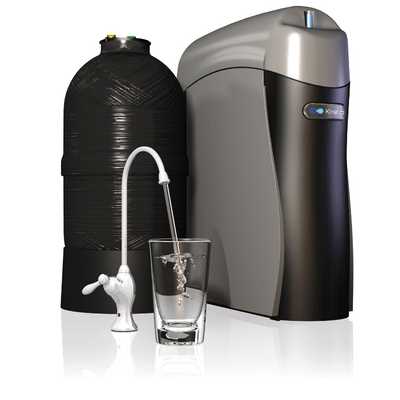

Understanding the internal components of an advanced water purification system is crucial for ensuring optimal performance. The intricate arrangement within these devices is designed to deliver high-quality results, but proper maintenance requires familiarity with each element. This overview provides insights into how each piece works together to create a reliable and efficient purification process.
Every mechanism inside the unit plays a specific role in filtering and purifying water. By grasping the layout of the system, users can better maintain its functionality, troubleshoot issues, and extend its lifespan. Whether you’re performing repairs or seeking to optimize performance, this guide offers a clear view of how everything fits together.
Delving deeper into the structure of the system reveals the interconnectedness of its various components. Each one contributes to achieving the desired outcome, ensuring a continuous supply of clean, safe water. A well-organized understanding of these elements will empower users to maintain and care for the filtration setup effectively.
Overview of Key System Components
In any advanced filtration setup, understanding the primary elements is crucial for maintaining efficiency and optimal performance. Each component works together to ensure the system functions smoothly and effectively, handling the essential tasks of purifying and distributing clean water.
- Main Processing Unit: The core of the system, responsible for filtering impurities and delivering purified water. It uses a combination of methods to achieve the highest level of cleanliness.
- Pre-treatment Section: This part prepares the incoming flow by removing larger particles and initial contaminants, ensuring that subsequent stages face less strain.
- Post-treatment Area: Final adjustments and purification take place here, often involving additional filters or refining steps to enhance water quality before it reaches the user.
- Storage Reservoir: Acts as a holding area for treated water, maintaining a supply ready for use while the system continues processing incoming flows.
- Control Valve: Regulates the flow of
Internal Structure Breakdown
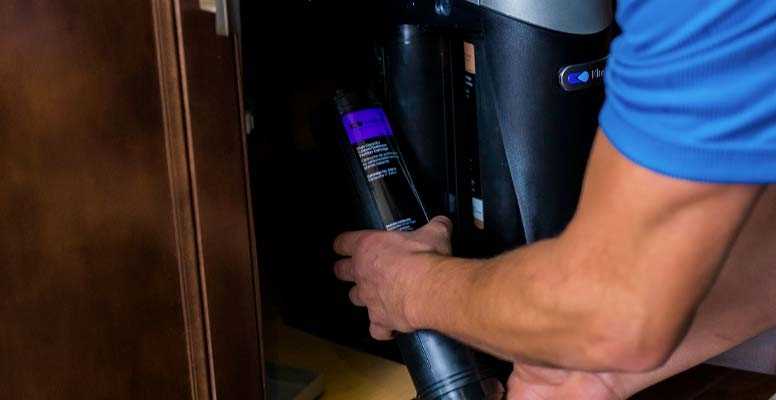

Understanding the internal layout of this system allows for a deeper insight into its efficient operation and design. The intricacies of its construction reveal how each component functions in harmony to deliver high performance, ensuring long-term reliability and effective output. By analyzing the core elements, one can appreciate the balanced configuration that leads to seamless functionality.
Main Filtration Chamber
The central compartment is where the initial processing takes place, ensuring the removal of unwanted materials. This chamber contains multiple layers that work together, offering both primary and secondary treatment processes, enhancing the overall filtration capability.
Supportive Components and Flow Pathways
A series of secondary elements guide the flow throughout the entire structure, ensuring smooth transitions between stages. These components assist in regulating pressure and flow, enabling the system to adapt to varying conditions, which optimizes performance and prevents overstrain on the main system.
Water Filtration Mechanism Explanation
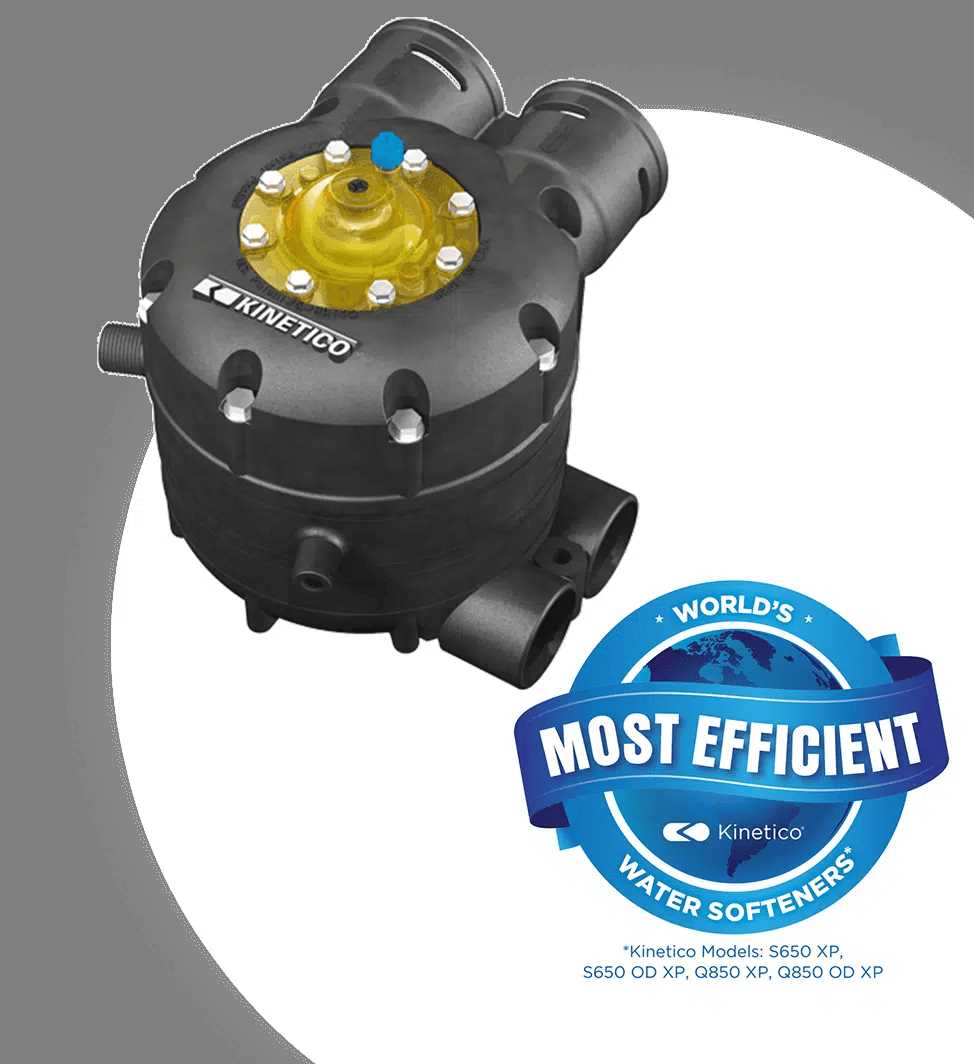

The process of purifying water is designed to remove unwanted substances and contaminants, ensuring a cleaner and safer supply for various uses. This involves multiple stages that work together to target specific impurities, enhancing the overall quality of the liquid. Each phase of this system serves a distinct purpose, gradually refining the water as it passes through different levels of treatment.
Initial Treatment Stage

The first step in the purification sequence involves the separation of larger particles, such as sediment, debris, or rust. This stage functions as a protective layer, preventing these materials from moving further into the purification process. By capturing these solid contaminants early on, the system ensures that subsequent stages can focus on more intricate impurities.
Advanced Filtration
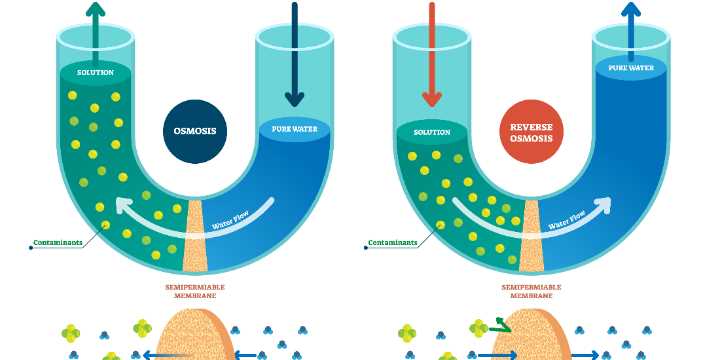
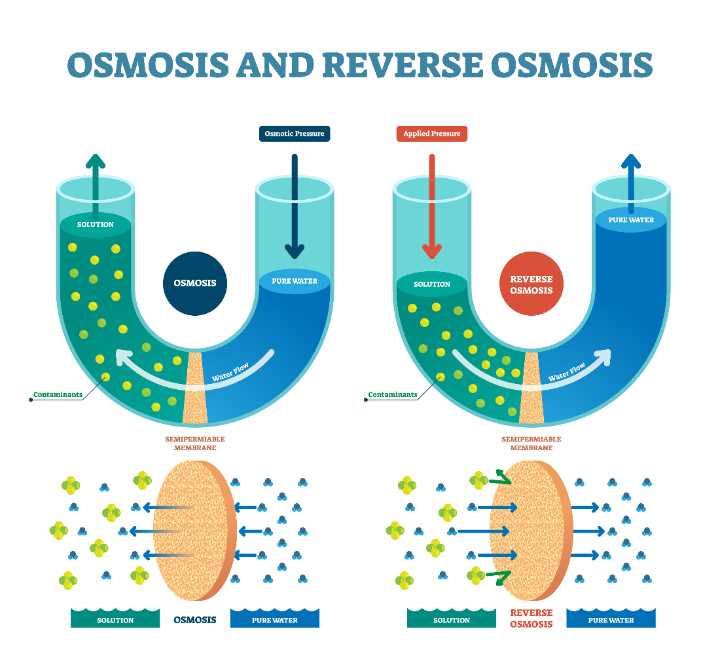
After the initial treatment, water undergoes advanced refinement where more delicate substances, like chemical traces and microorganisms, are addressed. Using specialized filters, this stage removes microscopic impurities that affect the taste, odor, and overall safety of the water. These filters, enhanced by various technologies, work to eliminate both organic and inorganic elements that standard filtration cannot manage.
Membrane Design and Functionality
The core of any advanced filtration system lies in the intricate design and operation of its membrane. This component serves as a critical element for ensuring the efficient separation of impurities from water. Its structural composition and method of functioning directly impact the overall filtration process, delivering purified water through selective permeability.
Material Composition
Membranes are typically composed of advanced materials designed to balance durability and effectiveness. These materials must endure constant water flow while maintaining precise filtration capabilities. Common options include polymer-based films and synthetic fibers, both engineered for long-term use in harsh conditions.
- Resilient against high pressure and varying water conditions
- Engineered to prevent clogging and ensure longevity
- Micro-porous structure to capture microscopic particles
Filtration Mechanism

The filtration process relies on the membrane’s ability to allow only specific molecules to pass through. This mechanism is crucial for eliminating contaminants while retaining essential minerals. Depending on its pore size and design, the membrane can efficiently filter out bacteria, viruses, and other harmful substances.
- Water passes through
Cartridge Replacement Guide
The filtration system requires periodic upkeep to ensure optimal performance. One of the essential maintenance tasks involves changing the core filtering elements. Regularly refreshing these components enhances the efficiency and prolongs the lifespan of your system.
Step 1: Turn off the water supply to the unit. This step prevents leaks and ensures a smooth replacement process.
Step 2: Carefully remove the protective housing by unscrewing it. You may need a wrench for additional grip, but be cautious not to apply too much force.
Step 3: Once opened, take out the old filter component and dispose of it properly. Check for any debris or sediment that may have accumulated in the housing.
Step 4: Insert the new filter into the housing, ensuring it is aligned properly. Double-check that it fits snugly without gaps or loose ends.
Valves and Flow Regulation System

The mechanism for controlling the movement and distribution of fluids plays a critical role in various applications, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. This section delves into the intricacies of the devices responsible for regulating flow, highlighting their functions, types, and importance in maintaining system integrity.
Types of Flow Control Mechanisms
Flow regulation devices are categorized into several types, each serving distinct purposes and featuring unique operational principles. Common types include:
Type Description Ball Valves Utilize a spherical disc to control flow, offering minimal resistance and reliable sealing. Gate Valves Employ a wedge-shaped gate to obstruct flow, suitable for on/off applications. Check Valves Prevent backflow by allowing fluid to flow in one direction only. Globe Valves Feature a spherical body and are designed for throttling flow, providing precise control. Importance of Flow Regulation
Effective flow control is essential for maintaining system efficiency, reducing wear and tear on components, and ensuring safety. Properly designed regulation mechanisms contribute to the longevity of the entire system, enhancing overall performance and reliability.
Tubing and Connection Setup
Establishing a proper arrangement of hoses and fittings is crucial for the effective operation of your water purification system. This section outlines the essential components and steps required to ensure optimal fluid flow and efficiency.
First and foremost, it’s important to select high-quality tubing that is compatible with the specific requirements of your filtration unit. The diameter and material of the tubing can significantly affect water pressure and flow rates. Ensure that the tubing is free from kinks and blockages, as these can impede performance.
Next, proper connections between the various components should be secured using appropriate fittings. It is advisable to check for leaks after assembling the connections. Tightening the fittings without overdoing it is vital to maintain a secure seal.
Additionally, pay attention to the routing of the tubing. Ensure that the layout minimizes sharp bends and avoids unnecessary stress on the hoses. A well-organized arrangement not only enhances performance but also simplifies maintenance and troubleshooting.
In conclusion, following these guidelines for tubing and connection setup will help achieve reliable operation and prolong the lifespan of your water treatment equipment.
Maintenance and Cleaning Procedures
Regular upkeep and sanitation are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of filtration systems. Implementing systematic procedures not only enhances functionality but also prevents potential issues that may arise from neglect. This section outlines essential practices to maintain the efficiency and cleanliness of your unit.
Routine Maintenance
To ensure smooth operation, it is vital to perform routine checks on all components. Inspect filters for signs of wear and replace them according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Additionally, monitor the system for leaks or unusual noises, which could indicate underlying problems. Keeping a maintenance log can help track service dates and component replacements, facilitating timely interventions.
Cleaning Recommendations
Cleaning should be conducted regularly to prevent the buildup of contaminants. Start by disconnecting the system from its power source. Use a mild detergent solution to wipe down exterior surfaces, ensuring all grime and residue are removed. For internal components, consult the manufacturer’s instructions for specific cleaning agents suitable for the materials used. Rinse thoroughly before reassembling the unit to avoid any chemical residue.
Commonly Replaced Parts
In the realm of water treatment systems, certain components are frequently subject to wear and tear, necessitating their replacement to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Understanding which elements are most often changed can help users maintain their systems effectively and prolong their lifespan.
- Filter Cartridges: These are essential for removing impurities from water. Over time, they become saturated and less effective, requiring regular replacement.
- Valves: Various valves control water flow and pressure within the system. Their functionality can decline due to mineral buildup or mechanical wear, making timely replacements necessary.
- Seals and O-rings: These components prevent leaks and maintain pressure. They can degrade over time, leading to potential leaks and inefficiencies.
- Membranes: In systems that utilize reverse osmosis, membranes play a critical role in filtration. They can become fouled or damaged, requiring replacement to maintain water quality.
- Pumps: Responsible for moving water through the system, pumps can experience failures due to motor issues or wear. Regular checks can help determine if replacement is needed.
Keeping track of these commonly replaced elements can enhance the longevity of water purification systems and ensure that users continue to enjoy clean and safe water.
Installation and Setup Instructions
This section provides essential guidance for properly installing and configuring the system. Following these steps will ensure optimal performance and longevity of the
Advanced Troubleshooting Tips
This section provides in-depth guidance for diagnosing and resolving common issues associated with your water treatment system. By following these expert recommendations, you can efficiently identify problems and implement effective solutions, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your unit.
Common Symptoms and Solutions
- Unusual Noises: If your system produces strange sounds, it may indicate a mechanical issue. Check for loose components or debris within the unit.
- Low Water Pressure: This can be caused by clogs or worn-out filters. Inspect and clean the filters regularly to maintain adequate flow.
- Unpleasant Odors: Bad smells may signal bacterial growth. Regular sanitization and proper maintenance can help prevent this issue.
Steps for Effective Troubleshooting
- Conduct a visual inspection of the entire system, looking for any obvious signs of wear or damage.
- Check the settings on your unit to ensure they align with the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Perform regular maintenance, such as replacing filters and cleaning components, to keep the system running smoothly.
- If issues persist, consult the user manual or reach out to customer support for further assistance.
Compatibility with Other Accessories
Ensuring seamless integration with various additional components is crucial for enhancing functionality and performance. Understanding the compatibility of these elements allows users to maximize the efficiency of their systems. The right combinations can lead to improved results, whether for filtration, purification, or overall system efficiency.
When selecting accessories, it is important to consider their specifications and how they interact with existing setups. Many users find that certain attachments or enhancements significantly contribute to the overall effectiveness, thereby optimizing the system’s capabilities. The ability to customize and expand through compatible accessories can transform a basic setup into a highly efficient solution.
Regularly checking compatibility guidelines from manufacturers can help avoid mismatches and ensure that users make informed decisions. This proactive approach can lead to better performance, longer service life, and overall satisfaction with the entire system. Keeping abreast of the latest advancements and compatible options is essential for any user looking to enhance their experience.
Performance Optimization Techniques
Enhancing the efficiency of water treatment systems involves several strategic approaches that maximize functionality while minimizing resource consumption. By implementing effective optimization methods, users can ensure their systems operate at peak performance, delivering reliable results over time.
- Regular Maintenance: Scheduling routine check-ups and replacing worn components can significantly enhance system longevity and efficiency.
- Proper Sizing: Ensuring that the equipment is appropriately sized for the specific application prevents strain and improves overall performance.
- Flow Rate Adjustments: Fine-tuning the flow rates can lead to better filtration and improved output quality.
In addition to the above techniques, optimizing the use of consumables can greatly impact performance:
- Utilizing Quality Media: Choosing high-grade filtration materials enhances purification efficiency and reduces the frequency of replacements.
- Monitoring System Pressure: Keeping track of pressure levels allows for adjustments that can prevent overload and maintain efficiency.
- Environmental Considerations: Placing the system in optimal environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity control, can reduce operational strain.
By employing these methods, users can significantly improve the reliability and efficiency of their water treatment systems, ensuring consistent performance and extended lifespan.