The intricate structure of a two-wheeled vehicle encompasses a variety of essential elements that work together to ensure smooth operation and optimal performance. Each individual component plays a critical role, contributing to the overall functionality and safety of the rider. By exploring these elements, one can gain a deeper appreciation for the engineering that allows for efficient movement and control.
From the framework that provides stability to the mechanisms that facilitate motion, the organization of these elements is both purposeful and fascinating. Understanding how each section interacts with others not only enhances the riding experience but also aids in maintenance and repair. Knowledge of these features empowers enthusiasts and casual riders alike to make informed decisions about their vehicles.
In this exploration, we will delve into the various sections that constitute a two-wheeled vehicle. Each segment, from the propulsion system to the steering apparatus, offers unique insights into the design and functionality, highlighting the innovation behind modern engineering. Whether for leisure or commuting, appreciating these components enriches one’s connection to the art of riding.
Understanding Bike Components
Exploring the various elements that contribute to a cycling experience is essential for both enthusiasts and casual riders. Each component plays a significant role in ensuring functionality, comfort, and performance, ultimately shaping how one interacts with their two-wheeled companion.
Key Elements of a Cycle
At the core of any cycle’s design are its essential elements, which can greatly influence handling and speed. The frame serves as the backbone, supporting all other elements while dictating the overall geometry. The wheels, crucial for movement, provide stability and traction, ensuring a smooth ride on diverse terrains.
Enhancements for Performance
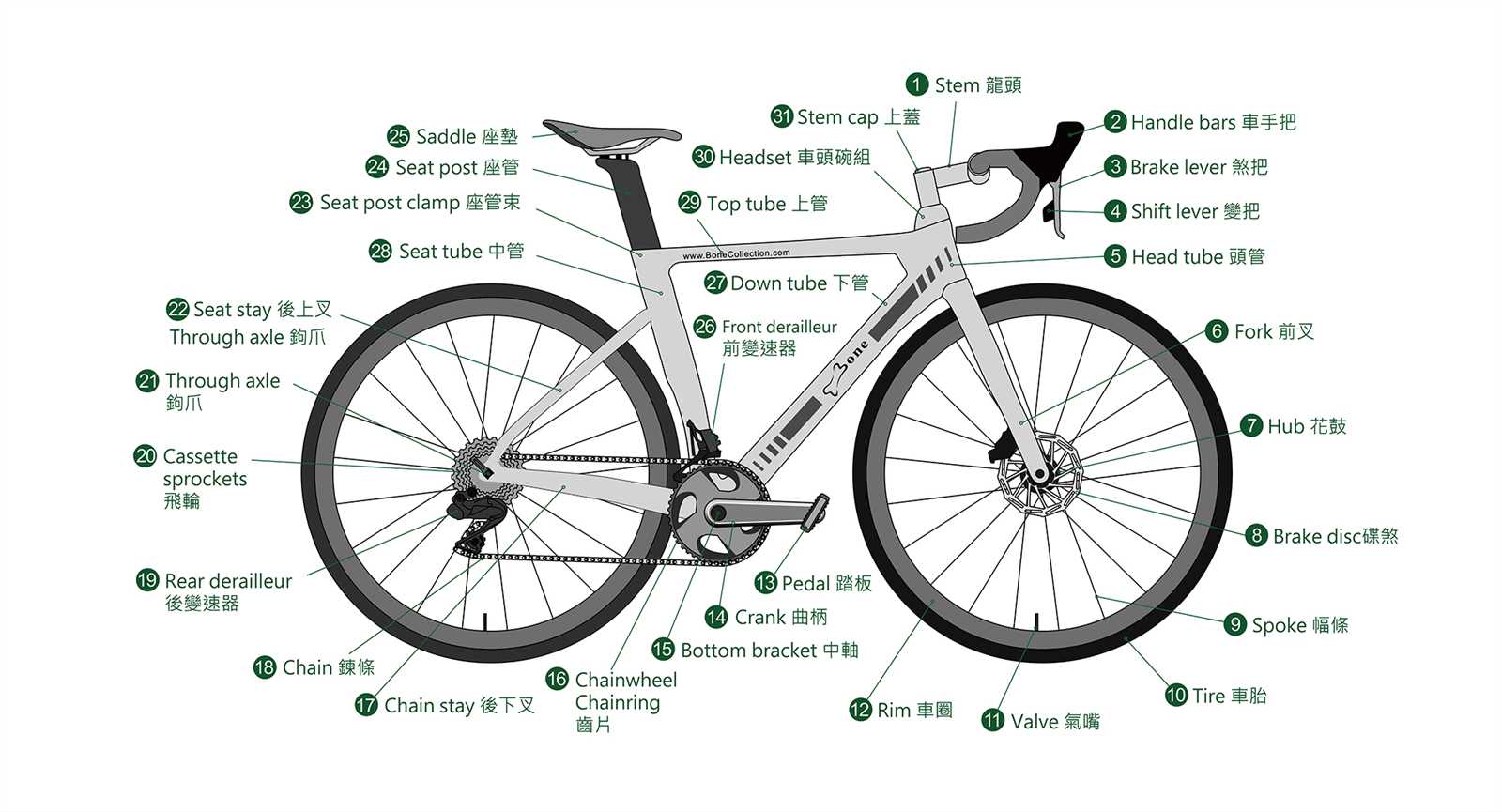
Various enhancements can optimize performance, making the journey more enjoyable. Gears allow riders to adjust resistance and speed according to their environment, while brakes are vital for safety, offering control over deceleration. Additionally, accessories such as handlebars and saddles can significantly impact comfort, tailoring the experience to individual preferences.
Understanding these crucial elements and enhancements empowers riders to make informed choices, enhancing both enjoyment and efficiency on their journeys.
Frame Types and Their Functions
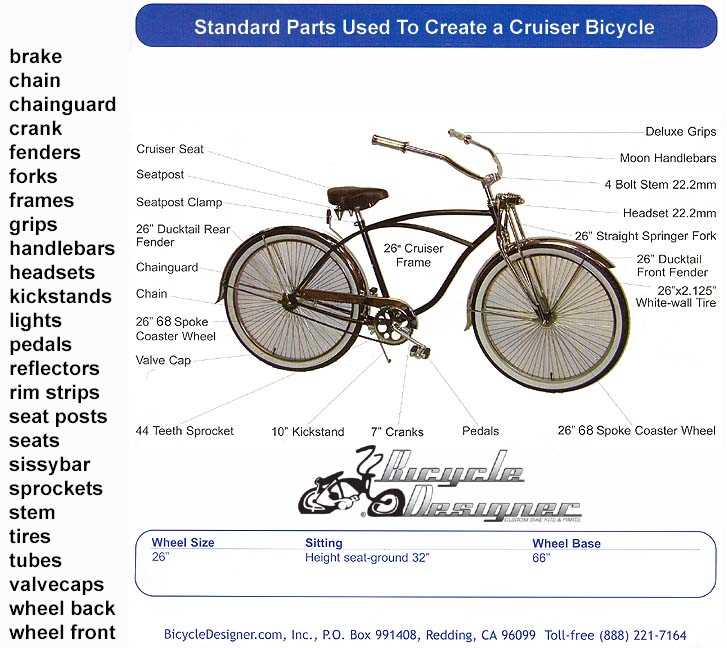
Understanding the various structures that form the foundation of a two-wheeled vehicle is essential for appreciating its design and performance. Each configuration offers unique advantages, catering to different riding styles, environments, and user preferences. By exploring these variations, one can gain insight into how each framework contributes to overall functionality.
Diamond Frame is the most prevalent design, characterized by its triangular shape. This structure provides excellent strength and stability, making it ideal for everyday commuting and recreational use. The design allows for efficient power transfer, enhancing the riding experience on various terrains.
Step-Through Frame features a lowered top tube, facilitating easy mounting and dismounting. This type is particularly beneficial for urban riders and those seeking comfort over performance. Its accessibility makes it a popular choice among casual users and individuals with mobility challenges.
Geared Frame incorporates additional features to accommodate gears, enhancing versatility in different conditions. This design is essential for those who frequently navigate hilly terrains or prefer adjustable speed options. The integration of gears allows for a more dynamic riding experience, tailored to the rider’s needs.
Fat Frame, designed to support wider tires, excels in providing traction on loose surfaces like snow or sand. This robust construction is favored by adventurers and those who explore off-road paths. Its ability to absorb shocks and maintain stability is crucial for tackling challenging environments.
Each framework type plays a significant role in the functionality and usability of a two-wheeled vehicle. By selecting the appropriate structure, riders can enhance their experience, whether they are commuting, exploring, or enjoying leisurely rides.
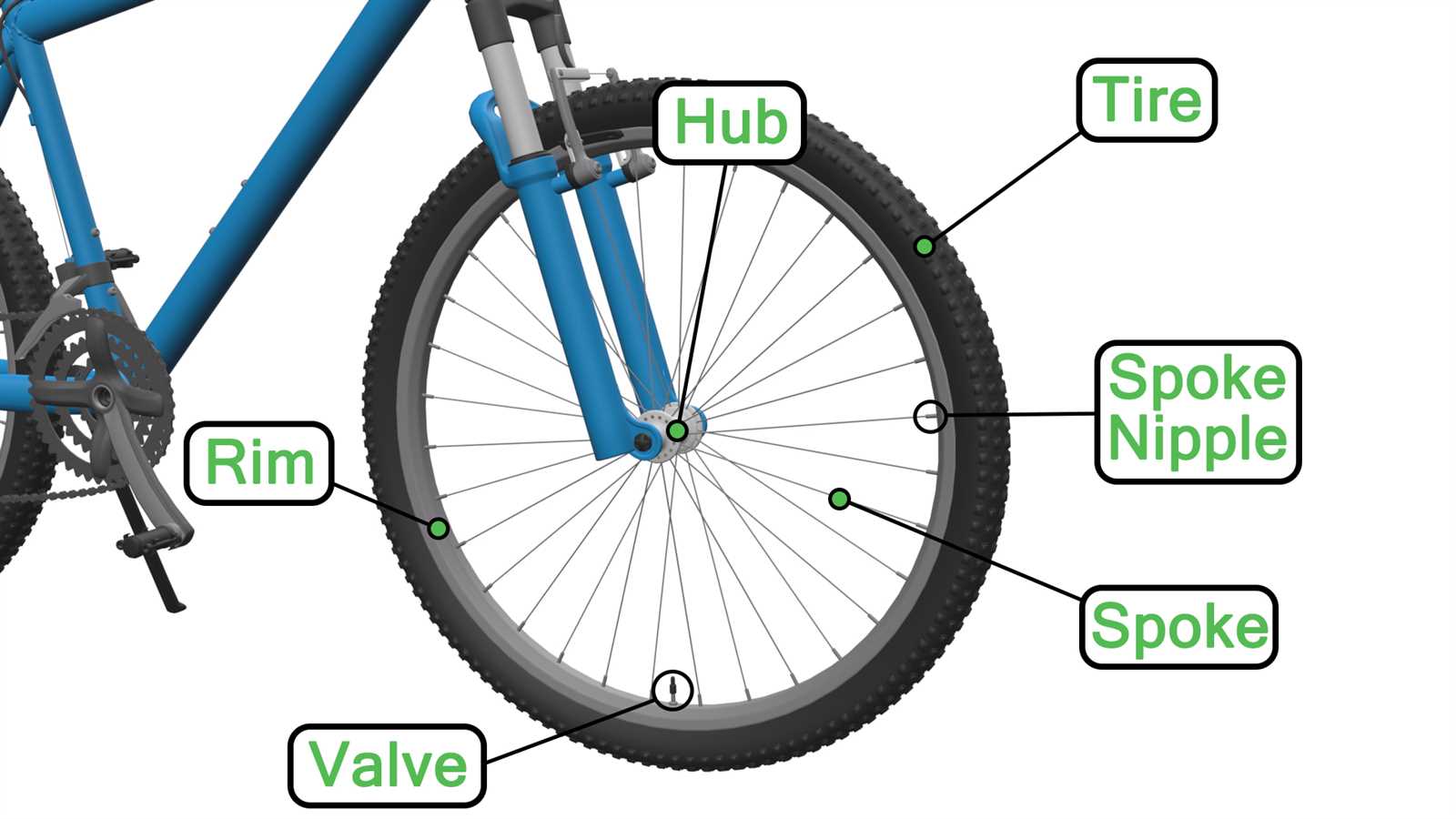
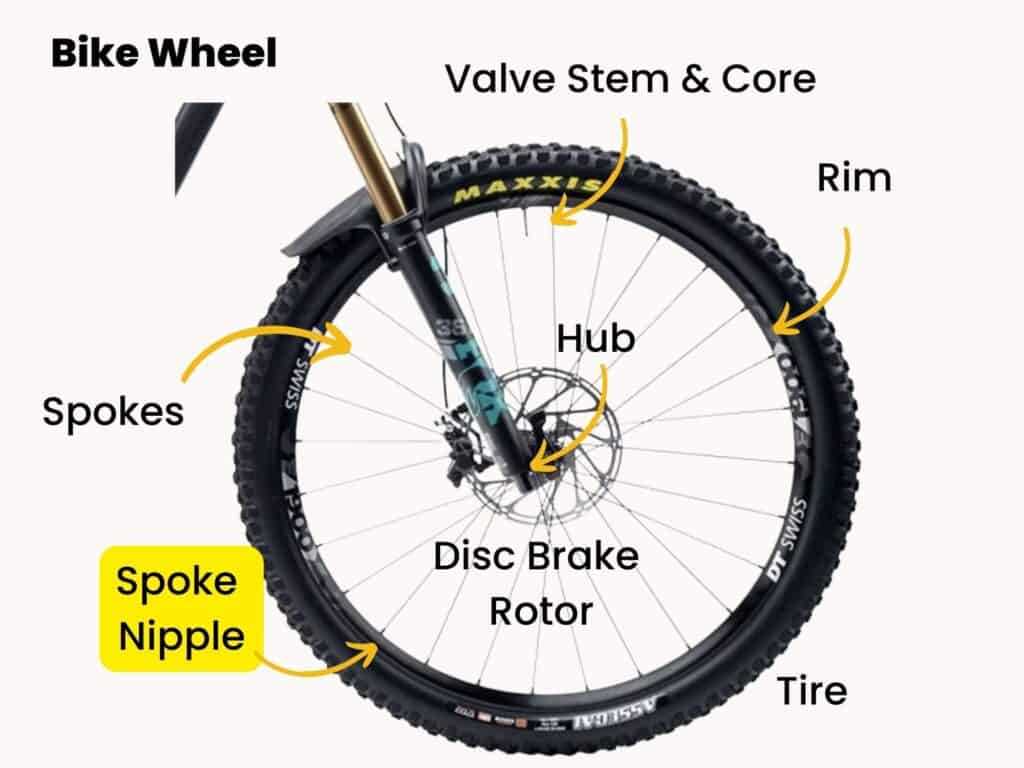
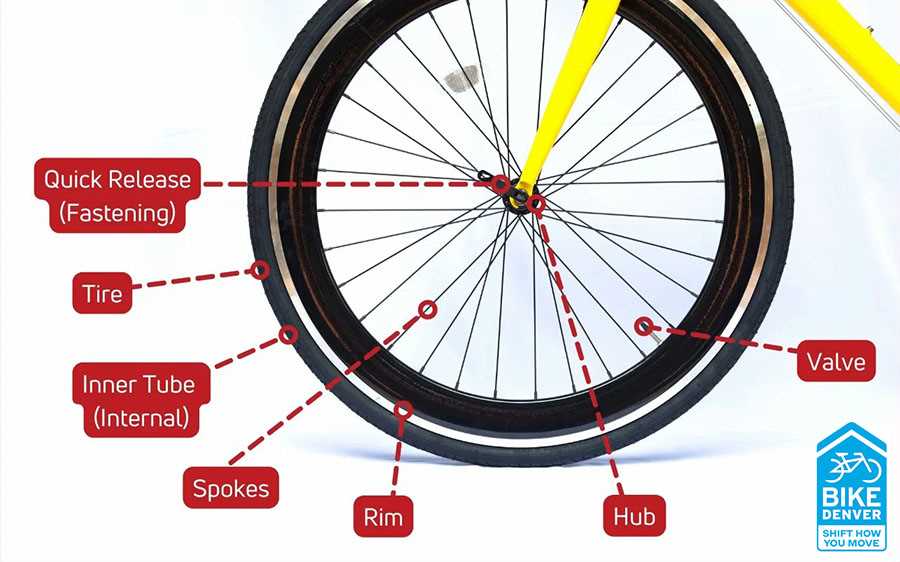
Wheels: Structure and Importance
The circular components of a two-wheeled vehicle are vital for its overall functionality and performance. They serve as the primary means of contact with the ground, facilitating movement and stability. Understanding their design and significance can enhance one’s appreciation for how these elements contribute to an efficient riding experience.
Design Features
Each circular element consists of several key features that work in harmony. The rim, typically made of durable materials, provides the framework, while the tire offers traction and cushioning. Within the structure, spokes connect the rim to the hub, ensuring strength and flexibility. This intricate design allows for better maneuverability and supports the weight of the rider effectively.
Significance in Performance
The effectiveness of the circular components directly impacts speed, handling, and comfort. A well-engineered set enhances performance, allowing for swift navigation through various terrains. Moreover, the quality of these elements can influence overall durability, ensuring a smooth ride over time. Regular maintenance of these circular structures is essential for optimal performance and longevity.
Braking Systems Explained
Effective deceleration is crucial for safety and control during any ride. Understanding the mechanisms that facilitate this function can greatly enhance both performance and reliability. This section delves into the various technologies employed to achieve responsive stopping power, ensuring a smoother experience on the road or trail.
Types of Braking Mechanisms
There are primarily two types of braking mechanisms used in modern two-wheeled vehicles: hydraulic and mechanical systems. Hydraulic systems utilize fluid pressure to amplify force, providing smoother and more consistent stopping. On the other hand, mechanical systems rely on cables and levers, offering simplicity and ease of maintenance.
Performance and Maintenance Considerations
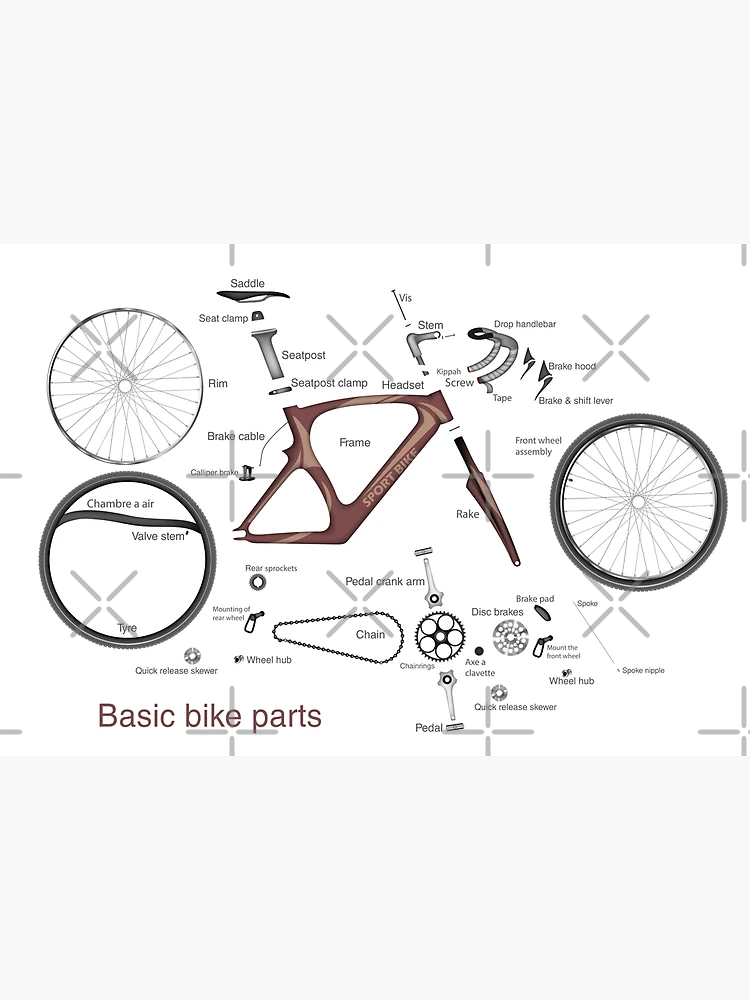
When evaluating braking systems, performance and upkeep are paramount. Hydraulic systems generally require less frequent adjustments but may necessitate periodic fluid replacement. In contrast, mechanical systems can be easily adjusted, but they might demand more regular maintenance to ensure optimal function. Understanding these aspects can help users make informed choices based on their riding style and environment.
Shifting Mechanisms in Detail
The ability to change gears smoothly and efficiently is crucial for enhancing performance and comfort during a ride. Understanding how these systems function can significantly improve the overall experience, allowing for precise control over speed and effort. This section delves into the intricacies of these mechanisms, highlighting their importance in achieving optimal gear transitions.
Types of Shifting Systems
There are primarily two categories of shifting systems: manual and automatic. Manual mechanisms require the rider to engage with levers or shifters to select the desired gear. This direct interaction provides a tactile feedback that many enthusiasts appreciate. Conversely, automatic systems utilize sensors and algorithms to adjust gears based on the rider’s cadence and power output, offering a more hands-free approach. Both systems have their unique advantages and applications, catering to different riding styles and preferences.
Components Involved
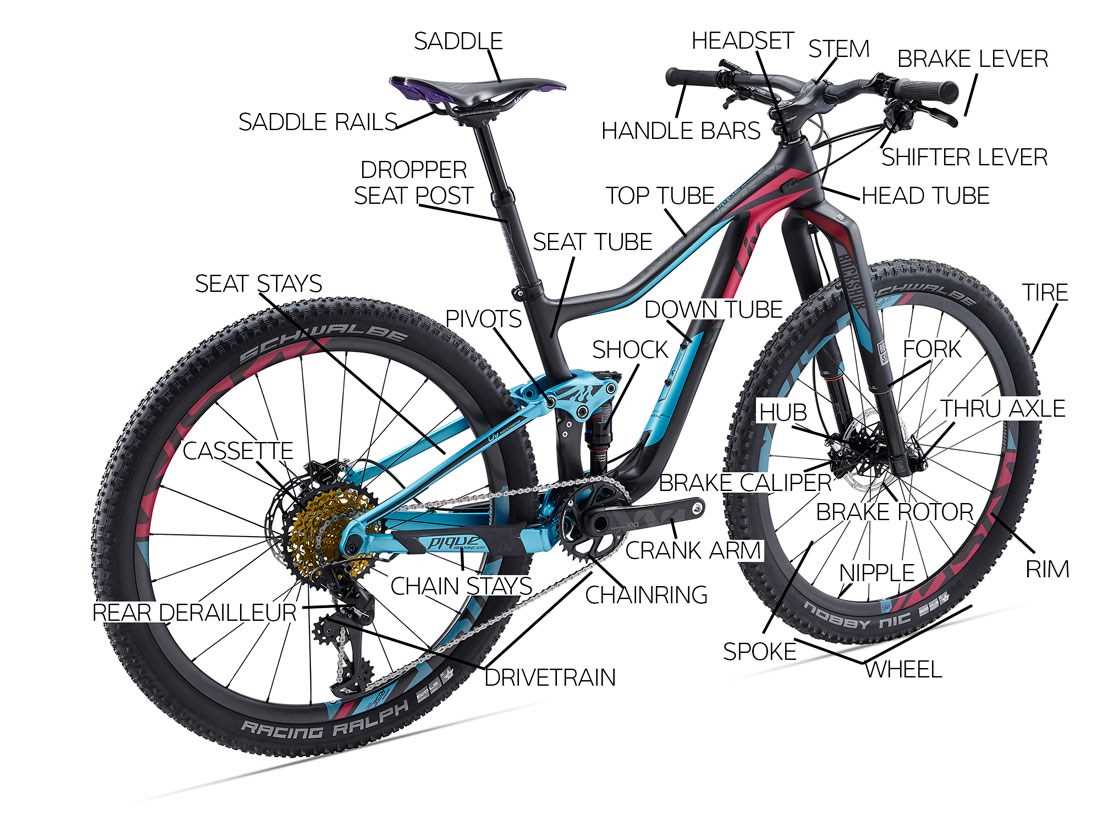

Central to the functionality are the derailleurs, which guide the chain across various sprockets. These components are operated by cables that connect to the shifters. Additionally, the shifters themselves can vary in design, with options ranging from integrated controls on the handlebars to standalone levers. Understanding the role of each component helps in troubleshooting and maintaining these essential systems, ensuring a seamless experience on the road.
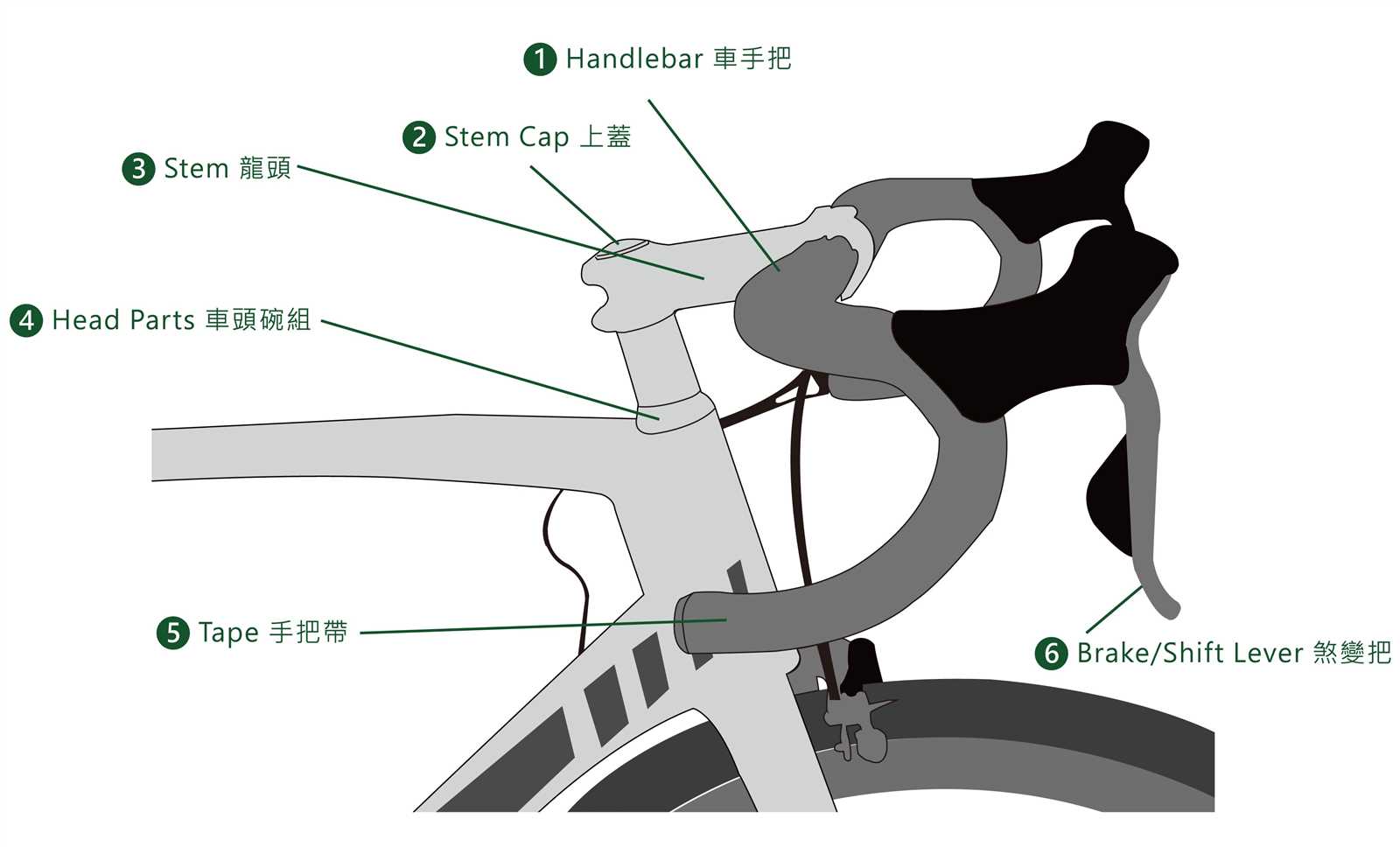
Handlebars: Styles and Ergonomics
The design and shape of the steering component play a crucial role in both the aesthetics and functionality of a two-wheeled vehicle. Different styles cater to various riding preferences and comfort levels, making it essential for enthusiasts to understand the available options. Ergonomics influences not only the rider’s posture but also their overall experience during journeys.
One popular style is the drop variant, characterized by its aerodynamic design. This configuration allows for a more aggressive riding position, reducing wind resistance during faster rides. Conversely, the flat style promotes a more upright posture, ideal for leisurely outings and urban commuting. Additionally, bullhorns offer a blend of both, providing versatility for various terrains.
Ergonomic considerations also extend to the width and grip of the component. A wider grip can enhance stability, especially during turns, while a narrower option might suit those seeking speed and agility. Materials used in construction further impact comfort, with options ranging from lightweight aluminum to more cushioned composites that absorb vibrations, ensuring a smoother ride.
Ultimately, selecting the right steering configuration is a balance between personal preference, intended use, and comfort. Understanding these elements can greatly enhance the overall enjoyment of the riding experience.
Pedals and Cranksets Overview
This section provides an insightful look into essential components that play a crucial role in transferring energy from the rider to the wheels. Understanding these elements is key for anyone looking to enhance performance and comfort during rides.
Functionality and Importance
The relationship between these components is vital for efficient motion. The pedals enable the rider to apply force, while the crankset translates this motion into rotational energy. Together, they form a harmonious system that affects speed, control, and overall riding experience.
Types and Variations
There are various types available, each designed for specific uses and preferences. Choosing the right combination can significantly impact performance, making it essential for enthusiasts and casual riders alike to explore their options.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Platform | Flat surface for easy foot placement and quick dismount. |
| Clipless | Allows secure attachment of shoes for enhanced power transfer. |
| Adjustable Cranksets | Offers the ability to customize length for improved comfort. |
| Single Speed | Simplified design for straightforward operation and maintenance. |
Forks: Types and Features
In the world of cycling, the front suspension system plays a crucial role in ensuring stability and comfort. Understanding the different variations available can enhance the riding experience, allowing enthusiasts to choose the most suitable option for their needs. Each type offers unique characteristics that cater to specific terrains and riding styles.
Types of Forks
There are primarily two main types of front suspensions: rigid and suspension forks. Rigid options provide a solid connection to the frame, making them ideal for smooth surfaces and urban environments. On the other hand, suspension forks feature a system designed to absorb shocks, greatly benefiting riders who tackle rough trails or uneven paths.
Key Features
When selecting a fork, several features come into play. Travel refers to the amount of movement the suspension allows, affecting how well it can handle bumps. Additionally, the material construction–whether aluminum or carbon fiber–determines weight and durability. Finally, adjustability can be an essential factor, enabling riders to fine-tune the performance based on personal preference and riding conditions.
Chain and Gearing Systems
The mechanisms responsible for transferring energy and enabling motion are crucial for performance and efficiency. These systems work in harmony to allow smooth transitions between various speeds, enhancing the overall experience of riding. Understanding their structure and functionality is essential for optimal operation.
At the heart of this system lies a series of interconnected links, which provide the necessary connection between the pedals and the wheels. This arrangement allows for precise adjustments to speed and torque, catering to different terrains and rider preferences. The design varies widely, from simple configurations to more complex setups, each tailored for specific purposes.
In addition to the chain, the arrangement includes sprockets and derailleur mechanisms. Sprockets play a pivotal role in determining gear ratios, affecting how power is translated into movement. The derailleur enables swift changes between gears, ensuring that riders can adapt seamlessly to varying conditions without losing momentum.
Maintenance of these systems is vital for longevity and performance. Regular cleaning and lubrication help prevent wear and tear, ensuring smooth operation. Understanding the importance of these components and their upkeep can significantly enhance the riding experience.
Suspension: Hardtail vs. Full-Suspension
When exploring different models of cycling, the method of shock absorption plays a crucial role in performance and comfort. The choice between a rigid setup and a fully cushioned system significantly impacts the rider’s experience on various terrains.
Hardtail Overview
A hardtail configuration features a solid rear end without any form of shock absorption. This design offers several advantages:
- Lightweight: The absence of rear suspension components reduces overall weight, making it easier to accelerate.
- Efficiency: Power transfer from pedals is more direct, enhancing climbing capabilities and speed on smooth surfaces.
- Lower Maintenance: With fewer moving parts, hardtail models require less upkeep and are generally more durable.
Full-Suspension Advantages
In contrast, a full-suspension model incorporates both front and rear shock absorbers, providing a different set of benefits:
- Improved Comfort: Enhanced shock absorption minimizes the impact from rough terrains, resulting in a smoother ride.
- Better Traction: The rear suspension allows for greater wheel contact with the ground, improving control on uneven surfaces.
- Versatility: Ideal for varied landscapes, these models excel in descending and technical situations where stability is paramount.
Ultimately, the decision between these two approaches depends on the rider’s preferences, intended use, and the type of terrain they will encounter.
Lighting and Safety Accessories
When traversing various terrains, the importance of visibility and protection cannot be overstated. Incorporating appropriate illumination and safety features enhances the overall experience and ensures a secure journey. This segment highlights essential elements designed to promote safety and visibility in outdoor exploration.
| Accessory Type | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Front Light | A bright light mounted at the front to illuminate the path ahead. | Improves visibility in low-light conditions; alerts others to your presence. |
| Rear Light | A flashing or steady light placed at the back to signal your position. | Enhances awareness for those behind you; reduces the risk of collisions. |
| Reflectors | Small, reflective devices affixed to various locations. | Increases visibility from all angles; works effectively in conjunction with lights. |
| Helmet Light | A light attached to the helmet for hands-free illumination. | Allows for better directional visibility; beneficial for navigating tricky terrain. |
| Safety Vest | A high-visibility garment worn over clothing. | Ensures you stand out in traffic; often features reflective materials. |
Integrating these features not only enhances safety but also fosters confidence during your adventures. Whether commuting or exploring scenic routes, proper illumination and protective gear are indispensable for a secure experience.
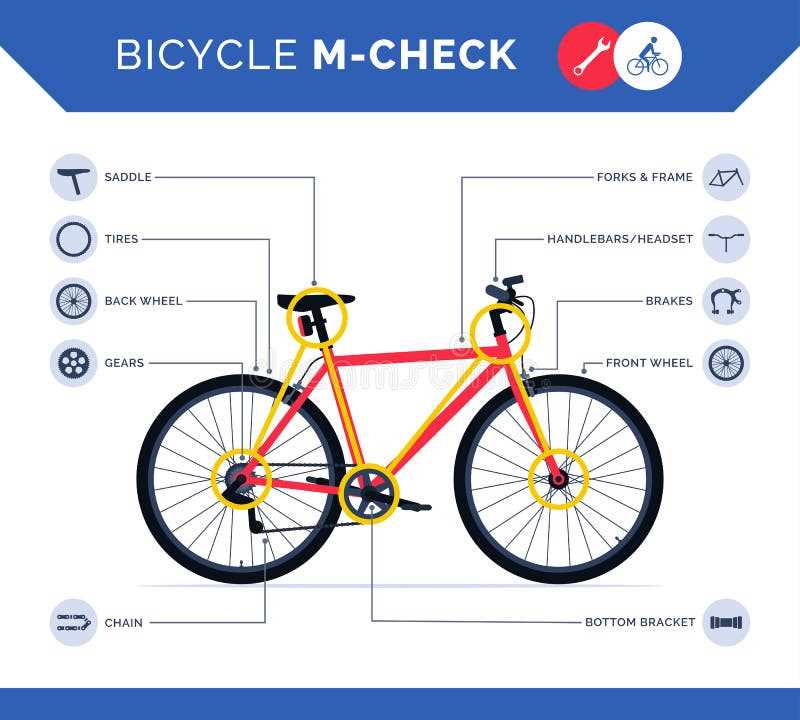
Importance of Bike Maintenance Parts
Regular upkeep of a two-wheeled vehicle is crucial for ensuring safety, performance, and longevity. Understanding the significance of each component involved in maintenance can lead to a more enjoyable and reliable riding experience. Proper care not only enhances functionality but also minimizes the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
Enhancing Performance
When each element is in optimal condition, overall efficiency improves. This means smoother rides and better handling, which can significantly elevate the experience of traversing different terrains. Regular inspections and timely replacements of worn-out elements are vital to maintaining this peak performance.
Safety Considerations
Ensuring that all crucial components are well-maintained is essential for rider safety. Neglected areas can lead to malfunctions that pose risks on the road. By prioritizing maintenance, riders can protect themselves and others, fostering a safer environment. Investing time and resources into upkeep not only prevents accidents but also promotes confidence during every journey.
Customizing Your Bike Setup

Personalizing your ride can greatly enhance your experience and performance. Tailoring various elements to suit your preferences and needs allows for a more enjoyable journey, whether you’re navigating city streets or tackling rugged trails. Understanding how different components interact and affect overall functionality is key to achieving an ideal configuration.
Begin by considering your riding style and intended use. Whether you prioritize speed, comfort, or stability, selecting the right elements can make all the difference. Adjustments such as seat height, handlebar position, and tire selection can significantly influence how you interact with your environment.
Don’t overlook the importance of accessories that can enhance your setup. Items like lighting, storage solutions, and protective gear contribute to a safer and more efficient ride. Experimenting with various configurations allows you to discover what works best for you, leading to a more satisfying experience on two wheels.