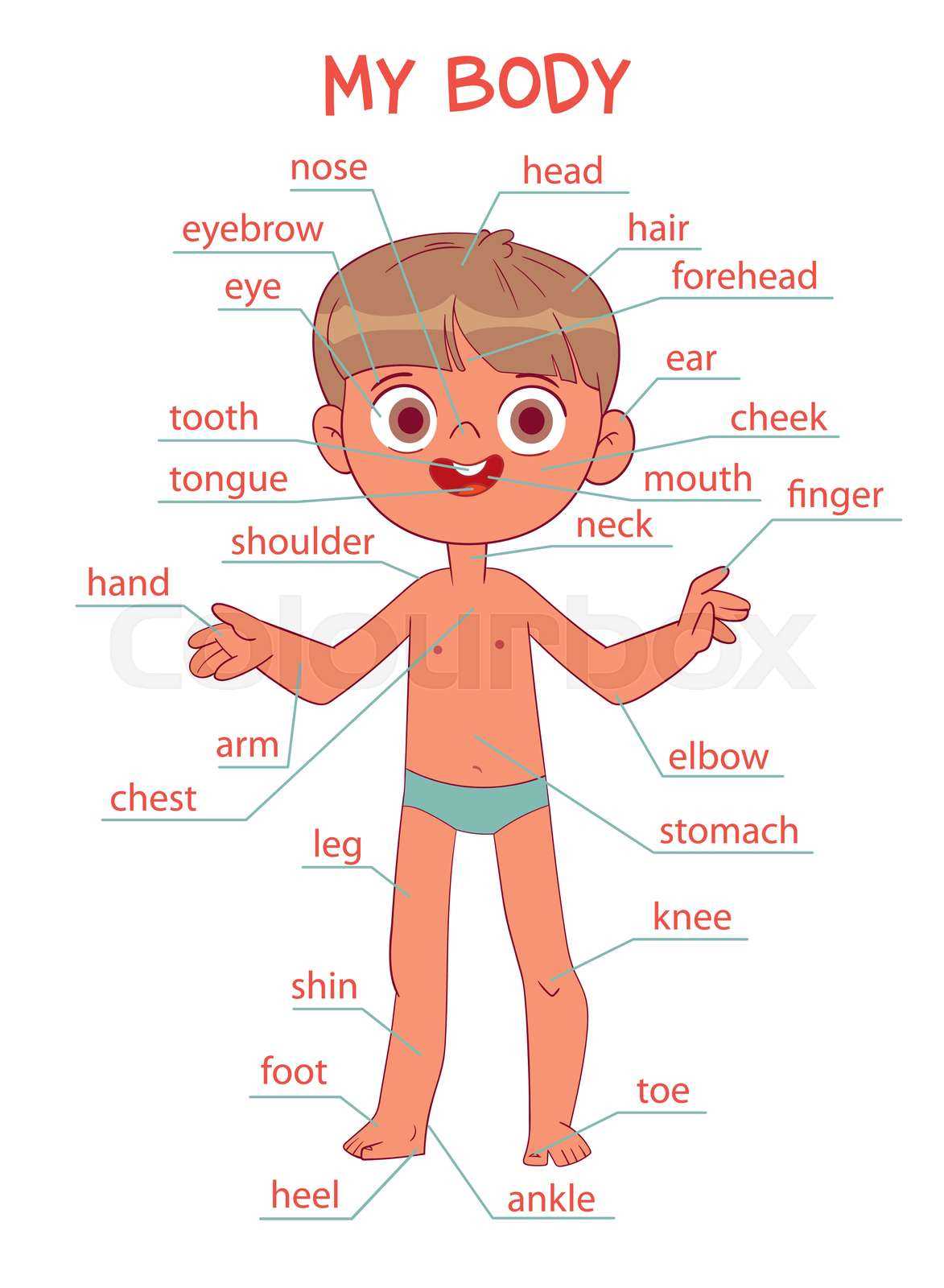
The intricate design of the human form reveals a complex network of systems that work harmoniously together. Each element serves a distinct purpose, contributing to overall functionality and well-being. Exploring these components enhances our appreciation for the remarkable engineering of life.
In this section, we will delve into various sections of the organism, highlighting their significance and interrelations. By gaining insight into these features, one can better understand the balance and coordination that sustains our physical existence.
Accompanying this exploration is a visual representation that illustrates the essential regions, allowing for a clearer understanding of their locations and roles. Such depictions can serve as valuable tools for both education and personal insight, enriching our knowledge of what makes us human.
Overview of Human Anatomy
The study of human structure reveals the intricate design and interconnectivity of various systems that work harmoniously to sustain life. Understanding this complexity is essential for fields such as medicine, biology, and health sciences. Each component plays a vital role, contributing to the overall functionality and health of the organism.
Major Systems
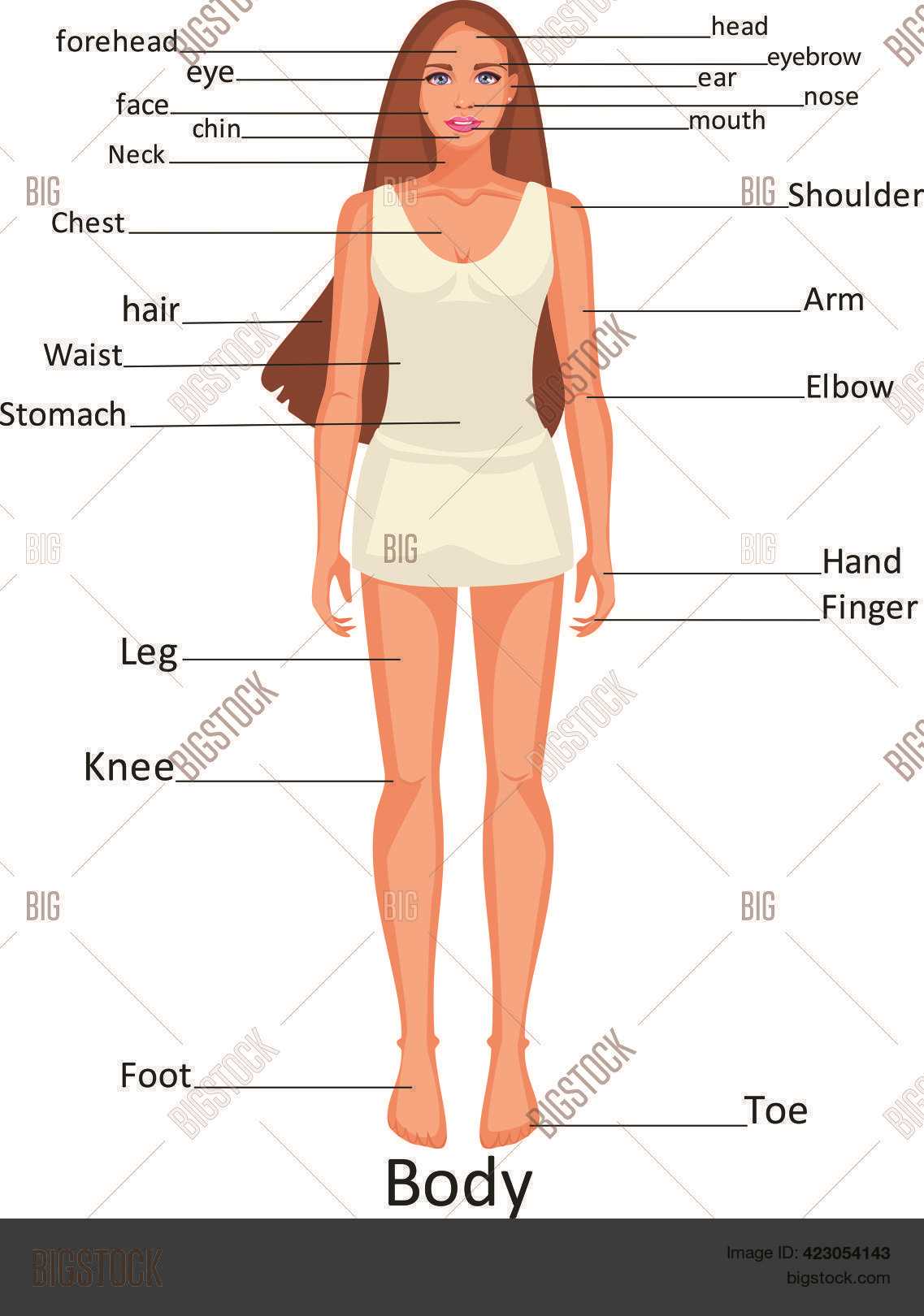
Human structure is composed of several key systems, including the circulatory, respiratory, digestive, and nervous systems. Each of these systems is specialized for particular functions, yet they collaborate to maintain homeostasis. For instance, the circulatory system ensures that oxygen-rich blood reaches all cells, while the respiratory system facilitates the exchange of gases necessary for cellular metabolism.
Interconnections and Functions
The interrelationships among various structures underscore the complexity of the organism. For example, the skeletal framework not only provides support but also protects vital organs. Muscles enable movement, working in tandem with bones to allow for a range of physical activities. Such interdependencies highlight the necessity of a comprehensive understanding of human form for advancements in healthcare and treatment approaches.
Key Functions of Body Systems
The intricate network of physiological structures operates seamlessly to sustain life and promote health. Each system plays a vital role, contributing to overall functionality and efficiency. Understanding these essential operations enhances our appreciation of how they work together to maintain balance and support various activities.
One fundamental aspect involves the transport of nutrients and oxygen, ensuring that all cells receive the necessary elements for energy production and growth. Another critical function is the regulation of temperature and fluid balance, which is vital for maintaining optimal conditions within the organism.
Additionally, systems are responsible for the elimination of waste, a crucial process that prevents the buildup of harmful substances. Defense mechanisms also play a significant role, safeguarding against infections and diseases, thereby preserving overall well-being.
Finally, communication between various components facilitates coordination, allowing for adaptive responses to internal and external changes. This harmonious interplay illustrates the complexity and efficiency of these essential systems, highlighting their importance in promoting life and health.
Major Organs and Their Roles
The human system is composed of essential structures that perform crucial functions, ensuring survival and overall well-being. Each of these vital entities works in harmony to maintain balance and facilitate numerous processes within the organism.
-
Heart: This muscular organ is responsible for pumping blood throughout the system, delivering oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products.
-
Lungs: These respiratory structures enable the exchange of gases, allowing oxygen to enter the bloodstream and carbon dioxide to be expelled.
-
Liver: This complex organ plays a key role in metabolism, detoxification, and the production of essential proteins.
-
Kidneys: These bean-shaped organs filter blood, removing waste and excess substances, while regulating fluid balance and electrolyte levels.
-
Brain: The control center of the entire system, this organ is responsible for processing information, coordinating actions, and regulating vital functions.
Each structure possesses unique characteristics and responsibilities, contributing to the intricate network that sustains life. Understanding their roles can provide insights into overall health and the interconnections between different functions.
Understanding Muscular Structure
The intricate network of muscles plays a vital role in movement, stability, and overall function. This complex system is essential for a wide range of activities, from simple gestures to elaborate athletic performances. Gaining insight into this structure can enhance appreciation for how movement occurs and the importance of muscular health.
Muscle tissues can be classified into several types, each serving distinct purposes:
- Skeletal Muscle: This type is responsible for voluntary movements and is attached to bones.
- Cardiac Muscle: Found exclusively in the heart, it functions involuntarily to pump blood.
- Smooth Muscle: This type is present in various organs and operates automatically to regulate processes like digestion.
Within each category, muscles consist of fibers that contract and relax. Understanding the characteristics of these fibers helps clarify their roles:
- Type I Fibers: Known for endurance, these fibers are resistant to fatigue.
- Type II Fibers: These fibers are more suited for short bursts of strength and power.
Moreover, the connection between muscles and the nervous system is crucial for coordinated movement. The interplay of signals ensures precise control and adaptation to varying physical demands. Recognizing this relationship emphasizes the significance of maintaining muscular health through regular exercise and proper nutrition.
In summary, comprehending the muscular framework reveals the complexities of movement and the necessity for well-functioning tissue in everyday life.
The Skeletal Framework Explained
The intricate structure of bones serves as the essential support system for living organisms, enabling movement, protection, and the maintenance of form. This framework not only provides stability but also plays a crucial role in various physiological functions, including the production of blood cells and mineral storage.
Components of the Framework
This framework is composed of numerous individual elements, each contributing uniquely to its overall functionality. Major segments include long, short, flat, and irregular types, which collectively create a complex architecture. The connections between these segments allow for flexibility and resilience, adapting to the stresses encountered during daily activities.
Functions Beyond Support
Beyond merely holding an organism upright, this structural system is vital for the production of essential substances. It serves as a reservoir for minerals, ensuring that vital nutrients are readily available. Furthermore, it plays a significant role in housing marrow, where red and white blood cells are generated, showcasing its importance in overall health.
In conclusion, understanding this remarkable framework highlights its significance in both mobility and overall well-being, demonstrating that it is far more than just a support system.
Circulatory System Components
The circulatory system serves as a vital network, ensuring the efficient transport of essential substances throughout the organism. This intricate system comprises various elements that work synergistically to maintain homeostasis and facilitate cellular functions.
Heart is the central organ, acting as a powerful pump that drives blood circulation. Its rhythmic contractions ensure that oxygen-rich blood reaches all tissues, while simultaneously returning deoxygenated blood for re-oxygenation.
Blood vessels form an extensive pathway, categorized into arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, veins return deoxygenated blood back, and capillaries facilitate the exchange of nutrients and waste at the cellular level.
Blood, a fluid medium, plays a crucial role in transporting oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, hormones, and immune cells. Its components, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, each contribute uniquely to overall health and defense mechanisms.
In summary, this intricate system is fundamental for sustaining life, enabling organisms to thrive by ensuring that vital substances circulate efficiently and effectively throughout their structure.
Nervous System Essentials
The nervous system serves as the communication network within an organism, orchestrating responses to internal and external stimuli. It plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and enabling interaction with the environment.
This complex system can be divided into several key components:
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Brain: The control center, responsible for processing information and making decisions.
- Spinal Cord: A pathway for signals between the brain and the rest of the organism.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Somatic Nervous System: Governs voluntary movements and sensory information.
- Autonomic Nervous System: Regulates involuntary functions, including heart rate and digestion.
Key functions of this intricate network include:
- Transmission of signals: Facilitating communication between different regions.
- Coordination of responses: Ensuring appropriate reactions to various stimuli.
- Information processing: Analyzing and interpreting sensory input.
Understanding the essentials of this system is vital for exploring its impact on overall health and behavior.
Respiratory Organs and Function
In this section, we explore the intricate network of organs responsible for the vital process of breathing. Our focus is on understanding how these structures facilitate the exchange of gases necessary for sustaining life. We delve into the anatomy and mechanics behind this physiological system, emphasizing the role each component plays in the process of respiration.
- Exploration of the primary organs involved in the intake and release of oxygen.
- An examination of the intricate pathways that oxygen follows through the body.
- An in-depth look at the specialized tissues responsible for the exchange of gases.
- Discussion on the crucial role of respiratory muscles in supporting the breathing process.
- Explanation of how these organs collaborate to maintain optimal levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the bloodstream.
Throughout this exploration, we uncover the remarkable adaptability and efficiency of the respiratory system, highlighting its essential function in sustaining human life.
Digestive System Breakdown
In this section, we delve into the intricate network that facilitates the transformation of nutrients into usable energy. Here, we explore the complex series of interconnected pathways that enable the breakdown of food into essential components vital for sustenance.
Essential Processes: The journey begins with the ingestion of sustenance, initiating a cascade of physiological events orchestrated by specialized organs and glands. These components collaborate seamlessly, harmonizing their efforts to ensure the efficient extraction of nourishment from ingested substances.
Key Players: Within this dynamic system, each participant fulfills a distinct role, contributing to the overall digestive process without redundancy. From initial entry through to absorption and eventual waste disposal, every stage is meticulously orchestrated to maximize nutritional uptake.
Efficient Transformation: Through enzymatic actions and mechanical breakdown, the complex matrix of nutrients undergoes systematic conversion into forms assimilable by the body. This meticulous conversion process optimizes the availability of essential components critical for physiological functions.
Integrated Harmony: The integration of various organs and tissues highlights the holistic synergy essential for sustaining metabolic equilibrium. This cooperative effort ensures that the digestive system operates with remarkable efficiency, enabling the body to derive maximum benefit from ingested resources.
Integumentary System Overview
The integumentary system serves as a protective barrier, playing a crucial role in maintaining overall health. This intricate network encompasses various structures that work synergistically to safeguard the internal environment from external threats while also performing vital functions essential for survival.
Key Components
- Skin: The primary organ that forms the outer layer, serving multiple functions including protection, sensation, and temperature regulation.
- Hair: Provides insulation and protection, as well as contributing to sensory perception.
- Nails: Protect the tips of fingers and toes, enhancing grip and tactile feedback.
- Glands: Include sweat and sebaceous glands, which regulate moisture and oil production.
Functions of the System
- Protection: Acts as a barrier against pathogens, chemicals, and physical injuries.
- Temperature Regulation: Maintains optimal internal temperature through sweating and blood flow adjustments.
- Sensory Perception: Contains nerve endings that detect touch, pain, and temperature changes.
- Vitamin D Synthesis: Facilitates the production of vitamin D when exposed to sunlight, essential for calcium metabolism.
Endocrine Glands and Hormones
The intricate network of glands plays a crucial role in regulating various functions through the secretion of hormones. These chemical messengers travel through the bloodstream, influencing numerous processes that maintain homeostasis and overall health.
Key functions regulated by these hormones include:
- Metabolism
- Growth and development
- Reproductive processes
- Response to stress
- Fluid balance
The major endocrine glands are:
- Pituitary Gland: Often referred to as the “master gland,” it controls other glands and various bodily functions.
- Thyroid Gland: Responsible for regulating metabolism and energy production.
- Adrenal Glands: Produce hormones that help manage stress and regulate metabolism.
- Pancreas: Plays a vital role in blood sugar regulation through insulin and glucagon secretion.
- Gonads: Ovaries and testes that influence reproductive functions and secondary sexual characteristics.
Understanding the role of these glands and their hormones is essential for recognizing how they impact health and well-being. Hormonal imbalances can lead to various health issues, emphasizing the importance of this system in daily life.
Reproductive Anatomy Essentials
The study of reproductive structures is fundamental to understanding human biology and the processes involved in reproduction. These systems are intricate and specialized, playing crucial roles in the continuation of species. An exploration of these anatomical components reveals their complexity and interconnectivity.
In human reproduction, male and female systems exhibit distinct features, each adapted to their specific functions. Understanding these unique characteristics enhances knowledge of reproductive health and development.
| Male Structures | Female Structures |
|---|---|
| Testes | Ovaries |
| Epididymis | Fallopian Tubes |
| Vas deferens | Uterus |
| Seminal Vesicles | Vagina |
| Prostate Gland | Clitoris |
Each element serves a vital purpose, contributing to the overall functionality of reproduction. Knowledge of these structures is essential for those studying medicine, biology, or health sciences.
Visualizing Anatomy with Diagrams
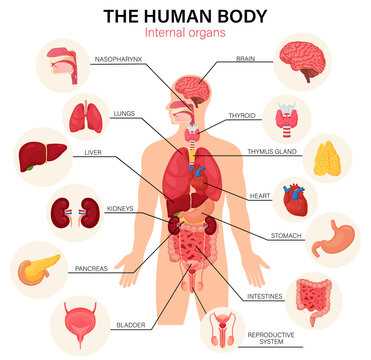
Understanding the complexities of human structure can be greatly enhanced through the use of illustrations. These graphical representations serve as powerful tools for learning, allowing individuals to grasp intricate details and relationships within the system. By translating intricate concepts into visual formats, learners can better retain and comprehend essential information.
The Importance of Illustrative Learning
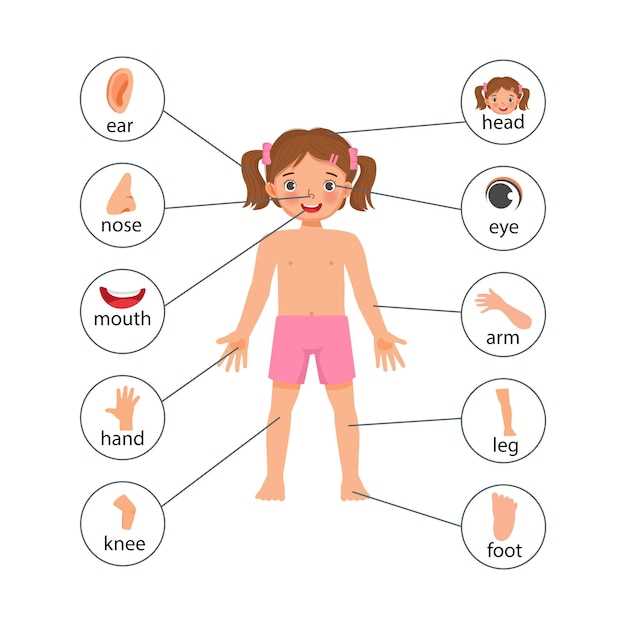
Illustrations play a crucial role in education, offering clarity where text alone may fall short. They provide an immediate visual context that aids memory retention and encourages active engagement. Through vibrant and precise imagery, students can explore the layout and function of various components, enhancing their overall knowledge and appreciation.
Enhancing Comprehension Through Visual Tools
Utilizing visual aids fosters deeper understanding by presenting information in a dynamic manner. Strong emphasis on clarity and detail in these representations can illuminate the connections between different elements, revealing the beauty and complexity of human architecture. Engaging with these resources not only makes learning enjoyable but also empowers individuals to visualize concepts more effectively.