| Pressure Tank |
Regulates the system’s pressure, ensuring consistent flow and preventing damage from sudden surges. |
Main Features of a Water Well System
Every resource extraction structure has several essential elements that contribute to its overall function. These components work together to ensure the efficient and consistent supply of resources, maintaining stability and performance in diverse conditions. Understanding how each element plays a role is crucial for anyone looking to maintain or improve such a system.
Primary Structural Elements
The core components of this system include mechanisms that regulate the flow of resources, devices to measure pressure, and systems to prevent contamination. Each of these plays a critical role in ensuring the system operates effectively under varying environmental conditions. Key features include flow control units, pressure regulation mechanisms, and contamination safeguards.
Operational Efficiency
Efficiency in these systems is ensured by strategic placement of valves, pumps, and filters. Optimized design allows for minimal energy loss, ensuring consistent resource delivery while keeping the operational costs low. These aspects of design contribute to long-term functionality and durability.
Function of the Well Casing
The casing serves as a critical barrier, preventing the surrounding environment from contaminating the interior of the structure. This protective layer ensures that external materials, including soil and debris, stay outside, maintaining the integrity of the enclosed space.
Durability is a key aspect of the casing, as it is designed to withstand various external forces and pressures. This robust construction allows the system to remain effective over long periods of use, ensuring continuous operation under challenging conditions.
In addition to protection, the casing also supports the internal components, keeping them stable and aligned. This structural role is essential for maintaining efficiency and preventing collapse or misalignment of key elements over time.
Role of the Well Screen in Filtration
The filtration process relies heavily on a specific component designed to prevent unwanted materials from entering the supply. This element ensures the flow remains uncontaminated, maintaining purity by trapping debris and particles before they reach critical levels. Its design allows only the appropriate size of substances to pass through while blocking larger particles that could hinder efficiency or cause damage.
- Prevents clogging by filtering out solid impurities
- Ensures steady and clean flow for extended operation
- Reduces the need for maintenance by minimizing blockages
This key part of the system is crucial for maintaining overall quality and durability. Without its proper functioning, impurities could accumulate, leading to potential issues that might require costly repairs or replacements.
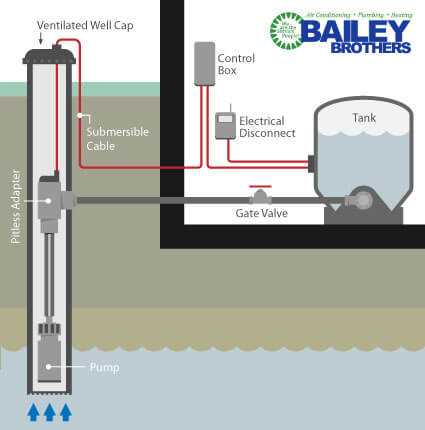
Importance of the Pump in Water Wells
The pump is a critical component that ensures the efficient delivery of resources from the ground. Without it, the extraction process becomes challenging and less reliable. The role of this mechanism is to facilitate the movement of liquid to the surface, making it accessible for everyday use. The efficiency and functionality of a pump directly impact the sustainability and performance of the entire system.
Role in the Extraction Process
In the extraction process, the pump acts as the driving force that propels resources upward, overcoming natural resistance. Its power determines the flow rate and consistency, which are vital for meeting daily requirements. A well-maintained pump ensures a steady supply, preventing disruptions and ensuring the stability of the system.
Maintenance and Longevity
Regular maintenance of the pump is crucial for its longevity and efficiency. Over time, wear and tear can affect its performance, leading to reduced output or mechanical failures. By conducting routine inspections and addressing issues early, the pump’s lifespan can be extended, ensuring reliable operation for years to come.
How Pressure Tanks Maintain Flow
Pressure tanks play a vital role in ensuring a consistent and reliable supply of fluid throughout a distribution system. By utilizing pressurized air and stored liquid, these vessels facilitate a seamless flow, reducing the need for constant pump operation and enhancing efficiency.
Functionality of Pressure Tanks
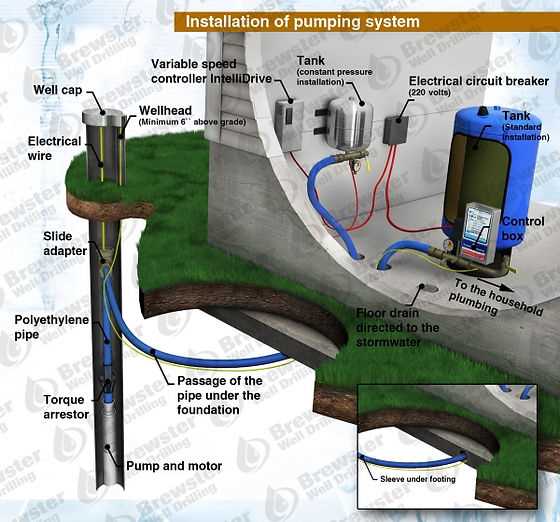
These tanks operate by maintaining a specific level of pressure, which allows for the following key functions:
- Pressure Regulation: They stabilize the system’s pressure, preventing fluctuations that could disrupt the flow.
- Flow Assurance: By providing a reservoir of fluid, they ensure that there is always a supply available for immediate use.
- Energy Efficiency: Reducing pump cycling saves energy, leading to lower operational costs.
Benefits of Utilizing Pressure Tanks
Implementing these vessels in a distribution system offers several advantages:
- Enhanced reliability and performance of the fluid supply.
- Decreased wear and tear on pumps due to reduced operational frequency.
- Improved overall system efficiency and longevity.
Key Elements of the Drop Pipe
The drop pipe is a crucial component in any system designed for fluid extraction. It plays a significant role in ensuring the efficient transfer of liquids from the ground to the surface. Understanding its essential features can help users maintain optimal performance.
Material Composition: The material used in constructing the drop pipe affects its durability and resistance to corrosion. Commonly, materials like PVC, steel, or polyethylene are utilized to enhance longevity and reliability.
Diameter: The diameter of the drop pipe is vital for determining the flow rate. A larger diameter allows for greater fluid movement, while a smaller diameter can restrict flow and create pressure issues.
Connection Points: The junctions within the drop pipe are essential for maintaining a secure seal. Properly fitted connections prevent leaks and ensure a continuous flow of liquids.
Length: The overall length of the drop pipe is tailored to the specific depth of extraction needed. It should be designed to reach the required depth without compromising structural integrity.
Weight: The weight of the drop pipe influences its installation and handling. Lighter materials may simplify installation but could also affect stability under certain conditions.
Well Cap: Protecting the Water Source
A cap serves as a crucial barrier, ensuring the integrity of a crucial resource. Its primary role is to prevent external contaminants from entering the source, safeguarding the purity and quality of the liquid stored within. This protective cover is essential for maintaining a safe and reliable supply, contributing to overall health and safety.
Importance of Proper Sealing
Ensuring a tight seal is vital for effective protection. A well-fitted cap minimizes the risk of debris, pests, and other harmful substances infiltrating the source. This not only preserves the quality of the resource but also reduces the need for costly treatments and interventions.
Material Choices and Durability
When selecting a cap, durability and resistance to environmental factors are key considerations. Materials such as high-density polyethylene or galvanized metal are popular due to their ability to withstand harsh conditions while maintaining a secure closure. Investing in quality components can enhance the longevity and reliability of the protective system.
Check Valve Purpose in Well Systems
The check valve serves a critical function within fluid transport systems, ensuring that the flow occurs in one direction only. This mechanism is essential for maintaining system efficiency and preventing potential backflow that could lead to various operational issues.
Functionality of the check valve lies in its ability to automatically close when the fluid attempts to reverse direction. This feature protects the entire system from pressure fluctuations and potential contamination, thereby ensuring consistent performance and reliability.
In addition, installing a check valve enhances the overall safety of the operation by reducing the risk of reverse flow. This is particularly important in systems where contamination could occur if the fluid were to flow backward, thus safeguarding both the equipment and the surrounding environment.
The Role of Electrical Connections
Effective electrical connections are vital for ensuring the proper operation of various systems designed for resource extraction. These connections facilitate the flow of energy, enabling essential components to function efficiently and reliably.
Importance of Reliable Connections
Reliable connections are crucial for several reasons:
- Ensuring consistent power supply to all operational components.
- Minimizing the risk of electrical failures that could disrupt functionality.
- Enhancing the overall safety of the system by reducing potential hazards.
Common Types of Connections

There are various types of connections employed in these systems:
- Direct wiring connections, providing a straightforward link between components.
- Plug-in connectors, allowing for easy maintenance and replacement.
- Wire terminals, offering secure attachment points for individual wires.
Proper Maintenance for Well Components
Ensuring the longevity and efficiency of underground systems requires regular attention and care. Routine checks and timely interventions are crucial for preventing significant issues that could disrupt functionality. Proper upkeep not only enhances performance but also prolongs the lifespan of the entire structure.
Regular Inspections
Conducting routine assessments is essential. Look for any signs of wear or damage, such as cracks or corrosion, that could lead to more serious problems. Make it a habit to check seals and connections to prevent any potential leaks or blockages.
Cleaning and Servicing

Regular cleaning of components is vital to avoid build-up that can impair functionality. Utilize appropriate cleaning methods for different materials to maintain their integrity. Additionally, servicing should be scheduled periodically to ensure all elements are operating efficiently and to address any minor issues before they escalate.