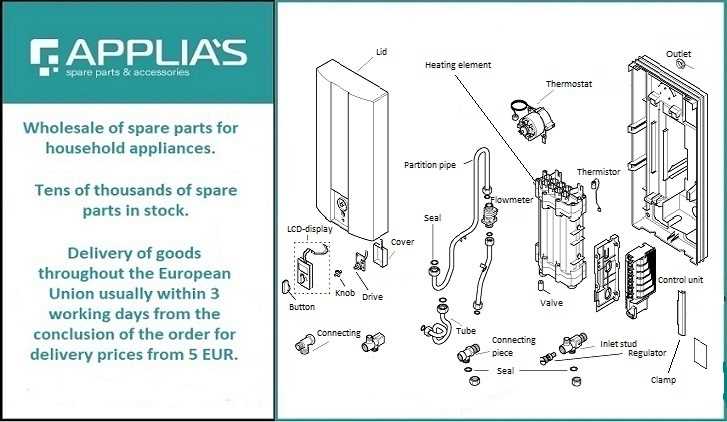
The effective operation of a heating system relies on a variety of interconnected elements that work in harmony. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring efficiency and functionality, contributing to the overall performance of the unit.
By exploring the essential features, one can gain insights into how they interact to produce the desired results. Recognizing these intricacies not only enhances user comprehension but also facilitates better maintenance and troubleshooting.
In this section, we will delve into the various key components, highlighting their specific functions and significance within the entire structure. Ultimately, this knowledge empowers users to make informed decisions regarding their heating systems.
Understanding Water Heater Components
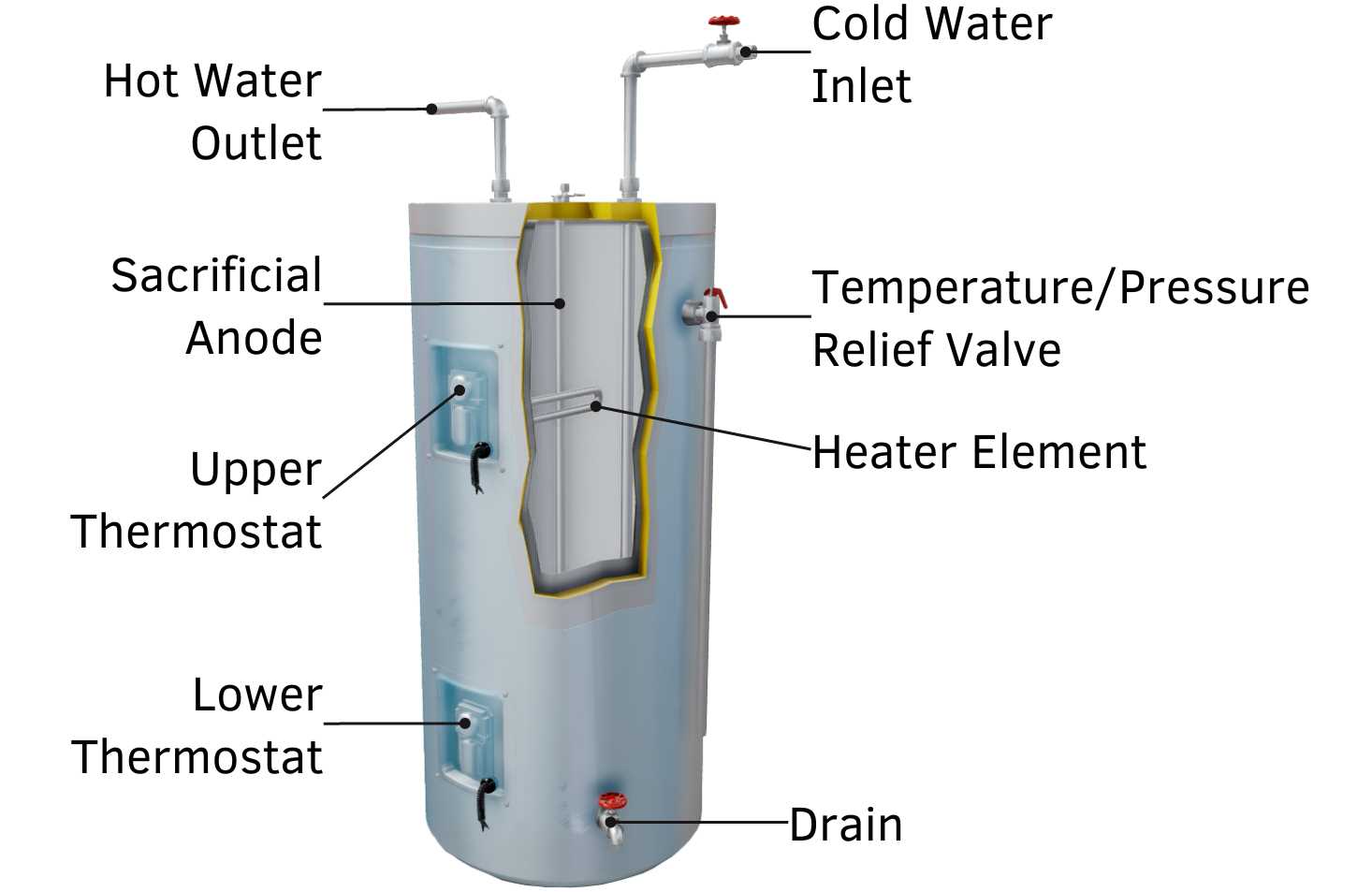
In the realm of temperature regulation devices, it is essential to grasp the essential elements that contribute to their functionality. Each component plays a pivotal role in ensuring efficiency and reliability, leading to optimal performance. A comprehensive understanding of these elements allows for better maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Elements and Their Functions
Among the crucial components, the storage tank stands out as it holds the heated fluid, providing a reserve for immediate use. Additionally, the heating element is responsible for elevating the temperature, utilizing either electricity or gas to achieve the desired warmth. Thermostats serve as the control center, maintaining the appropriate temperature by regulating the heating process.
Importance of Maintenance
Regular upkeep of these integral parts is vital for longevity and efficiency. Inspecting connections, checking for leaks, and ensuring that the control mechanisms are functioning correctly can prevent costly repairs and enhance performance. Understanding these components fosters a proactive approach to managing your heating system.
Types of Water Heaters Explained
Understanding the various types of devices designed for heating liquids can greatly assist in selecting the right option for your needs. Each variety comes with distinct characteristics, efficiencies, and suitable applications, making it essential to recognize their unique features.
Conventional Units are typically the most familiar and widely used. These systems operate by storing heated liquid in a large tank, ensuring a ready supply for household use. They are often favored for their reliability and simplicity, although they may require more space.
Tankless Systems, on the other hand, provide heated liquid on demand. These compact units heat fluid as it flows through, eliminating the need for a storage tank. This design not only saves space but also enhances energy efficiency, as they only operate when needed.
Heat Pump Models utilize ambient heat from the environment to warm the liquid. These innovative systems are highly efficient, making them an eco-friendly choice, although they may perform best in moderate climates.
Solar Variants harness energy from the sun to heat liquids, representing a sustainable option. These systems often require a backup method for overcast days but can significantly reduce energy costs in the long run.
Lastly, Point-of-Use Devices are designed for specific applications, providing immediate access to heated liquid where it’s needed most, such as in sinks or remote locations. Their installation flexibility makes them a practical choice for many scenarios.
By exploring these different types, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your preferences and requirements, optimizing both efficiency and comfort in your living space.
Main Parts of a Water Heater
Understanding the essential components of a heating unit is crucial for effective operation and maintenance. Each element plays a specific role in ensuring the system functions efficiently, providing a reliable source of hot liquid for various needs.
Heating Elements

The primary function of this unit revolves around the heating elements, which are responsible for increasing the temperature of the liquid. These can be electric or gas-based, depending on the model, and are vital for achieving the desired warmth.
Thermostat and Controls
The thermostat is an integral component that regulates the temperature within the system. It works in conjunction with control mechanisms to maintain a consistent heat level, ensuring safety and efficiency. Regular checks on these controls can prevent overheating and other potential issues, making it an essential aspect of maintenance.
Heating Elements and Their Function
In modern appliances designed for thermal energy generation, the core components are crucial for achieving efficient temperature regulation. These elements convert electrical energy into heat, facilitating the warming of fluids within the system.
Types of Heating Elements
Various types exist, each tailored for specific applications. Resistive heating is common, utilizing materials that generate heat when electricity flows through them. Immersion elements are designed to directly heat the surrounding medium, providing rapid and effective results.
Role in Efficiency
The performance of these elements directly impacts the overall efficiency of the unit. Proper maintenance and timely replacement can enhance energy consumption and extend the lifespan of the appliance, ensuring optimal functionality over time.
Importance of the Thermostat
The thermostat plays a crucial role in managing temperature regulation within heating systems. Its functionality ensures that the desired warmth is maintained, providing comfort and efficiency in energy usage.
Temperature Control
By continuously monitoring the temperature, the thermostat allows for precise adjustments. This capability prevents overheating and minimizes energy waste, ultimately leading to cost savings.
Safety Mechanism
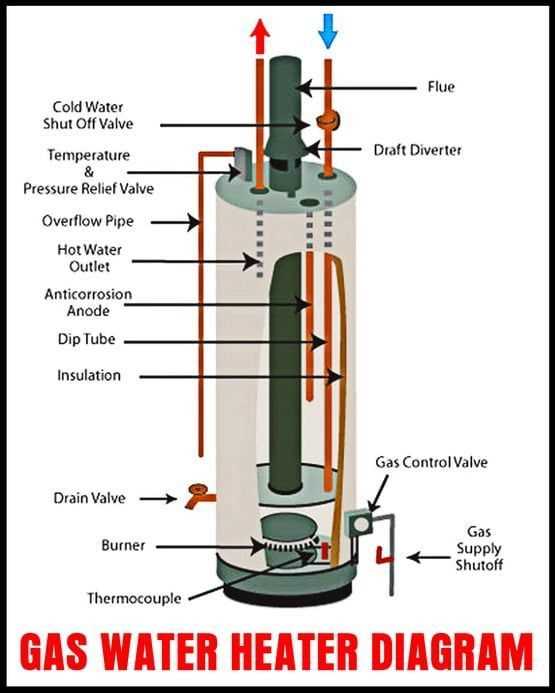
In addition to regulation, a properly functioning thermostat serves as a safety device. It helps prevent dangerous overheating situations, ensuring that the system operates within safe parameters. Regular maintenance of this component is essential for optimal performance and safety. Neglecting it could lead to significant issues.
Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Proper insulation plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal temperatures and reducing energy consumption in heating systems. By minimizing heat loss, effective insulation not only enhances performance but also contributes significantly to sustainability and cost savings.
Benefits of Quality Insulation
High-quality insulating materials help maintain consistent temperatures, reducing the need for frequent energy input. This results in lower utility bills and a decreased environmental impact, promoting a more eco-friendly approach to heating solutions.
Choosing the Right Insulation
Selecting the appropriate insulating material is essential for maximizing efficiency. Factors such as thermal resistance, moisture control, and durability should be considered to ensure long-lasting performance and effectiveness in energy conservation.
Understanding the Pressure Relief Valve
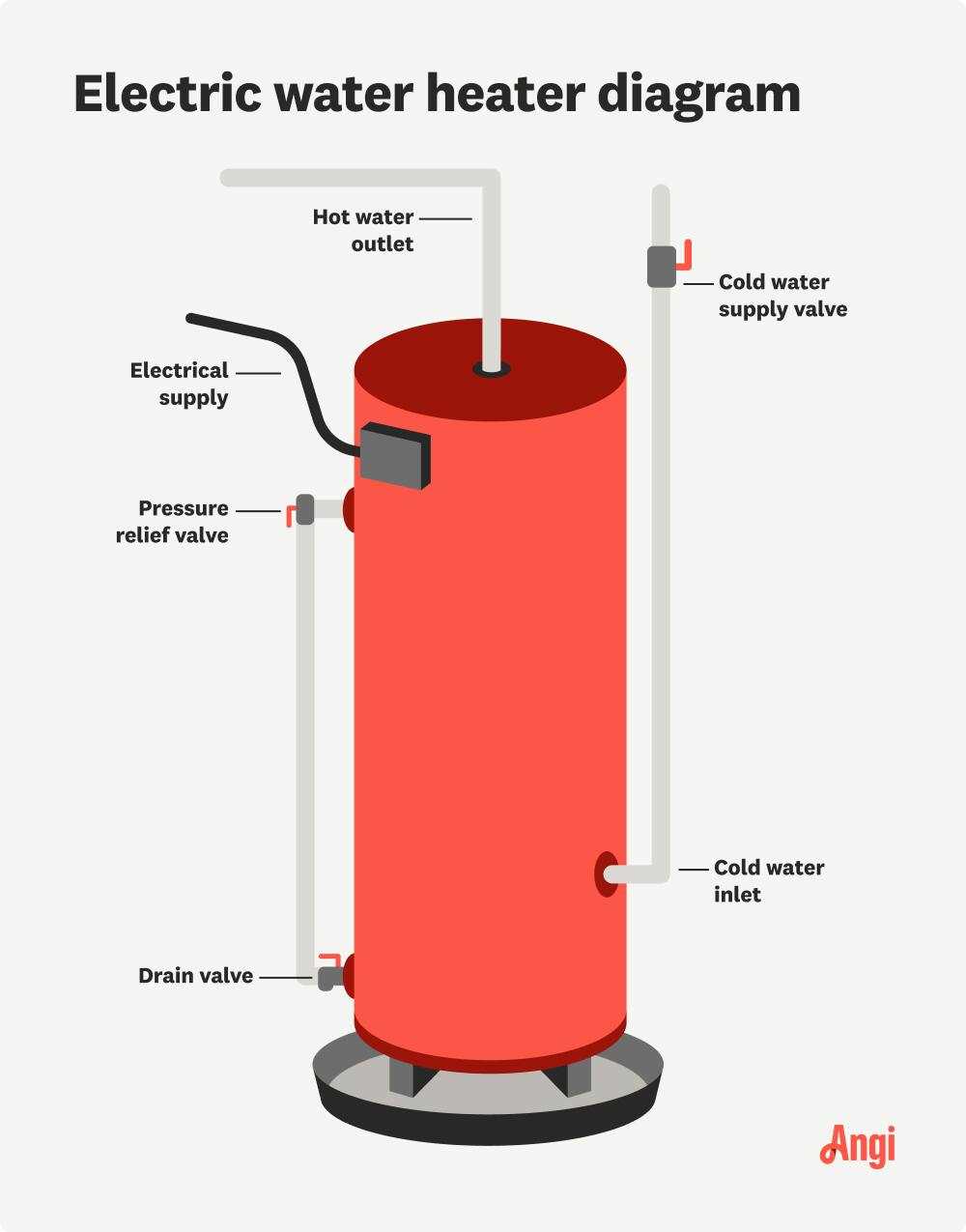
The pressure relief valve serves as a crucial safety mechanism in various heating systems. Its primary function is to prevent the buildup of excessive pressure, which can lead to hazardous situations. By automatically releasing excess pressure, this component ensures the overall integrity and safety of the entire system.
Functionality and Importance
This valve operates by monitoring internal pressure levels. When the pressure exceeds a predetermined threshold, the valve activates, allowing excess steam or fluid to escape. This process not only protects the apparatus but also enhances its efficiency by maintaining optimal operating conditions.
Maintenance and Safety Considerations
Regular inspection and maintenance of the pressure relief valve are essential for ensuring reliable performance. Users should check for signs of wear or malfunction and address any issues promptly. A well-functioning valve is vital for safeguarding against potential failures, making it a key component in promoting a safe and efficient environment.
Cold Water Inlet vs. Hot Water Outlet
The efficient functioning of any system relies on the distinct roles of its components, particularly those responsible for fluid dynamics. Understanding the interaction between the entry and exit points of the liquid is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring reliability.
Cold water inlet serves as the entry point where unheated liquid enters the unit, preparing for the heating process. This section is typically connected to the main supply, ensuring a constant flow of fresh fluid, which is essential for maintaining optimal temperature levels.
Conversely, the hot water outlet is the point where heated liquid exits the system, ready for use. This component is designed to efficiently transport the heated fluid to fixtures or appliances, contributing to the overall efficiency of the unit.
In summary, while the cold water inlet introduces unheated fluid for processing, the hot water outlet ensures that the heated liquid is effectively delivered, highlighting the importance of both elements in the overall mechanism.
Role of the Anode Rod
The anode rod serves a critical function in extending the lifespan of a storage tank system by preventing corrosion. This sacrificial element plays a pivotal role in protecting the internal structure, ensuring optimal performance and durability over time.
Functionality
- Corrosion Prevention: The rod attracts corrosive elements, thereby protecting the tank.
- Material Composition: Typically made of magnesium, aluminum, or zinc.
- Replacement Needs: Should be inspected and replaced regularly for maximum effectiveness.
Importance
- Enhances Longevity: Prolongs the life of the entire system.
- Reduces Maintenance Costs: Minimizes the need for repairs and replacements.
- Ensures Efficiency: Helps maintain optimal performance levels over time.
Electrical Wiring in Water Heaters
Understanding the electrical connections within these appliances is crucial for safe and efficient operation. Proper wiring ensures functionality and can prevent potential hazards.
- Power Supply: The initial source of electricity must match the requirements of the device.
- Voltage Rating: It’s important to consider the appropriate voltage level to avoid malfunctions.
- Grounding: Proper grounding is essential to ensure safety and prevent electrical shock.
When installing, it is advisable to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines meticulously.
- Turn off the main power supply.
- Connect wires according to the specified colors.
- Secure all connections to avoid loose contacts.
Regular inspections of the electrical system can help maintain optimal performance and enhance longevity.
Maintenance of Water Heater Parts
Regular upkeep is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the device. Proper care not only enhances efficiency but also prevents potential issues that could arise from neglect. Following a systematic approach can help maintain functionality and safety.
| Task | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Flush Tank | Annually | Remove sediment buildup by flushing the tank with water. |
| Inspect Anode Rod | Every 3 years | Check the rod for corrosion and replace if necessary. |
| Test Pressure Relief Valve | Every 6 months | Ensure the valve opens correctly to release excess pressure. |
| Check Thermostat Settings | Monthly | Verify and adjust temperature settings for efficiency. |
Common Issues with Water Heater Components
Understanding typical challenges associated with these devices is essential for maintenance and efficiency. Problems can arise from various elements, impacting performance and longevity. Recognizing these issues early can prevent costly repairs and ensure optimal operation.
Temperature Regulation Problems
One frequent concern is the inability to maintain the desired temperature. This may result from a malfunctioning thermostat or sediment buildup, affecting heat distribution. Regular checks and flushing can help mitigate these issues.
Leaking Tanks
Leaks can indicate severe damage, often due to corrosion or faulty seals. If not addressed promptly, this can lead to significant water damage and higher utility costs. It is advisable to inspect connections and the outer casing regularly.