Exploring the intricate elements that contribute to the functionality of a two-wheeled vehicle opens up a world of engineering marvels. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring seamless movement and performance, highlighting the ingenuity behind design and construction.
In this section, we will embark on a journey to uncover the various elements involved, focusing on their relationships and interactions. By understanding these connections, enthusiasts can appreciate the sophistication involved in maintaining and enhancing the overall experience.
From the frame that supports to the mechanisms that propel, the comprehensive overview will serve as a valuable resource for both novices and seasoned riders alike. Prepare to delve into the ultimate guide that dissects these essential components, elevating your knowledge and appreciation of the craft.
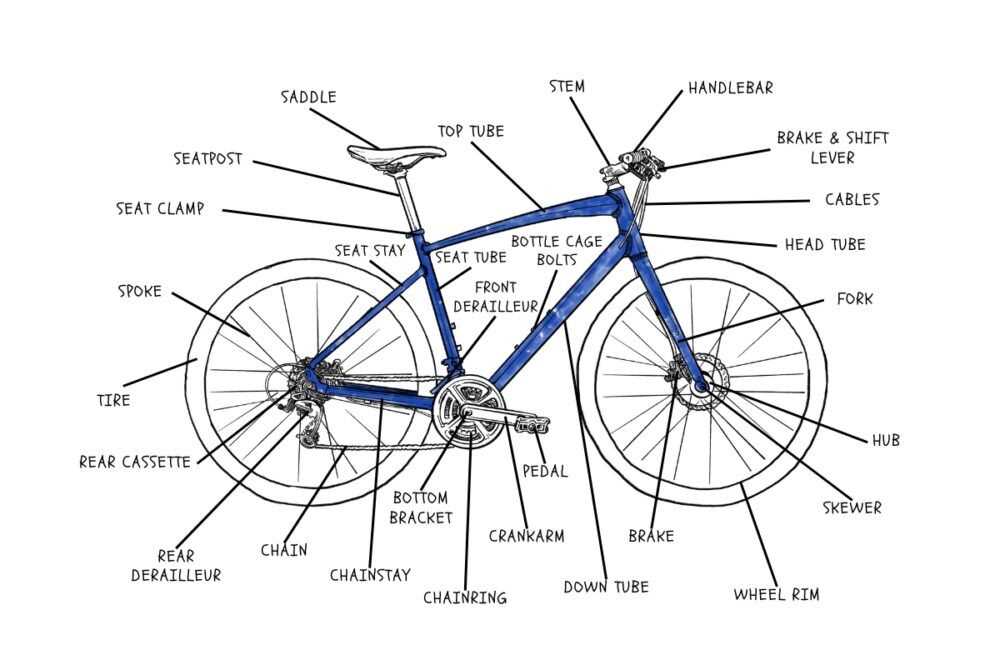
Understanding Bike Components
Grasping the intricacies of two-wheeled vehicles involves exploring the various elements that contribute to their functionality and performance. Each component plays a pivotal role in ensuring a smooth and efficient ride, forming a harmonious system that balances speed, control, and comfort.
Frames serve as the foundational structure, providing stability and support. Wheels are critical for movement, affecting agility and traction. Additionally, braking systems enhance safety, allowing for effective stopping power in various conditions. The transmission system enables the rider to adjust speed and power, while handlebars ensure proper steering and maneuverability.
Furthermore, seats contribute to rider comfort, influencing endurance during longer journeys. Understanding these elements and their interactions can significantly enhance the overall experience of navigating through different terrains.
Essential Parts of a Bicycle
Understanding the fundamental components of a two-wheeled vehicle is crucial for both maintenance and performance. Each element plays a vital role in ensuring smooth operation and safety, contributing to an enjoyable riding experience.
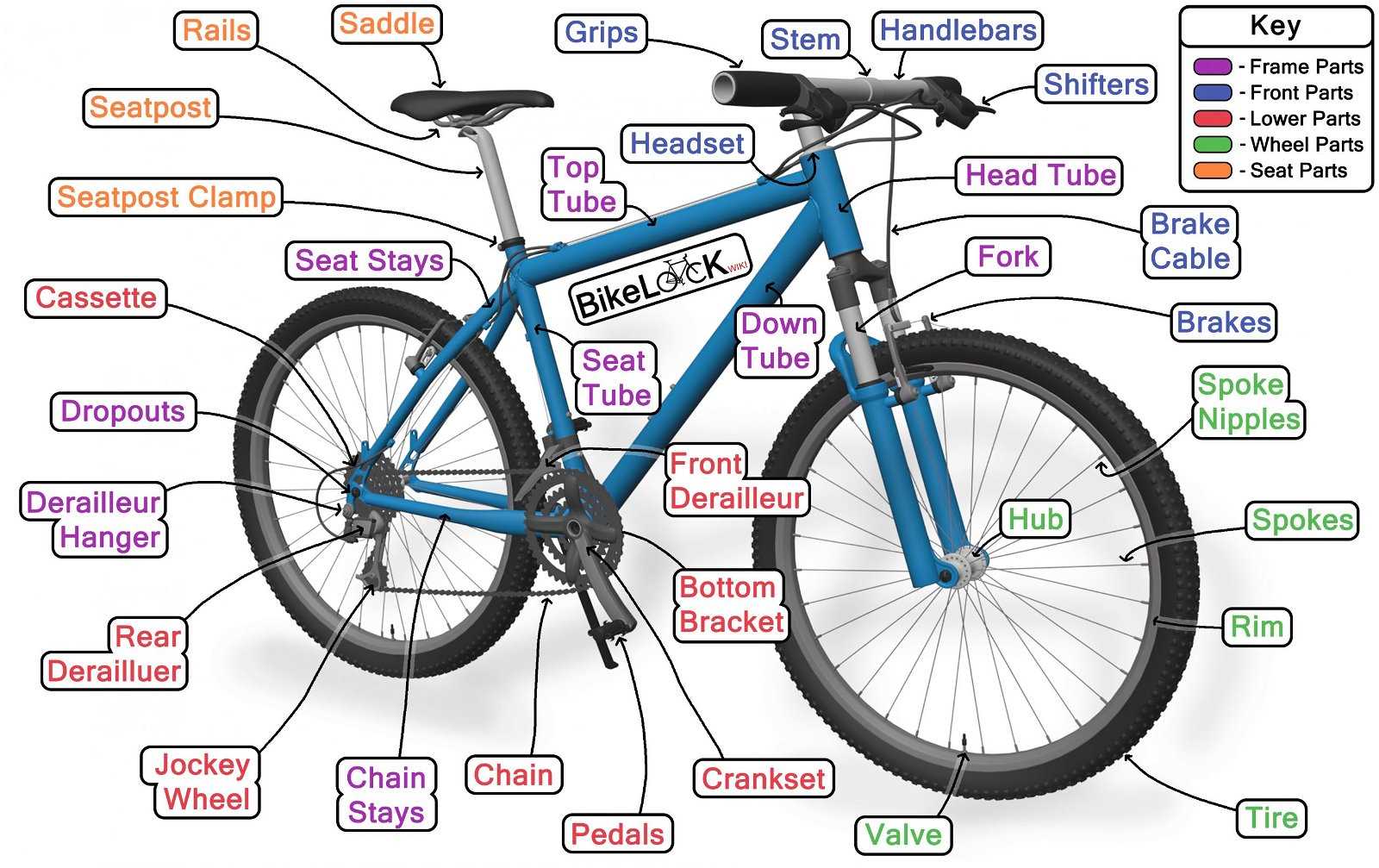
Key Components
- Frame: The structure that supports all other elements.
- Wheels: Allow for movement and stability.
- Handlebars: Provide steering control and comfort.
- Seat: Ensures rider comfort and positioning.
- Brakes: Essential for slowing down and stopping effectively.
- Pedals: Enable the rider to propel the vehicle forward.
Additional Features
- Gear System: Facilitates changing speeds and adapting to terrain.
- Chain: Connects pedals to the rear wheel for movement.
- Suspension: Enhances comfort by absorbing shocks from uneven surfaces.
- Lights: Improves visibility during low-light conditions.
Frame Types and Their Functions
Different structures play a crucial role in the performance and suitability of two-wheeled vehicles. Each configuration is designed with specific uses in mind, influencing factors such as stability, agility, and comfort. Understanding these variations helps riders choose the most appropriate model for their needs.
Steel frames are known for their durability and shock absorption. They offer a comfortable ride, making them popular among commuters and long-distance travelers. The flexibility of steel can handle various terrains, providing a smooth experience.
Aluminum frames are lightweight and stiff, making them ideal for competitive settings. They allow for quick acceleration and responsive handling. However, they may lack some of the comfort offered by their steel counterparts, especially on rough surfaces.
Carbon fiber frames represent the pinnacle of modern engineering. They are extremely light and strong, allowing for advanced designs that improve aerodynamics. While often more expensive, their performance benefits make them a favorite among serious enthusiasts.
Ti frames combine the best attributes of both steel and aluminum. They are lightweight yet resilient, providing a balance between comfort and efficiency. This versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of cycling activities.
Each structure not only affects the overall weight and handling but also influences the rider’s experience and enjoyment. Understanding these differences allows enthusiasts to make informed decisions and enhance their riding adventures.
Exploring Gear Systems in Bicycles
The mechanisms that allow for varied speeds and smooth transitions are crucial for enhancing performance and comfort during rides. Understanding how these systems function provides insight into their importance for efficiency and adaptability on different terrains.
At the core of these mechanisms lies the ability to adjust the resistance and power applied by the rider. This adjustment is made possible through a series of interconnected components that work in harmony to optimize pedaling efficiency.
Ultimately, the choice of gearing can significantly impact the riding experience, affecting everything from acceleration to climbing ability. Exploring the intricacies of these systems unveils their role in achieving the ideal balance between speed and control.
Brakes: Types and Mechanisms
Effective stopping power is crucial for safety and performance in cycling. Various systems are employed to provide the necessary control and responsiveness, each with its unique characteristics and benefits. Understanding these options can help riders choose the best setup for their needs.
| Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rim | Utilizes pads that grip the outer edge of the wheel. | Lightweight, easy to maintain. | Less effective in wet conditions, can wear out rims. |
| Disc | Employs a rotor attached to the hub, with calipers that squeeze the rotor. | Consistent performance in all weather, improved modulation. | Heavier, requires more complex maintenance. |
| V-Brake | A type of rim brake that provides greater leverage through a dual-arm system. | Strong stopping power, lightweight. | Less effective in wet conditions, can be affected by mud. |
| Cantilever | Similar to V-brakes, but arms are mounted on a pivot for more clearance. | Good for wider tires, versatile setup. | More difficult to adjust, can be less powerful. |
Each braking system has its own set of mechanisms, affecting overall performance and rider experience. Selecting the right type ensures optimal control and safety on every journey.
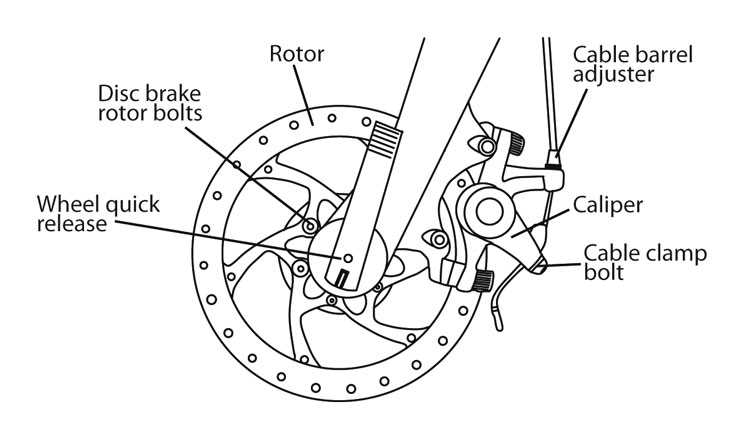
Wheels: Structure and Importance
Understanding the construction and significance of rolling components is essential for anyone interested in cycling. These circular mechanisms play a crucial role in overall performance, affecting speed, stability, and maneuverability. Their design is a perfect blend of engineering and functionality, enabling smooth transitions over various terrains.
The primary elements that constitute these rolling systems include the rim, spokes, hub, and tire. Each component contributes to the overall efficiency and effectiveness, ensuring a balanced experience for the rider. Below is a table summarizing these key elements and their functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Rim | Supports the tire and provides structural integrity. |
| Spokes | Connect the rim to the hub, distributing weight and absorbing shocks. |
| Hub | Central part that houses the axle and allows rotation. |
| Tire | Provides traction, cushioning, and protection against punctures. |
These elements work in harmony to create a reliable and efficient rolling mechanism, underscoring their importance in enhancing the overall cycling experience. Proper maintenance and understanding of their roles can lead to improved performance and longevity.
Suspension Systems Explained
The functionality of a well-designed suspension mechanism is crucial for enhancing comfort and control during movement. This system acts as a buffer, absorbing shocks and vibrations, allowing for a smoother experience on various terrains. Its effectiveness directly influences performance, handling, and overall ride quality.
Suspension mechanisms can be broadly categorized into two main types: active and passive systems. Active systems utilize electronic components to adjust to changing conditions, optimizing performance in real time. In contrast, passive systems rely on mechanical components that provide a consistent response based on their design and materials.
Key elements of suspension systems include springs, dampers, and linkages. Springs store energy during compression, while dampers control the rate at which this energy is released, preventing excessive bouncing and maintaining stability. Linkages connect these components, allowing for coordinated movement and ensuring proper alignment with the frame.
When selecting a suspension system, factors such as weight, travel distance, and intended use play significant roles. For instance, those seeking a robust experience on rugged trails may prioritize systems with greater travel, while urban commuters might opt for lighter setups that enhance agility.
Ultimately, understanding the intricacies of suspension systems can lead to more informed choices, enhancing both safety and enjoyment on every journey.
Handlebars: Styles and Adjustments
The choice of steering components can significantly impact comfort and control while navigating various terrains. Different configurations cater to diverse riding styles and personal preferences, making it essential to understand their characteristics and adjustment options.
There are several primary styles of steering components:
- Flat: Offers a low profile and is ideal for aggressive riding positions.
- Rise: Provides additional height, promoting a more upright posture and comfort over long distances.
- Dropped: Enables a more aerodynamic stance, often favored in racing.
- Curved: Allows for multiple hand positions, enhancing versatility and reducing fatigue.
Adjustments can further tailor the experience:
- Height: Adjusting the elevation can help achieve a more comfortable grip and reduce strain.
- Angle: Modifying the tilt can influence aerodynamics and overall handling.
- Width: Selecting the appropriate span can affect balance and control during maneuvers.
Exploring these options ensures a customized setup that enhances both performance and enjoyment on every journey.
Pedals and Their Variations
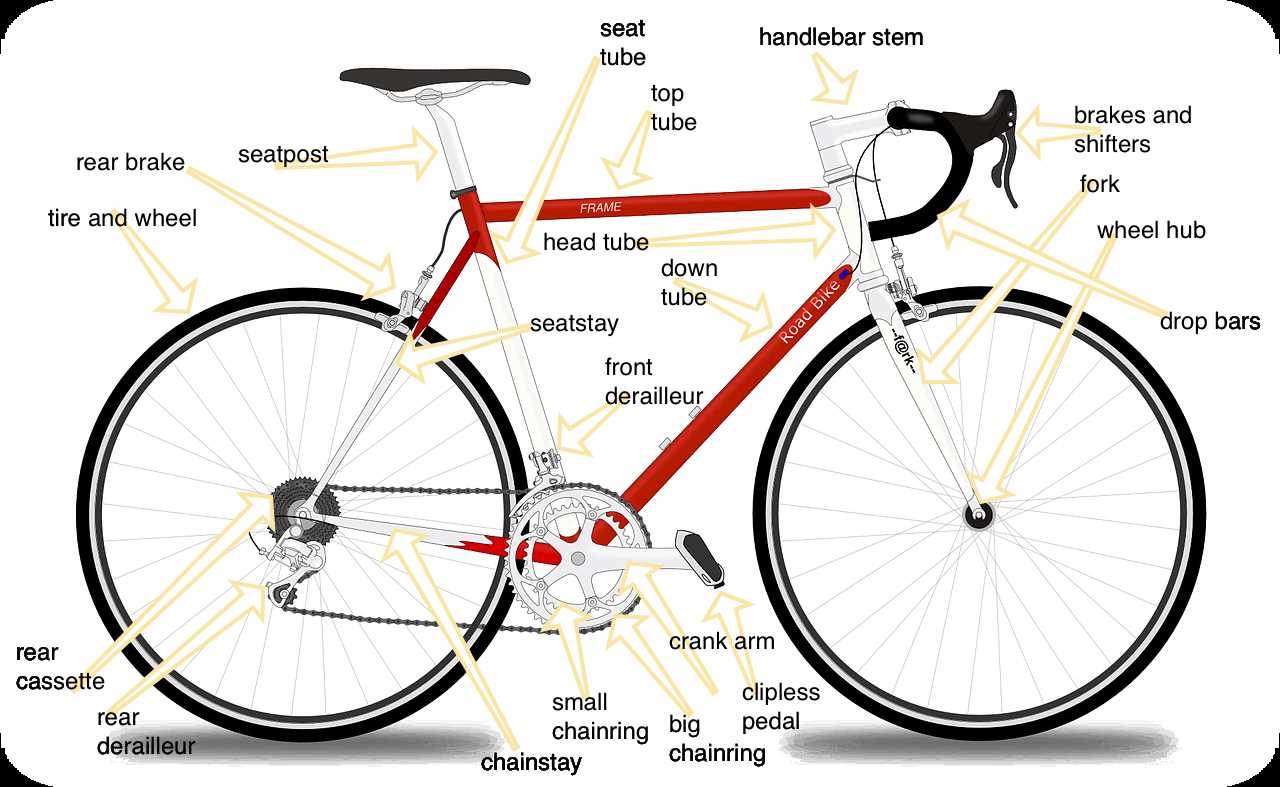
The foundation of an efficient riding experience lies in the choice of foot interface systems. These essential components come in various designs, each catering to specific styles and preferences, enhancing performance and comfort.
Types of Foot Interface Systems

There are primarily two categories: platform and clipless. Platform systems provide a flat surface, allowing freedom of movement, while clipless systems secure the footwear, offering improved power transfer and stability during rides.
Choosing the Right System
Selecting the ideal foot interface depends on individual riding goals and terrain. Casual riders may prefer platform systems for ease, while enthusiasts often opt for clipless for enhanced efficiency and control.
Chain: Role in Bicycle Mechanics
The chain serves as a critical component in the overall functioning of a two-wheeled vehicle, facilitating the transfer of energy from the rider to the wheels. Its efficiency directly impacts performance, making it essential for both speed and control.
Functionality and Efficiency
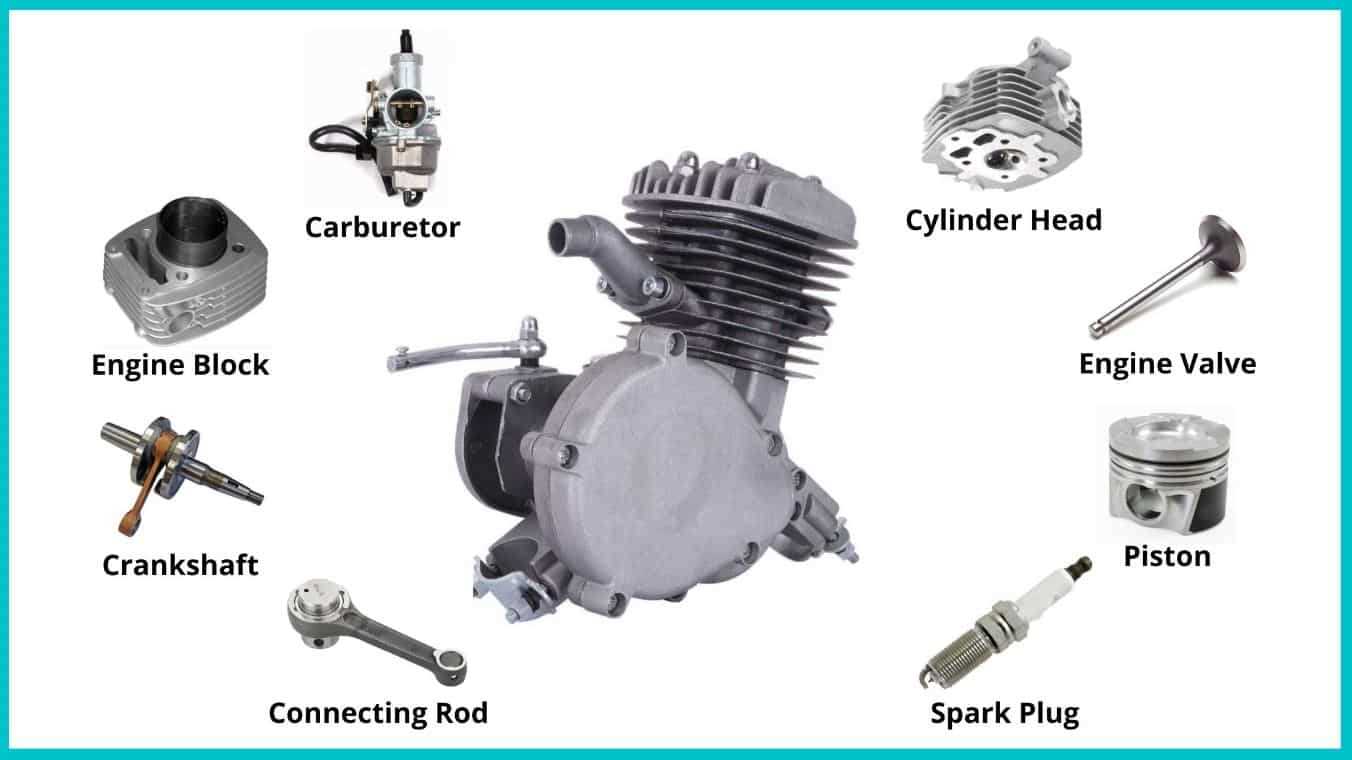
At its core, the chain connects the pedals to the rear wheel, converting the rider’s effort into motion. This link ensures that the rotational force generated by pedaling is effectively transmitted, enabling smooth acceleration and maintaining optimal velocity.
Maintenance and Longevity
Regular upkeep is vital for the chain’s durability and performance. Lubrication reduces friction, while cleaning prevents dirt accumulation, ensuring that the mechanism operates seamlessly. Neglecting these practices can lead to premature wear and decreased efficiency.
Understanding Bike Accessories
In the world of two-wheeled transportation, various enhancements play a crucial role in improving both functionality and comfort. These additions not only elevate the overall riding experience but also ensure safety and convenience during journeys. Exploring the vast array of available options can help enthusiasts make informed decisions about what to incorporate into their setup.
Essential Enhancements serve to address specific needs. From lighting systems that illuminate paths during low visibility to locking mechanisms that provide security, these accessories cater to practical requirements. Riders should prioritize those that align with their typical routes and usage patterns.
Comfort features such as cushioned grips or adjustable seats can significantly improve long-distance travels. By investing in these items, individuals can enjoy extended rides without discomfort, enhancing their overall enjoyment and performance.
Finally, personalization options allow riders to express their individuality. Whether through colorful decals or unique gear configurations, customizing one’s setup can foster a deeper connection to the riding experience. Embracing these accessories not only contributes to practicality but also transforms the journey into a more enjoyable and expressive adventure.
Maintenance Tips for Bike Parts
Ensuring longevity and optimal performance of your two-wheeled vehicle requires regular care and attention. A proactive approach to upkeep can prevent issues and enhance the overall riding experience. By focusing on various components, you can ensure a smooth journey every time you hit the road.
Regular Cleaning

Keeping your ride clean is essential. Dirt and grime can lead to wear and tear. Utilize a gentle soap and water solution to remove debris. Pay special attention to the chain, gears, and brake mechanisms. A clean machine not only looks great but also functions more effectively.
Lubrication and Inspection
Routine lubrication is crucial for moving elements. Apply a suitable lubricant to the chain and other pivot points to minimize friction. Additionally, inspect components for any signs of damage or wear. Regular checks can help identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring safety and performance.