mineral wool, each offering unique advantages in terms of thermal resistance and longevity. The choice of insulation directly influences not only the efficiency of the system but also its operational lifespan.
Energy efficiency is further improved by ensuring that insulation covers all surfaces adequately. Gaps or weak points in the insulation can lead to significant energy loss, undermining the benefits of even the best materials. Regular inspections and maintenance are essential to identify potential issues early and maintain optimal performance.
Investing in quality insulation solutions can yield substantial savings over time, making it a wise choice for both residential and commercial applications. By enhancing thermal efficiency, users can enjoy consistent performance while contributing to a more sustainable energy future.
Water Inlet and Outlet Connections Explained
The connection points for liquid entry and exit play a crucial role in the overall functionality of a heating appliance. Understanding how these interfaces work can enhance efficiency and ensure optimal performance. This section delves into the significance, structure, and function of these connections, shedding light on their integral role in the system.
Importance of Connections
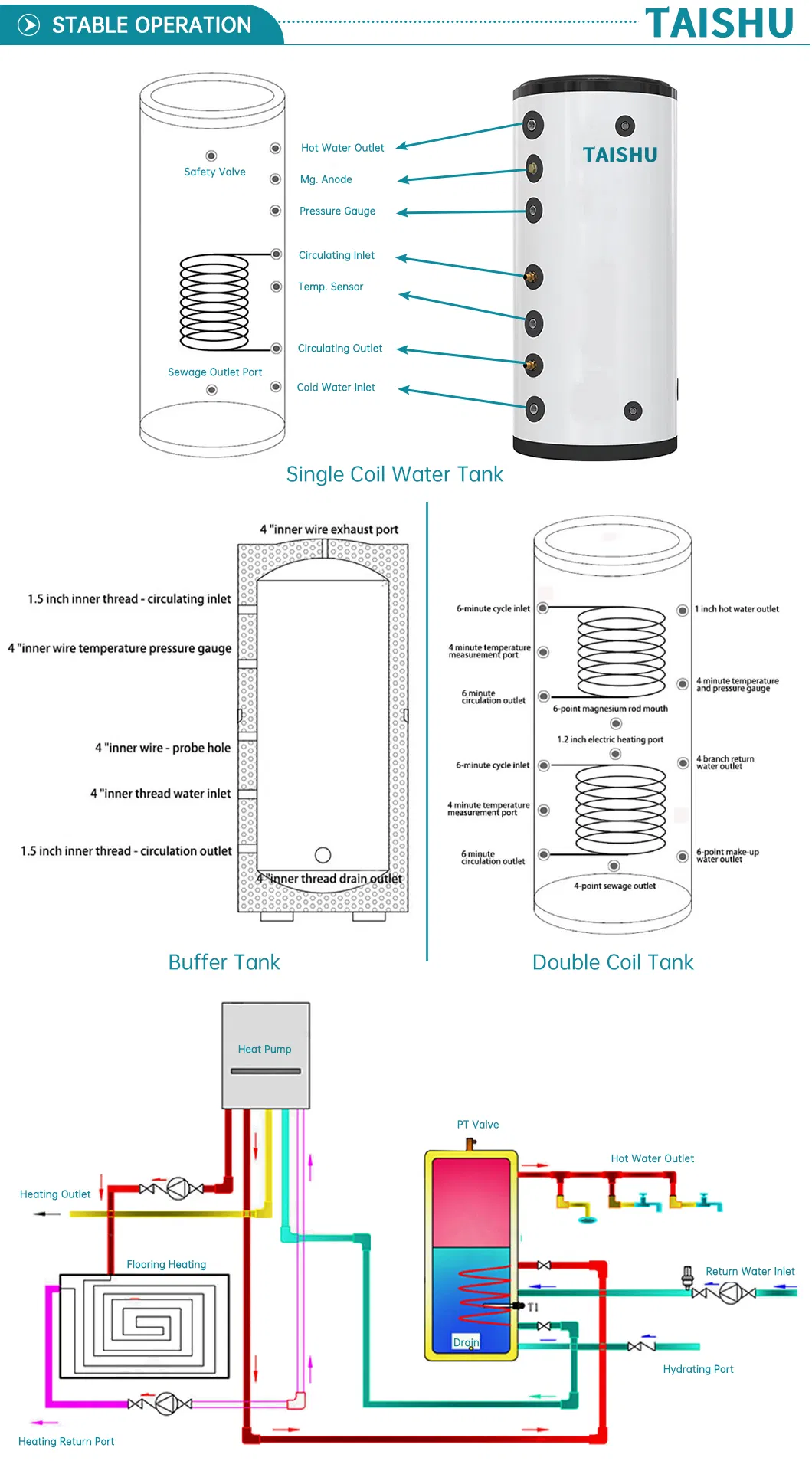
Connections facilitate the flow of liquid, which is essential for temperature regulation. Proper functioning of these interfaces contributes to:
- Effective heat transfer
- Consistent temperature control
- Reduction of energy wastage
- Minimized risk of leaks or failures
Types of Connections
There are typically two primary connections involved:
- Entry Point: This is where the fluid enters the system. It is often designed to maintain a steady flow and may include filters or valves to control pressure and prevent debris from entering.
- Exit Point: This allows the heated fluid to leave the system. This connection must be robust to handle varying pressures and prevent leaks, ensuring safe operation.
Pressure Relief Valve and Its Function

The pressure relief valve is a critical component designed to enhance safety and functionality in thermal systems. Its primary role is to prevent excess pressure build-up, which could lead to catastrophic failures. This device automatically releases excess pressure, maintaining optimal operating conditions and safeguarding the overall integrity of the system.
When pressure within the system exceeds a predetermined threshold, the valve opens, allowing steam or fluid to escape. This action not only protects the equipment but also prevents potential hazards, such as explosions or leaks. Proper maintenance and regular inspection of this component are essential to ensure its effectiveness and reliability.
In summary, the pressure relief valve serves as a crucial safety mechanism, playing a vital role in regulating internal pressure and preventing dangerous situations. Understanding its function and importance is key for anyone involved in the operation or maintenance of thermal systems.
Drain
The process of removing excess liquid from a system is essential for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring longevity. Proper drainage mechanisms facilitate the safe disposal of fluids, preventing potential issues such as leaks or damage.
Effective drainage typically involves several key components:
- Outlet Valve: A crucial element that allows for the controlled release of accumulated fluids.
- Drain Hose: A flexible conduit that directs the expelled liquid away from the system.
- Drain Pan: A containment unit designed to catch any spillage during the drainage process.
- Filters: Devices that help to trap sediment and debris, ensuring a clear flow and reducing blockages.
Regular maintenance of these components is vital for efficiency. Neglecting drainage can lead to:
- Clogged pathways, causing backflow.
- Increased pressure within the system, leading to potential ruptures.
- Decreased performance and higher energy consumption.
In summary, a well-designed and maintained draining system is integral for the effective functioning of any apparatus requiring fluid management. Ensuring the integrity of the drainage components will safeguard against future complications and enhance operational reliability.