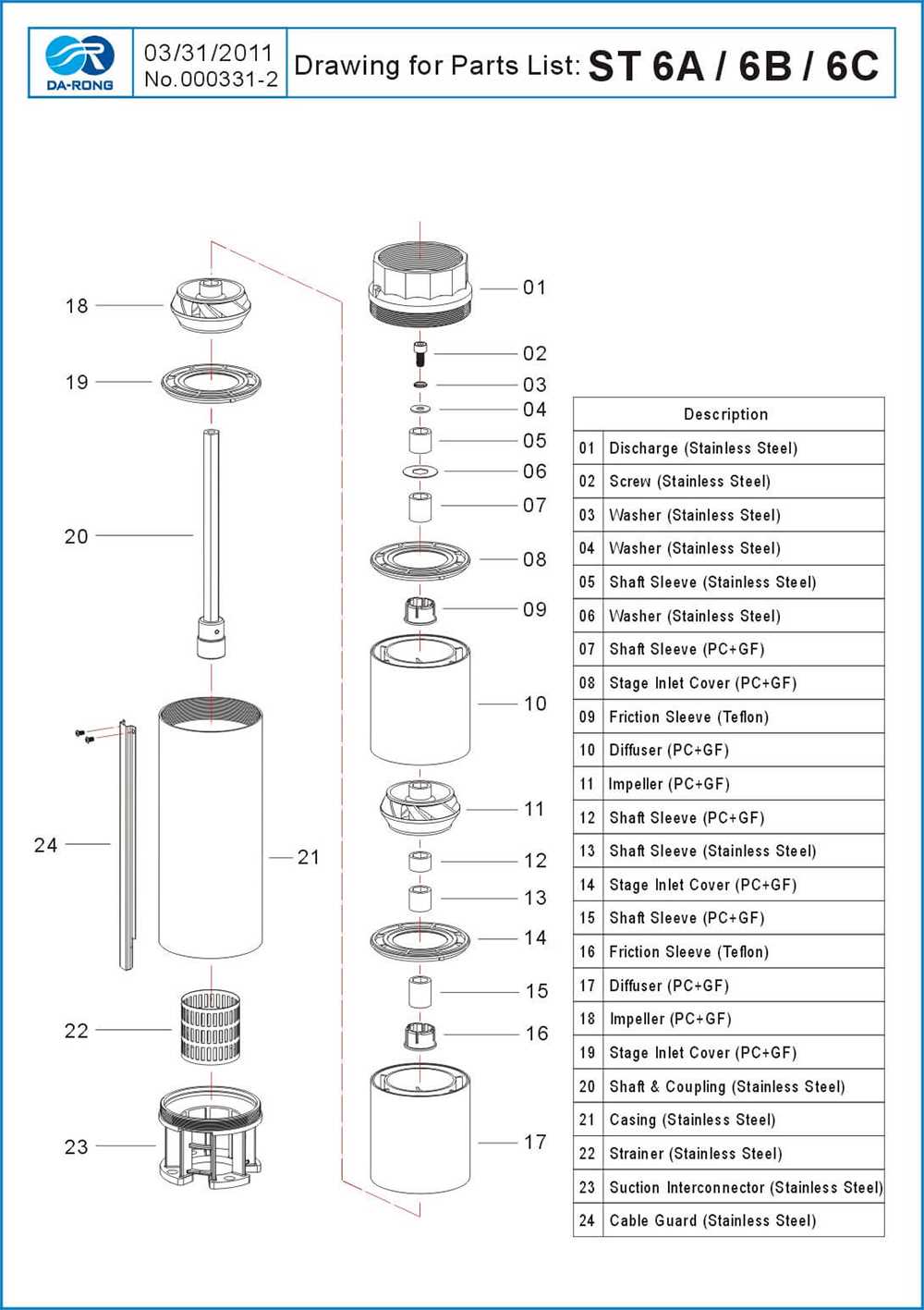
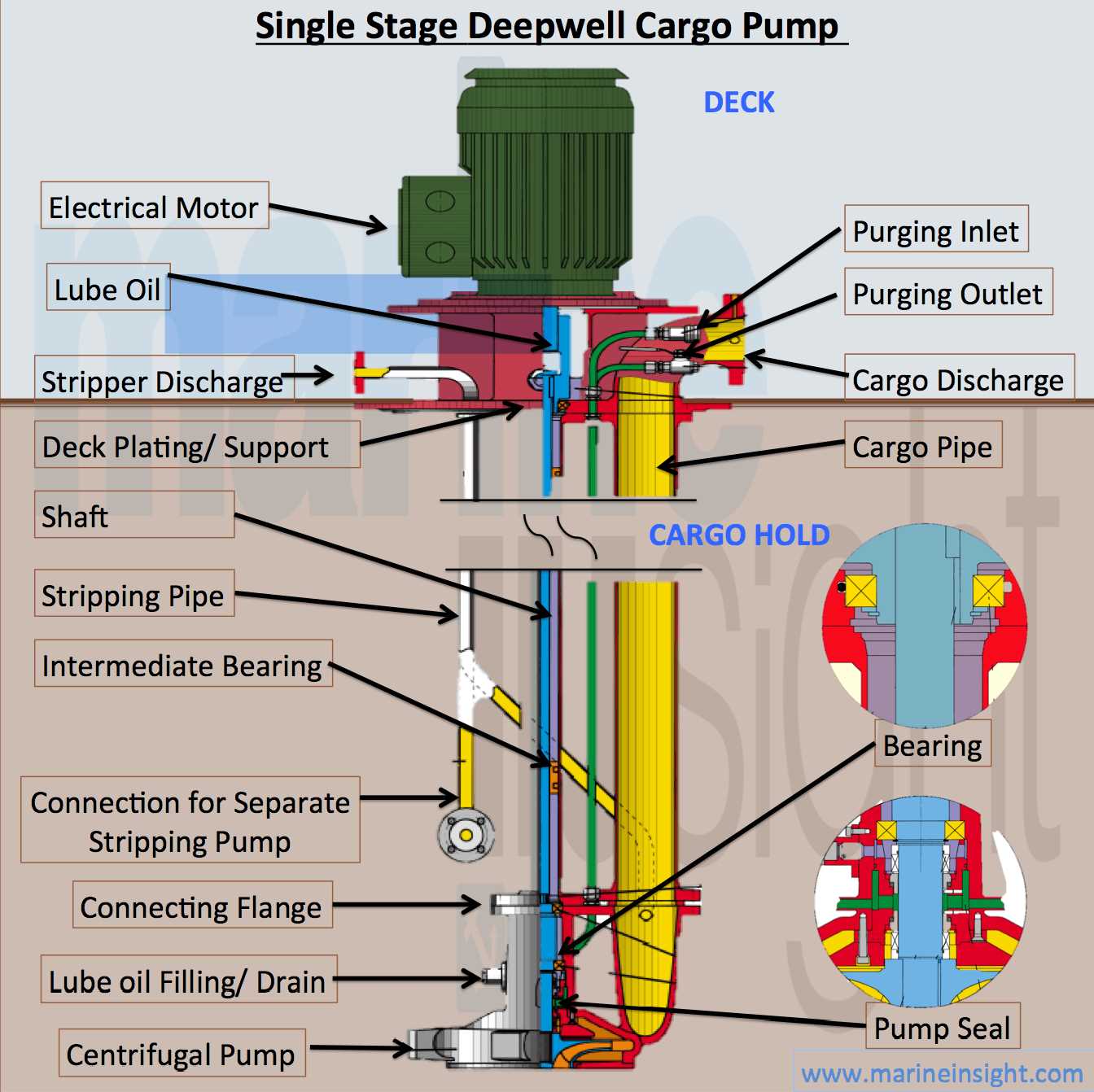
In the realm of fluid extraction systems, comprehending the essential elements involved is crucial for both maintenance and troubleshooting. These systems consist of various intricate components that work harmoniously to ensure optimal functionality. A thorough understanding of these mechanisms can significantly enhance efficiency and prolong the lifespan of the entire assembly.
Each component plays a vital role, contributing to the overall operation and effectiveness of the setup. Familiarity with these individual elements, their positions, and interconnections can aid in diagnosing issues swiftly and implementing effective solutions. This knowledge is invaluable for both novice users and experienced professionals alike.
Moreover, recognizing the unique characteristics and functions of each segment allows for informed decision-making when it comes to repairs or upgrades. Whether addressing minor repairs or conducting extensive overhauls, a detailed comprehension of the system’s anatomy is essential for achieving optimal performance and reliability.
Understanding Water Well Pump Components
Grasping the various elements involved in this mechanism is essential for effective operation and maintenance. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring the entire system functions seamlessly, contributing to the overall efficiency and reliability of the setup.
1. Motor: The driving force behind the system, responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
2. Shaft: A vital connector that transmits rotational energy from the motor to the working mechanism.
3. Impeller: This component creates the necessary force to move fluid through the system, often designed to optimize flow and efficiency.
4. Discharge Head: The top assembly that allows the fluid to exit the unit, often equipped with features to facilitate monitoring and control.
5. Check Valve: A safety element that prevents backflow, ensuring that the fluid remains within the desired pathway.
Familiarity with these components not only aids in troubleshooting but also enhances overall knowledge of the system’s functionality.
Types of Water Well Pumps Explained
Understanding the various mechanisms used for extracting groundwater is essential for selecting the right equipment for specific needs. Each type offers distinct advantages, making them suitable for different applications and depths.
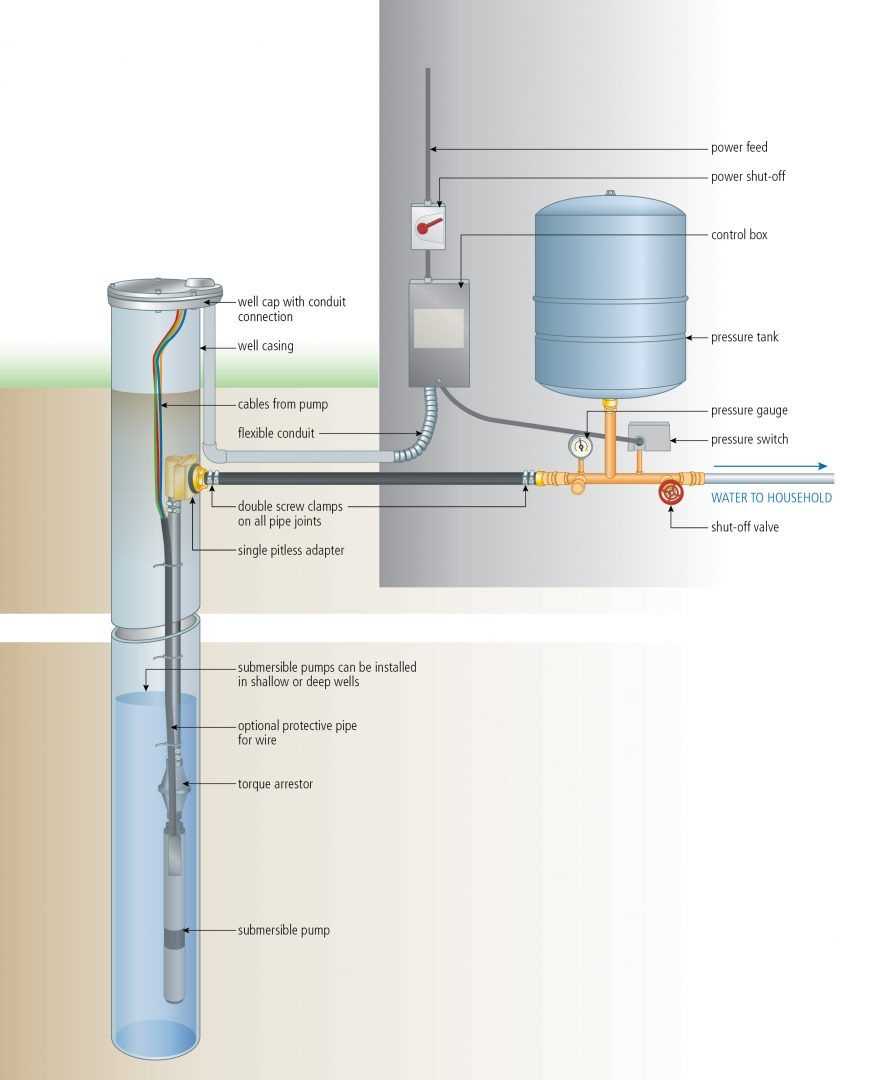
- Submersible Units: These are designed to be submerged underwater, featuring a hermetically sealed motor and pump that work together to deliver fluids efficiently.
- Jet Systems: Operating on the principle of creating a vacuum, these systems are typically placed above ground and are ideal for shallow sources.
- Diaphragm Mechanisms: Known for their ability to handle varied liquid types, these units use a flexible membrane to create pressure and move fluids.
- Hand Operated Models: A manual option that relies on human effort, these are useful in remote locations where electricity is unavailable.
Each of these systems has unique characteristics that cater to different extraction requirements, ensuring efficiency and reliability in accessing underground resources.
Key Parts of Submersible Pumps
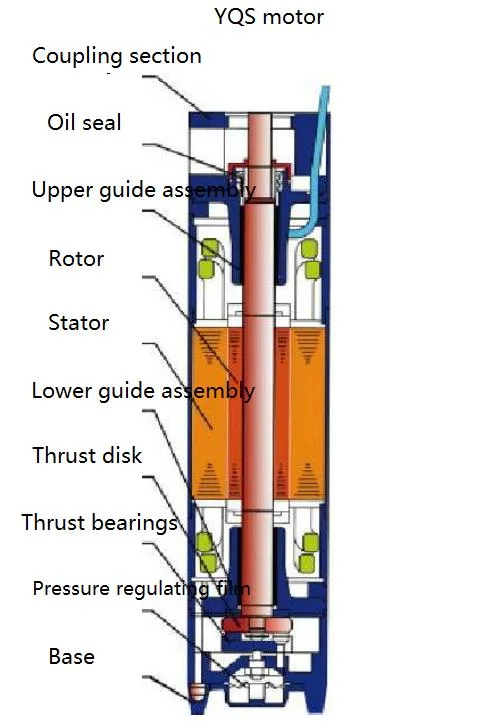
Understanding the essential components of these submerged devices is crucial for efficient operation and maintenance. Each element plays a specific role in the overall functionality, ensuring that the mechanism operates smoothly and effectively. Below are the primary components that contribute to their performance.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Motor | Drives the entire assembly, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to create movement. |
| Impeller | A rotating component that propels fluids, generating flow and pressure within the system. |
| Diffuser | Helps to channel and convert the kinetic energy from the impeller into pressure, aiding in fluid delivery. |
| Discharge Head | Serves as the outlet for the fluid, facilitating its transfer to the surface or desired location. |
| Strainer | Filters out debris and particles, protecting internal components from damage and ensuring longevity. |
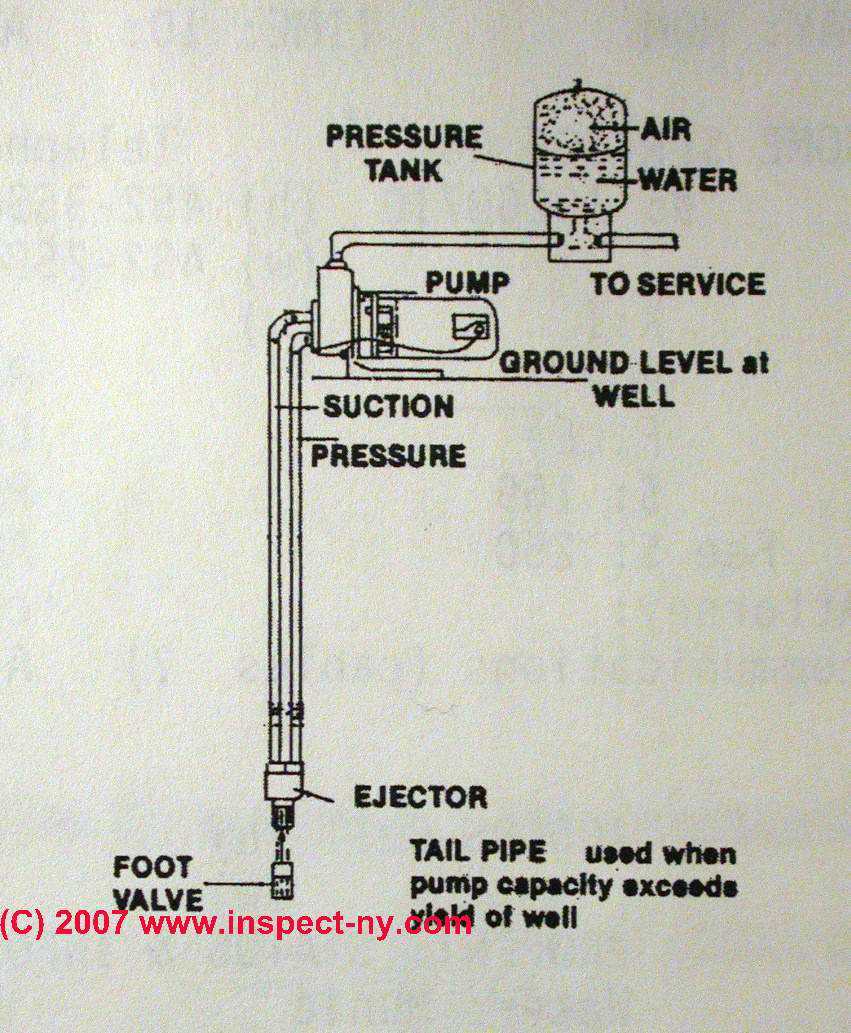
Surface Pump Mechanisms and Functionality
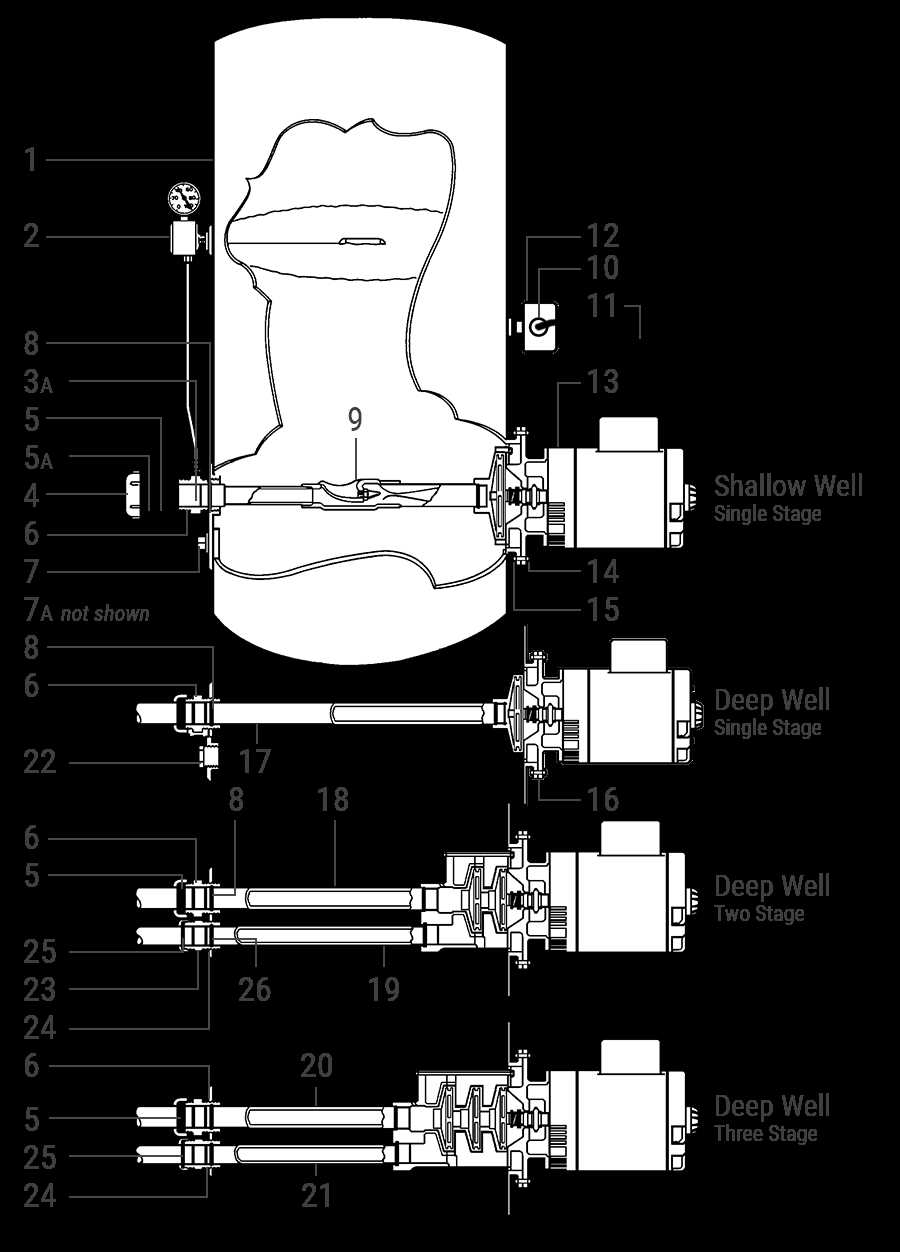
This section explores the essential components and operational principles behind surface extraction systems. Understanding these mechanisms allows for a deeper appreciation of their effectiveness in fluid management.
Key Components
These systems typically consist of a motor, an impeller, and a casing. The motor drives the impeller, generating the necessary force to move the liquid. The casing encases these components, ensuring that the fluid is directed efficiently.
Operational Principles
At the core of their functionality is the conversion of mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. As the impeller spins, it creates a centrifugal force that pushes the liquid through the casing. This process results in an increase in pressure, allowing for effective transport to desired locations. Efficiency and performance depend significantly on the design and quality of these components.
Common Materials Used in Pumps

Understanding the materials utilized in fluid transfer mechanisms is crucial for ensuring durability and efficiency. Various substances are employed, each selected for specific properties that enhance performance in diverse environments. This section explores the prevalent materials found in these devices and their unique characteristics.
Metals
Metals are frequently chosen for their strength and resistance to wear. Commonly used alloys include stainless steel and cast iron, known for their longevity and ability to withstand harsh conditions.
Plastics
Plastics offer a lightweight alternative with excellent corrosion resistance. Materials like polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polypropylene are often used in applications requiring chemical compatibility and low maintenance.
| Material | Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant, strong | Abrasive liquids, high-pressure systems |
| Cast Iron | Durable, wear-resistant | Heavy-duty machinery |
| PVC | Lightweight, chemical-resistant | Chemical transport, low-pressure systems |
| Polypropylene | Flexible, resistant to many chemicals | Wastewater applications |
Diagram of Pump Assembly Parts
This section provides an overview of the key components involved in the mechanical system designed for fluid extraction. Understanding the assembly and its individual elements is essential for efficient operation and maintenance.
Key Components Overview
Each segment of the mechanism plays a crucial role in ensuring functionality. From the motor to the impeller, familiarity with these elements allows for better troubleshooting and enhancements.
Component Functions
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Motor | Drives the entire mechanism, converting electrical energy into mechanical motion. |
| Impeller | Creates the necessary pressure to move the fluid through the system. |
| Seal | Prevents leakage and ensures optimal performance by maintaining pressure. |
| Housing | Encases the internal components, providing protection and support. |
Essential Tools for Pump Maintenance

Maintaining your system requires specific instruments that ensure efficiency and longevity. Having the right tools at your disposal not only simplifies the upkeep process but also enhances the performance of your equipment.
Basic Maintenance Instruments
- Wrenches: Useful for tightening and loosening various fittings.
- Screwdrivers: Essential for assembling and disassembling components.
- Pliers: Help in gripping and bending materials as needed.
Advanced Diagnostic Tools
- Pressure Gauge: Measures the system’s pressure to detect issues.
- Multimeter: Evaluates electrical connections and current flow.
- Flow Meter: Assesses the efficiency of fluid movement.
Identifying Pump Failure Symptoms
Recognizing the signs of malfunction is crucial for maintaining efficiency in any fluid-moving system. Early detection can prevent extensive damage and costly repairs.
- Reduced Flow Rate: A noticeable decrease in the amount of liquid being moved can indicate an issue.
- Unusual Noises: Grinding, whining, or any unexpected sounds may suggest mechanical problems.
- Vibrations: Excessive shaking or vibrations during operation can point to misalignment or wear.
- Overheating: Elevated temperatures can signify a lack of lubrication or excessive friction within components.
- Leakage: Any signs of fluid escaping from connections or seals should be investigated immediately.
By staying vigilant and understanding these symptoms, timely interventions can be made to ensure continued performance and longevity.
Safety Precautions During Pump Repair
Ensuring a secure environment is essential when undertaking maintenance on any mechanical system. Adopting appropriate safety measures can prevent accidents and injuries, safeguarding both the individual performing the task and the surrounding area. Understanding potential hazards and preparing accordingly is crucial for a successful repair process.
Before beginning any repair work, it is vital to disconnect the power source to eliminate the risk of electrical shock. Verify that all switches and circuit breakers are turned off, and use lockout/tagout procedures to ensure no accidental reactivation occurs. Properly grounding tools and equipment can further reduce the risk of electrical incidents.
Wearing suitable personal protective equipment (PPE) is imperative. This includes gloves, goggles, and sturdy footwear to protect against sharp objects and heavy components. Additionally, maintaining a clean and organized workspace minimizes the chances of slips, trips, and falls.
When handling tools and equipment, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use the correct tools for each task. Improvised tools can lead to mistakes and injuries. If lifting is necessary, employing proper lifting techniques or mechanical aids can prevent strain and injury.
Lastly, being aware of potential hazards associated with the specific system being serviced is essential. Familiarize yourself with any chemicals or fluids involved, and take precautions to manage spills or leaks effectively. By following these guidelines, you can ensure a safe and efficient repair experience.
Replacement Parts for Water Pumps
When maintaining any fluid-moving device, understanding the necessary components for replacement is crucial. These essential elements ensure optimal performance and longevity, helping to avoid costly repairs and downtime. Whether dealing with mechanical failures or routine wear, knowing which items to keep on hand can make all the difference in efficiency.
Common Components Needing Replacement

Several key elements often require attention during maintenance. Seals and gaskets are prone to deterioration over time, leading to leaks and inefficiencies. Impellers, which play a vital role in creating flow, may become damaged due to debris or wear, necessitating timely replacement. Additionally, motors may need servicing or replacement if they show signs of electrical failure or overheating.
Choosing Quality Replacements
Opting for high-quality replacements is essential for ensuring reliability and performance. When sourcing these components, consider reputable manufacturers and check compatibility with existing systems. Investing in durable materials can significantly reduce the frequency of future replacements, ultimately saving time and resources.
Best Practices for Pump Efficiency
Maximizing the performance of a fluid transfer system is essential for achieving optimal results and minimizing operational costs. Adopting effective strategies can significantly enhance the functionality and lifespan of the system.
Regular Maintenance: Conducting routine inspections and servicing ensures that all components are functioning as intended. This practice helps to identify potential issues early, preventing costly repairs and downtime.
Appropriate Sizing: Selecting the correct dimensions for the equipment is crucial. Oversized or undersized units can lead to inefficiencies, resulting in increased energy consumption and reduced effectiveness.
Monitor Operating Conditions: Keeping an eye on the working environment and parameters allows for adjustments that can improve efficiency. Temperature, pressure, and flow rate should be regularly evaluated to maintain peak performance.
Utilize Quality Components: Investing in high-quality elements contributes to the overall reliability of the system. Premium materials often provide better durability and performance, leading to fewer issues in the long run.
Optimize Energy Use: Implementing energy-efficient practices, such as variable frequency drives, can greatly reduce consumption. This adjustment allows the system to adapt to varying demands while conserving energy.