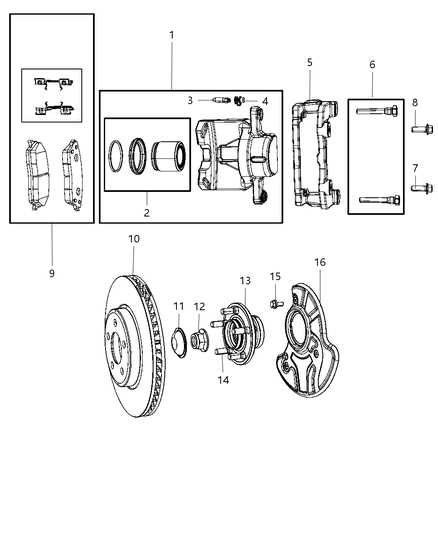
The intricate mechanisms responsible for halting vehicle motion play a crucial role in ensuring safety and efficiency. Grasping the relationship between various elements within these systems can significantly enhance one’s comprehension of their functionality and maintenance. This section aims to explore the essential elements involved in these stopping technologies.
Each component contributes uniquely to the overall performance, influencing how effectively a vehicle can slow down or come to a complete stop. By delving into these elements, we can uncover the ultimate design principles that govern their operation. Through detailed exploration, readers will gain insights into the various shapes and materials that define this critical system.
Ultimately, understanding these components not only aids in effective troubleshooting but also fosters a greater appreciation for the engineering behind modern transportation. Engaging with this knowledge can empower users to make informed decisions regarding vehicle care and upgrades.
Understanding Brake Pad Components

In the realm of vehicle safety and performance, the interaction between various elements is crucial for effective stopping power. This section delves into the essential components that contribute to this vital system, highlighting their roles and significance in maintaining optimal functionality.
Friction Material: The most prominent element, responsible for generating the necessary friction when in contact with the rotor. This material is designed to withstand high temperatures and provide consistent performance under varying conditions.
Backing Plate: Serving as the foundation, this component supports the friction material and ensures proper alignment. Its durability is key to withstanding the stresses encountered during operation.
Shims: Often overlooked, these thin layers act as insulators, reducing noise and vibration. They enhance the overall comfort of the driving experience by minimizing unwanted sounds.
Wear Indicators: Integrated into the assembly, these indicators provide a visual signal when replacement is necessary. They play a critical role in ensuring safety by alerting drivers to potential wear issues.
Adhesive Bonding: This element secures the friction material to the backing plate, ensuring that they work cohesively. The quality of this bond is vital for performance and longevity.
Understanding these components not only enhances awareness of vehicle maintenance but also emphasizes the importance of each element in ensuring safe driving practices. Regular inspections can prevent premature wear and enhance the overall efficiency of the system.
Functionality of Brake Pads
The components responsible for slowing down vehicles play a crucial role in ensuring safety and performance. Their primary purpose is to create friction against rotating elements, allowing for effective deceleration. Understanding their operation reveals insights into their importance in everyday transportation.
- Friction Generation: These elements are designed to create high levels of friction when pressed against the rotor, leading to a reduction in speed.
- Heat Dissipation: They effectively manage and dissipate heat generated during the stopping process, preventing overheating and ensuring longevity.
- Noise Reduction: Modern formulations are designed to minimize noise, providing a quieter driving experience.
- Wear Indicator: Many come equipped with features that signal when replacement is necessary, enhancing maintenance awareness.
Ultimately, these elements are vital for vehicle safety, impacting stopping distances and overall driving dynamics.
Types of Brake Pads Explained
When it comes to vehicle stopping mechanisms, understanding the various types available is crucial for optimal performance and safety. Different formulations offer unique characteristics that can affect durability, noise levels, and overall efficiency. Here’s a breakdown of the main categories you may encounter.
Common Categories
- Organic: These are made from natural materials, providing a quieter operation and good initial stopping power. However, they may wear out faster than other options.
- Metallic: Composed of metal fibers, these types offer excellent heat dissipation and durability, making them ideal for high-performance scenarios. They can be noisier and create more dust.
- Semimetallic: A hybrid of organic and metallic, these options balance performance and noise reduction. They typically provide good stopping power while maintaining decent longevity.
- Ceramic: Known for their low dust production and quiet operation, these are becoming increasingly popular among everyday drivers. They offer excellent performance at both low and high temperatures.
Choosing the Right Type
Selecting the right option depends on various factors, including driving style, vehicle type, and environmental conditions. Consider the following:
- Assess your driving habits–do you often drive in heavy traffic or require high performance?
- Evaluate the climate–hotter environments may benefit from specific materials that withstand heat better.
- Think about your vehicle’s specifications and manufacturer recommendations.
Making an informed choice can significantly enhance the performance and longevity of your vehicle’s stopping system.
Common Materials Used in Pads
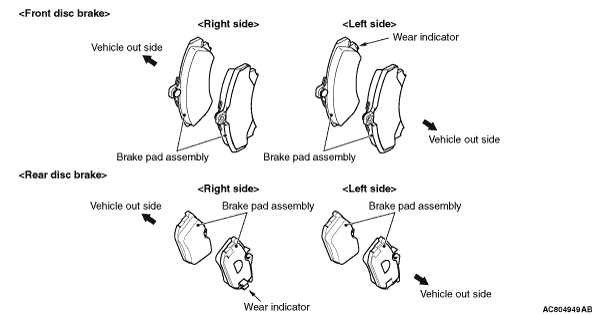
The effectiveness and performance of friction components rely heavily on the materials from which they are constructed. Various substances are employed to achieve optimal stopping power, durability, and heat resistance, catering to different driving conditions and vehicle types.
Types of Materials
Manufacturers often utilize a mix of organic, semi-metallic, and ceramic materials. Each type has distinct characteristics, contributing to its suitability for specific applications.
| Material Type | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Organic | Made from natural fibers; low noise and dust | Daily driving, light vehicles |
| Semi-metallic | Contains metal fibers; better heat transfer | Performance vehicles, heavy-duty use |
| Ceramic | Low dust, high heat resistance | Luxury vehicles, electric cars |
Choosing the Right Material
Selecting the appropriate composition is crucial for achieving the ultimate balance between performance and longevity. Understanding the differences helps in making informed decisions based on driving habits and vehicle specifications.
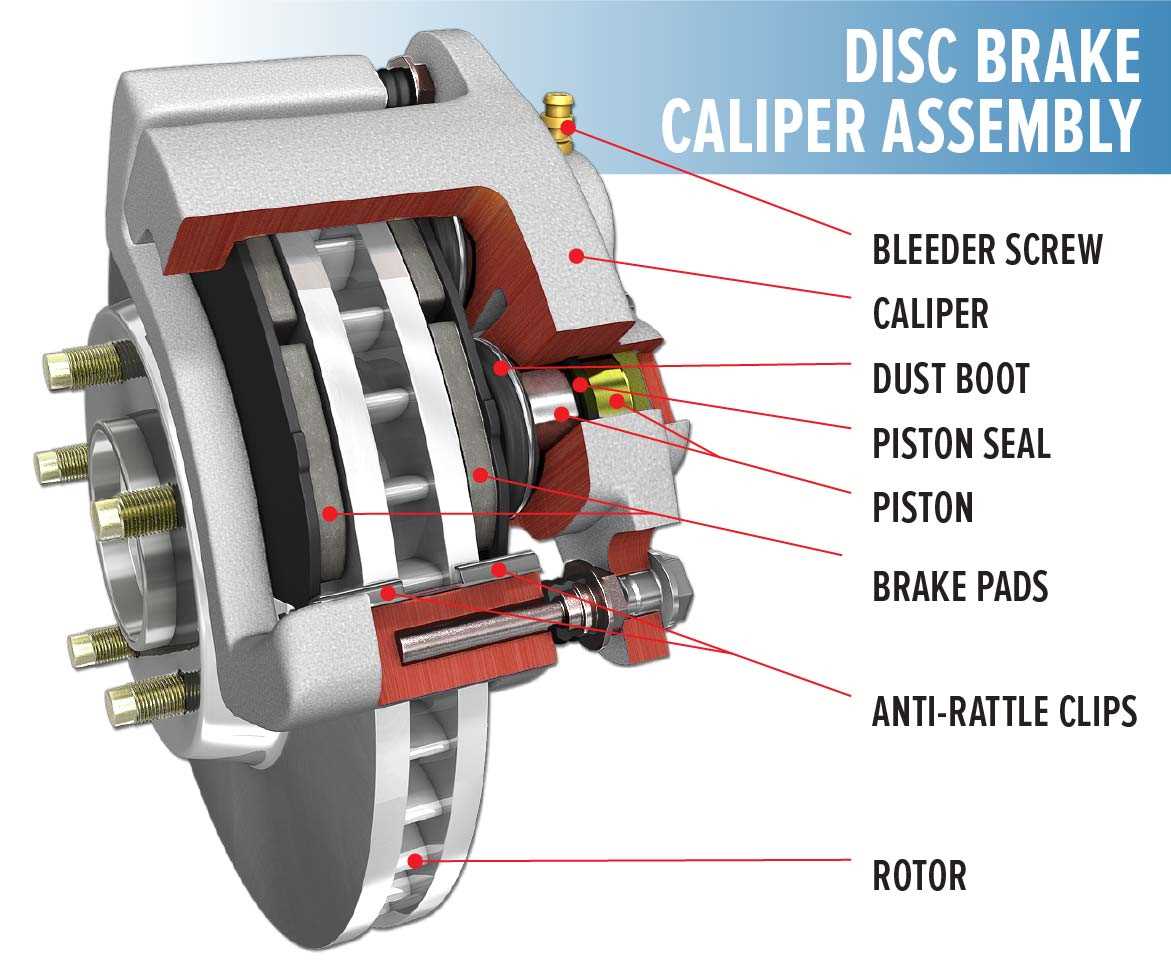
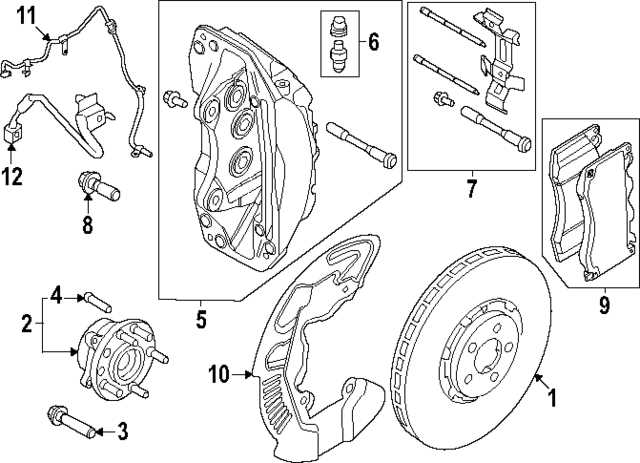
Brake Pad Assembly Overview
This section provides a comprehensive look at the components involved in the friction material setup used in vehicle stopping mechanisms. Understanding the assembly is crucial for maintenance and performance enhancement.
Key elements include:
- Friction Material: The primary element responsible for generating the necessary grip to slow down or stop the vehicle.
- Backing Plate: A sturdy base that supports the friction material and connects to the caliper assembly.
- Shims: Thin layers that reduce noise and vibrations during operation.
- Adhesives: Special substances that bond the friction material to the backing plate, ensuring durability and performance.
In summary, each component plays a vital role in the overall functionality and safety of the stopping system, ensuring that vehicles can operate effectively under various conditions.
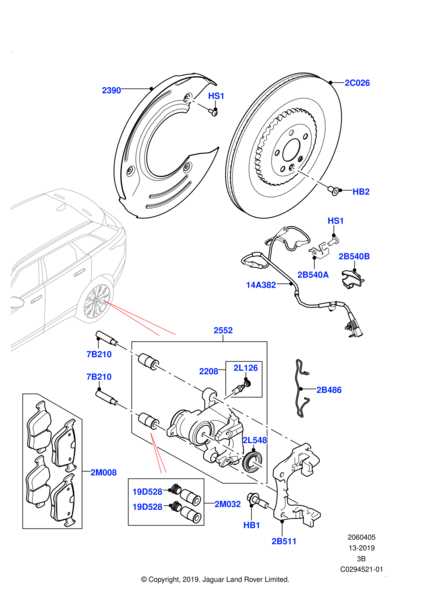
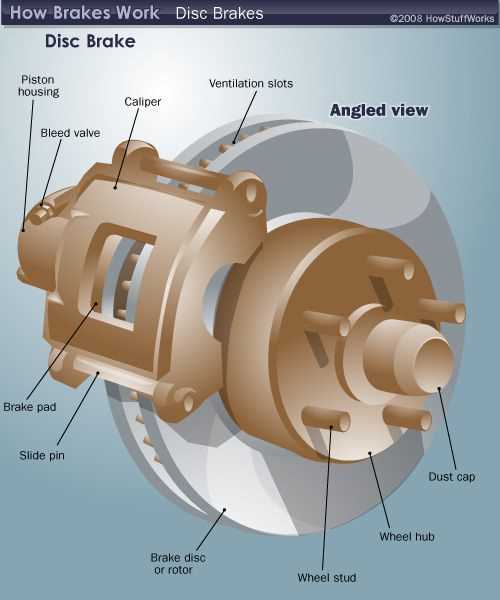
Key Parts in Brake Systems
Understanding the crucial components that contribute to the effectiveness of a stopping mechanism is essential for ensuring safety and performance. Each element plays a specific role in creating friction and dissipating energy, leading to reliable deceleration when needed.
Main Components
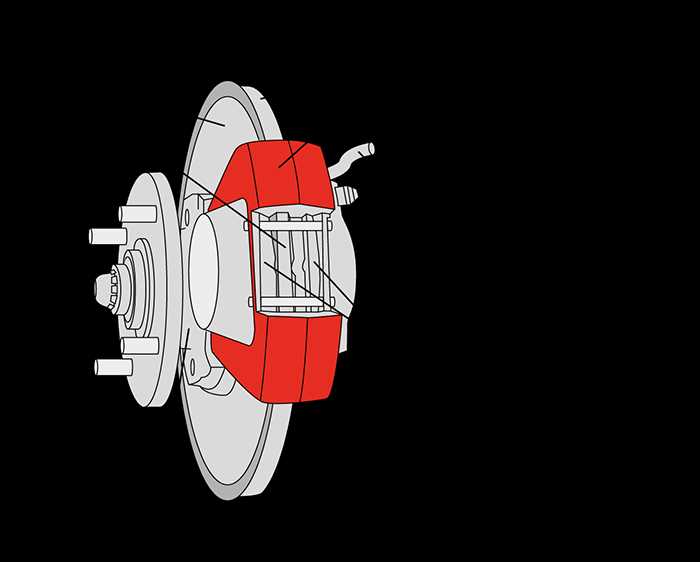
- Friction Material
- Backing Plate
- Caliper
- Piston
- Rotor
Supporting Elements
- Brake Lines
- Fluid Reservoir
- Master Cylinder
- Shims
- Anti-Rattle Clips
Each of these components works in harmony to achieve the ultimate goal of efficient stopping power and overall vehicle control.
Wear Indicators and Their Role
In any friction system, monitoring the condition of key components is crucial for ensuring safety and performance. Indicators designed to signal when replacement is necessary serve an essential function, preventing potential damage and enhancing longevity.
Functionality of these indicators allows users to receive timely alerts regarding wear levels. When components reach a certain threshold, these signals become prominent, prompting maintenance or replacement actions. This proactive approach can ultimately prevent failures that might lead to serious consequences.
Importance of wear indicators extends beyond mere convenience; they are vital for maintaining optimal operation. By integrating these signals into the system, manufacturers ensure that users can easily assess component status, thereby improving overall reliability and safety.
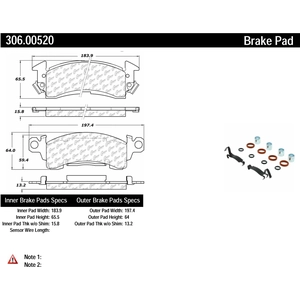
Importance of Pad Thickness
The thickness of friction materials plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and safety in vehicles. When these components are adequately thick, they provide effective stopping power and enhance longevity. Conversely, insufficient thickness can lead to decreased efficiency and increased wear on other associated systems.
Performance and Safety
One of the primary functions of these elements is to create friction that allows vehicles to slow down or stop. Optimal thickness ensures that there is enough material to generate the necessary friction without compromising performance. When they become too thin, the effectiveness diminishes, potentially leading to longer stopping distances and increased risk of accidents.
Longevity and Maintenance
Regular monitoring of the thickness of these components is essential for vehicle maintenance. Thicker materials not only perform better but also wear down at a slower rate, reducing the frequency of replacements. This not only saves money but also contributes to overall vehicle reliability.
Maintenance Tips for Brake Pads
Ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your stopping system is crucial for vehicle safety. Regular attention and care can prevent costly repairs and enhance performance. Here are some essential tips to maintain these critical components effectively.
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Inspection | Check for wear and tear periodically. Look for uneven surfaces or grooves that indicate excessive usage. |
| Keep Clean | Remove dust and debris from the area. Use a soft brush or cloth to prevent buildup that can lead to reduced efficiency. |
| Monitor Performance | Pay attention to any unusual noises or vibrations when stopping. These signs may indicate the need for maintenance. |
| Proper Installation | Ensure that components are installed correctly. Misalignment can lead to premature wear and reduced effectiveness. |
| Use Quality Materials | Invest in high-quality components. Cheaper alternatives may wear out faster and compromise safety. |
| Consult a Professional | If unsure about maintenance, seek assistance from a certified technician. Regular professional check-ups can prevent major issues. |
Signs of Worn Brake Pads
Understanding the indicators of degraded stopping components is crucial for maintaining vehicle safety. Recognizing these signs early can prevent more significant issues and ensure optimal performance on the road.
One common indication is a squeaking or squealing noise when engaging the stopping mechanism. This sound often signals that the material has worn down significantly. Additionally, a grinding noise may emerge, which typically suggests that the protective layer has completely eroded, leading to metal-on-metal contact.
Another sign to monitor is a decrease in responsiveness when applying the stopping system. If the vehicle takes longer to come to a halt, it might be time to check the condition of the stopping components. Vibrations or pulsations felt through the pedal can also indicate uneven wear, requiring immediate attention.
Lastly, visual inspection can reveal significant wear; if the thickness of the material appears less than a quarter of an inch, replacement is advisable. Regularly assessing these signs can lead to better vehicle maintenance and enhanced safety on the road.
Installation Process of Brake Pads
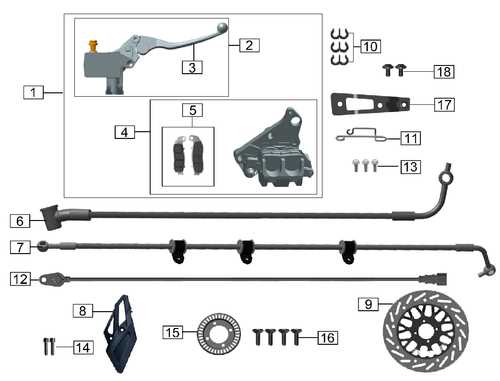
The process of replacing the friction components in a vehicle’s stopping system is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and safety. This guide will outline the essential steps to ensure a successful installation, highlighting key considerations to keep in mind throughout the procedure.
Preparation: Before beginning, gather all necessary tools, including a jack, lug wrench, and appropriate hand tools. Ensure the vehicle is on a flat surface and securely lifted. Always prioritize safety by wearing protective gear and utilizing wheel chocks to prevent rolling.
Removing the Old Components: Start by loosening the wheel fasteners before lifting the vehicle. Once elevated, remove the wheel to access the assembly. Detach the existing friction elements by unfastening the retaining hardware, ensuring to note the arrangement for accurate reinstallation. Carefully extract the worn components, inspecting the caliper for any signs of damage.
Installing the New Components: Clean the assembly area thoroughly to eliminate debris and contaminants. Position the new friction elements in the same orientation as the originals, ensuring a snug fit. Reattach any necessary hardware, tightening to the manufacturer’s specifications to prevent loosening during operation.
Final Steps: Once everything is securely in place, reattach the wheel and lower the vehicle. Tighten the wheel fasteners in a crisscross pattern to ensure even pressure. Finally, pump the brake pedal several times to set the new components and check for proper function before taking the vehicle on the road.
How to Choose Quality Brake Pads
Selecting high-performing friction materials is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient vehicle operation. Understanding the various options available can significantly enhance your driving experience and maintain optimal vehicle performance.
Assessing Material Types
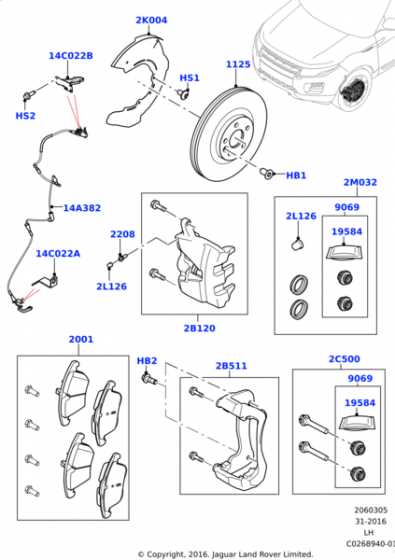
Different compositions offer varying levels of durability and performance. Organic materials are quieter and produce less dust, while metallic options provide superior heat resistance and longevity. Semi-metallic blends strike a balance between the two, catering to diverse driving conditions.
Evaluating Performance Standards
Look for products that meet or exceed industry standards. Certifications such as DOT approval indicate reliable performance. Additionally, reading reviews and seeking recommendations can help you identify trusted brands that prioritize quality.
Impact of Pad Quality on Safety
The quality of friction components plays a crucial role in the overall safety of vehicles. High-grade materials ensure effective stopping power, while inferior options may compromise performance, leading to dangerous situations on the road. Understanding the relationship between component quality and safety is essential for both manufacturers and consumers.
Performance Reliability
Components made from superior materials offer consistent performance across various conditions, including wet or icy surfaces. Reliable stopping distances are vital for preventing accidents. When lower-quality options are used, the risk of diminished effectiveness increases, potentially resulting in longer stopping distances and increased likelihood of collisions.
Durability and Wear
Durability is another important factor influenced by material quality. Higher-quality components tend to have better resistance to wear, leading to prolonged lifespan and reduced maintenance needs. In contrast, subpar materials may wear out quickly, increasing the frequency of replacements and raising safety concerns due to the unpredictability of performance degradation over time.