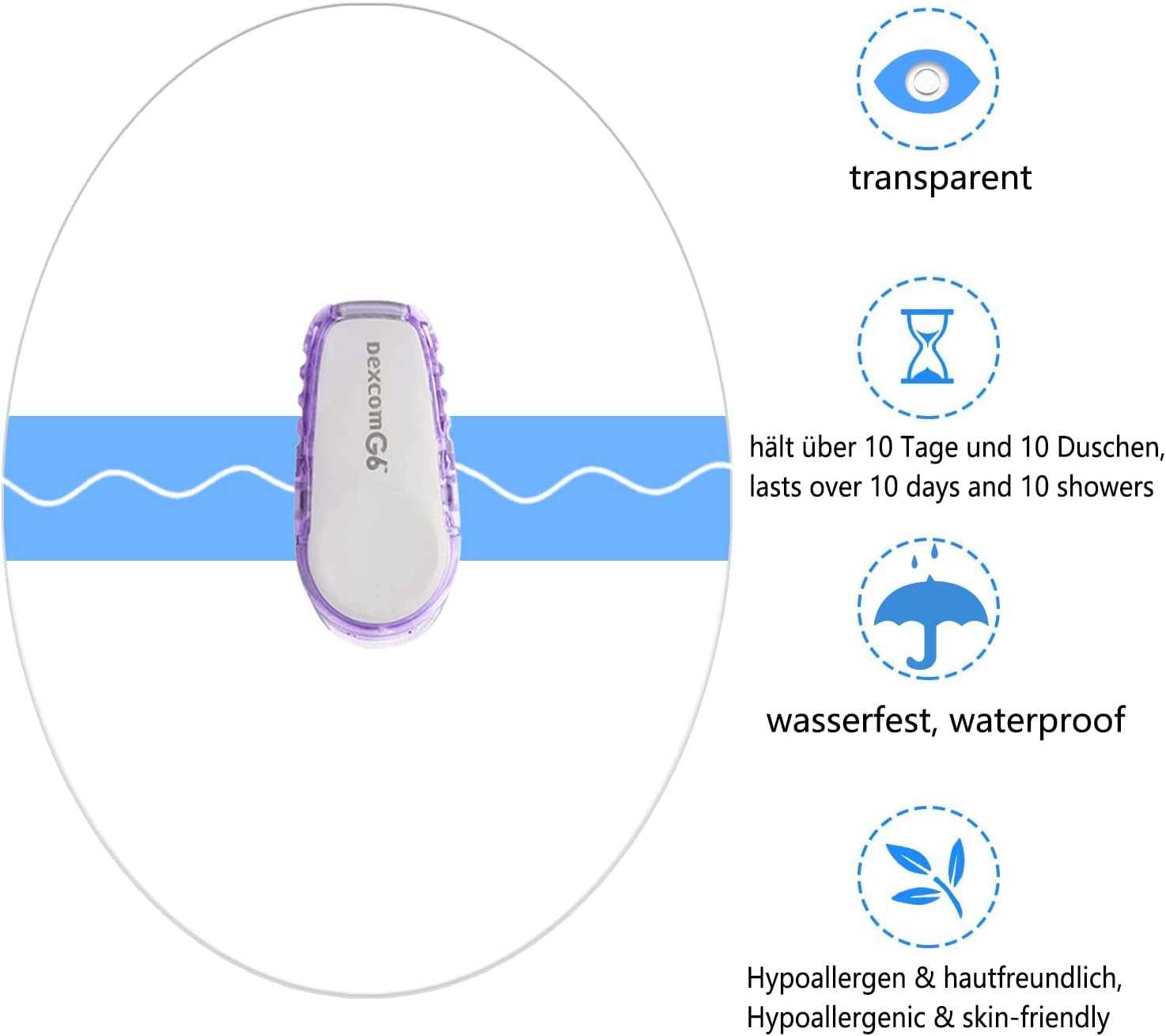
The realm of continuous glucose monitoring has evolved significantly, offering individuals with diabetes the ability to track their glucose levels in real-time. This innovative technology relies on a sophisticated assembly of elements that work together to deliver accurate and timely information. By examining the configuration of these essential components, users can gain a deeper insight into how these devices function and their importance in managing blood sugar levels effectively.
Each element within this monitoring system plays a critical role, contributing to the overall performance and reliability of the device. From the sensor that detects glucose levels to the transmitter that relays data to the receiver, understanding the interplay between these components can enhance the user’s experience. This knowledge empowers individuals to optimize their usage and ensure they are getting the most out of their glucose monitoring systems.
Moreover, familiarity with the individual components can also aid in troubleshooting potential issues, allowing users to identify when maintenance or replacements are necessary. With this understanding, individuals can engage more confidently with their monitoring devices, leading to improved health outcomes and better diabetes management.
This section aims to explore the essential elements of a particular glucose monitoring system, highlighting their functions and significance in the overall performance of the device. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate readings and user convenience, making it imperative to understand their specific characteristics and interactions.
- Sensor:
The sensor is a critical element responsible for detecting glucose levels in interstitial fluid. Its design allows for continuous monitoring, providing real-time data to the user.
- Transmitter:
This device component wirelessly communicates the data gathered by the sensor to the receiver or smartphone application, ensuring that users can access their glucose levels promptly.
- Receiver:
The receiver displays the glucose readings and trends, offering users insights into their glucose levels over time. It may come in the form of a handheld device or a compatible smartphone app.
- Adhesive Patch:
This component secures the sensor to the skin, ensuring stability and comfort during wear. Its design aims to be skin-friendly to minimize irritation.
- Calibration Tools:
Some systems may require additional calibration tools or guidelines to ensure the readings remain accurate, enhancing the reliability of the device.
Understanding these components provides valuable insight into how the system operates and the ways in which it can support users in managing their glucose levels effectively.
Overview of Sensor Technology
Sensor technology plays a crucial role in modern healthcare, enabling precise monitoring of physiological parameters. These devices have evolved significantly, allowing for real-time data collection and enhanced patient outcomes. By utilizing advanced materials and innovative designs, they provide a seamless integration into daily life, improving the management of various health conditions.
Key Components of Sensor Technology
- Transducers: These elements convert physical changes into electrical signals, serving as the core of most sensing devices.
- Microprocessors: Integrated circuits process the data collected by sensors, translating it into actionable information.
- Power Supply: Efficient energy sources ensure that sensors operate continuously without frequent interruptions.
Advancements in Sensing Techniques
- Continuous Monitoring: Recent innovations allow for the ongoing assessment of biometric data, improving chronic condition management.
- Wearable Technology: Compact designs facilitate the integration of sensors into wearable devices, promoting user convenience and accessibility.
- Data Connectivity: Enhanced communication capabilities enable seamless data transfer to smartphones and cloud platforms, providing users with real-time insights.
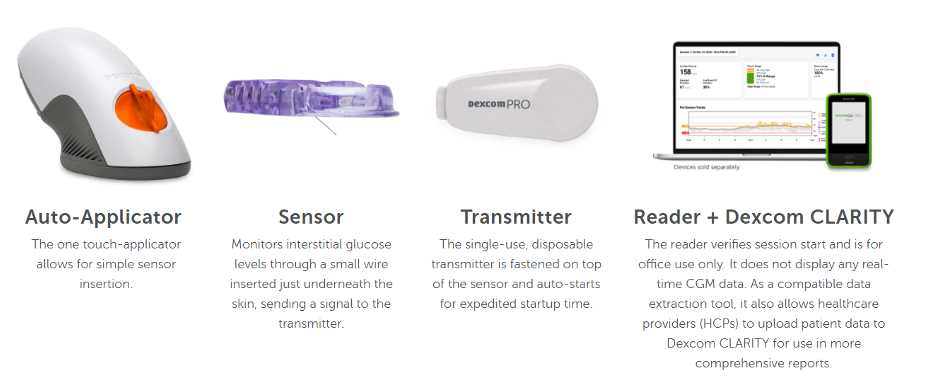
Transmitter: Key Features Explained
The transmitter serves as a crucial component in continuous glucose monitoring systems, responsible for wirelessly transmitting data collected from sensors to a receiving device. Its design incorporates advanced technology to ensure accurate readings and seamless communication, making it an essential element for effective diabetes management.
Wireless Communication
This device utilizes Bluetooth technology to send real-time glucose levels to compatible smartphones or receivers. The wireless connection ensures that users can conveniently monitor their glucose data without the need for cumbersome cables or manual data entry.
Battery Life and Performance
The efficiency of the power source is vital for continuous operation. The transmitter is engineered for extended battery life, enabling prolonged use without frequent replacements. Users benefit from a reliable performance that supports their daily routines without interruptions.
Durability is another key feature, as the transmitter is designed to withstand daily wear and tear while maintaining functionality. This ensures longevity and reliability, contributing to a hassle-free user experience.
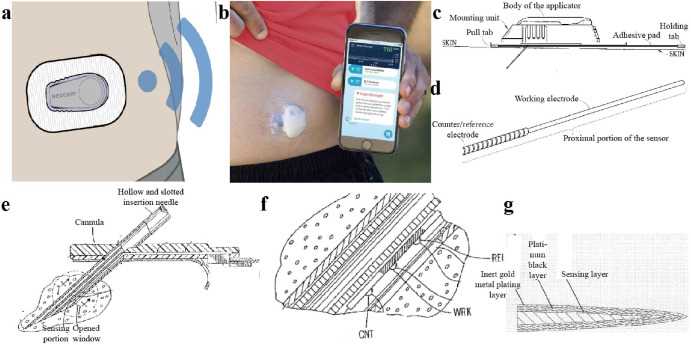
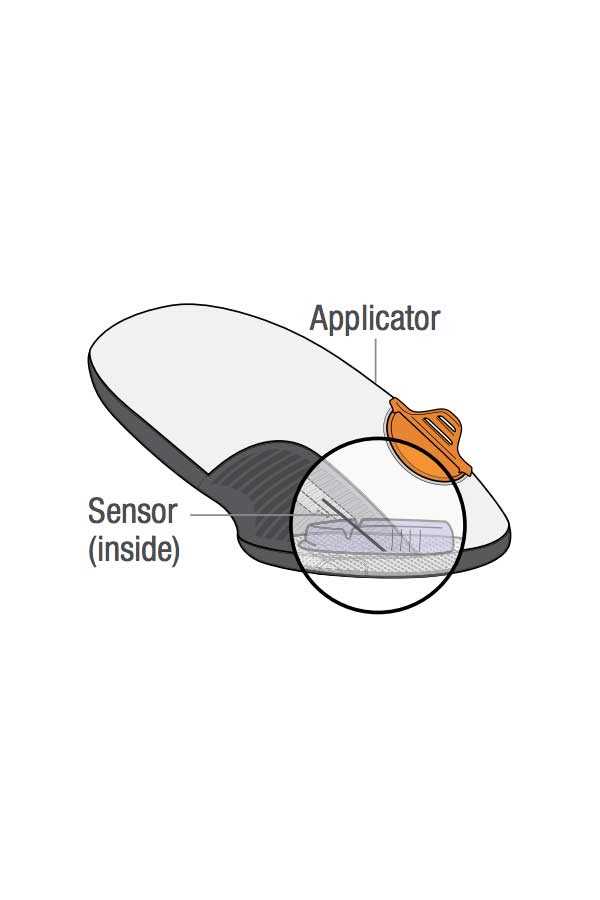
Components of the Sensor Pod
The sensor pod consists of several essential elements that work together to ensure accurate monitoring and transmission of glucose levels. Each component plays a vital role in the pod’s overall functionality, contributing to its effectiveness and reliability in managing diabetes.
1. Sensor Needle: This is the critical part that penetrates the skin to measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. Its design ensures minimal discomfort while providing accurate readings.
2. Adhesive Layer: The adhesive layer secures the pod to the skin, allowing it to remain in place during daily activities. It is designed to be skin-friendly, reducing the risk of irritation.
3. Electronics Module: This component houses the circuitry and processing units that interpret the sensor’s readings and communicate with external devices. It is essential for the pod’s functionality and data management.
4. Power Source: Typically consisting of a small battery, this element powers the electronics module and enables the sensor to operate efficiently over its lifespan.
5. Wireless Transmitter: This feature allows the sensor pod to transmit data to compatible devices, such as smartphones or glucose monitors, providing real-time insights into glucose levels.
Understanding these components helps in appreciating the technology behind continuous glucose monitoring systems and their role in enhancing diabetes management.
Battery Specifications and Lifespan
The power source is a crucial component of any electronic device, influencing both its functionality and durability. Understanding the specifications of the energy source and its expected lifespan can help users make informed decisions regarding usage and maintenance.
Technical Characteristics
Typically, the energy source is designed to provide a stable voltage and sufficient capacity to ensure uninterrupted operation. Most commonly, lithium-based options are utilized due to their high energy density and relatively low self-discharge rates. This results in prolonged use between charges, allowing users to go about their daily activities without frequent interruptions for power replenishment.
Longevity Factors
Several factors affect the lifespan of the power source. Usage patterns, environmental conditions, and charging habits all play significant roles. For optimal longevity, it is advisable to avoid extreme temperatures and to follow manufacturer recommendations for charging cycles. Regular monitoring of the energy levels can also prevent unexpected failures, ensuring that the device remains operational when needed most.
Calibration Process for Accuracy
Ensuring precision in measurements is vital for optimal performance and reliability in any monitoring system. The calibration procedure involves specific steps to guarantee that the readings are both consistent and reflective of actual conditions. By adhering to a systematic approach, users can maintain the effectiveness of their device over time.
Steps for Calibration
- Gather Necessary Equipment
- Prepare the Calibration Solution
- Power On the Device
- Access Calibration Settings
- Input Reference Values
- Verify Calibration Accuracy
- Document Calibration Results
Maintaining Calibration
Regular checks and adjustments can help sustain the accuracy of measurements. Here are some tips to consider:
- Schedule routine calibration intervals.
- Store the device in a stable environment to avoid fluctuations.
- Utilize high-quality reference solutions for testing.
- Monitor for any discrepancies in readings and recalibrate as needed.
Connecting to Mobile Applications
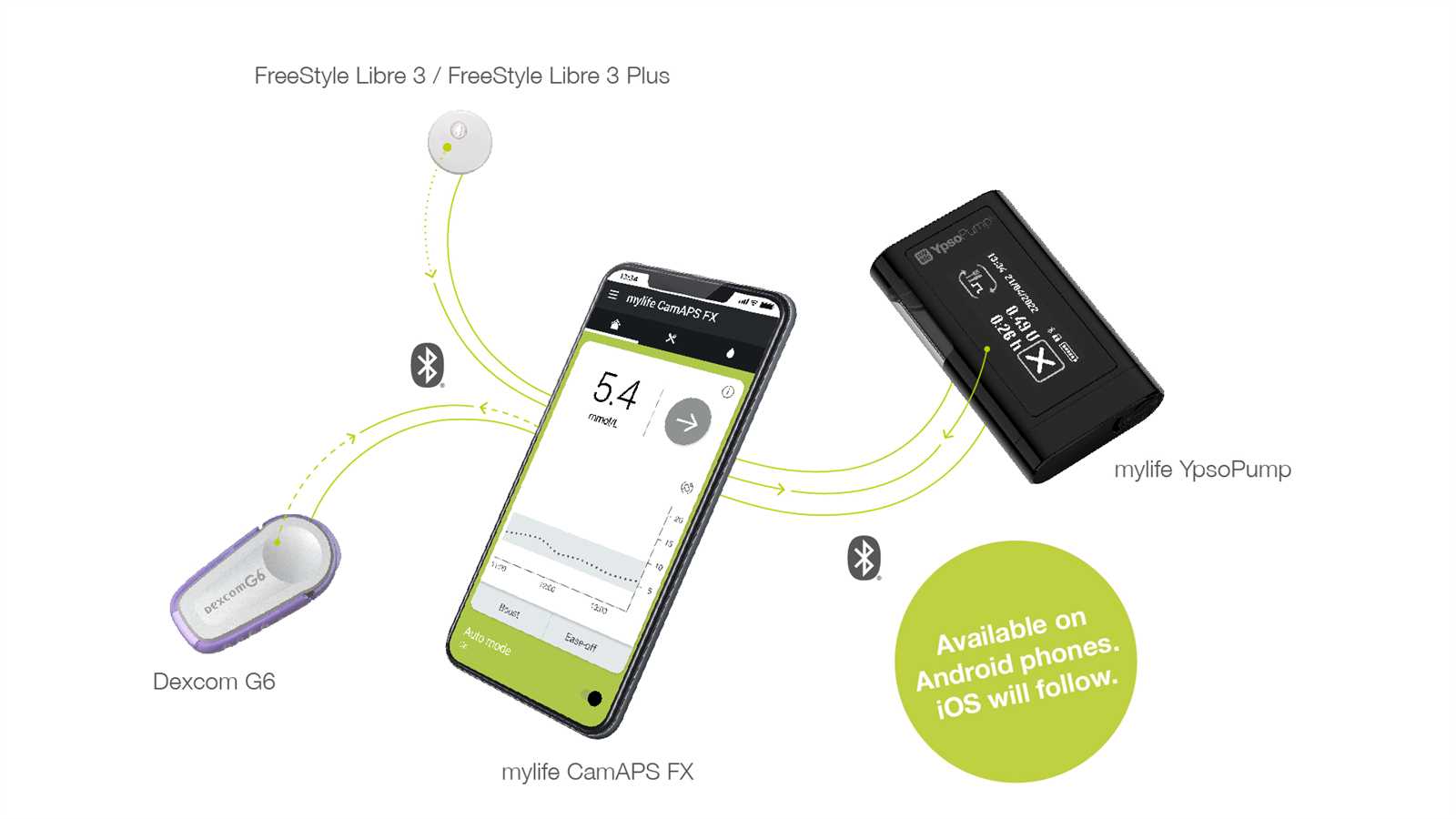
Integrating a continuous glucose monitoring system with mobile applications enhances the user experience by providing real-time data access and insights. This connectivity facilitates seamless tracking of glucose levels and alerts users to fluctuations, ensuring proactive management of their health.
To establish this connection, users typically download the associated mobile application from their device’s app store. After installation, the app guides them through the setup process, which may involve creating an account and pairing the device via Bluetooth. Once connected, users can access various features, including data logging, trend analysis, and personalized notifications.
Regular updates to both the monitoring device and the application are essential for optimal performance. Users should ensure that their mobile devices are compatible with the application to avoid connectivity issues. Utilizing these advanced features empowers individuals to take charge of their health, making informed decisions based on accurate and timely information.
Interpreting Glucose Readings Effectively

Understanding blood sugar measurements is crucial for maintaining optimal health. Accurate interpretation of these values allows individuals to make informed decisions regarding their diet, exercise, and medication. By recognizing patterns and fluctuations, users can better manage their glucose levels and enhance their overall well-being.
When assessing glucose levels, consider the following factors that influence readings:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Timing | The time of day and recent activities can affect readings. Morning levels may differ from those taken after meals or exercise. |
| Food Intake | The types of food consumed directly impact glucose levels. Carbohydrates, in particular, can cause significant spikes. |
| Physical Activity | Exercise can lower blood sugar levels, making it essential to monitor readings before and after workouts. |
| Stress | Emotional or physical stress can elevate glucose levels, making it important to recognize its influence. |
By being mindful of these elements, individuals can interpret their glucose measurements more effectively and take necessary actions to maintain stable levels.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
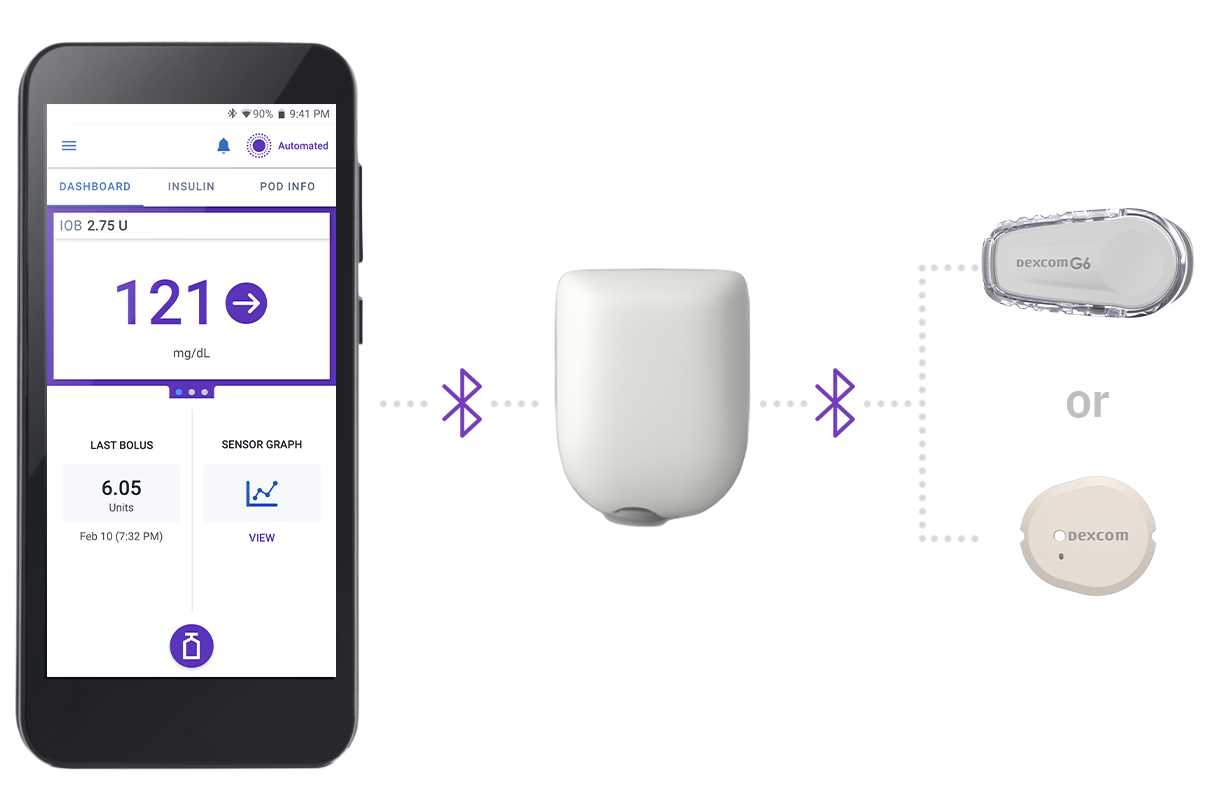
Ensuring the extended life of your device involves a combination of regular care and attention to detail. By implementing a few essential practices, users can enhance the performance and durability of their equipment, ultimately leading to a more reliable experience over time.
Regular Cleaning
Keeping the device free from dirt and moisture is crucial. Use a soft, lint-free cloth to gently wipe the exterior and connectors. Avoid using harsh chemicals that could damage sensitive components. Regular cleaning helps maintain functionality and reduces the risk of malfunctions.
Proper Storage and Handling
When not in use, store the device in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Handle the unit with care, avoiding drops or impacts that could compromise its integrity. Thoughtful storage and handling practices significantly contribute to its overall longevity.
Common Troubleshooting Steps
When encountering issues with your glucose monitoring system, it’s important to follow a systematic approach to identify and resolve problems. This section outlines several common methods that can help restore proper functionality and ensure accurate readings.
Initial Checks
- Verify that the device is properly charged and powered on.
- Ensure that all components are securely connected and free from damage.
- Check for any visible signs of wear or malfunction, such as cracks or loose parts.
Signal and Connectivity Issues
- Confirm that the receiver or smartphone is within the optimal range for signal reception.
- Restart the device to refresh the connection.
- Inspect the app settings to ensure that notifications and alerts are correctly configured.
If problems persist after following these steps, consult the user manual or contact customer support for further assistance.
Replacement Guidelines for Each Part
Ensuring the functionality of your monitoring system requires an understanding of how to effectively replace its components. Each element plays a crucial role in the overall performance and accuracy of the device, and knowing when and how to replace them can enhance your experience and reliability.
Understanding Component Lifespan
The lifespan of individual components can vary significantly. Regularly assessing their condition is essential. Monitor for signs of wear or malfunction, and refer to user manuals for recommended replacement timelines. Keeping track of these intervals can prevent unexpected disruptions in functionality.
Replacement Process
When replacing a component, ensure you have the appropriate tools and follow specific procedures for each item. Carefully detach the old component, following manufacturer instructions to avoid damage. Install the new part with precision, ensuring secure connections to maintain optimal performance.
Accessories Enhancing User Experience
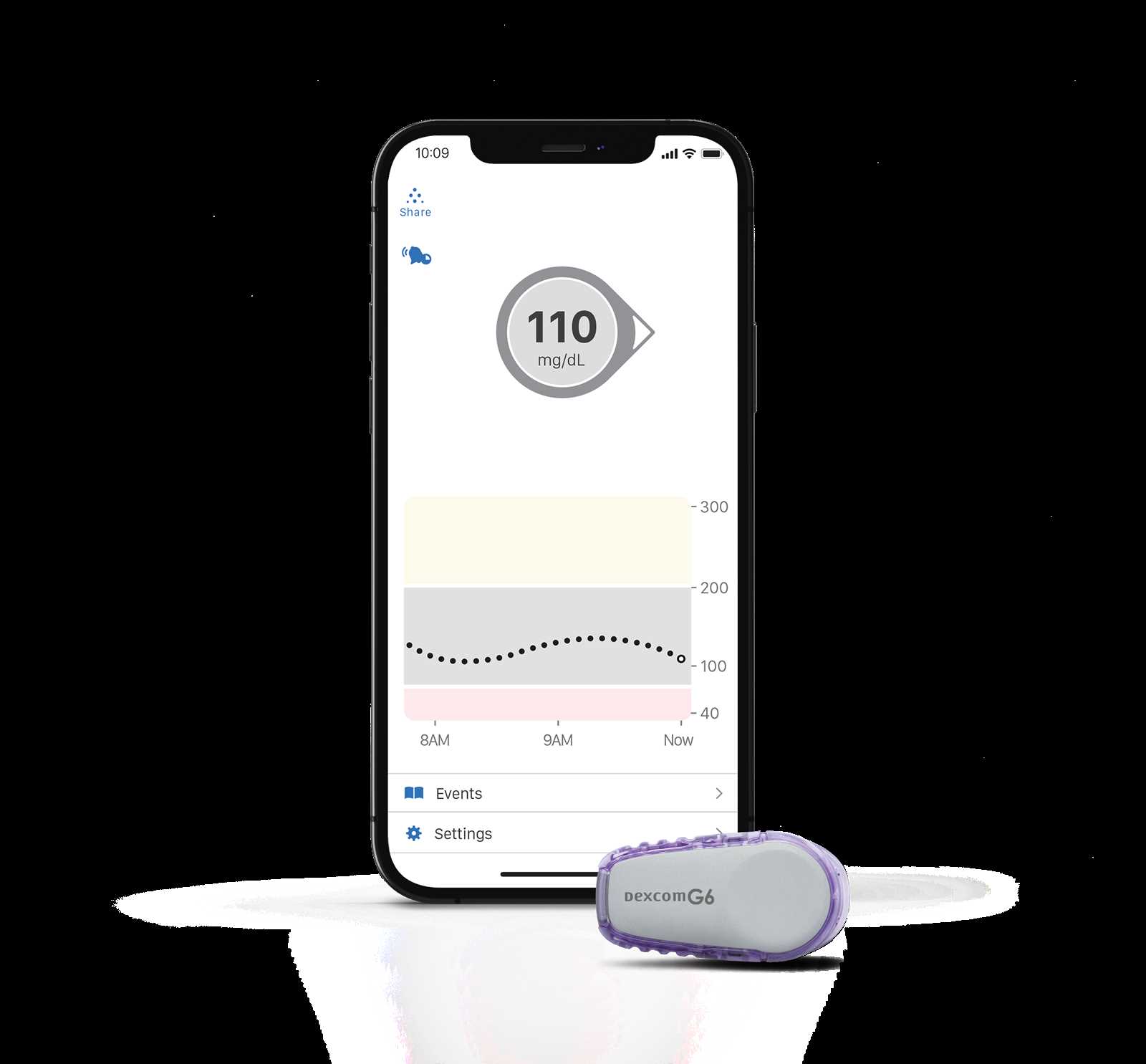
Various enhancements can significantly improve the overall experience for users managing their health. These supplementary items are designed to provide added convenience, comfort, and functionality, ensuring that individuals can maintain a seamless connection with their monitoring devices.
One essential accessory includes protective cases, which safeguard the equipment from everyday wear and tear. These cases not only offer durability but also add a personalized touch, allowing users to express their style. Another valuable addition is adhesive patches, which help secure the device in place, ensuring accurate readings and preventing any disruptions during daily activities.
Additionally, compatible application tools facilitate easy management and analysis of data. These tools often come with intuitive interfaces, making it easier for users to track trends and make informed decisions regarding their health. Supportive wearables, such as arm bands or clips, enhance comfort while keeping the device easily accessible, fostering a user-friendly experience.
In summary, incorporating these accessories not only enhances the functionality of health monitoring devices but also promotes a more engaging and efficient user journey.
Safety Precautions and Usage Tips
Ensuring the safe and effective operation of medical devices is paramount for user health and well-being. Adhering to specific guidelines can help minimize risks and enhance the overall experience with the equipment. This section outlines essential precautions and recommendations for optimal usage.
Before utilizing the device, it is crucial to familiarize yourself with the manufacturer’s instructions and safety warnings. Proper handling and maintenance can significantly reduce the likelihood of complications. Below is a table summarizing key safety tips:
| Precaution | Description |
|---|---|
| Cleanliness | Ensure that the area where the device is used is clean and free from contaminants. |
| Calibration | Regularly calibrate the device as per the manufacturer’s guidelines to ensure accurate readings. |
| Storage | Store the device in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to prevent damage. |
| Monitoring | Consistently monitor readings and consult a healthcare professional if abnormalities are detected. |
| Emergency Preparedness | Have a plan in place for emergencies, including access to backup devices or supplies. |
By following these guidelines, users can enhance their experience and ensure safe operation while utilizing their medical equipment effectively.