
When maintaining or repairing a car, understanding the layout and structure of various elements is crucial. The arrangement of mechanical and electrical components inside an automobile determines not only its performance but also the ease of maintenance. Knowing how everything fits together allows for more efficient work and reduces the chances of errors during the repair process.
Each vehicle consists of multiple interconnected systems that work harmoniously to provide safety, efficiency, and comfort. Identifying key elements in these systems helps owners or technicians make informed decisions during troubleshooting or part replacement. Clear visual representations of these systems are invaluable when working on routine maintenance or complex repairs.
Visual guides offer a detailed perspective on how each piece functions within the broader mechanical network, enabling precise interventions. For anyone working on vehicle upkeep, having a clear understanding of this structure simplifies the task at hand and ensures all parts are correctly assembled or replaced.
Overview of 2006 Chevy Malibu Components
This section provides a general outline of the key structural and mechanical elements that contribute to the functionality and performance of the vehicle. By understanding these essential systems, drivers and mechanics can maintain, repair, or upgrade various areas, ensuring the car operates at peak efficiency.
Mechanical Systems
The vehicle is composed of several interconnected mechanical systems that work together to deliver smooth and efficient performance. Below are the main systems that ensure reliable operation.
- Engine Assembly: The heart of the vehicle, responsible for powering the entire system.
- Transmission: Transmits power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring proper gear shifts and speed adjustments.
- Exhaust System: Channels emissions away from the engine, improving both performance and environmental impact.
Electrical Components
The electrical framework plays a vital role in controlling various automated and safety features, from ignition to lighting.
- Battery and Alternator: These components ensure power supply to the vehicle’s electrical systems and maintain energy storage.
- Fuse Box: Protects the system from overloads by regulating electrical flow.
- Lighting: Ensures visibility, safety, and communication with other road users through exterior and interior lights.
These systems, along with the suspension, steering, and braking systems, form the core framework, allowing the vehicle to perform safely and efficiently acros
Engine System Layout and Key Parts
The engine system is composed of multiple essential components working together to ensure efficient performance and power delivery. Each part plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall functionality and reliability of the vehicle. Understanding the layout of the system helps in diagnosing potential issues and optimizing maintenance.
Below is an overview of the primary components within the engine system and their functions:
- Engine Block: The foundation of the entire system, housing cylinders and other key parts that facilitate combustion.
- Cylinder Head: Positioned atop the engine block, this component contains the combustion chambers, valves, and spark plugs.
- Crankshaft: Converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion to drive the vehicle.
- Camshaft: Controls the opening and closing of intake and exhaust valves, ensuring precise timing for air and fuel intake.
- Timing Belt/Chain: Synchronizes the rotation of the camshaft and crankshaft, ensuring valves open and close at the correct times.
- Pistons: Move up and down within the cylinders to convert fuel into energy through combustion.
- Fuel Injectors: Deliver fuel into the combustion chamber for efficient combustion and power generation.
- Intake and Exhaust Valves: Regulate airflow into the engine and expel exhaust gases, maintaining optimal performance.
- Oil Pump: Circulates engine oil to lubricate moving parts, reducing friction and preventing wear.
- Water Pump: Manages coolant flow to prevent the engine from overheating.
- Battery and Charging Circuit: The power source for the entire system, it supplies energy to start the engine and supports electrical functions when the engine is off. The alternator ensures the battery remains charged while the engine is running.
- Fuses and Relays: Protective devices that prevent electrical overload by interrupting current flow during faults. They safeguard vital components from damage.
- Wiring Harness: A bundle of wires and connectors that transmit power and signals throughout the vehicle. This is the backbone that connects various electronic systems and sensors.
- Switches and Sensors: Components that monitor conditions and trigger actions within the system, such as turning lights on or adjusting engine parameters.
- Fuel Tank: Serves as the storage unit for gasoline or diesel, designed to prevent leaks and evaporation.
- Fuel Pump: Responsible for transporting fuel from the tank to the engine under the required pressure.
- Fuel Filter: Removes impurities and contaminants from the fuel, protecting the engine and maintaining efficiency.
- Fuel Injectors: Deliver precise amounts of fuel into the combustion chamber, contributing to effective combustion.
- Fuel Lines: Transport fuel between the tank, pump, filter, and injectors, ensuring a safe and reliable flow.
Transmission Structure and Component Diagram
The transmission system plays a crucial role in delivering power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring smooth transitions between different gears. Its design is a combination of mechanical, hydraulic, and sometimes electrical components, working together to regulate the vehicle’s speed and torque. By understanding the layout and functions of each element within the transmission, one can better appreciate its importance in overall vehicle performance and maintenance.
The core of the transmission includes several interconnected parts that work in unison. These elements typically consist of the gearbox, clutch, torque converter, and control mechanisms. Each of these components serves a specific function in shifting gears, controlling speed, and managing torque distribution. The configuration may vary depending on the type of transmission, such as automatic or manual, but the fundamental structure remains consistent across various systems.
The gearbox houses multiple gears of varying sizes, responsible for adjusting the ratio of engine power to wheel speed. In manual transmissions, the clutch allows the driver to manually disengage the engine from the wheels during gear changes, while automatic systems use a torque converter to manage this process without manual intervention. The hydraulic or electronic control systems manage the precise timing and smoothness of these transitions, ensuring efficient power delivery.
Brake System Breakdown for Malibu 2006
The braking system is one of the most critical components in any vehicle, ensuring safety and control in various driving conditions. Understanding its structure and function is essential for maintenance and repair. This section provides a detailed overview of the primary elements involved in the braking mechanism, helping users better comprehend how each part contributes to the overall performance and safety of the vehicle.
Main Components of the Braking Mechanism
The system is composed of several essential parts, working together to bring the car to a stop. These include the master cylinder, which generates hydraulic pressure, the brake lines that carry this pressure to the wheels, and the calipers that apply force to the brake pads. Each part has a specific role, and issues in any of these can significantly affect braking efficiency.
Disc and Drum Brakes: Different Configurations
Modern vehicles often feature a combination of disc brakes on the front wheels and drum brakes on the rear wheels. Disc brakes provide more stopping power and better heat dissipation, while drum brakes are typically simpler in design. Understanding the differences between these systems allows for more informed decisions when it comes to maintenance or repairs.
Proper care of these components, including regular inspections and timely replacements, is key to ensuring the system functions at its best, providing reliable stopping power when it’s needed most.
Electrical System and Wiring Overview
The electrical system in modern vehicles is a complex network responsible for powering various components and ensuring their proper functionality. It integrates numerous circuits that control everything from lighting and climate control to engine management and safety features. Understanding this system helps in diagnosing issues and maintaining optimal performance.
Below is an outline of the main elements found in an automotive electrical system:
Proper upkeep of the wiring and electrical components is crucial. Faulty connections, worn-out cables, or defective sensors can lead to larger problems, from minor inconveniences to significant system failures.
Exhaust System Components and Functionality
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in a vehicle’s performance and efficiency by managing the gases produced during combustion. This intricate network of parts not only directs harmful emissions away from the engine but also minimizes noise and enhances the overall driving experience. Understanding the various components and their functions is essential for maintaining optimal vehicle operation and meeting environmental regulations.
Main Components of the Exhaust System
The exhaust assembly comprises several key elements, each serving a specific purpose. These components work together to ensure efficient exhaust flow and proper filtration of harmful substances. Below is a table summarizing the primary elements of the system and their functionalities.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Exhaust Manifold | Collects exhaust gases from the engine’s cylinders and directs them into the exhaust system. |
| Catalytic Converter | Converts toxic gases into less harmful emissions before they exit the vehicle. |
| Oxygen Sensor | Monitors the level of oxygen in the exhaust gases to optimize fuel efficiency and emissions. |
| Muffler | Reduces noise produced by the engine and the exhaust gases as they exit the system. |
| Exhaust Pipes | Transport exhaust gases from the manifold through the system to the tailpipe. |
| Tailpipe | Discharges exhaust gases into the atmosphere, completing the exhaust process. |
Impact on Performance and Environment
The functionality of the exhaust system significantly influences both vehicle performance and environmental impact. A well-maintained assembly ensures efficient gas flow, which can enhance horsepower and fuel efficiency. Conversely, a malfunctioning system can lead to increased emissions and reduced engine performance. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are essential to uphold both performance standards and compliance with environmental regulations.
Fuel System Layout and Key Features
The fuel system in a vehicle is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. This system is designed to store, filter, and deliver fuel to the engine, maintaining a steady flow to meet varying demands. Understanding its configuration and components can enhance maintenance and troubleshooting efforts.
Key Components

Key Features
- Efficiency: The layout is designed to minimize fuel loss and maximize performance, allowing for smoother acceleration and better mileage.
- Safety: Components are engineered to withstand pressure and prevent leaks, incorporating various safety mechanisms.
- Accessibility: Strategic placement of key parts facilitates easy maintenance and replacement, reducing service time.
- Compatibility: Designed to work seamlessly with other engine systems, ensuring optimal overall performance.
Suspension and Steering Parts Overview
The suspension and steering systems play a crucial role in ensuring vehicle stability, comfort, and control. These components work together to absorb shocks from the road, maintain tire contact, and facilitate steering responsiveness. Understanding these systems is essential for proper maintenance and repairs, ultimately enhancing vehicle performance and safety.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Shock Absorbers | Devices that dampen the impact of road irregularities, improving ride quality. |
| Sway Bar | A stabilizing bar that reduces body roll during cornering, enhancing handling. |
| Control Arms | Linkages that connect the chassis to the wheels, allowing for controlled wheel movement. |
| Steering Rack | A mechanism that translates the driver’s input into wheel movement, critical for steering. |
| Ball Joints | Flexible connectors between control arms and wheel hubs, allowing for smooth movement. |
| Tie Rods | Links that connect the steering rack to the steering knuckles, enabling wheel direction change. |
| Struts | Combined shock absorbers and structural components that support vehicle weight and provide stability. |
Regular inspection and timely replacement of these components are vital to ensure optimal functionality and longevity of the vehicle’s handling characteristics.
Interior and Dashboard Parts Arrangement
The configuration of interior components plays a crucial role in the functionality and aesthetics of a vehicle. Proper organization ensures ease of access to controls, enhances driver comfort, and contributes to the overall driving experience. Understanding the layout of these elements is essential for maintenance, upgrades, and repairs.
Central Console and Control Layout
The central console serves as the focal point for numerous controls, including climate settings, audio systems, and navigation features. This area is typically designed to keep essential functions within reach of the driver while maintaining a clean and uncluttered appearance. Buttons and switches should be intuitively placed to allow for quick adjustments without diverting attention from the road.
Dashboard Instrumentation and Display Features
The arrangement of dashboard instruments provides critical information at a glance. Speedometer, tachometer, and warning lights are strategically positioned to maximize visibility and minimize distraction. Digital displays may offer additional functionality, such as trip information and fuel economy, enhancing the user experience. Understanding the layout not only aids in identifying potential issues but also assists in optimizing performance through informed adjustments.
Cooling System Components and Diagram
The cooling system of an automobile plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal engine temperature, preventing overheating and ensuring efficient performance. This intricate assembly comprises various components that work in harmony to regulate heat. Understanding each element’s function helps in troubleshooting issues and ensuring longevity.
Key components of the cooling system include the radiator, water pump, thermostat, hoses, and cooling fan. Each part contributes to the overall efficiency of heat dissipation, allowing the engine to operate within its ideal temperature range.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Radiator | Facilitates heat exchange, allowing coolant to dissipate heat into the air. |
| Water Pump | Circulates coolant throughout the engine and radiator. |
| Thermostat | Regulates coolant flow based on engine temperature. |
| Hoses | Transport coolant between the engine, radiator, and other components. |
| Cooling Fan | Assists in cooling the radiator by pulling air through it when needed. |
Each of these components is integral to the cooling system’s functionality. Regular maintenance and inspections can prevent failures and ensure optimal engine performance over time.
Exterior Body Parts and Their Placement
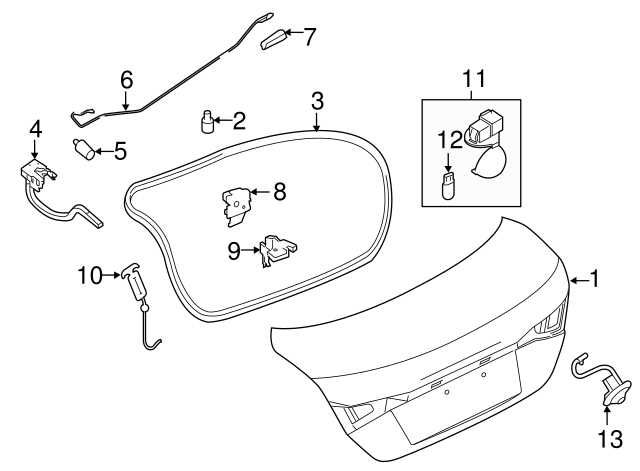
The outer structure of a vehicle plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. Understanding the various components that comprise the exterior framework is essential for maintenance and repair. This section will provide insights into the arrangement of these elements and their specific functions, contributing to the overall integrity and appearance of the automobile.
Front Fascia: This component serves as the vehicle’s initial contact point with the environment, housing the headlights and grille. Proper alignment ensures optimal airflow to the engine and enhances visual appeal.
Hood: The hood provides access to the engine compartment while protecting vital machinery from external elements. Its placement must ensure a snug fit to prevent vibrations and noise during operation.
Doors: Positioned on either side, doors facilitate entry and exit for passengers. Their alignment is critical for security and ease of use, as well as maintaining the vehicle’s overall profile.
Fenders: Located above the wheels, fenders protect the body from debris and moisture. Their design is crucial for aerodynamic efficiency and should seamlessly integrate with adjacent panels.
Trunk Lid: This element offers access to the storage compartment at the rear of the vehicle. Proper sealing is necessary to prevent water intrusion and maintain a clean, polished look.
Side Panels: These sections connect the front and rear of the vehicle, providing structural support and enhancing its aesthetic flow. Correct positioning is vital for reducing wind resistance and improving fuel efficiency.
Understanding the arrangement of these external components is essential for effective maintenance and ensuring a harmonious blend of functionality and design.
Air Conditioning System Parts Layout
The air conditioning system is a crucial component for maintaining comfort within a vehicle, especially during hot weather. Understanding the arrangement of its elements is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This section provides an overview of the layout of the various components that work together to ensure a properly functioning cooling system.
Main Components
- Compressor
- Condenser
- Evaporator
- Expansion Valve
- Receiver-Drier
Component Interactions
Each element plays a specific role in the cooling process:
- Compressor: Pressurizes refrigerant and circulates it through the system.
- Condenser: Converts refrigerant gas into liquid by dissipating heat.
- Expansion Valve: Regulates refrigerant flow and reduces pressure before it enters the evaporator.
- Evaporator: Absorbs heat from the cabin air, cooling it before distribution.
- Receiver-Drier: Removes moisture from the refrigerant, ensuring optimal system performance.
Understanding the configuration and functionality of these components allows for better diagnosis and repair, ensuring the air conditioning system operates efficiently.
Headlights, Taillights, and Lighting Components
Illumination elements play a crucial role in ensuring visibility and safety on the road. These components not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of vehicles but also serve essential functions during night driving and adverse weather conditions. Understanding the different types of lighting fixtures and their configurations is vital for effective maintenance and replacement.
Types of Lighting Fixtures
Vehicles are equipped with various illumination fixtures, each designed for specific functions. These include front-facing lights for visibility, rear lights for signaling, and additional components such as fog lights and turn signals. Proper functionality of each fixture is necessary for compliance with safety regulations and for ensuring the safety of the driver and other road users.
Component Overview
| Component | Function | Common Issues |
|---|---|---|
| Headlights | Illuminate the road ahead | Burnt out bulbs, misalignment |
| Taillights | Indicate presence and actions of the vehicle | Non-functional lights, cracked lenses |
| Turn Signals | Signal directional changes | Flashing too fast or too slow |
| Fog Lights | Improve visibility in foggy conditions | Cloudy lenses, poor alignment |