
The functionality of modern transport systems relies heavily on the intricate assembly of various components that work in unison to achieve seamless movement of materials. These mechanical systems are widely used in diverse industries, ranging from manufacturing to logistics, where they ensure efficient and continuous flow of goods. Understanding how the individual units are arranged and how they interact is key to maintaining and optimizing performance.
Each element within the transport mechanism has a specific role, contributing to the overall operational efficiency. Whether it’s for guiding the movement, providing support, or enabling control, every piece has been designed to serve a critical function. Exploring the design and alignment of these elements can offer insights into improving durability, reducing maintenance, and ensuring smooth operation in various applications.
By examining the layout and connection of these functional units, it becomes easier to identify areas where improvements can be made, whether through better maintenance practices or by upgrading specific sections. A deeper understanding of this system not only enhances efficiency but also increases
Conveyor System Components Overview
In any modern material handling setup, various interconnected elements work together to facilitate the efficient movement of items. These elements, designed for smooth operations, play a crucial role in ensuring that materials flow seamlessly from one point to another within an industrial environment. By understanding the primary functional units, it becomes easier to grasp how the system operates as a whole, optimizing productivity and minimizing potential disruptions.
The core structure typically includes driving mechanisms that power the motion, guiding frameworks that support the load, and auxiliary units responsible for specialized tasks. Each element must function in harmony, providing the strength, precision, and adaptability required for handling different loads and operational conditions. Whether dealing with light packages or heavy materials, the proper selection and arrangement of these components directly impact the overall efficiency.
Power transmission elements form the heart of the operation, converting energy into controlled motion, while support structures ensure stability and load-bearing capacity. Additional features, like speed regulators and sensors, enhance control and safety, adapting the system to various industrial needs. Together, these components create a synchronized process that can handle diverse operational demands.
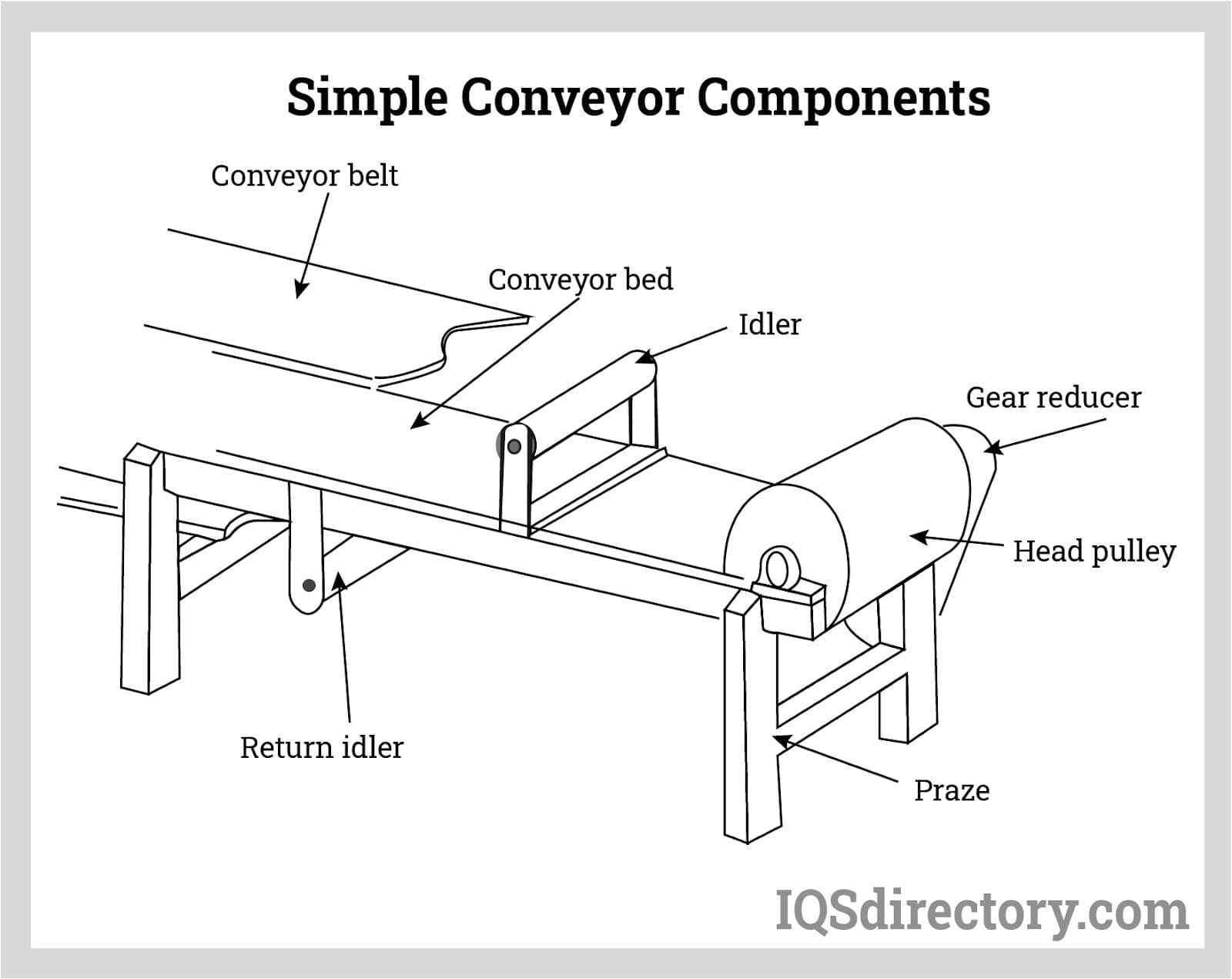
Main Structural Elements of a Conveyor
When examining the key components responsible for the movement of materials, it’s crucial to understand the fundamental support structures that enable seamless operation. These elements are designed to provide stability, ensure proper load distribution, and allow for smooth transitions during operation.
Frame serves as the backbone, offering robust support for all other sections. Its design can vary depending on the intended application, but its main function remains providing a strong, reliable base that withstands wear and tear over time.
Rollers play an essential role in the overall function by facilitating movement. Positioned at specific intervals, they reduce friction and support the moving components, ensuring smooth transportation of materials across the structure.
Bearing assemblies work to minimize resistance during operation. By reducing friction at critical points, they allow the moving parts to rotate efficiently, increasing the system’s overall lifespan and performance.
Additionally, supports and brackets secure the framework and moving sections in place, ensuring everything stays aligned. These elements are essential in maintaining the correct orientation and balance, especially when dealing with varying load sizes.
Types of Conveyor Belts
The systems used for transporting materials vary depending on their design, purpose, and the specific needs of different industries. They come in multiple forms, each offering distinct advantages based on the requirements of the task at hand. Understanding the different styles and their capabilities helps in selecting the most suitable option for a given operation.
Flat Belt: This type is among the most common due to its simplicity and versatility. It is typically used to move goods across short distances with light to moderate loads. The flat surface makes it ideal for items that need to stay stable during movement.
Modular Belt: Composed of interlocking segments, this option is known for its flexibility and durability. It can handle a variety of materials and is often used in industries that require easy cleaning and maintenance, like food processing.
Cleated Belt: This design incorporates raised sections, or cleats, that help prevent items from slipping during transport. It is highly effective when moving materials at an incline or when extra grip is needed.
Incline Belt: Specifically designed for moving objects upwards, this variation usually includes additional features like textured surfaces
Drive Mechanism and Motors
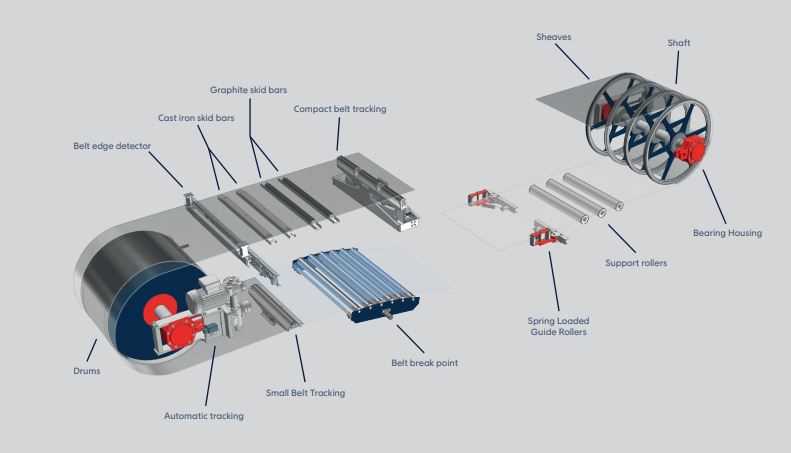
The drive system serves as the core element responsible for motion, transforming power into rotational or linear movement. By converting energy, it allows the system to function smoothly and efficiently, providing the necessary force for operation. Various types of mechanisms and power units are employed, depending on the application, to deliver precise control and reliable performance.
Types of Drive Mechanisms
There are several types of drive systems used to generate movement, each tailored for specific operational needs. These may include belt-driven setups, direct coupling systems, or even gear-based arrangements. The selected method determines the efficiency and smoothness of the motion, influencing the overall functionality and responsiveness of the system.
Motor Selection and Efficiency
The choice of motor is essential for ensuring that the system operates within the desired parameters. Various electric motors, such as AC or DC types, are commonly implemented, depending on the required power and torque. The efficiency of these motors directly impacts the system’s energy consumption and long-term reliability, making proper selection critical for optimal performance.
Understanding Rollers and Pulleys
In mechanical systems, cylindrical and rotational components play a crucial role in the movement of objects along a defined path. These elements, often placed at key intervals, facilitate smooth and efficient motion by reducing friction and distributing weight evenly. Their structure and material selection are tailored to the type of load they handle, making them vital for the overall operation of the system.
Key Functions of Cylindrical Components
Cylindrical units, often mounted horizontally, support and guide materials by rotating freely on an axis. This allows for the smooth transfer of objects with minimal resistance. The material composition of these components is important, as it must provide durability and reduce wear over time. Additionally, the size and shape of the cylindrical parts are engineered to meet the requirements of various applications, ensuring the proper balance of speed and strength.
The Role of Rotational Discs
Rotational discs, on the other hand, manage the directional movement of materials by adjusting tension and aligning the motion. These discs ensure a controlled and stable flow
Support and Tensioning Systems
Efficient movement systems rely on robust mechanisms that ensure smooth operation and control of motion. These structures provide stability, support, and the necessary tension to maintain proper functioning under varying loads and speeds. A well-designed support system not only keeps components in place but also allows for adjustments, enhancing performance and longevity.
Structural Components
The key elements of these systems are designed to distribute the weight evenly and prevent any undue strain on the main components. The support frameworks are made of durable materials to withstand wear and tear while providing reliable guidance for the moving sections. These elements are essential in maintaining balance and ensuring that the system operates efficiently without disruptions.
Tensioning Mechanisms
Tensioning mechanisms play a critical role in adjusting the tightness of the moving components. Proper tension ensures optimal interaction between parts, preventing slipping or excessive stretching. By keeping the system properly tensioned, these mechanisms minimize friction and extend the lifespan of the moving elements. Adjustable tensioners offer flexibility, allowing for real-time adjustments in response to varying loads or environmental conditions.
Safety Features and Sensors
Ensuring safety in automated systems is crucial for maintaining smooth operations and preventing accidents. Various mechanisms and sensors are integrated to monitor and control movement, providing real-time feedback to operators. These safety elements play a vital role in minimizing risks and enhancing the overall efficiency of the system.
Key Safety Mechanisms
Automatic shut-off devices, emergency stop buttons, and obstacle detection sensors are common features designed to protect both personnel and equipment. These components detect irregularities or hazardous conditions, triggering a response to halt the system instantly, thereby preventing damage or injury.
Types of Sensors
Sensors used for safety can be broadly categorized based on their functions. Proximity sensors, for instance, are used to detect objects or human presence near moving elements, while pressure sensors monitor load conditions to avoid overloads. Additionally, temperature sensors are essential for detecting overheating, ensuring that the system operates within safe limits.
| Sensor Type | Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Proximity Sensor | Detects objects or personnel near moving parts | Safety zones, collision prevention |
| Pressure Sensor | Monitors load to prevent overloading | Weight detection, system balancing |
| Temperature Sensor | Detects overheating or temperature anomalies | Motor protection, cooling systems |
Material Handling Accessories
Efficient transport systems rely on a variety of essential tools that enhance functionality and optimize performance. These accessories ensure smooth movement, control, and security of materials during transit. Each element plays a critical role in maintaining operational efficiency and safety in various industries.
Types of Accessories
Among the most commonly used accessories are guides, rollers, and support frames. These components provide necessary assistance in aligning, directing, and stabilizing the movement of items across a system. They help in reducing wear and tear while maintaining consistency in the flow of materials.
Benefits of Integration
Integrating the right accessories can dramatically improve throughput and minimize downtime. Their design often contributes to increased safety, reduced maintenance, and enhanced productivity. Proper selection and installation are crucial for achieving optimal results in material handling operations.
Lubrication and Maintenance Parts
Proper maintenance and lubrication are crucial to ensuring smooth and efficient operation of mechanical systems. Regular upkeep not only extends the lifespan of the equipment but also minimizes downtime and enhances overall productivity. This section outlines the key elements involved in keeping the system running optimally through effective lubrication and preventive measures.
Essential Maintenance Components
- Grease fittings
- Oil reservoirs
- Seals and gaskets
- Drive belts
- Bearings and rollers
Lubrication Procedures
- Identify the lubrication points and the type of lubricant required.
- Apply lubricant regularly according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Check for leaks and ensure that seals are intact to prevent contamination.
- Inspect all moving elements for wear or damage that may affect efficiency.
Control Systems for Conveyor Operations
Efficient management of material handling systems relies heavily on the integration of advanced control mechanisms. These systems coordinate various components to ensure smooth and synchronized movement, optimizing overall productivity and reducing the risk of malfunction. By using intelligent automation, the entire process can be monitored and adjusted in real time, allowing for quicker responses to any irregularities.
At the core of these systems are sensors and actuators that continuously collect data and trigger specific actions. Feedback loops help maintain optimal performance by adjusting speed, direction, and power based on real-time input. The role of these control systems is crucial in maintaining operational efficiency and ensuring that the flow of materials remains uninterrupted.
Modern setups also include user-friendly interfaces that allow operators to monitor performance and intervene when necessary. These systems are designed with flexibility in mind, easily adapting to changes in workflow or requirements. Advanced technologies, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), play an essential role in automating processes, offering precise control over the machinery.
Common Conveyor Accessories and Attachments
In any automated material handling system, various components work in tandem to enhance functionality and improve overall efficiency. These elements play a critical role in optimizing the flow and movement of items, ensuring smooth and reliable operations in industrial environments.
Types of Attachments
- Belts: Essential for the movement of items, these come in various materials such as rubber, metal, and plastic to suit different load types and speeds.
- Rollers: These facilitate easy movement by reducing friction and supporting the main transport system.
- Guides: Used to direct materials along the path, preventing deviation and ensuring items stay in alignment.
- Stops: Placed strategically to control the flow of items, these can be adjusted to accommodate different types of loads.
Useful Accessories
- Dividers: These are used to separate items, helping in organizing and streamlining operations in sorting systems.
- Drive Motors: These power the movement system, ensuring consistent and controlled motion across the entire mechanism.
- Guardrails: Installed along the sides, they provide safety by preventing items from falling off and helping maintain orderly movement.