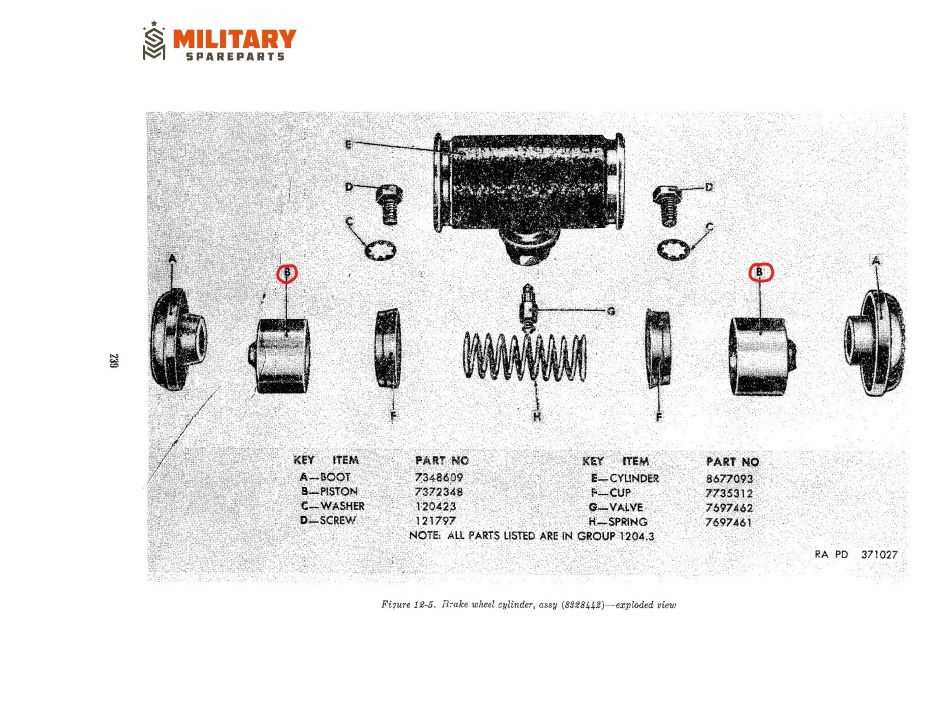
In the realm of automotive engineering, the effective functioning of braking systems is paramount. This section delves into the intricate assembly that plays a crucial role in halting vehicle movement. Gaining insight into the individual elements and their interactions enhances comprehension of overall performance.
The assembly under discussion is essential for ensuring safe and reliable deceleration. By examining its structure, one can appreciate the precision involved in its design and manufacturing. Each element serves a specific purpose, contributing to the cohesive operation of the entire braking system.
Furthermore, understanding how these components work together can assist in diagnosing potential issues and performing maintenance effectively. A thorough knowledge of this assembly empowers vehicle owners and technicians alike, fostering a greater appreciation for the engineering marvels behind everyday transportation.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the essential elements that contribute to the functionality of braking systems in vehicles. Understanding these components is crucial for both maintenance and repair, ensuring safety and efficiency on the road.
Below is a structured outline highlighting the key features and roles of each component:
- Introduction to Braking Mechanisms
- Overview of the Primary Functions
- Types of Hydraulic Systems
- Sealing Elements: Ensuring Fluid Integrity
- Piston Mechanics: The Force Behind Stopping
- Housing Structure: Supporting Components
- Spring Mechanisms: Restoring Position
- Fluid Channels: Pathways for Movement
- Maintenance Considerations: Extending Lifespan
- Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- Final Thoughts on Component Interactions
This framework serves as a guide for readers to explore the various elements involved, enhancing their understanding of how these components work together to ensure reliable operation.
Key Functions of Wheel Cylinders
The components responsible for activating braking mechanisms play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and performance of vehicles. Their primary purpose revolves around generating the necessary force to facilitate smooth stopping and efficient handling during various driving conditions. Understanding their key functionalities helps in appreciating their importance within the braking system.
Force Generation
One of the essential roles of these components is to convert hydraulic pressure into mechanical force. When the brake pedal is engaged, hydraulic fluid is transmitted through the lines, creating pressure that pushes the pistons. This action translates into a force that presses the friction material against the braking surface, enabling the vehicle to slow down or stop effectively.
Pressure Regulation
Another vital function involves the regulation of pressure within the braking system. These components help maintain optimal fluid pressure to ensure consistent performance across all wheels. By managing the distribution of force, they prevent uneven wear on braking materials, enhancing overall vehicle control and extending the lifespan of critical components.
Detailed Breakdown of Parts
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the various components that make up a hydraulic mechanism commonly used in braking systems. Understanding the individual elements is crucial for effective maintenance and repair. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the system operates smoothly and efficiently.
Key Elements of the System
Each element within this hydraulic assembly contributes to its overall functionality. Below is a list of essential components and their respective roles:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Housing | This outer casing protects internal components and provides structural integrity. |
| Piston | The moving part that compresses the hydraulic fluid to create pressure for effective braking action. |
| Seal | A crucial element that prevents fluid leakage and maintains pressure within the assembly. |
| Spring | This component ensures that the piston returns to its original position after the braking action is released. |
| Fluid Inlet | The entry point for hydraulic fluid, allowing for the transfer of pressure within the mechanism. |
Understanding Functionality
Each of these components interacts seamlessly to deliver optimal performance. Proper knowledge of their functions aids in diagnosing issues and performing effective repairs when necessary.
Common Wheel Cylinder Issues
Problems related to hydraulic mechanisms in vehicles can significantly affect braking performance. Identifying these issues early is crucial for ensuring safety and functionality. Below are some prevalent concerns encountered with these essential components.
- Leakage: Fluid leaks can lead to a reduction in hydraulic pressure, resulting in diminished braking power. Inspecting seals and connections regularly is important to prevent this issue.
- Corrosion: Exposure to moisture and contaminants can cause rust, affecting the overall integrity of the mechanism. Regular cleaning and maintenance can help mitigate this problem.
- Contamination: The presence of debris or foreign substances in the hydraulic fluid can hinder performance. Ensuring that the fluid is clean and free of impurities is essential.
- Worn Components: Over time, internal parts can wear down, leading to inefficient operation. Routine inspections can help identify signs of wear before they escalate into major problems.
- Incorrect Installation: Improper assembly can lead to misalignment and malfunction. It is vital to follow manufacturer guidelines during installation to ensure optimal performance.
Addressing these common challenges promptly can enhance the reliability and safety of the braking system. Regular maintenance and vigilant inspection are key to prolonging the lifespan of these crucial components.
How to Identify Cylinder Wear
Recognizing deterioration in braking components is crucial for maintaining vehicle safety and performance. Signs of wear can manifest in various ways, and understanding these indicators can help ensure timely maintenance and prevent costly repairs.
Visual Inspection
- Look for visible cracks or surface irregularities on the outer shell.
- Check for rust or corrosion that may indicate moisture exposure.
- Examine the sealing surfaces for any signs of damage or wear.
Functional Assessment
- Listen for unusual noises during braking, which may signal internal wear.
- Monitor braking performance; reduced efficiency can indicate issues.
- Feel for pulsations or vibrations in the brake pedal when engaged.
Regular evaluations can help catch these issues early, ensuring optimal functionality and safety on the road.
Importance of Proper Maintenance
Regular upkeep of critical components in any vehicle is essential for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Neglecting these elements can lead to severe malfunctions, resulting in costly repairs and potential hazards on the road. Establishing a routine maintenance schedule not only enhances the lifespan of these mechanisms but also promotes smoother operation and improved reliability.
Enhancing Safety
Prioritizing maintenance significantly reduces the risk of unexpected failures that could jeopardize the safety of drivers and passengers. When all components are in optimal condition, the likelihood of accidents decreases, allowing for a more secure driving experience.
Cost-Effectiveness
Investing time and resources into regular inspections and servicing can save money in the long run. Addressing minor issues before they escalate into major problems minimizes repair costs and prolongs the life of vital systems. This proactive approach ensures that vehicles remain efficient and dependable, providing greater peace of mind.
Tools Needed for Inspection
To ensure optimal performance and safety, a thorough examination of brake components is essential. This process requires specific instruments to accurately assess the condition of various elements. Having the right tools on hand can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the inspection.
The following tools are typically required for a comprehensive evaluation:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Torque Wrench | Used to apply a specific torque to fasteners, ensuring proper tightness. |
| Caliper | Essential for measuring the thickness and diameter of components accurately. |
| Flashlight | Illuminates hard-to-reach areas for better visibility during the inspection. |
| Brake Fluid Tester | Checks the moisture content in the brake fluid, indicating the need for replacement. |
| Inspection Mirror | Helps view inaccessible areas, ensuring no components are overlooked. |
Step-by-Step Disassembly Guide
This section provides a comprehensive approach to carefully dismantling the essential components of a braking mechanism. Understanding the procedure not only ensures effective maintenance but also enhances safety and performance.
Follow these systematic steps to disassemble the unit properly:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Ensure the vehicle is securely lifted and supported on jack stands to prevent movement. |
| 2 | Remove the wheel assembly to gain access to the braking mechanism. |
| 3 | Disconnect the brake line, allowing fluid to drain safely into a container. |
| 4 | Unscrew the retaining bolts to detach the main body from its mounting. |
| 5 | Carefully pull the components apart, taking note of their arrangement for reassembly. |
| 6 | Inspect each element for wear or damage, replacing any faulty parts as necessary. |
| 7 | Clean the disassembled pieces thoroughly before proceeding with reassembly. |
Completing these steps will help ensure that the braking system functions optimally and safely. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for specific instructions and torque specifications.
Reassembly Tips for Wheel Cylinders
Reassembling these crucial components requires careful attention to detail to ensure proper function and longevity. Following a systematic approach can help avoid common pitfalls during the reassembly process. Familiarizing yourself with the individual elements and their arrangement is essential for achieving optimal performance.
Start by organizing all the components in a clean workspace. Ensure that each piece is free from dirt and debris, as contaminants can lead to premature wear or failure. Use a clean cloth to wipe down surfaces and inspect for any signs of damage that may necessitate replacement.
When putting everything back together, refer to the original layout or guide you may have. Each element should be positioned accurately to ensure a secure fit. Take your time to align components correctly, avoiding any forceful manipulation that might cause misalignment or damage.
It’s also beneficial to apply a light coat of lubricant to seals and moving parts during reassembly. This helps facilitate smoother operation and reduces friction, promoting the longevity of the system. Ensure that all fasteners are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications to prevent leaks or failures.
Finally, conduct a thorough inspection after reassembly to confirm that everything is in place and functioning as intended. This final check can save you time and effort in the long run by ensuring that your components are ready for reliable performance.
Choosing Quality Replacement Parts
When it comes to maintaining the efficiency and safety of your vehicle, selecting high-grade components is crucial. Opting for reliable alternatives ensures not only the longevity of the system but also optimal performance. This section explores essential factors to consider while making your choice.
- Material Quality: Always prioritize components made from durable materials that can withstand wear and tear.
- Brand Reputation: Research manufacturers with a proven track record of producing dependable components. Trusted brands often invest in quality control and testing.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the chosen replacements are suitable for your specific vehicle model. Mismatched components can lead to functionality issues.
- Warranty: Look for options that come with a warranty. A guarantee from the manufacturer signifies confidence in their product’s reliability.
- Reviews and Ratings: Check online reviews to gauge the experiences of other customers. Positive feedback can help validate your choice.
By taking these factors into account, you can make informed decisions that enhance the overall performance of your vehicle, leading to safer and smoother rides.
Impact of Cylinder Condition on Safety
The condition of hydraulic mechanisms plays a crucial role in ensuring safe vehicle operation. When these components are well-maintained, they contribute to the overall reliability of the braking system. Conversely, neglecting their upkeep can lead to serious consequences, compromising the effectiveness of braking and potentially putting lives at risk.
Signs of Deterioration
Identifying wear or damage in hydraulic mechanisms is essential for maintaining safety. Here are some common indicators that suggest a need for inspection or replacement:
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Leaking Fluid | Presence of fluid around components indicates possible damage or wear. |
| Reduced Performance | Longer stopping distances may signal that hydraulic force is not being properly transmitted. |
| Unusual Noises | Grinding or hissing sounds may suggest internal issues affecting operation. |
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Routine inspections and maintenance of hydraulic mechanisms are vital for preventing failures. Ensuring that all components are in optimal condition not only enhances performance but also significantly boosts safety levels. Regular checks can help detect problems early, allowing for timely repairs and reducing the risk of accidents on the road.
FAQs about Wheel Cylinder Repairs
This section addresses common inquiries related to the maintenance and repair of hydraulic components crucial for braking systems. Understanding these aspects can aid in making informed decisions and ensure optimal performance.
- What are the signs that indicate a need for repair?
Look for leaks, reduced braking efficiency, or unusual noises when braking. These can signify potential issues that need attention.
- How often should these components be inspected?
Regular inspections are recommended every 20,000 miles or as specified by your vehicle’s maintenance schedule. This helps catch problems early.
- Can I perform repairs myself?
If you have basic mechanical skills and the right tools, minor repairs may be manageable. However, for complex issues, consulting a professional is advisable.
- What is the typical cost of repairs?
Costs can vary widely depending on the extent of the damage and labor charges, generally ranging from $150 to $500.
- Is it necessary to replace all components at once?
While it may not be required, replacing all relevant components can enhance system reliability and performance.