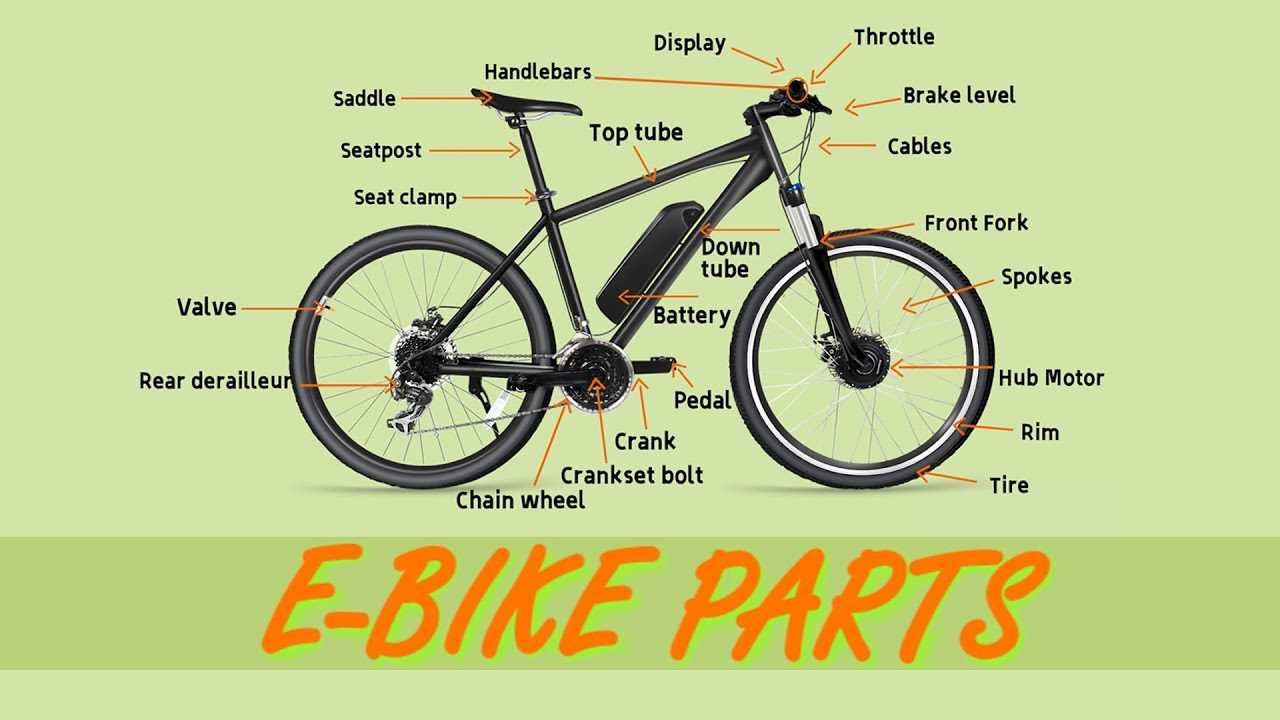
In the realm of outdoor adventures, the intricacies of a rugged two-wheeled machine play a crucial role in enhancing performance and ensuring a thrilling experience. Each element serves a unique function, contributing to the overall efficiency and functionality of the vehicle.
Exploring these crucial elements allows enthusiasts to appreciate the engineering marvel that supports their journeys through challenging terrains. Knowledge of these components not only improves maintenance skills but also enhances the rider’s ability to choose the right equipment for their specific needs.
Diving into the details reveals how each section interacts harmoniously, ultimately creating a seamless ride. Understanding these essentials empowers riders to make informed decisions, optimizing their experience on the trails.
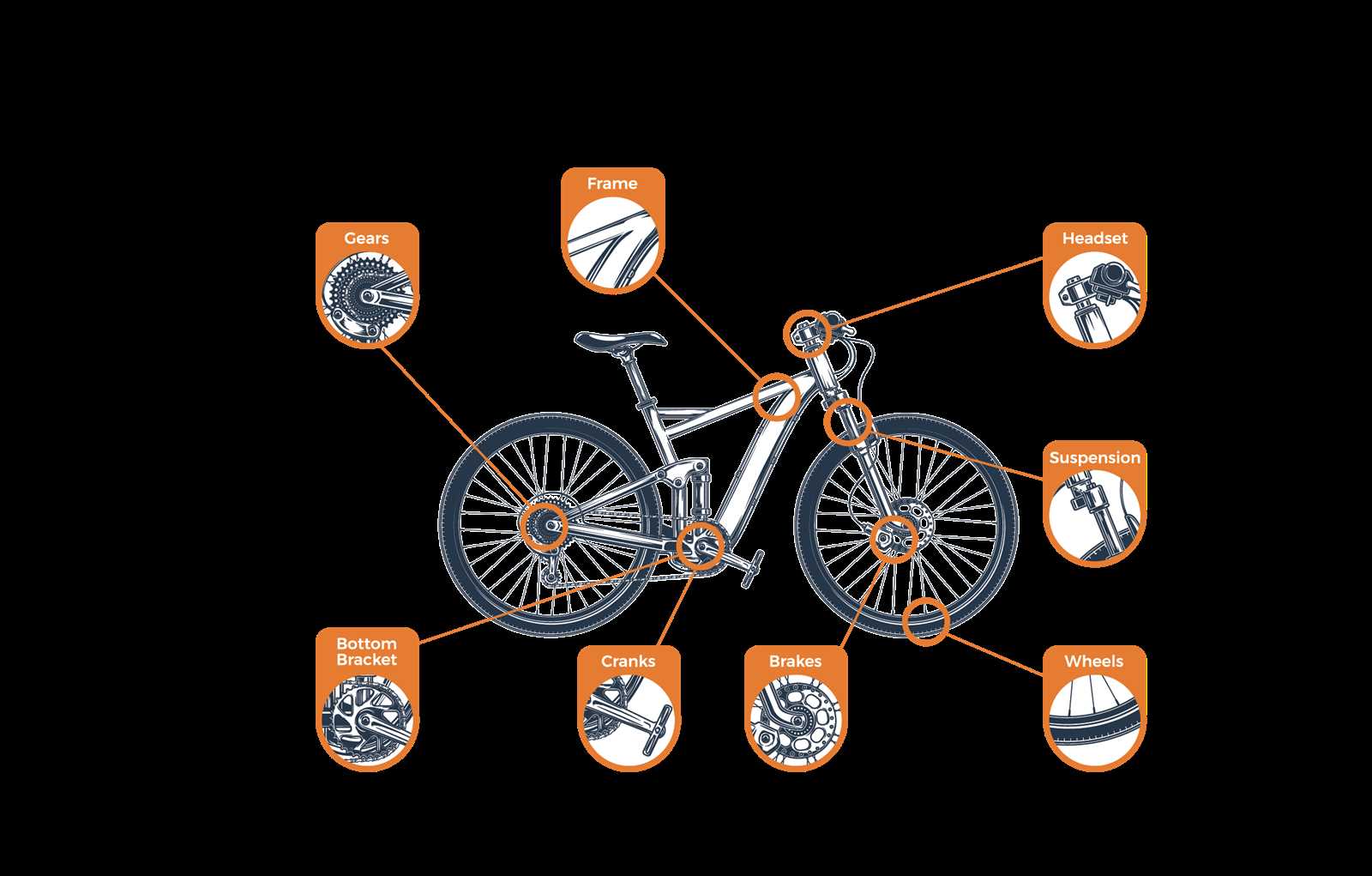
Understanding Mountain Bike Components
This section explores the essential elements that contribute to the functionality and performance of a cycling machine designed for rough terrains. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and efficient ride, allowing enthusiasts to tackle challenging trails with confidence.
Key Elements of the Cycling System
Within this type of vehicle, various elements work in harmony to enhance durability, control, and speed. A closer examination reveals how these components influence the overall riding experience.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Frame | The structure that supports all other elements and affects handling and weight. |
| Suspension | Mechanism that absorbs shocks from rough surfaces, improving comfort and stability. |
| Wheels | Circles that provide movement and traction, crucial for navigating uneven paths. |
| Brakes | Systems that slow down or stop the machine, essential for safety and control. |
| Drivetrain | Assembly that transfers energy from the rider to the wheels, affecting speed and efficiency. |
Importance of Each Component
Understanding the significance of each element allows riders to make informed choices about upgrades and maintenance. This knowledge enhances not only performance but also the overall enjoyment of outdoor adventures.
Frame: The Bike’s Backbone
The structure of a two-wheeled vehicle serves as its essential support system, providing stability and strength. This central component connects all other elements, ensuring they function harmoniously together.
Durability is crucial; a robust frame withstands various terrains and impacts, enhancing performance. Materials like aluminum and carbon fiber are popular choices due to their lightweight yet resilient properties.
Furthermore, the design influences handling and comfort. A well-engineered frame allows for optimal rider positioning, contributing to an enjoyable experience on rugged paths. Ultimately, investing in a quality frame is vital for any enthusiast seeking adventure.
Wheels: Types and Specifications
The wheels of a two-wheeled vehicle play a crucial role in determining its performance and handling characteristics. Various designs and specifications cater to different riding styles and terrain types, allowing riders to choose the most suitable option for their needs.
One common type is the standard rim, typically constructed from aluminum or carbon fiber, offering a balance of weight and strength. Wider rims are favored for improved traction and stability, especially on uneven surfaces. Additionally, the diameter of the wheel significantly affects speed and maneuverability, with larger wheels providing better rolling efficiency over obstacles.
Another important aspect is the tire selection. Tires come in different tread patterns, which influence grip and control. Some feature aggressive treads for off-road conditions, while others are smoother for paved paths. Tire width also varies, with wider options enhancing comfort and traction, while narrower designs may reduce rolling resistance.
Overall, understanding the various types and specifications of wheels is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring an enjoyable riding experience. Riders should consider their preferences and the environments in which they ride to make informed choices.
Tires: Choosing the Right Grip
Selecting the appropriate surface contact is crucial for achieving optimal performance on rugged terrains. The choice impacts not only speed but also stability and control, making it essential to understand the various options available. Different conditions demand distinct characteristics in tread patterns, rubber compounds, and overall tire design.
Tread Patterns
The design of the tread significantly influences traction. Aggressive patterns with deeper lugs are ideal for loose or muddy environments, providing enhanced grip. Conversely, smoother treads excel on hard-packed surfaces, allowing for reduced rolling resistance and increased speed. Understanding the terrain where the ride will take place is vital for making the right choice.
Rubber Compound
The material used in tire construction also plays a key role in performance. Softer compounds offer better grip but may wear out more quickly, while harder compounds provide longevity at the expense of traction. Balancing durability with grip ensures that the chosen tires perform optimally across different conditions, enhancing overall riding experience.
Brakes: Stopping Power Explained
The ability to halt swiftly and safely is crucial for any rider. Efficient deceleration mechanisms are vital for maintaining control, especially in challenging environments. Understanding how these systems operate can enhance performance and safety.
There are various types of stopping systems, each with unique characteristics that influence their effectiveness. The choice of braking system can significantly affect the handling and responsiveness of the vehicle.
| Brake Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Disc Brakes | Consistent performance in wet conditions, excellent stopping power. | Heavier, more complex maintenance. |
| Rim Brakes | Lightweight, easier to maintain, cost-effective. | Less effective in wet conditions, wear on the wheel rim. |
| Hydraulic Brakes | Superior modulation and power, reduced finger effort. | Higher cost, requires specialized maintenance. |
| Mechanical Brakes | Simpler setup, adjustable tension. | Less power and modulation compared to hydraulic systems. |
Ultimately, the right choice of stopping system depends on personal preferences, riding style, and the terrain encountered. Familiarity with the strengths and weaknesses of each system allows riders to make informed decisions, ensuring safety and performance.
Gear System: Shifting Mechanisms
The shifting mechanisms are crucial for optimizing performance, allowing riders to effortlessly adjust their gear ratios according to terrain and riding conditions. This seamless transition enhances efficiency, contributing to an enjoyable and controlled experience.
Types of Shifting Mechanisms
There are primarily two types of shifting systems: mechanical and electronic. Mechanical systems rely on cables and levers, providing a direct connection and tactile feedback. Conversely, electronic systems use motors for precision, ensuring smooth and accurate shifts with minimal effort.
Benefits of Proper Shifting
Effective gear shifting not only improves speed and acceleration but also reduces strain on the rider. By selecting the right gear, cyclists can maintain optimal cadence, enhancing overall performance and longevity of the transmission system. This ultimately leads to a more enjoyable riding experience.
Suspension: Types and Functions
The suspension system plays a crucial role in enhancing the performance and comfort of a cycling experience. It serves to absorb shocks and maintain stability, allowing riders to tackle various terrains with ease.
There are several types of suspension systems, each with its unique characteristics:
- Hardtail: Features a rigid rear with front suspension, ideal for climbing and efficiency.
- Full Suspension: Combines front and rear systems, providing superior comfort and control over rough paths.
- Single Pivot: Offers simplicity and efficiency, using a single point for rear movement.
- Multi-Pivot: Enhances performance by allowing multiple points of movement for better handling.
The functions of these systems are equally diverse:
- Shock absorption to reduce impact from obstacles.
- Improved traction on uneven surfaces.
- Enhanced rider comfort during long rides.
- Stability during high-speed descents.
Understanding these types and their functions can ultimately elevate your riding experience and allow for better decision-making when choosing a suitable setup.
Handlebars: Control and Comfort
The steering mechanism of a two-wheeled vehicle plays a crucial role in determining the rider’s experience, influencing both handling and overall satisfaction during rides. A well-designed control system enhances stability, responsiveness, and comfort, allowing enthusiasts to navigate various terrains with ease.
Key Features

- Ergonomic Shape: Supports natural hand positioning.
- Material Quality: Impacts durability and weight.
- Width and Rise: Affects leverage and control.
Choosing the Right Handlebar
- Assess Riding Style: Consider whether you prioritize speed or comfort.
- Test Different Shapes: Find what feels best in your hands.
- Evaluate Compatibility: Ensure it fits well with other components.
Pedals: Varieties and Benefits
When it comes to enhancing performance and comfort during cycling, the choice of foot platforms plays a crucial role. These components not only connect the rider to the vehicle but also significantly influence the overall experience, making it essential to understand their various types and advantages.
Types of Foot Platforms
There are several types of foot platforms available, each designed to meet different riding styles and preferences. Flat platforms offer a simple design, allowing for easy foot placement and removal, ideal for casual rides and technical trails. In contrast, clipless systems secure the foot to the platform, providing better power transfer and control, which is particularly beneficial for more aggressive riding and competitive scenarios.
Advantages of Different Systems
The selection of foot platforms can greatly enhance the cycling experience. Flat models are versatile and user-friendly, promoting confidence for beginners and facilitating quick dismounts. On the other hand, clipless options improve efficiency by allowing cyclists to pull up as well as push down during pedaling, maximizing energy output. Additionally, the right choice can enhance stability, control, and comfort over various terrains, making every ride more enjoyable.
Chain: Role in Power Transfer
The chain is a critical component that facilitates the transfer of energy generated by the rider. It plays a vital role in ensuring that the force applied to the pedals effectively translates into forward motion. Understanding its function is essential for maximizing performance and efficiency.
Mechanics of Engagement: When the pedals are turned, the chain engages with the sprockets, creating a connection that allows for the transfer of torque. This engagement ensures that energy is not wasted and is instead directed toward propulsion.
Efficiency Factors: The condition of the chain significantly impacts overall performance. A well-maintained chain reduces friction and enhances the smoothness of power transfer, while a worn or poorly lubricated chain can lead to energy loss and diminished speed.
Ultimately, the chain’s role in energy transfer is fundamental to achieving optimal riding experience and performance. Proper care and understanding of this component can lead to enhanced rides and greater enjoyment on the trail.
Seat: Finding the Perfect Fit
Choosing the right seating option is crucial for an enjoyable riding experience. Comfort and support play significant roles in enhancing performance and reducing fatigue during long journeys.
Height Adjustment: Ensuring the correct elevation allows for optimal leg extension. An ideal position helps prevent strain on knees and enhances pedaling efficiency.
Width Considerations: A well-fitted surface should match your sit bones’ width. This alignment minimizes discomfort and promotes stability while navigating diverse terrains.
Padding Preference: The choice between firmness and softness varies by individual. It’s essential to test different levels to determine what suits your riding style best.
Ultimately, investing time in finding the right fit can transform your outdoor adventures, making them more enjoyable and less taxing on the body.
Fork: Importance in Ride Quality
The front suspension element plays a crucial role in overall performance and comfort during rides. Its design and functionality significantly influence how well the vehicle absorbs shocks from uneven terrain, affecting stability and control.
Impact on Handling
A well-engineered front suspension enhances maneuverability, allowing riders to navigate through challenging trails with greater ease. This aspect is vital for maintaining confidence, especially in technical sections.
Influence on Comfort
The ability to absorb bumps and vibrations contributes to a smoother experience. Riders benefit from reduced fatigue, enabling longer journeys without compromising enjoyment or safety.
Dropper Post: Enhancing Performance
The inclusion of a specific component in cycling enhances overall capability and rider comfort, significantly improving the experience during diverse terrains. This innovation allows for swift adjustments while navigating challenging routes, providing a seamless transition between different riding positions.
Advantages of a Dropper Post
- Improved Control: Riders can easily lower their seating position, optimizing balance and stability during descents.
- Increased Confidence: The ability to quickly adjust height encourages more aggressive riding styles.
- Versatility: Suitable for various terrains, from steep climbs to technical drops.
Installation and Maintenance Tips

- Ensure proper fit with the frame for maximum performance.
- Regularly check cable tension to prevent malfunction.
- Keep the post clean and lubricated for smooth operation.